1994 JEEP CHEROKEE front
[x] Cancel search: frontPage 468 of 1784

POWER SEATS
CONTENTS
page page
DIAGNOSIS............................. 1
GENERAL.............................. 1POWER SEAT MOTOR REPLACEMENT....... 2
SWITCH TESTING....................... 2
GENERAL
The power seat can be adjusted in 6 different direc-
tions (Fig. 1). The control switch is on the lower out-
board side of the seat.
The front lever on the switch raises or lowers (tilts)
the front of the seat cushion. The center lever raises
or lowers the complete seat by moving the switch up
or down. The center lever also moves the seat for-
ward or rearward by moving the switch forward or
rearward. The rear lever raises or lowers (tilts) the
back of the seat cushion.
There are 3 reversible motors that operate the
power seat. The front and rear of the seat are oper-
ated by different motors. They can be raised or low-
ered independently of each other. Moving the center
position seat switch to either the UP or DOWN posi-
tion, runs both the front and rear motors at the same
time.
The forward-rearward motor is operated by the
center position seat switch. When the switch is held
in the FORWARD position, battery voltage is applied
through the switch contacts to pin S3 and the for-ward-rearward motor. The motor is grounded
through pin S4 and the contacts of the back switch to
pin 2 and to ground. The motor runs to drive the seat
forward until the switch is released.
With the switch in the REAR position, pin S4 re-
ceives battery voltage and pin S3 is grounded. This
reversed polarity causes the motor to run in the op-
posite direction and drive the seat backward.
The front motor works in a similar way when the
front height switch is operated.
To raise the entire seat, the center position seat
switch is held in the UP position. This applies bat-
tery voltage to both pins S1 and S5 and the front and
rear motors. Pins S2 and S6 are grounded through
the down switches and the lower switch. Both motors
run to drive the entire seat up. A similar action oc-
curs to move the entire seat down.
Each motor contains a self-resetting circuit breaker
to protect it from overload. Consecutive or frequent
resetting must not be allowed to continue. Make nec-
essary repairs.
DIAGNOSIS
Refer to Group 8W-Wiring Diagrams for a complete
circuit diagram.
Before any testing is attempted the battery should
be fully charged and all connections and pins cleaned
and tightened to insure proper continuity and
grounds.
With the dome light on, apply switch in direction
of the failure. If the dome light dims, the seat may
be jamming. Check for binding. If the dome light
does not dim, then proceed with the following electri-
cal tests.
SEAT MOTOR ASSEMBLY
²Position seat switch to move all 3 seat motors. The
seat should move in all directions. If not, go to No
Seat Motors Operate. If one or more motors operate,
refer to switch testing.
Test seat switch. If OK, replace defective motor.
NO SEAT MOTORS OPERATE
Circuit breaker installed.
²Probe 30 amp circuit breaker, cavity #16 on fuse
panel. If battery voltage is present, replace circuit
breaker.
Fig. 1 Power Seat Switch
JPOWER SEATS 8R - 1
Page 472 of 1784

POWER WINDOWS
CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION........................... 1
DIAGNOSIS (Figs. 1 and 2)............... 1SWITCH TESTING....................... 5
WINDOW REGULATOR REPLACEMENT...... 9
DESCRIPTION
All XJ vehicles, equipped with power windows,
have a cable driven window regulator system. A per-
manent magnet motor moves each power window.
Each motor raises or lowers the glass when voltage
is supplied to the motor. The direction the motor
turns depends on the polarity of the supply voltage.
The control switches control the supply voltage polar-
ity.
With the ignition switch in the ON position voltage
from the 60 amp fuse in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter is applied through the power window circuit
breaker. Power then goes to the master switch termi-
nal BY and to the passenger's window switches.
When the driver's window switch is moved UP, the
contacts close a current path to:
²terminal DV
²driver's side front window motor
²terminal CV
²the DOWN contact of the driver's side front win-
dow to ground.
The motor then moves the glass up.
Current flows in a similar way when the UP con-
tact in one of the passenger's window switches is
closed. Current flow through the passenger's window
motors must go through the driver's and the passen-
ger's window switches before it reaches ground.
Each motor is protected by a built-in circuit
breaker. If a window switch is held on too long with
the window obstructed or after the window is fully
up or down, the circuit breaker opens the circuit. The
circuit breaker resets automatically as it cools. Do
not allow frequent or consecutive resetting of the cir-
cuit breaker to continue.
DIAGNOSIS (Figs. 1 and 2)
For information concerning wiring or connectors,
refer to Group 8W - Wiring Diagrams.
NO WINDOWS OPERATE
²Measure voltage at power window feed connector
at fuse panel. Meter should read battery voltage. If
not, replace 60 amp fuse in Power Distribution Cen-
ter.
²Turn ignition switch to OFF and measure resis-
tance from side of cigar lighter socket to ground.
Meter should read zero ohms. If not, repair open to
ground.
²Remove master door lock/power window switch as-
sembly mounting screws. Measure resistance at BLK
wire (terminal DX) at driver's side switch. Meter
should read zero ohms. If not, repair open to ground
splice of instrument panel harness.
²Turn ignition switch to ON and measure voltage
at terminal BY at driver's side switch. Meter should
read battery voltage. If not, repair open to circuit
breaker.
²Operate window switch. If the windows move up
and down go to Switch Testing.
²Perform Switch Test Driver's Door. If switch
passes test, replace defective motors.
ONE WINDOW OPERATES
Remove door panel of inoperative window,
probe harness side of unplugged motor connec-
tor.
²Measure voltage at terminal A of connector, hold-
ing switch in the DOWN position. Meter should read
battery voltage. If not, repair open back to master
switch. If additional switch is in circuit (not driver's
side motor), refer to Switch Testing.
²Measure resistance at terminal B of connector,
holding switch in the DOWN position. Meter should
read zero ohms. Caution, maintain DOWN position
while meter lead is attached. If not, repair open back
to master switch. If additional switch is in circuit
(not driver's side motor), refer to Switch Testing. If
both tests are OK, replace regulator.
JPOWER WINDOWS 8S - 1
Page 494 of 1784

WIRING DIAGRAMS
CONTENTS
page page
FUSE CHARTS AND RELAY BANKS......... 8
GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 1
SPLICE LOCATIONS..................... 53
WIRING AND COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION . 13WIRING DIAGRAMS XJ.................. 149
WIRING DIAGRAMS XJ RHD............. 271
WIRING DIAGRAMS YJ.................. 73
GENERAL INFORMATION
INDEX
page page
Circuit Identification........................ 2
Component Identification.................... 2
Connector and Terminal Assembly Replacement . . 5
Connector Replacement.................... 4
Connectors.............................. 3
Fusible Link Replacement................... 4
Fusible Links............................. 3
Locating A System........................ 2Secondary Ignition Wiring................... 1
Splice Locations.......................... 2
Symbols, Fuses and Abbreviations............ 6
Terminal Replacement...................... 5
Troubleshooting Wiring Problems.............. 3
Wire Code Identification.................... 2
Wiring Diagram Sheets and Indexes........... 1
Wiring Repair............................ 4
The wiring diagrams contain the latest information
at the time of publication.
Throughout this group references may be made to
a particular vehicle by letter or number designation.
A chart showing the breakdown of these designations
is included in the Introduction Section at the front of
this service manual.
SECONDARY IGNITION WIRING
Secondary ignition wiring is shown in Figures 1
and 2. For additional information on ignition systems
or distributor operation refer to Group 8D Ignition
Systems.
WIRING DIAGRAM SHEETS AND INDEXES
The diagrams are organized to show the basic ve-
hicle and all of its options. Add-on or non-factory op-
tions are not covered. The diagram pages are
identified by a sheet number which is located at the
lower right or left hand corner of each sheet.Page
numbers at the top of each page do not apply to
diagram sheets.
Diagram sheets show all information relating to
the system. This includes feeds, grounds, switch in-
ternal circuity, connectors, splices, and pin identifica-
tion for controllers and modules. All components,switches, and relays are shown in the at rest position
with the key removed from the ignition and the doors
closed.
In certain instances a wire may be referenced to
another sheet. When this happens, the wire will be
identified as to where it is going.
The index used for the diagrams is located at the
beginning of the section. The main system and all re-
lated components are covered.
Fig. 1 Secondary Ignition Wiring 2.5L
JWIRING DIAGRAMS 8W - 1
Page 495 of 1784

WIRE CODE IDENTIFICATION
Each wire shown in the diagrams contains a code
(Fig. 3) which identifies the main circuit, part of the
main circuit, gauge of wire, and color. The color is
shown as a two letter code which can be identified by
referring to the Wire Color Code Chart (Fig. 4). If the
wire has a tracer and it is a standard color an aster-
isk will follow the main wire color. If the tracer is
non-standard the main wire color will have a slash (/)
after it followed by the tracer color.
CIRCUIT IDENTIFICATION
All circuits in the diagrams use an alpha/numeric
code to identify the wire and its function. To identify
which circuit code applies to a system, refer to the
Circuit Identification Code Chart. This chart shows
the main circuits only and does not show the second-
ary codes that may apply to some models.
LOCATING A SYSTEM
To locate a system or component in the diagrams,
refer to the alphabetical index at the front of the di-
agrams. Determine the diagram sheet number. Sheet
numbers are located at the lower right or left handcorner of each sheet.Page numbers at the top of
the page do not apply to diagram sheets.
The index identifies the main system and all com-
ponents that relate to that system. There are also
sections of the index that identify specific compo-
nents only (for example modules, lamps, etc.). Refer
to a components name in the index if you are unclear
as to what a system may be called.
Diagram sheets are arranged starting with the bat-
tery and fuses. Then working into charging, starting,
and ignition systems. After this they start at the
front of the vehicle and work to rear. The diagrams
end with connector identification pages.
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION
When looking for a components location in the vehicle
refer to the Component Identification section index.
This section shows the wire harness routing and the
components location in the vehicle. When using this sec-
tion refer to the wiring diagrams for the general loca-
tion of the component. Then use the component
identification index to locate the proper figure number.
SPLICE LOCATIONS
Splice locations are indicated in the diagrams by a
diamond with a splice circuit code within it (Fig. 5
example 1). If there is more than one splice per cir-
cuit a small box will be connected to it with the
splice number in it (Fig. 5 example 2).
To locate a splice in the wiring harness determine
the splice number from the wiring diagrams then re-
fer to the splice location index. This section shows
the general location of the splice in the harness.
Fig. 2 Secondary Ignition Wiring 4.0L
Fig. 3 Wire Color Code Identification
Fig. 4 Wire Color Code Chart
8W - 2 WIRING DIAGRAMSJ
Page 506 of 1784

WIRING AND COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION
CONTENTS
page page
XJ ................................... 25
XJ RHD ............................... 43YJ ................................... 13
The wiring and components shown in this section
are divided into sections by vehicle line. When locat-
ing a specific wire routing or component, first turn to
the appropriate index, then look up thefigure num-
berthat refers to the component.Page numbers at
the top of the page do not refer to figure num-
bers.
YJ
Caption Fig.
Battery and Starter Wiring.......................8
Body Wiring...............................1,2
Chassis Wiring...............................3
Engine Compartment Wiring......................7
Engine Wiring 2.5L...........................10Caption Fig.
Engine Wiring 4.0L...........................11
Front End Wiring.............................12
Instrument Panel Wiring.......................5,6
Steering Column Wiring.........................4
Transmission Wiring...........................9
JWIRING AND COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION 8W - 13
Page 516 of 1784
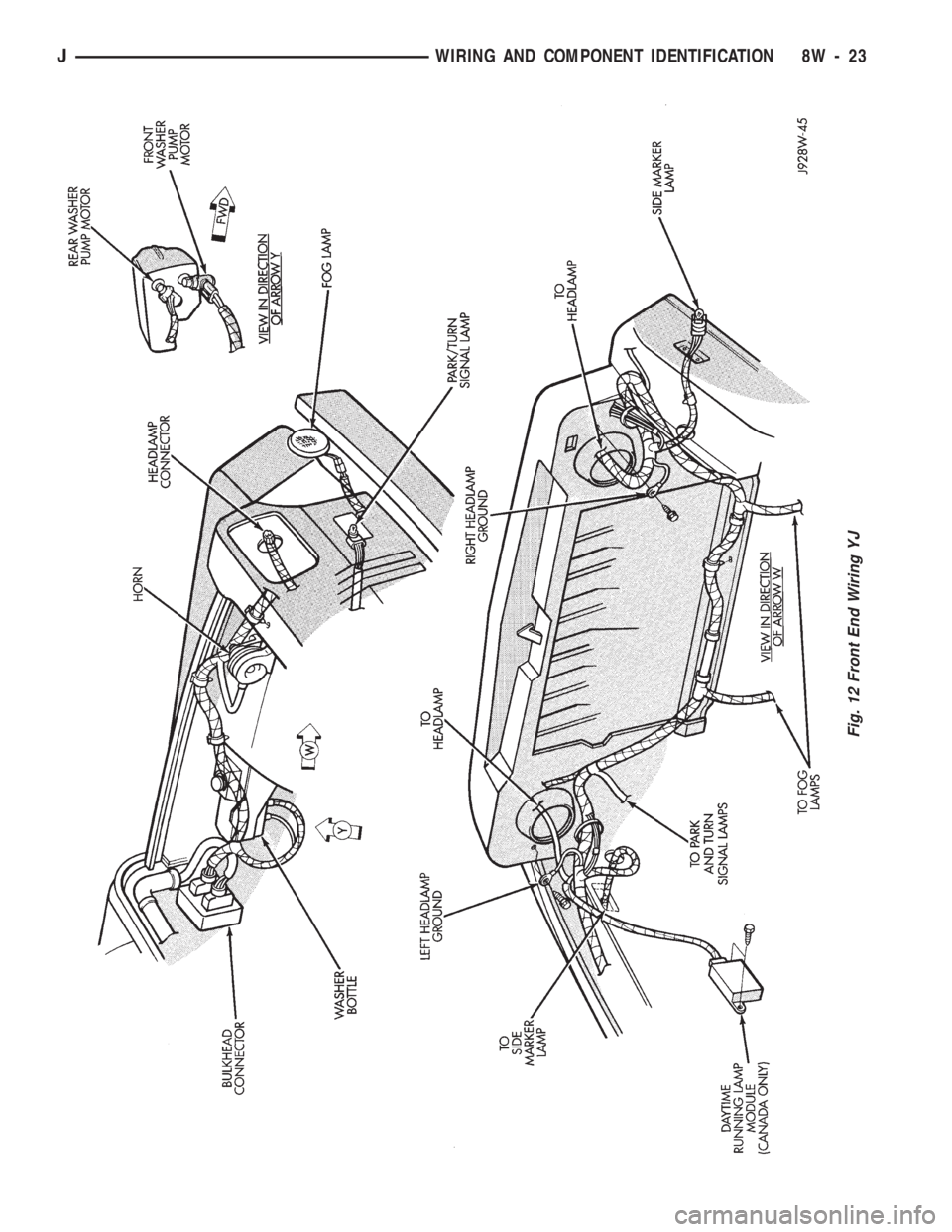
Fig. 12 Front End Wiring YJ
JWIRING AND COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION 8W - 23
Page 518 of 1784

XJ
Caption Fig.
Anti-Lock Brake System Wiring XJ..................3
Body Wiring XJ............................7,8
Door Wiring (Front) XJ.........................11
Engine Compartment Wiring 2.5L XJ................17
Engine Compartment Wiring 4.0L XJ.............18, 19
Engine Wiring 2.5L XJ.........................21
Engine Wiring 4.0L XJ.........................22
Front Cross-body Wiring XJ......................4
Front End Wiring XJ..........................16
Instrument Panel to Body Wiring XJ................14Caption Fig.
Instrument Panel Wiring XJ...................12, 13
Liftgate Wiring XJ.............................1
Power Seat Wiring XJ.........................15
Rear Door Wiring XJ...........................6
Roof Wiring (Rear) XJ..........................9
Roof Wiring XJ..............................5
Steering Column Wiring XJ......................10
Trailer Tow Wiring XJ..........................2
Transmission Wiring XJ........................20
JWIRING AND COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION 8W - 25
Page 520 of 1784
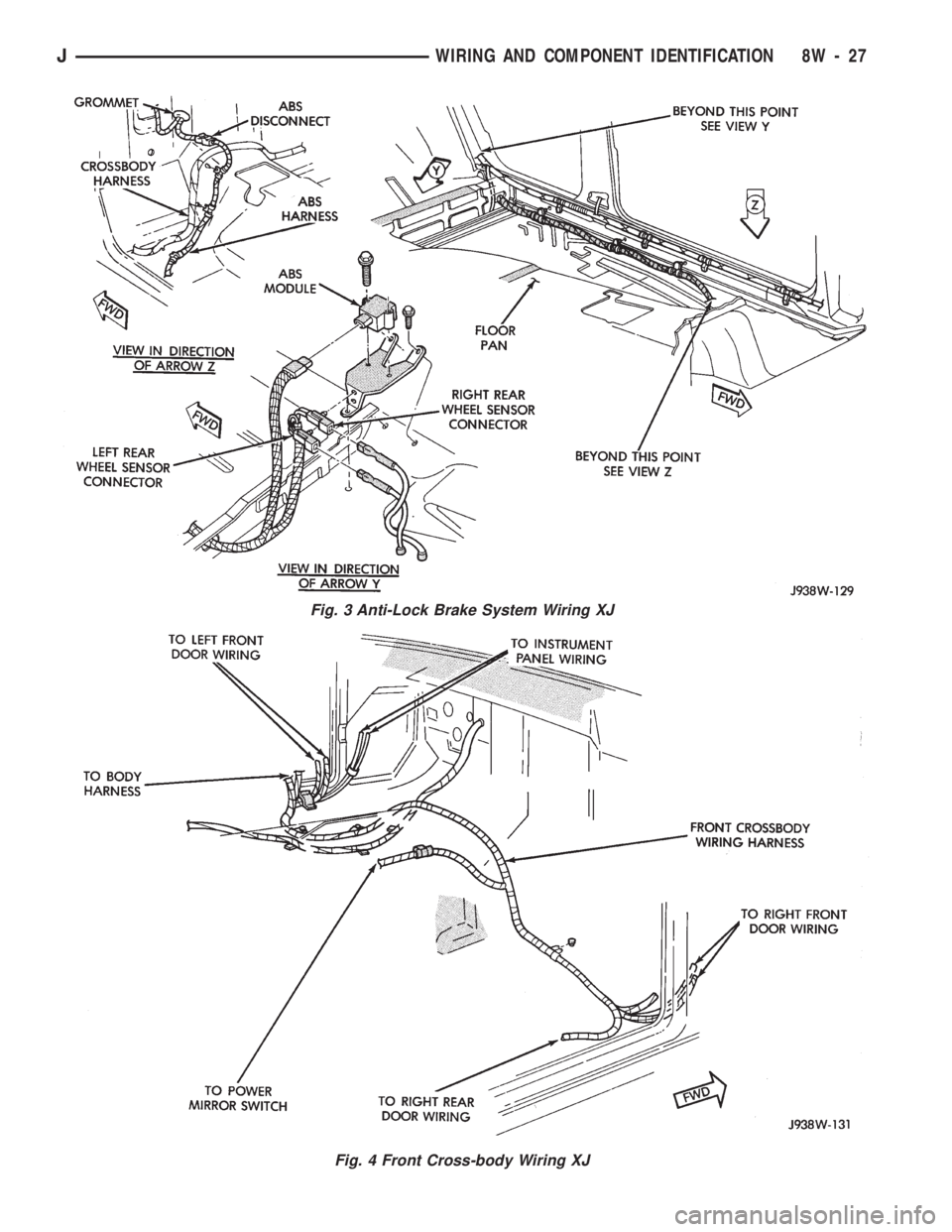
Fig. 3 Anti-Lock Brake System Wiring XJ
Fig. 4 Front Cross-body Wiring XJ
JWIRING AND COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION 8W - 27