1994 JAGUAR XJ6 engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 229 of 521

12.1.5. ABS Components
Hydraulic Module
The hydraulic module is located under the bonnet adjacent
to the engine compartment firewall. It is secured within a steel mounting bracket at three securing points. All elec- tronic and power connections are made through one cable
loom connect ion.
The hydraulic pump
(1 Fig. 1) is a reciprocating two-circuit pump in which one brake circuit is assigned to each pump
circuit. The pump supplies adequate pressure and volume
supply to the brake circuits under anti
-lock braking condi- tions. The pump is driven by and electric motor (2 Fig. 1). The
pump housing incorporates two low pressure accumulators
and damping chambers for each brake circuit.
A modulator valve block
(3 Fig. 1) incorporates the ABS CM or ABS / TC CM (4 Fig. 1). Vehicles with traction control are
fitted with a throttle position actuator (5 Fig. I), which is an
electrical device controlled by the ABS 1 TC CM.
Valve blocks on vehicles without traction control comprise
six solenoid valves, three normally open (NO) inlet valves
and three normally closed
(NC) outlet valves. These valve
blocks have three outlet ports. Valve blocks on vehicles with
traction control comprise nine solenoid valves, four
NO inlet valves,four NC outlet valves and one special isolating valve.
Fig. 2 shows a hydraulic module for vehicles with traction
control. The valve block (2 Fig. 2) has four outlet ports (Indi- vidual control of the driven wheels).
A BS CM, A BS / TC CM
The ABS CM or ABS TCI CM locates beneath the modulator
valve block and is secured by
two screws. The CM houses
the solenoids which operate the inlet and outletvalves of the
modulator valve block. When fitted, the valve stems locate
in the
CM mounted solenoids. There is no electrical connec- tion between the CM and the modulator valve block. Fig. 3 shows an ABS TC 1 CM having nine solenoids.
The
CM functions include the following:
0 Providing control signals for the operation of ABS
and traction control solenoid valves
0 Calculating wheel speed from voltage signals trans- mitted by the wheel speed sensors
0 Monitoring of all electrical components
0 On Board Diagnostics (OBD): storage of possible fail- ures in a non-volatile memory.
The signals from the four wheel speed sensors are indepen
- dently processed by the ABS CM or ABSITC CM, calculating
numerical values which correspond directly to the wheel
speed. These values are converted into control signals for
pressure modulation during ABS control.
The ABS and traction control
are continuously monitored,
whilst the ignition is on,for possiblefaults and interruptions.
If a fault is detected, the module deactivates the ABS and
indicates this by lighting the ABS warning lamp. In a fault
condition, conventional braking is unaffected. The module
stores fault codes in a non
-volatile memory which can be
read via the OBD link.
U: For electrical diagnostic information on the ABS I traction control systems, refer to EDM, Section 12. Fia.
1
Fia. 2
Fin. 3 I
J70286
Issue 1 August 1994 X300 VSM
Page 257 of 521

Body Components & Trim d-!P
13.2
13.2.1 Doors, Description
Doors are of welded, mild steel frames welded to the door panels; sponge rubber primary and secondary seals are
mounted on the doors. Internal insulation is provided by a foam water shedder attached to the door by press fitting and doublesided adhesive tape.
Front and rear door armrests are attached to supports riveted to each door frame; the attaching screws are fitted
with access covers. Upper and lower trim pads and a door pocket are attached to each of the doors by clips and screws. multi-plug connectors are used to provide a means of connecting the guard lamps, window lift switches and loud- speakers, external mirror and regulator (front doors only), which are housed within the doors.
Central locking is provided subject to market variations: Dead Locking for UK
/ Europe and Driver only unlock for N America. Door locks are eight disc, bayonet fixing, barrels with integral lock / unlock switches. Keys include ‘in-key’
transponders which are programmed to the vehicle via the Jaguar Diagnostic System also operate the engine immobi
- lisation system.
CAUTION: When removing the door panel water shedder, a foam membrane attached to each door panel by a com- bination of pressfitting (upper area) and bydouble-sided tape (bottom area), it is important that the shed- der is refitted correctly to maintain the water seal.
It is advisable not to disturb the bottom (taped) portion of the water shedder unless absolutely necessary
- it is possible to unclip the top of the shedder and bend it over to gain access to the inner panel.
If
it is necessary to disturb the bottom attachment, eg to remove the water shedder from the door panel,
the existing water shedder must be discarded and a new one fitted to ensure that the seal is maintained.
On refitting, the new water shedder should be pressed onto the door panel at the top and then the adhes- ive tape backing strip peeled off to enable the shedder to be pressed home at the bottom.
DOORS AND FUEL FILLER FLAP
13.2.2 front and Rear Door Trim Pad Veneer Panel,
Renew
SRO 76.47.11
76.47.12
. Reposition the inner door handle. See Fig. 1.
Remove the inner handle escutcheon plate blanking plate.
Undo and remove the inner handle escutcheon plate se-
. Remove the plate and gasket.
. Carefully Undo and remove the veneer panel.
Undo and remove the retaining clip securing screws.
. Remove the retaining clip assemblies.
9 Place the veneer panel aside.
Place the new veneer panel to the front.
Fit the retaining clip assemblies.
. Fit and tighten the retaining clip securing screws.
. Fit and fully seat the veneer panel to the door.
. Reposition the inner door handle.
. Fit the gasket and plate over the inner door handle.
. Fit and tighten the escutcheon plate securing screw.
. Refit the blanking plate.
curing
screw.
Fig.
1
0
0
0
0
Issue 1 August 1994 2 X300 VSM
Page 312 of 521

Climate Control Systems
Description U-
HFC 134A - ICI Klea or
equivalent
Polyalkyleneglycol (PAG) Compressor lubricant
Refrigerant
111.
Notes
Recyclable. NOT
compatible
with CFC 12
Absorbs water readily. NOT
compatible with mineral based
oils
SERVICE MATERIALS
Standard for Recovery I Recycle 1 Recharge Equipment.
Recovery rate
Cleaning capability
Oil separator
.Moisture indicator
Vacuum pump
Filter Replaceable with moisture indicator
Charge Hoses
Feature Requirement
0,014 - 0,062 m3 / min. (1,36 kg in 20 minutes)
15 parts per million (ppm) moisture; 4000 ppm oil; 330 ppm non condensable gases
in air
With hermetic compressor and automatic oil return
Sight glass type, sensitive to 15 ppm minimum
2 stage 0,07 - 0,127 m3 I min.
Selectable charge weight and automatic delivery
Dedicated HFC 134A port connections.
Iv. SERVICE DATA
Application
Charae weight
Lubricant capacity
Compressor pressure relief valve
Drive belt 12 cylinder
Drive belt tension
All figures apply to a cold belt
Special note
Drive belt tension measuring point
Drive belt 6 cyclinder
Drive belt tension
All figures apply to a cold belt
Drive belt tension measuring point
Specification
160 - 200 ml
Opening point 34 Bar. Closing point 27,6 Bar.
Maximum leakage rate of 113 liters 1 minute @ 41 Bar
7 rib Poly
-vee; 1450 mm long
Burroughs method
- New belt 790 N; If tension falls
below 270 N reset at 630 N
Clavis method
- New belt 114 to 120 Hz; If tension falls
below 70 Hz reset at 87 to 93 Hz
For new belt; rotate engine 3 revolutions minimum and
retension
Mid-way between crankshaft and compressor pulley ~
4
rib Poly-vee X 1010 mm long
Burroughs method
- New belt 556 to 578 N; If tension
falls below 245 N reset at 378 to 400
N
Clavis method - New belt 167 to 173 Hz; If tension falls
below 85 Hz reset at 127 to 133 Hz
Mid
-way between crankshaft and compressor pulley on
the upper run
1 Charge pressure I Heating element to increase pressure
Issue 1 August 1994 X300 VSM iii
Page 319 of 521

Climate Control Systems
14.4 TEMPERATURE CONTROL
14.4.1 Coolant Circuit
The main coolant system supplies liquid at engine temperature to the heater matrix to provide heat to the vehicle
interior. Unlike previous air blend / constant matrix temperature systems, in-car temperature is now controlled by
mixing recirculated coolant in the heater circuit with engine-temperature coolant. Matrix temperature is controlled
by a valve which opens to raise temperature (admit engine coolant) and closes to reduce it (recirculates coolant within
the circuit). The coolant flow valve operates on a six (6) second 'duty cycle', during which it may be open for whatever
period thecontrol system dictates. FACEvent airtemperature of howeveriscontrolled bythe'cool air by-passdamper'
which allows incoming air to flow around the top of the the heater matrix and thus remain unheated.
Because the engine coolant pump is driven proportionally to engine speed, the coolant delivery rate changes with
engine revolutions thus causing temperature variations. To stabilize the flow through the matrix, and thus the
temperature, an electrically driven circulation pump has been introduced into the system.
1
1. Engine 2. Coolant flow valve 3. Circulation pump
4. Heater matrix
5. Bottom hose
6. Engine cooling system radiator
Fig.
1 Coolant circuit, schematic view
Issue 1 August 1994 6 X300 VSM
Page 320 of 521

Climate Control Systems
Manual Inputs
Automatic inputs
outputs
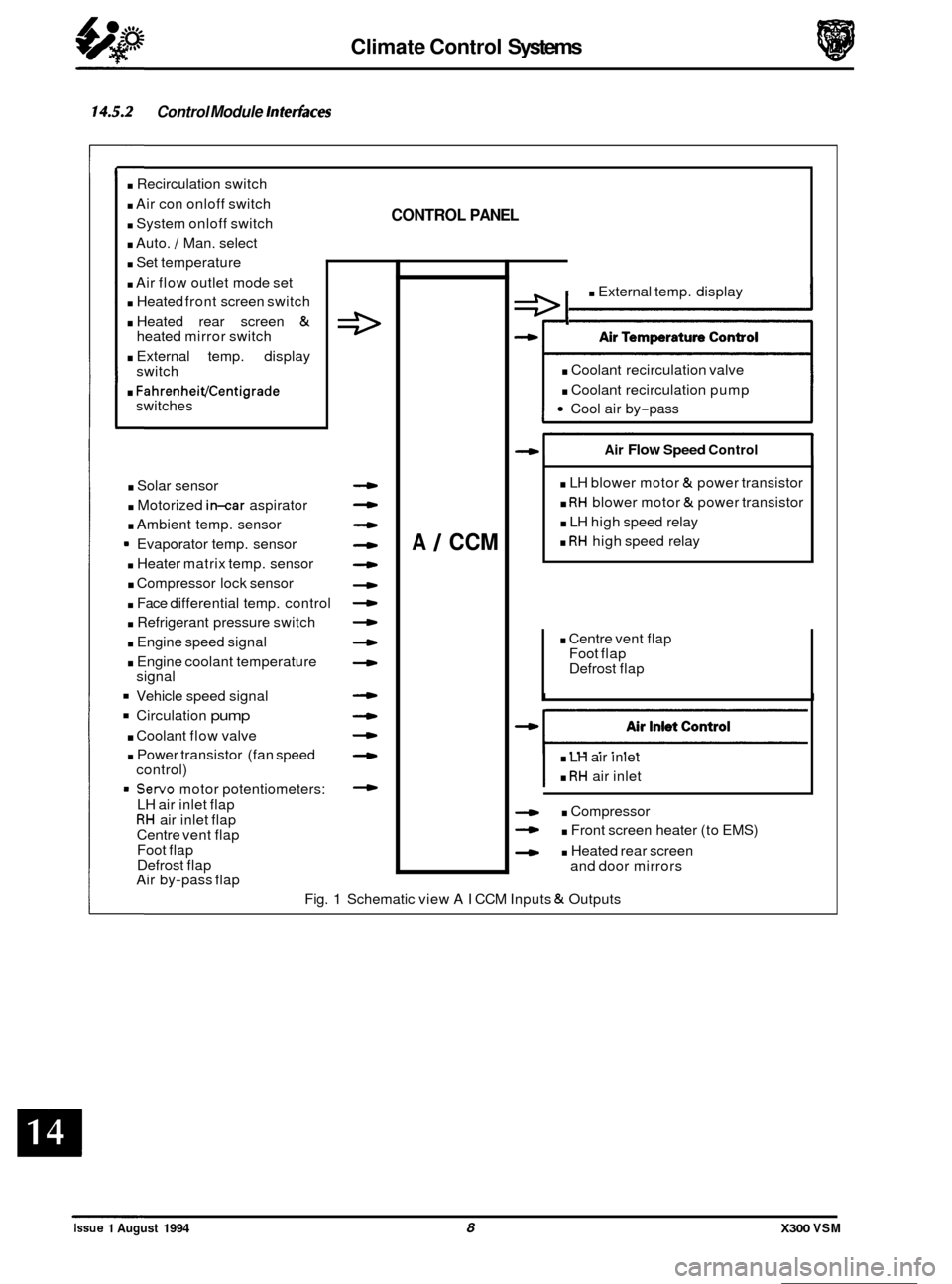
14.5 AIR CONDITIONING CONTROL MODULE (A/CCM)
14.5.1 Description
Theclimate control system peripheralscommunicate with theA/CCMvia three main devicecategories, plusthevehicle
power supply and ground connections.
Control panel Face Vent Temperature Control
Temperature and solar sensors
Flap
servo motor potentiometers
Circulation pump
& coolant flow valve
Power
transistor(fan speed control)
Compressor lock sensor
(12 cylinder only)
Instrument pack (coolant temp
& road speed) (engine revolutions via engine control module)
Blower motors (Left
& Right) & associated relays
Flap
servo motors
Heated front
/ rear screens & exterior mirror relays
Motorized in
-car aspirator
Compressor clutch request to engine control module (not
heater-only cars)
Circulation pump relay
Coolant flow valve
X300 VSM Issue 1 August 1994 7
Page 321 of 521
Climate Control Systems
. Centre vent flap
Foot flap
Defrost flap
I I
14.5.2 Control Module Interfaces
. Recirculation switch
. Air con onloff switch
. System onloff switch
. Auto. / Man. select
. Set temperature
. Air flow outlet mode set
. Heated front screen switch
. Heated rear screen &
. External temp. display
. FahrenheiVCentigrade
heated mirror switch
switch
switches
. Solar sensor
. Motorized in-car aspirator
. Ambient temp. sensor
9 Evaporator temp. sensor
. Heater matrix temp. sensor
. Compressor lock sensor
. Face differential temp. control
. Refrigerant pressure switch
. Engine speed signal
. Engine coolant temperature
Vehicle speed signal
Circulation pump
. Coolant flow valve
. Power transistor (fan speed
= Servo motor potentiometers:
signal
control)
LH air inlet flap
RH air inlet flap
Centre vent flap
Foot flap
Defrost flap
Air by
-pass flap
CONTROL PANEL
4
-
4
4
4
4
4
4
A 1 CCM
e I . External temp. display
. Coolant recirculation valve
. Coolant recirculation pump
Cool air by-pass
Air Flow Speed Control
. LH blower motor & power transistor
. RH blower motor & power transistor
. LH high speed relay
. RH high speed relay
. LH air inlet
. RH air inlet
. Compressor
- . Front screen heater (to EMS)
- . Heated rear screen
and door mirrors
Fig.
1 Schematic view AI CCM Inputs & Outputs
0
0
0
0
Issue 1 August 1994 8 X300 VSM
Page 322 of 521

Climate Control Systems
CONTROL MODULE FAULT & CONDITION SELF-ANALYSIS
0 14.6 14.6.1 System Health
The climate control system has a 'self-test' facility, accessible from the control panel. The self test sequence has two
basic modes:
0 System error information is stored in the A/CCM up to a maximum of five faults. Should a fault occur there will
be an audible 'beep' and the message 'Er' will be displayed on the control panel LCD for approximately five (5)
seconds after ignition on. Please note that this will happen only once in any ignition switch cycle. The error
source may be accessed by the procedure described in 'Self Test System Diagnosis', this section.
0 Panel communication check may be initiated by following the instruction in 'Self Test System Diagnosis', this
section.
Nsfe: Displayed error codes are NOT directly related to Jaguar Diagnostic Equipment (JDE) but more detailed fault
related information may be accessed using Portable Diagnostic Unit (PDU).
14.6.2 System Protection
Power to the compressor clutch may be cut should either the engine management or air conditioning control systems
detect certain conditions; these conditions may be caused by Fault or Demand and can be classified thus:
0 Engine coolant overheat,
0 Refrigerant excessive pressure.
0 Refrigerant, insufficient pressure or low charge weight.
0 Speed differential between compressor and crankshaft caused by belt slippage or compressor seizure (indi-
cated by A/C state lamp flashing once per second) - 12 cylinder engine only. This feature, 'lock sensing' is fully
explained
in the EDM.
Demand
0 Engine maximum power requirement
0 Electrical system drain at engine idle.
X300 VSM 9 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 325 of 521

Climate Control Systems
14.8 REFRIGERATION CYCLE:
The Compressor draws low pressure, low temperature re- frigerant from the evaporator and by compression, raises re- frigerant temperature and pressure. High pressure, hot
vaporized refrigerant enters the Condenser where it is
cooled by the flow of ambient air.
A change of state occurs
as the refrigerant cools in the condenser and it becomes a
reduced temperature high pressure liquid.
From the condenser the
liquid passes into the Receiver / Drier which has three functions,
a) Storage vessel for varying system refrigerant demand.
b) Filter to remove system contaminants. c) Moisture removal via the dessicant.
With the passage through the
receiver/drier completed the,
still high pressure liquid refrigerant enters the Expansion
Valve where it is metered through a controlled orifice which
has the effect of reducing the pressure and temperature.
The refrigerant, now
in a cold atomized state, flows into the
evaporator and cools the air which is passing through the
matrix.
As heat is absorbed by the refrigerant
it once again changes
state, into a vapour, and returns to the compressor for the
cycle to be repeated (Fig.
1).
There is an automatic safety valve incorporated in the com- pressor which will operate should the system pressure be in
excess of 41 bar. The valve will reseat when the pressure
drops below 27,6 bar.
W Thedivisionof HIGHandLOWsideissimplythesys- tem pressure differential created by the compressor
discharge (pressure), suction (inlet) ports and the
relative inlet and outlet ports
ofthe expansion valve.
This differential is critical to system fault diagnosis
and efficiency checks.
Twelve Cylinder Vehicles only:
Dual pressure switch: This two-function pressure switch
cuts electrical power to the compressor clutch if the system
pressure is outside of the range
of 2 Bar (1st Function) to 30
Bar (2nd Function).
Six Cylinder Vehicles only:
There are two switches incorporated into the high side of the
system which have the following functions:
a) Trinary; This three function pressure switch, cuts electri
-
cal power to the compressor clutch should the system pres- sure not be in a range of 2 bar (1st function) to 30 bar (2nd
function). The switch also provides a ground signal to oper
- ate the appropriate relay (within the 'Stribel,' unit) to ener- gize both engine cooling fans when maximum A/ C cooling
is required. Operation pressure, 20 bar input (3rd function).
b) Pressure Switch Slow Cooling Fans; When the system
pressure is 12 bar, medium A/ C demand, the operation of
this switch connects both engine cooling fans in series to op- erate at half battery voltage and so, half fan speed. 1.
Compressor
2. Condenser
3. Receiver / Drier 4. Expansion Valve
5. Evaporator
6. Pressure switch - Dual type
on 12
cyl & Trinary on 6 cyl
Fig. 1
0
0
Issue 1 August 1994 12 X300 VSM