1994 JAGUAR XJ6 brake light
[x] Cancel search: brake lightPage 9 of 521

Terrn(s1 Abbreviation Definition Previously used (if applicable) term(s) (or Eng- lish Eauivalentl
5
Babbitt metal
backlight
back
-up lamp
balk ring
t
battery positive Voltage B+
Barometric Absolute Pressure BARO
Sensor
base Idle
base timing
battery
before bottom dead center BBDC
before top dead center BTDC
blower BLR
Body Processor Module BPM
British Standards BS
I British Standards Automotive BSAu
brake horsepower
brake mean effective pressure BMEP
brake
ontoff BOO
brake rotor
I bottom dead center BDC
bypass air BPA
bumper guard
I
bushing I
rotating component of manual transmission
which prevents premature engagement of
gears
The positive Voltage from
a battery or any
circuit connected directly to it.
sensor measuring the pressure of
surrounding air at any given temperature
and altitude
Idle
rpm determined by the throttle lever
being hard
-set on the throttle body with the
IAC solenoid disconnected
Spark advance in degrees before top dead
center of the base engine without any control
from the PCM
Electrical storage device producing DC
Voltage by means of electrochemical
reaction
event occurring before BDC
event (usually ignition) occurring before TDC
Device which supplies a current of air at
moderate pressure, e.g. heater or
AJC blower
Control module for body electrical systems,
e.g. interior lamps, windshield wash wipe
control etc..
standard specification issued by the British
Standards Institution
effective horsepower developed by an
engine or motor, as measured by a brake
applied to its output shaft
that part of the effective pressure developed
in a cylinder that would result in a cylinder
output equal to the bhp of the engine
indicates the position of the brake pedal
process of bedding
-in the internal working
surfaces of e.g. an engine by avoiding excess
build
-up of heat
lowest point of piston travel in a
reciprocating engine
mechanical control of throttle bypass air
cylindrical plain bearing white
metal
backlight,
rear screen reversing lamp
baulk ring
B+,
+ve, VSS
BARO, APS
CCM (Central
Control Module).
CPU
brake disc
running
-in
overrider bush
Issue 1 August 1994 8 X300 VSM
Page 34 of 521

2.2 VEHICLE RECOVERY
8 2.2.1 General
m: Prior to vehicle recovery, always ensure the vehicle
keys are available and the vehicle security system is
'OFF'.
The safest and preferred method of vehicle recovery is by
flat bed transporter, although a rear suspended tow may
also be used.
The front and rear towing eyes are provided for use only in
an emergency to move the vehicle
if it is causing an
obstruction, on police instructions, or, when winching the
vehicle onto a recovery transporter.
m: A towing shackle cannot be fastened to the front
towing eye until the grille vane has been removed.
To do this, remove the (three) quarter
-turn fasteners
securing the grille vane (Fig. I), and place the vane
safely to one side. The towing shackle may now be
secured to the towing eye.
0 When thevehicle is being towed (see Towing Recovery), the
gear lever must be set to neutral, 'N' (see Gear-shift Inter- lock) and the ignition key turned to position 'II'to release the
steering lockand renderthe indicators, horn and brake lights
operational.
2.2.2 Gear-shift Interlock
The gear selector lever may only be moved from the park 'F" position by turning the ignition key to position '11' on the key
switch and applying pressure to the footbrake pedal.
To remove the ignition key from the key switch, the gear
selector lever must be moved to park
'P. With the key removed, the gear selector lever will be locked
in park
'P'.
2.2.3
In the event of electrical failure or when moving the vehicle
without power, the gear selector lever can be manually
unlocked from park
'P'. Below the left-hand side of the 'J' gate (Fig. Z), is the gear- shift interlock manual release catch. With a flat bladed
screwdriver, remove the plug, arrowed (Fig. 2). Insert
ignition key and press down catch whilst simultaneously
moving the gear
-shift lever from 'P' position.
Gear-shift Interlock - Manual Override
U: Gear-shift lever can only be moved approximately
25mm with the key still inserted.
Remove key and replace plug. Fig.
1
Fin. 2
Page 35 of 521

gg Jacking, lifting & Vehicle Recovery
2.2.4 Transporting
If thevehicle is being transported on a trailer or flatbed transporter (Fig. I), the handbrake must be applied, the wheels
chocked and if fitted with an automatic transmission, the gear selector lever moved to neutral, 'N' (see Gear-shift
Interlock).
e
JOS-031
Fig. 1
CAUTION: Do not select 'P' because the parking lock mechanism may be damaged by the continuous slight forward
and backward movement of the vehicle on the transporter.
There are four tie-down brackets on the vehicle underbody. Do not attach the tie down hooks of the transporter to the
towing eyes of the vehicle.
2.2.5 Towing Recovery
Adhereto local regulationsforthetowing ofvehicles. In certain countriesthe registration number ofthetowing vehicle
and an 'ON TOW sign or warning triangle must be displayed in a prominent position at the rear of the vehicle which
is being towed.
WARNING: WHEN THE ENGINE
IS NOT RUNNING, THE STEERING AND BRAKES WILL NO LONGER BE
ACCUMULATOR. THEREFORE, BE PREPARED FOR
HEAVY STEERING AND THE NEED FOR GREATLY
INCREASED BRAKE PEDAL PRESSURE.
POWER-ASSISTED.
APPLICATIONS
OF THE BRAKE PEDAL WILL GRADUALLY DEPRESSURIZE THE
*The vehicle may be towed by another for a SHORT DISTANCE ONLY (maximum
0,8km / O.Smile), with the gear lever
in neutral (N) provided that a speed of 48 km / h (30 mile / h) is not exceeded.
2.2.6
The vehicle must be towed with the rear wheels clear of the ground, see suspended towing.
Vehicles with Defective Automatic Transmission:
Issue 1 August 1994 4 X300 VSM
Page 146 of 521

Automatic Transmission (AJ16)
8.1.5 TRANSMISSION ROTARY SWITCH, RENEW
0 (4,OL)
SRO 44.15.36
. Check the shift cable adjustment.
. Switch the ignition ON, apply the footbrake and move the
Switch the ignition OFF and disconnect the battery.
. Open the armrest lid.
. Release and remove the ashtray securing screws.
. Displace the ashtray assembly for access.
. Disconnect the cigar lighter / illumination harness con-
. Place the ashtray assembly aside.
. Displace and remove the console veneer panel rear fin-
isher.
Carefully displace the Performance Mode switch from the
gear surround finisher.
. Disconnect the Performance Mode switch from the har-
ness multi-pin plug.
Displace and remove the Performance Mode switch sur-
round finisher.
Displace and remove the shift lever surround finisher.
. Release and remove the veneer panel wing nuts.
= Displace and remove the console finisher veneer panel.
Cut and remove the rotary switch harness securing straps.
= Disconnect the rotary switch harness multi-pin plugs.
. Reposition the tunnel carpet for access to the harness
Displace and reposition the grommet down through the
. Feed the harness through the tunnel to the underside of
. Raise the vehicle on a ramp.
. From beneath the vehicle, release and remove the rotary
switch harness to transmission
'F" clip securing nut; dis-
place and reposition the 'P' clip from the stud.
Release and remove the rotary switch harness to trans-
mission 'P' clip securing screw.
Release and remove the rotary switch protection cover
(1 Fig.1) securing bolts; displace and remove the switch
cover.
shift
lever to
'N'.
n ect o rs .
@
grommet.
tunnel.
the vehicle.
Disconnect the transmission multi-pin socket (2 Fig.1).
. Reposition the harness clear of the transmission unit.
. Release and remove the rotary switch securing nuts.
. Displace and remove the switch assembly.
. Displace and remove the 'P' clips from the harness.
. Fit and align the 'P' clips to the new harness / switch as-
. Displace the rubber sealing plug (3 Fig.1) from the rotary
sembly.
switch.
i3 2 JLL-690
Fig.
1
X300 VSM 9 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 208 of 521
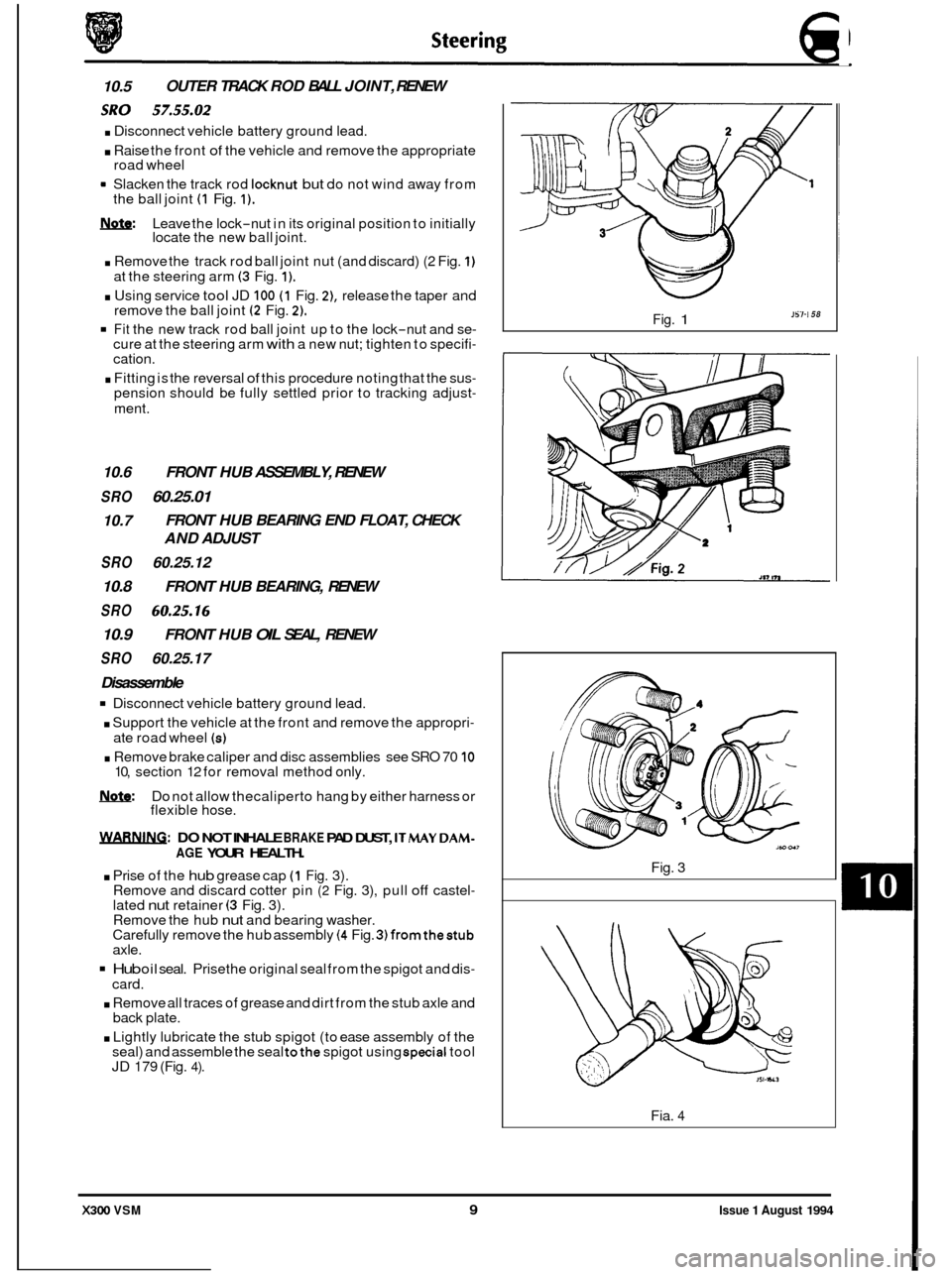
10.5 OUTER
TRACK ROD BALL JOINT, RENEW
sRo . Disconnect 57.55.02 vehicle battery ground lead.
. Raise the front of the vehicle and remove the appropriate
road wheel
Slacken the track rod
locknut but do not wind away from
the ball joint (1 Fig. 1).
m: Leave the lock-nut in its original position to initially
locate the new ball joint.
. Remove the track rod ball joint nut (and discard) (2 Fig. 1)
at the steering arm (3 Fig. 1).
. Using service tool JD 100 (1 Fig. 2), release the taper and
remove the ball joint (2 Fig. 2).
Fit the new track rod ball joint up to the lock-nut and se- cure at the steering arm with a new nut; tighten to specifi- cation.
. Fitting is the reversal of this procedure noting that the sus- pension should be fully settled prior to tracking adjust-
ment.
0 10.6 FRONT HUB ASSEMBLY, RENEW
SRO 60.25.01
10.7
SRO 60.25.12
10.8 FRONT HUB BEARING, RENEW
SRO 60.25.16
10.9
SRO 60.25.17
Disassemble
Disconnect vehicle battery ground lead.
. Support the vehicle at the front and remove the appropri-
. Remove brake caliper and disc assemblies see SRO 70 10
IWQ: Do not allow thecaliperto hang by either harness or
flexible hose.
FRONT HUB BEARING END FLOAT, CHECK
AND ADJUST
FRONT HUB
OIL SEAL, RENEW
ate road wheel (s)
10, section 12 for removal method only.
WARNIM: DO NOT INHALE BRAKE PAD DUST, ITMAY DAM-
0
AGE YOUR HEALTH.
. Prise of the hub grease cap (1 Fig. 3).
Remove and discard cotter pin (2 Fig. 3), pull off castel- lated nut retainer (3 Fig. 3).
Remove the hub nut and bearing washer.
Carefully remove the hub assembly (4 Fig. 3)fromthestub axle.
Hub oil seal. Prise the original seal from the spigot and dis-
card.
. Remove all traces of grease and dirt from the stub axle and
back plate.
. Lightly lubricate the stub spigot (to ease assembly of the
seal) and assemble the seal tothe spigot using special tool JD 179 (Fig. 4).
JS7-i 58 Fig. 1
Fig. 3
Fia.
4
X300 VSM 9 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 217 of 521

Suspension Systems
11.4.3 Front End Inspection
Do not check and adjust front wheel alignment without carrying out the following inspection for front end damage and
wear:
. Check for specified air pressure in all four tires.
Raise front of vehicle off the floor; grasping upper and lower surface of the tire, shake each front wheel to check for
. Check front suspension lower arm ball joint and mounts for looseness, wear and damage.
Check steering gear mountings and all steering linkages for looseness.
. Renew parts if necessary.
. Grasp upper and lower surface of tire and shake each wheel to check wheel bearing end play.
. Check the action of the front dampers and the condition of their attachments, as sticking or binding front dampers
worn
bearings.
Check brake caliper mountings.
may not allow the vehicle to settle in to a normal level position, possibly affecting the front-wheel alignment.
m: Front wheel bearings are adjustable (0.001 to 0.003 in. endfloat).
11.4.4
. Check the wheel bearings.
. Inspect the front suspension upper joint and renew front suspension lower wishbone if needed.
Raise vehicle and position floor jacks beneath the front suspension lower wishbone.
Grasp the lower edge of the tire and move the wheel in and out.
While moving the wheel, observe the upper and lower wishbone.
. Movement between the vertical links and the wishbones indicates abnormal ball joint wear.
. Renew ball joints.
. Check the front wheel bearings.
. Check for excessive play and wear.
Upper / Lower Ball Joint Inspection
11.4.5 Damper Inspection
m: The gas-pressurized hydraulic front dampers are not serviceable, adjustable or refillable.
Verify that all attachments of the suspension components and the front dampers are tight. Renew any front damper
. Check front dampers for external damage.
. Check for oil leakage and vehicle sag.
that
has a damaged integral lower mounting bushing.
0 Oil Leak
Leakage is the condition in which the entire damper body is covered with oil and from where
it will drip on to
the pavement. Due to correct damper lubrication a light film of oil (weepage) can usually be seen on the upper
portion of the damper.
Should there be any leakage, ensure that the fluid does not originate from sources other than the front damper.
Renew worn or damaged dampers.
0 Vehicle Sag
Renewing front dampers will not correct the problem of vehicle sag, as basically this is controlled by the spring
units.
issue 1 August 1994 4 X300 VSM
Page 224 of 521

12.1 ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ASS), GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The anti-lock braking system (ABS) components are combined with a hydraulic booster and tandem master cylinder (TMC) to provide a two-circuit braking system. The anti-lock braking system comprises the following components:
0 Four inductive wheel speed sensors, hub end mounted
0 ABS warning light
0 Hydraulic module.
The hydraulic module consists of an electric motor driven pump,
two low pressure accumulators, valve block and an
ABS electronic control module.
m: Electronic control modules for vehicles without traction control are designated ABS CM. Control modules for
vehicles with traction control are designated ABS /TC CM.
The valve block houses solenoid operated valves which are activated by voltage signals from the control module. The
signals are generated using wheel speed information received from the wheel speed sensors.
For vehicles without traction control the valves operate on three circuits, two front and one rear, as necessary to pre
- vent wheel locking during braking. Brake pressure is modulated individually at thefront wheels and collectively at the
rear. Rear wheel control operates on a 'select low' principle i.e. locking in either wheel is sensed, and controlled brake
pressure is applied to both wheels.
For vehicles with traction control the valves operate on four circuits. During ABS control the rear wheel are controlled
on a 'select low' principle (as above), but during traction control operation the rear wheels are controlled individually.
0
1yQfB: Functional and diagnostic information for the ABS CM and the ABS/TC CM is contained in the Electrical Diag-
nostic Manual (EDM), Section 12.
ABS Warning lamp / Traction Control Warning lamp /Fluid level Indicator
The ABS and traction control warning lamps, mounted in the instrument panel, indicate a fault in the ABS or traction
control. These systems are inhibited or disabled when the lamps are lit, although conventional braking is unaffected.
When the ignition is switched on, an ABS self test is initiated. During this test, the ABS and traction control warning
lamps are
lit for approximately 1.7 seconds and then extinguish. A fault is indicated if the warning lamps remain lit or
come on whilst the vehicle is being driven.
W: The ABS self test is masked by the 5 second lamp test initiated when the ignition is switched on.
The fluid level indicator lamp, mounted in the instrument panel, is
lit when the brake fluid falls below the minimum
mark on the brake fluid reservoir.
ABS / Traction Control - Inhibit / Disable
Faults conditions are detected by the ABS/TC CM which disables the ABS and traction control until the fault is rectified.
The ABS and traction control warning lights on the instrument pack remains lit whilst a fault exists. The system will
be disabled when the following conditions occur:
0
0 Valve failure
0 Sensor failure
0 Main driver failure (internal ABS /TC CM fault)
0 Redundancy error (internal ABS JTC CM fault)
0 Overvoltage J undervoltage
0 Pump motor failure.
0 Throttle valve actuator motor failure (traction control vehicles only).
0 Throttle valve actuator potentiometer failure (traction control warning light only).
X300 VSM 1 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 229 of 521

12.1.5. ABS Components
Hydraulic Module
The hydraulic module is located under the bonnet adjacent
to the engine compartment firewall. It is secured within a steel mounting bracket at three securing points. All elec- tronic and power connections are made through one cable
loom connect ion.
The hydraulic pump
(1 Fig. 1) is a reciprocating two-circuit pump in which one brake circuit is assigned to each pump
circuit. The pump supplies adequate pressure and volume
supply to the brake circuits under anti
-lock braking condi- tions. The pump is driven by and electric motor (2 Fig. 1). The
pump housing incorporates two low pressure accumulators
and damping chambers for each brake circuit.
A modulator valve block
(3 Fig. 1) incorporates the ABS CM or ABS / TC CM (4 Fig. 1). Vehicles with traction control are
fitted with a throttle position actuator (5 Fig. I), which is an
electrical device controlled by the ABS 1 TC CM.
Valve blocks on vehicles without traction control comprise
six solenoid valves, three normally open (NO) inlet valves
and three normally closed
(NC) outlet valves. These valve
blocks have three outlet ports. Valve blocks on vehicles with
traction control comprise nine solenoid valves, four
NO inlet valves,four NC outlet valves and one special isolating valve.
Fig. 2 shows a hydraulic module for vehicles with traction
control. The valve block (2 Fig. 2) has four outlet ports (Indi- vidual control of the driven wheels).
A BS CM, A BS / TC CM
The ABS CM or ABS TCI CM locates beneath the modulator
valve block and is secured by
two screws. The CM houses
the solenoids which operate the inlet and outletvalves of the
modulator valve block. When fitted, the valve stems locate
in the
CM mounted solenoids. There is no electrical connec- tion between the CM and the modulator valve block. Fig. 3 shows an ABS TC 1 CM having nine solenoids.
The
CM functions include the following:
0 Providing control signals for the operation of ABS
and traction control solenoid valves
0 Calculating wheel speed from voltage signals trans- mitted by the wheel speed sensors
0 Monitoring of all electrical components
0 On Board Diagnostics (OBD): storage of possible fail- ures in a non-volatile memory.
The signals from the four wheel speed sensors are indepen
- dently processed by the ABS CM or ABSITC CM, calculating
numerical values which correspond directly to the wheel
speed. These values are converted into control signals for
pressure modulation during ABS control.
The ABS and traction control
are continuously monitored,
whilst the ignition is on,for possiblefaults and interruptions.
If a fault is detected, the module deactivates the ABS and
indicates this by lighting the ABS warning lamp. In a fault
condition, conventional braking is unaffected. The module
stores fault codes in a non
-volatile memory which can be
read via the OBD link.
U: For electrical diagnostic information on the ABS I traction control systems, refer to EDM, Section 12. Fia.
1
Fia. 2
Fin. 3 I
J70286
Issue 1 August 1994 X300 VSM