1994 HONDA INTEGRA Oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: Oil pressurePage 291 of 1413

Fuel Supply System
Fuel Injectors
- --l- - \-l-l
116l- -ltc l-/---r- / ---i- \
The Fuel Injectors a.e a solenoid-actuated constant-stroke pintle type consisting of a solenoid, plungel n€edle valvs and
housing. When cur.ent is applied to the solsnoid coil, the vslve litts up and pressurized fuel is injected. Because the nee-
dle valve litt and the luel pressure are constant, the iniection quantity is determined by the length of time that the valv€
is open (i.e., the duration the cu.rent is supplied to the solenoid coill. The Fu€l Iniector is sealed by an O-ring and seal
ring at the top and bottom. These seals also reduce operating nois6.
O.RII{G FUEL RAIL
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MlL) indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) l6: A problem in
the Fuel lniector circuit.
FILTER
PTUNGER
-_-- - ___L-
IrGl- lto l--|.---:_-
- Tho MIL has boen roportod on.- Wilh tho SCS .hon connocto.conoctod (soo pago 11-34),code 16 is indicalod.
Do the ECM Besel Procedure (seepage l l -351.
Intermittant tailura, aystam ir OKat thir tim. (t..1 drivo m.y b.nocaar!ry1.Ch.ck lor poor connactiona ot100!6 wir6!.t C221 (loortod rtright .hock low.rl, C121,C122,Cl23, Cl24 llu6l InFctorrl, lndECM.
ls the MIL on and does itindicate code l6?
NOTE: lf engine willnot start, it may tak6lO seconds ol cranking to sgt th6 code.
{To page 1 1-1O31
11-102
Page 294 of 1413
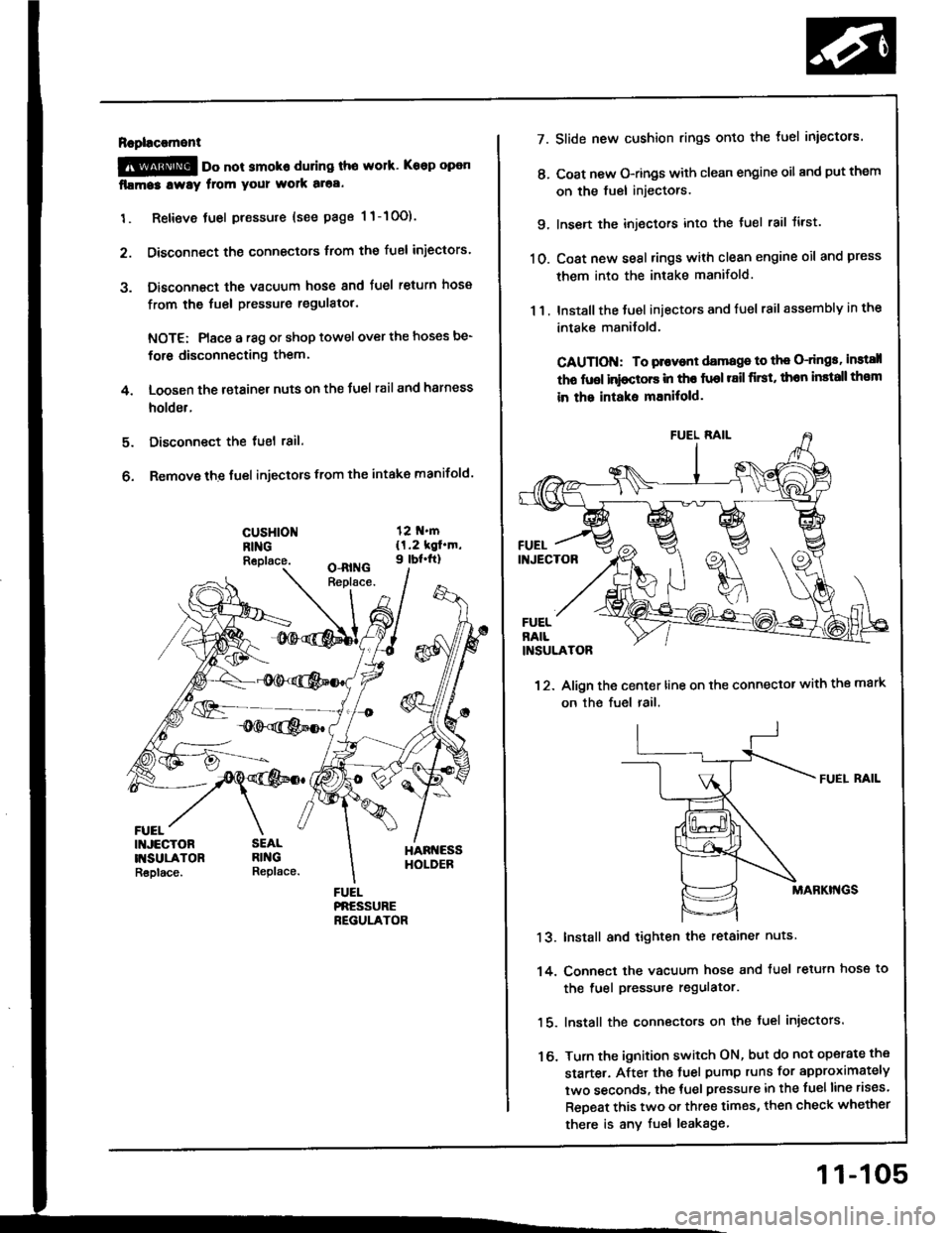
Rapl!c!ment
@ oo not smoko during tho work. Keep open
fllma3 lway from your wolk aloa.
1. Retieve tuel pressure {see page 1 1-10O).
2. Disconnect the connectors trom the fuel iniectors.
3. Disconnect the vacuum hose and fuel return hosa
from the fuel pressure regulatol.
NOTE: Place a r8g or shop towel over the hoses be-
for6 disconnecting them.
4. Loosen the retainer nuts on the Juel rail and harness
holder.
Disconnect the tuel 18il.
Remove the fuel injectors from the intake manifold.
5.
6.
cusHloNRINGReplace.
FUEL
7.
t'.
9.
10.
13.
14.
16.
11.
Slide new cushion rings onto the luel iniectors.
Coat new O-rings with clean engine oil and put them
on the fuel injectors.
Insen the injectors into the tuel rail tirst.
Coat new seal rings with clean engine oil and press
them into the intake manifold.
Install the Juel iniectors and fuel rail assembly in the
intake manilold.
CAUTION: To plovont damage to th€ O-dngs, instsll
tho fuol inioctors in tho fuol r8il first, thon install th€m
in the intaks mEnitold.
12. Align the center line on the connector with the mark
on the fuel rail.
FUEI. RAIL
MABKI'{GS
Install and tighten the retainer nuts
Conn€ct the vacuum hose and tuel retuln hose to
the fuel pressure regulator.
lnstall the connecto.s on the fuel injectors.
Turn the ignition switch ON, but do not operate the
starte.. After the tuel pump runs for approximately
two seconds, the tuel pressure in the fuelline rises.
ReDeat this two or three times, then check whether
there is any fuel leakage
11-105
Page 296 of 1413

Raplacoment
@ oo not amoko whil6 working on fuel sys-
tam. Koop open flamo away tlom your work atea'
1. Place a shop towel under the fuel pressure regula-
tor, then reliev€ tuel pressure (see page 1l-10O).
2. Disconnect the vacuum hose and fuel return hose.
3. Remove the two 6 mm retainer bolts.
12 N.m{1.2 kgl.m,9 rbf.ft)
NOTE:
a Replaco the O-ring.
a When assembling the fuel pressure regulator, ap-
ply clean engine oil to the O-ring and assemble
it into its proper position, taking care not to
damage the O-dng.
Rsplace.
11-107
Page 394 of 1413

Special Tools
Rol. No. Tool NumbslDescriptionOty Page Reference
o
IA\
,6\
@
€/
o
@rt)
@
@
\9
@
@
@
@
@
@
OTGAB PF50l OO
oTGAB-PF50101
oTGAE-PG40200
oTHAC-PK4010A
oTHAE-PL50lOO
oTLAE-PX40100
OTLAJ PT30l OA
OTMAJ-PY4O'I 1A
oTMAJ-PY40120
oTPAZ -OO10100
07406-OO20003
o7406 0070000
07736 A01000A
o7746-O010100
o7746-O010500
07746-OO10600
07746 0030100
o7749-O010000
07947-6340500
Mainshatt Holder
Clutch Spring Compressor Bolt Assembly
Housing Puller
Clutch Spring Compressor Attachment
Clutch Spring Compressor Attachment
Test Harness
A/T Oil Pressure Hose, 221O mm
A/T Oil Pressure Adapter
SCS Short Connector
A/T Oil Pressure Gauge Set w/panel
A/T Low Pressure Gauge w/panel
Adjustable Bearing Puller, 25-40 mm
Attachment, 32 x 35 mm
Attachment, 62 x 68 mm
Attachment, 72 x 75 mm
Driver, 40 mm l.D.
Driver
Oriver Attachment
'I
I
1
1,1
1
1
1,|
1
1
1
1
1
I
I'I
1
14-1 1 1.160
14-144,147
14-1 1 3
14- 144,147
14 144,'t47
14-49,90
14-94
14-94't 4-44
14-94
14-94
14-150,151
14-139,140
14-140.1 50,1 51,1 52, 1 53
14-150,152
14-134
1 4-1 39,'140, 1 50.1 51,1 52
14,150
Edrn$r--€
o
a)
a6l@o
@@@@(r)
*@ Must be used with commercially available 3/8 in. x 16 threads/in. slide hammer.
@
14-2
Page 395 of 1413

The Automatic Transmission is a combination of a 3-e,ement torque convefter and triple-shaft electfonically controlled
automatic transmission which provides 4 speeds forward and 1 speed reverse. The entire unit is positioned in line with
the engine.
Torque Converter, Gears and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump, turbine and stator assembly in a single unit, The torque converter is connected
to the engine crankshaft so they turn together as a unit as the engine turns. Around the outside of the torque converter
is a ring gear which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being staned. The entire torque converter assem-
bly serves as a flywheel while transmitting power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has three parallel shafts, the mainshaft. countershaft and sub-shaft. The mainshatt is in line with the
engine crankshaft.
The mainshaft includes the clutches for 1 st, and 2ndl4th, and gears for 3rd. 2nd, 4th, reverse and l st (3rd gear is in-
tegral with the mainshaft, while reverse gear is integral with the 4th gear).
The countershaft includes the 3rd clutch and gears Ior 3rd, 2nd,4th, reverse, lst and parking. Reverse and 4th gears
can be locked to the countershaft at its center, providing 4th gear or reverse, depending on which way the selector is moved.
The sub-shaft includes the lst-hold clutch and gears for 1st and 4th
The gears on the mainshait are in constant mesh with those on the countershaft and sub-shaft. When certain combina-
tions of gears in the transmission are engaged by the clutches, power is transmitted from the mainshaft to the counter-
shaft via the sub-shatt to provide @, E, tr. tr and @ position.
Electronic Control
The electronic control system consists of the Transmission Control Module {TCM), sensors, and 4 solenoid valves. Shift-
ing and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all conditions.
The TCM is located below the dashboard, behind the left side kick panel on the driver's side.
Hydraulic Control
The valve bodies include the main valve body, secondary valve body, regulator valve body. servo body, and lock-up valve
body throuqh the respective separator plates.
They are bolted on the torque converter housing.
The main valve body contains the manual valve, 1-2 shift valve, 2-3 shift valve, Clutch Pressure Cont.ol (CPC) valve,
4th exhaust valve, relief valve, and oil pump gears.
The secondary valve body contains the 4-3 kick-down valve,3-2 kick-down valve,2-3 orifice cont.ol valve, 3-4 shitt
valve, orifice control valve. modulator valve, and servo control valve
The regulator valve body contains the pressure regulator valve. lock-up control valve, torque converter check valve, and
cooler check valve.
The servo bodv contains the servo valve which is integrated with the reverse shift fork, throttle valve B, and accumulators.
The lock-ug valve bodv contains the lock-up shift valve and lock-up timing B valve. and is bolted on the secondary valve
body.
Fluid from the regulator passes through the manual valve to the various control valves.
Shitt Control Mochanism
Input to the TCM i.om various sensors located throughout the car determines which shift control solenoid valve should
be activated.
Activating a shift control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This pressurizes
a line to one of the clutches. engaging that clutch and its corresponding gear.
Lock-up Mechanism
In @ position. in 2nd, 3rd and 4th, and E position in 3rd, pressurized tluid can be drained from the back of the tor-
que converter through an oil passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held against the torque converter cover. As this
takes Dlace, the mainshaft rotates at the same speed as the engine crankshatt. Together with hydraulic control, the TCM
optimizes the timing ol the lock-up mechanism.
The lock-up valves control the range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B, and throttle valve B
When lock-up control solenoid valves A and B activate, modulator pressure changes. Lock-up control solenoid valves
A and B are mounted on the torque converter housing, and are controlled by the TCM.
(cont'd)
14-3
Page 398 of 1413

Description
Clutches
The four speed automatic transmission uses hydraulically actuated clutches to engage or disengage the transmission gears.
When clutch pressure is introduced into the clutch drum, the clutch piston is applied. This presses the iriction discs and
steel plates together, locking them so they don't slip. Power is then transmitted through the engaged clutch pack tojts hub-mounted gear.
Likewise, when clutch pressure is bled from the clutch pack. the piston releases the friction discs and steel plates, and
they are {ree to slide past each other while disengaged. This allows the gear to spin independently on its shaft, transmit-
ting no power.
1st ClutchThe l st clutch engages/disengages 1st gear, and is located at the end of the mainshaft, just behind the right side cover.
The 1st clutch is supplied clutch pressure by its oil feed pipe within the mainshaft.
1st-hold clutchThe 1st-hold clutch engages/disengages 1st-hold or I Fosition, and is located at the center ol the sub-shaft. The 1st-
hold clutch is supplied clulch pressure by its oil feed pipe within the sub-shait.
2nd ClutchThe 2nd clutch engages/disengages 2nd gear, and is located at the center of the mainshaft. The 2nd clutch is joined
back-to-back to the 4th clutch. The 2nd clutch is supplied clutch pressure through the mainshaft by a circuit connected
to the regulator valve body.
3rd Clutch
The 3rd clutch engages/disengages 3rd gea.. and is located at the end oJ the countershaft, opposite the right side cover.
The 3rd clutch is supplied clutch pressure by its oil feed pipe within the countershaft,
4th clurch
The 4th clutch engages/disengages 4th gear. as well as reverse gear, and is located at the center of the mainshaft.
The 4th clutch is joined back-to-back to the 2nd clutch. The 4th clutch is supplied clutch pressure by its oil feed pipe
within the mainshalt.
One-way Clutch
The one-way clutch is posjtioned between the parking gear and 1st gear. with the parking gear splined to the counter-
shaft. The 1st gear provides the outer race, and the parking gear provides the inner race surface. The one-way clutch
locks up when power is transmitted from the mainshaft 1st gear to the countershaft lst ggel _The 1st clutch and gears remain engaged in the 1st. 2nd. 3rd, and 4th gear ranges in the @, E or E position.
However, the one-way clutch disengages when the 2nd. 3rd, or 4th clutches/gears are applied in the E, lD.l o, Eoosttton.
This is because the increased rotational speed of the gears on the countershaft over-ride the locking "speed range" of
the one-way clutch. Thereafter, the one-way clutch free-wheels with the lst clutch still engaged.
COUNTERSHAFT 1ST GEAR
FREE
:>
LOCKS
aF
NOTE:View trom right side cover side.
14-6
Page 415 of 1413

Hydraulic Control
The valve bodies include the main valve body, secondary valve body, regulator valve body, servo body and lock-up valve
body.
The oil pump is driven by splines behind the torque converter which is attached to the engine. Oil flows th.ough the
regulator valve to maintain specified pressure through the main valve body to the manual valve, directing pressure to
each of the clutches,
SHIFT CONTROL SOLEIIOIDVALVE ASSEMBLY
RTGHT SIDE COVER
LOCK.UP VALVE BODY
VALVE BODY
REGULATOR VBODY
SOLENOID VALVEASSEMBLY
4<.__i: )o.-
OIL PUMP GEARS
14-23
Page 417 of 1413

Rcgulator Valve
The r€gulator valve maintains a constant hydraulic pressure from the oil pump to the hydraulic control system, whil€
alEo furnishing oil to the lubricating system and torque convener.
Oil flows through B and B'. The oil which enters through B flows thfough the valve orifice to A, pushing the regulator
valve to the right. Acco.ding to the level of hydraulic pressure through B, the position of the valve changes, and the
amount of the oil thlough D from B'thus changes. This operation is continued. thus maintaining the line pressure.
IEI{GINE ]IIOT RUNNINGI{ENGINE RUNNING)
Siator Reaction Hydtaulic Pressure Control
Hydraulic pressure increase, according to torque, is performed by the regulator vslve using stator torque reaction. Thestator shaft is splined to the stator and its a.m end contacts the fegulator spring cap. When the car is accelerating orclimbing (Torque Convener Range). stator torque reaction acts on the stator shalt and the stator shaft arm pushes thersgulator spring cap in this - direction in proportion to the reaction. The spring compresses and the regulator valve movesto increase the regulated control pressure or line pressure. Line pressure is maximum when the stator reaction is maximum.
TOR VALVE
(cont'd)
From OIL PUMP
STATOR SHAFTSTATOR SHAFT ARM
14-25