1993 FORD MONDEO window
[x] Cancel search: windowPage 24 of 279
the tyre to cause deflation. If removal of a nail
reveals that the tyre has been punctured, refit
the nail, so that its point of penetration is
marked. Then immediately change the wheel,
and have the tyre repaired by a tyre dealer. Do
not drive on a tyre in such a condition. If in any
doubt as to the possible consequences of any
damage found, consult your local tyre dealer
for advice.
8General tyre wear is influenced to a large
degree by driving style - harsh braking and
acceleration, or fast cornering, will all produce
more rapid tyre wear. Interchanging of tyres
may result in more even wear; however, it is
worth bearing in mind that if this is completely
effective, the added expense is incurred of
replacing simultaneously a complete set of
tyres, which may prove financially restrictive
for many owners.
9Front tyres may wear unevenly as a result of
wheel misalignment. The front wheels should
always be correctly aligned according to the
settings specified by the vehicle
manufacturer.10Don’t forget to check the spare tyre for
condition and pressure.
11Legal restrictions apply to many aspects
of tyre fitting and usage, and in the UK this
information is contained in the Motor Vehicle
Construction and Use Regulations. It is
suggested that a copy of these regulations is
obtained from your local police, if in doubt as
to current legal requirements with regard to
tyre type and condition, minimum tread depth,
etc.
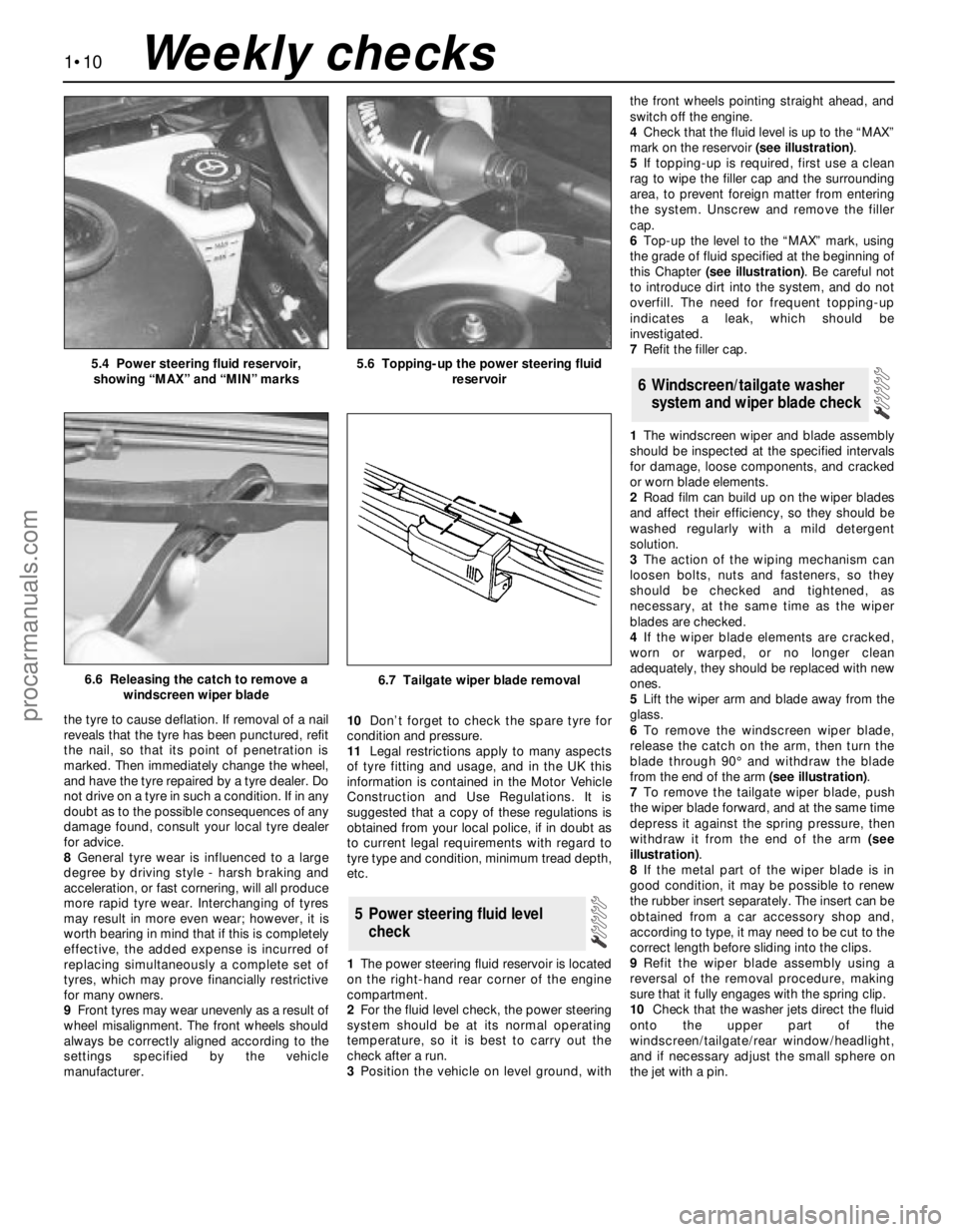
1The power steering fluid reservoir is located
on the right-hand rear corner of the engine
compartment.
2For the fluid level check, the power steering
system should be at its normal operating
temperature, so it is best to carry out the
check after a run.
3Position the vehicle on level ground, withthe front wheels pointing straight ahead, and
switch off the engine.
4Check that the fluid level is up to the “MAX”
mark on the reservoir (see illustration).
5If topping-up is required, first use a clean
rag to wipe the filler cap and the surrounding
area, to prevent foreign matter from entering
the system. Unscrew and remove the filler
cap.
6Top-up the level to the “MAX” mark, using
the grade of fluid specified at the beginning of
this Chapter (see illustration). Be careful not
to introduce dirt into the system, and do not
overfill. The need for frequent topping-up
indicates a leak, which should be
investigated.
7Refit the filler cap.
1The windscreen wiper and blade assembly
should be inspected at the specified intervals
for damage, loose components, and cracked
or worn blade elements.
2Road film can build up on the wiper blades
and affect their efficiency, so they should be
washed regularly with a mild detergent
solution.
3The action of the wiping mechanism can
loosen bolts, nuts and fasteners, so they
should be checked and tightened, as
necessary, at the same time as the wiper
blades are checked.
4If the wiper blade elements are cracked,
worn or warped, or no longer clean
adequately, they should be replaced with new
ones.
5Lift the wiper arm and blade away from the
glass.
6To remove the windscreen wiper blade,
release the catch on the arm, then turn the
blade through 90° and withdraw the blade
from the end of the arm (see illustration).
7To remove the tailgate wiper blade, push
the wiper blade forward, and at the same time
depress it against the spring pressure, then
withdraw it from the end of the arm (see
illustration).
8If the metal part of the wiper blade is in
good condition, it may be possible to renew
the rubber insert separately. The insert can be
obtained from a car accessory shop and,
according to type, it may need to be cut to the
correct length before sliding into the clips.
9Refit the wiper blade assembly using a
reversal of the removal procedure, making
sure that it fully engages with the spring clip.
10Check that the washer jets direct the fluid
onto the upper part of the
windscreen/tailgate/rear window/headlight,
and if necessary adjust the small sphere on
the jet with a pin.
6 Windscreen/tailgate washer
system and wiper blade check
5 Power steering fluid level
check
1•10
5.4 Power steering fluid reservoir,
showing “MAX” and “MIN” marks5.6 Topping-up the power steering fluid
reservoir
6.7 Tailgate wiper blade removal6.6 Releasing the catch to remove a
windscreen wiper blade
Weekly checks
procarmanuals.com
Page 33 of 279
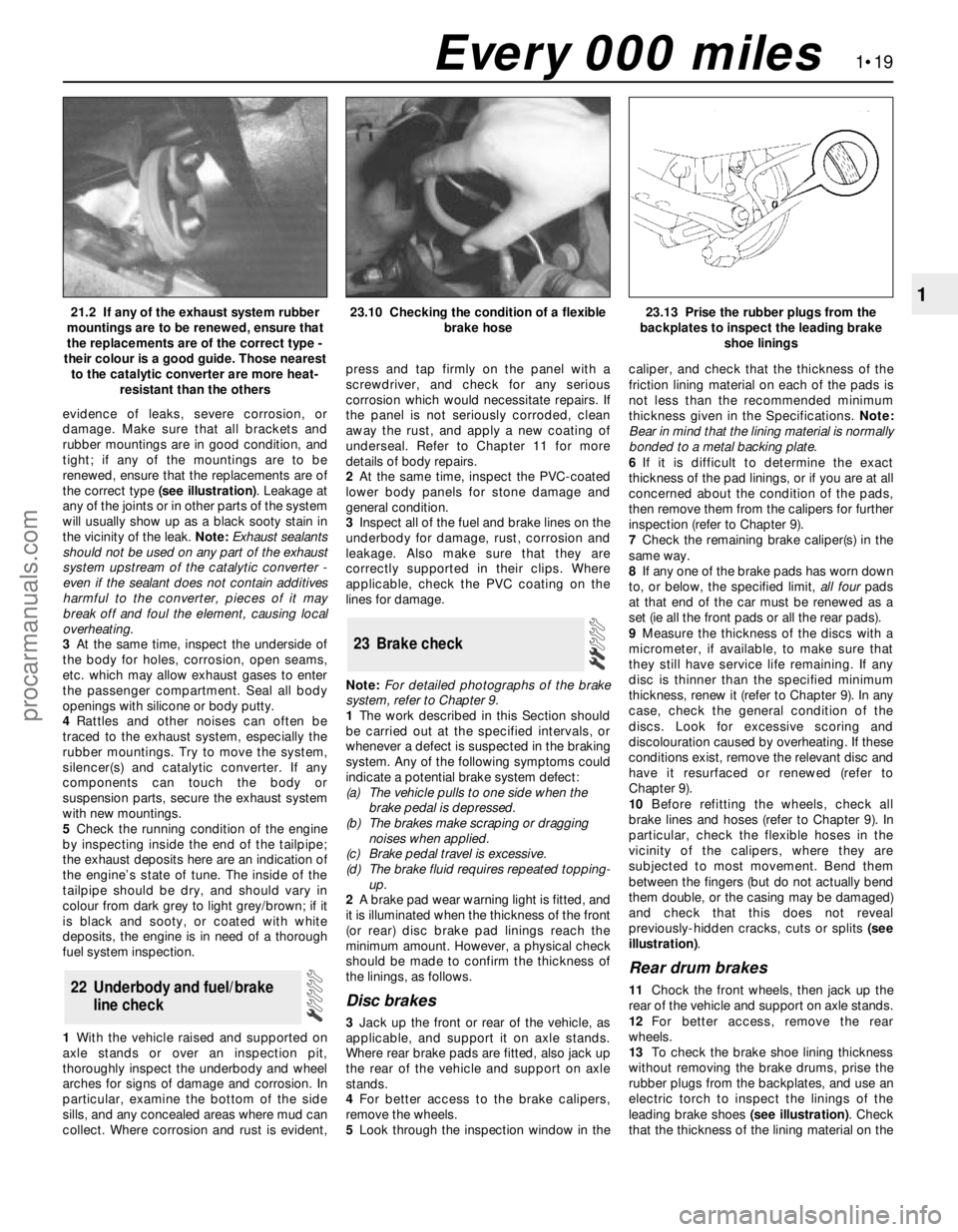
evidence of leaks, severe corrosion, or
damage. Make sure that all brackets and
rubber mountings are in good condition, and
tight; if any of the mountings are to be
renewed, ensure that the replacements are of
the correct type (see illustration). Leakage at
any of the joints or in other parts of the system
will usually show up as a black sooty stain in
the vicinity of the leak. Note:Exhaust sealants
should not be used on any part of the exhaust
system upstream of the catalytic converter -
even if the sealant does not contain additives
harmful to the converter, pieces of it may
break off and foul the element, causing local
overheating.
3At the same time, inspect the underside of
the body for holes, corrosion, open seams,
etc. which may allow exhaust gases to enter
the passenger compartment. Seal all body
openings with silicone or body putty.
4Rattles and other noises can often be
traced to the exhaust system, especially the
rubber mountings. Try to move the system,
silencer(s) and catalytic converter. If any
components can touch the body or
suspension parts, secure the exhaust system
with new mountings.
5Check the running condition of the engine
by inspecting inside the end of the tailpipe;
the exhaust deposits here are an indication of
the engine’s state of tune. The inside of the
tailpipe should be dry, and should vary in
colour from dark grey to light grey/brown; if it
is black and sooty, or coated with white
deposits, the engine is in need of a thorough
fuel system inspection.
1With the vehicle raised and supported on
axle stands or over an inspection pit,
thoroughly inspect the underbody and wheel
arches for signs of damage and corrosion. In
particular, examine the bottom of the side
sills, and any concealed areas where mud can
collect. Where corrosion and rust is evident,press and tap firmly on the panel with a
screwdriver, and check for any serious
corrosion which would necessitate repairs. If
the panel is not seriously corroded, clean
away the rust, and apply a new coating of
underseal. Refer to Chapter 11 for more
details of body repairs.
2At the same time, inspect the PVC-coated
lower body panels for stone damage and
general condition.
3Inspect all of the fuel and brake lines on the
underbody for damage, rust, corrosion and
leakage. Also make sure that they are
correctly supported in their clips. Where
applicable, check the PVC coating on the
lines for damage.
Note:For detailed photographs of the brake
system, refer to Chapter 9.
1The work described in this Section should
be carried out at the specified intervals, or
whenever a defect is suspected in the braking
system. Any of the following symptoms could
indicate a potential brake system defect:
(a) The vehicle pulls to one side when the
brake pedal is depressed.
(b) The brakes make scraping or dragging
noises when applied.
(c) Brake pedal travel is excessive.
(d) The brake fluid requires repeated topping-
up.
2A brake pad wear warning light is fitted, and
it is illuminated when the thickness of the front
(or rear) disc brake pad linings reach the
minimum amount. However, a physical check
should be made to confirm the thickness of
the linings, as follows.
Disc brakes
3Jack up the front or rear of the vehicle, as
applicable, and support it on axle stands.
Where rear brake pads are fitted, also jack up
the rear of the vehicle and support on axle
stands.
4For better access to the brake calipers,
remove the wheels.
5Look through the inspection window in thecaliper, and check that the thickness of the
friction lining material on each of the pads is
not less than the recommended minimum
thickness given in the Specifications. Note:
Bear in mind that the lining material is normally
bonded to a metal backing plate.
6If it is difficult to determine the exact
thickness of the pad linings, or if you are at all
concerned about the condition of the pads,
then remove them from the calipers for further
inspection (refer to Chapter 9).
7Check the remaining brake caliper(s) in the
same way.
8If any one of the brake pads has worn down
to, or below, the specified limit, all fourpads
at that end of the car must be renewed as a
set (ie all the front pads or all the rear pads).
9Measure the thickness of the discs with a
micrometer, if available, to make sure that
they still have service life remaining. If any
disc is thinner than the specified minimum
thickness, renew it (refer to Chapter 9). In any
case, check the general condition of the
discs. Look for excessive scoring and
discolouration caused by overheating. If these
conditions exist, remove the relevant disc and
have it resurfaced or renewed (refer to
Chapter 9).
10Before refitting the wheels, check all
brake lines and hoses (refer to Chapter 9). In
particular, check the flexible hoses in the
vicinity of the calipers, where they are
subjected to most movement. Bend them
between the fingers (but do not actually bend
them double, or the casing may be damaged)
and check that this does not reveal
previously-hidden cracks, cuts or splits (see
illustration).
Rear drum brakes
11Chock the front wheels, then jack up the
rear of the vehicle and support on axle stands.
12For better access, remove the rear
wheels.
13To check the brake shoe lining thickness
without removing the brake drums, prise the
rubber plugs from the backplates, and use an
electric torch to inspect the linings of the
leading brake shoes (see illustration). Check
that the thickness of the lining material on the
23 Brake check
22 Underbody and fuel/brake
line check
1•19
121.2 If any of the exhaust system rubber
mountings are to be renewed, ensure that
the replacements are of the correct type -
their colour is a good guide. Those nearest
to the catalytic converter are more heat-
resistant than the others23.10 Checking the condition of a flexible
brake hose23.13 Prise the rubber plugs from the
backplates to inspect the leading brake
shoe linings
Every 000 miles
procarmanuals.com
Page 109 of 279

rings, and intend to re-use the same injectors,
remove the old nose seal and O-rings, and
discard them.
22Further testing of the injector(s) is beyond
the scope of the home mechanic. If you are in
doubt as to the status of any injector(s), it can
be tested at a dealer service department.
23Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure, noting the following points:
(a) Lubricate each nose seal and O-ring with
clean engine oil on installation.
(b) Locate each injector carefully in the fuel
rail recess, ensuring that the locating tab
on the injector head fits into the slot
provided in the rail. Tighten the bolts to
the specified torque.
(c) Fit a new seal to each fuel rail nose, and
ensure the seals are not displaced as the
rail is refitted. Ensure that the fuel rail is
settled fully in the manifold before
tightening the three bolts evenly and to
the torque wrench setting specified.
(d) Fasten the fuel feed and return quick-
release couplings as described in Sec-
tion 3.
(e) Ensure that the breather hose, vacuum
hose and wiring are routed correctly, and
secured on reconnection by any clips or
ties provided.
(f) On completion, switch the ignition on and
off five times, to activate the fuel pump and
pressurise the system, without cranking
the engine. Check for signs of fuel leaks
around all disturbed unions and joints
before attempting to start the engine.
Fuel pressure regulator
Check
24Refer to the fuel pump/fuel pressure
check procedure (see Section 8).
Renewal
25Relieve the residual pressure in the fuel
system (see Section 2), and equalise tank
pressure by removing the fuel filler cap.
Warning: This procedure will
merely relieve the increased
pressure necessary for the engine
to run - remember that fuel will
still be present in the system components,
and take precautions accordingly before
disconnecting any of them.26Disconnect the battery negative (earth)
lead - see Chapter 5, Section 1.
27Remove the plenum chamber (see
Section 4).
28Disconnect the vacuum hose from the
regulator.
29Unscrew the two regulator retaining bolts,
place a wad of clean rag to soak up any spilt
fuel, and withdraw the regulator (see
illustration).
30Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure, noting the following points:
(a) Renew the regulator sealing O-ring
whenever the regulator is disturbed.
Lubricate the new O-ring with clean
engine oil on installation.
(b) Locate the regulator carefully in the fuel
rail recess, and tighten the bolts to the
specified torque wrench setting.
(c) On completion, switch the ignition on and
off five times, to activate the fuel pump and
pressurise the system, without cranking
the engine. Check for signs of fuel leaks
around all disturbed unions and joints
before attempting to start the engine.
Idle speed control valve
Check
31Disconnect the battery negative (earth)
lead - see Chapter 5, Section 1.
32Raise the front of the vehicle, and support
it securely on axle stands.
Warning: Do not place any part of
your body under a vehicle when
it’s supported only by a jack!
33Unplug the valve’s electrical connector
(see illustration).
34Connect a 12-volt battery across the
valve’s terminals - positive (+) to terminal 37
(the green/yellow wire) and negative (-) to
terminal 21 (the black/yellow).
Caution: It is essential that the
correct polarity is observed, or
the diode incorporated in the
valve may be damaged.
35A distinct click should be heard each time
contact is made and broken. If not, measure
the resistance between the terminals. If the
resistance is as specified, the valve is okay
(but there may be a problem with the wiring or
the ECU). If the resistance is not as specified,
renew the valve (see below).36Plug in the valve’s electrical connector.
Renewal
37Disconnect the battery negative (earth)
lead - see Chapter 5, Section 1.
38Raise the front of the vehicle, and support
it securely on axle stands.
Warning: Do not place any part of
your body under a vehicle when
it’s supported only by a jack!
39Unplug the valve’s electrical connector.
40Unscrew the two retaining bolts, and
withdraw the valve from the inlet manifold
(see illustration).
41Since the valve’s individual components
are not available separately, and the complete
assembly must be renewed if it is thought to
be faulty, there is nothing to be lost by
attempting to flush out the passages, using
carburettor cleaner or similar solvent. This
won’t take much time or effort, and may well
cure the fault.
42Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure, noting the following points:
(a) Clean the mating surfaces carefully, and
always fit a new gasket whenever the
valve is disturbed.
(b) Tighten the bolts evenly and to the
specified torque wrench setting.
(c) Once the wiring and battery are
reconnected, start the engine and allow it
to idle. When it has reached normal
operating temperature, check that the idle
speed is stable, and that no induction (air)
leaks are evident. Switch on all electrical
loads (headlights, heated rear window,
etc), and check that the idle speed is still
correct.
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•11
4
16.43 Location of idle-increase solenoid
valve (A) and diode (B)
16.29 Disconnect vacuum hose, and
unscrew bolts (arrowed) to withdraw fuel
pressure regulator16.33 Access to idle speed control valve is
from underneath vehicle - unplug electrical
connector (arrowed) to check valve16.40 Unscrew bolts (arrowed) to remove
idle speed control valve
procarmanuals.com
Page 115 of 279

5Undo the sensor’s retaining screw and
withdraw the sensor. The sensor’s bracket
cannot be unbolted from the cylinder
block/crankcase unless the transmission and
flywheel/driveplate have been removed (see
Chapter 2).
6Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure.
General information
The charging system includes the
alternator, an internal voltage regulator, a no-
charge (or “ignition”) warning light, the
battery, and the wiring between all the
components. The charging system supplies
electrical power for the ignition system, the
lights, the radio, etc. The alternator is driven
by the auxiliary drivebelt at the front (right-
hand end) of the engine.
The purpose of the voltage regulator is to
limit the alternator’s voltage to a preset value.
This prevents power surges, circuit overloads,
etc., during peak voltage output.
The charging system doesn’t ordinarily
require periodic maintenance. However, the
drivebelt, battery and wires and connections
should be inspected at the intervals outlined
in Chapter 1.
The dashboard warning light should come
on when the ignition key is turned to positions
“II” or “III”, then should go off immediately the
engine starts. If it remains on, or if it comes on
while the engine is running, there is a
malfunction in the charging system (see
Section 11). If the light does not come on
when the ignition key is turned, and the bulb is
sound (see Chapter 12), there is a fault in the
alternator.
Precautions
Be very careful when making electrical
circuit connections to a vehicle equipped with
an alternator, and note the following:
(a) When reconnecting wires to the alternator
from the battery, be sure to note the
polarity.
(b) Before using arc-welding equipment to
repair any part of the vehicle, disconnect
the wires from the alternator and the
battery terminals.
(c) Never start the engine with a battery
charger connected.
(d) Always disconnect both battery leads
before using a battery charger.
(e) The alternator is driven by an engine
drivebelt which could cause serious injury
if your hand, hair or clothes become
entangled in it with the engine running.
(f) Because the alternator is connected
directly to the battery, it could arc or
cause a fire if overloaded or shorted-out.
(g) Wrap a plastic bag over the alternator,
and secure it with rubber bands, beforesteam-cleaning or pressure-washing the
engine.
(h) Never disconnect the alternator terminals
while the engine is running.
1If a malfunction occurs in the charging
circuit, don’t automatically assume that the
alternator is causing the problem. First check
the following items:
(a) Check the tension and condition of the
auxiliary drivebelt - renew it if it is worn or
deteriorated (see Chapter 1).
(b) Ensure the alternator mounting bolts and
nuts are tight.
(c) Inspect the alternator wiring harness and
the electrical connections at the
alternator; they must be in good
condition, and tight.
(d) Check the large main fuses in the engine
compartment (see Chapter 12). If any is
blown, determine the cause, repair the
circuit and renew the fuse (the vehicle
won’t start and/or the accessories won’t
work if the fuse is blown).
(e) Start the engine and check the alternator
for abnormal noises - for example, a
shrieking or squealing sound may indicate
a badly-worn bearing or brush.
(f) Make sure that the battery is fully-charged
- one bad cell in a battery can cause
overcharging by the alternator.
(g) Disconnect the battery leads (negative
first, then positive). Inspect the battery
posts and the lead clamps for corrosion.
Clean them thoroughly if necessary (see
Section 3 and Chapter 1). Reconnect the
lead to the negative terminal.
(h) With the ignition and all accessories
switched off, insert a test light between
the battery negative post and the
disconnected negative lead clamp:
(1) If the test light does not come on, re-
attach the clamp and proceed to the next
step.
(2) If the test light comes on, there is a short
in the electrical system of the vehicle. The
short must be repaired before the
charging system can be checked.
(3) To find the short, disconnect the
alternator wiring harness:
(a) If the light goes out, the alternator is
at fault.
(b) If the light stays on, remove each fuse
until it goes out - this will tell you
which component is short-circuited.
2Using a voltmeter, check the battery
voltage with the engine off. It should be
approximately 12 volts.
3Start the engine and check the battery
voltage again. Increase engine speed until the
voltmeter reading remains steady; it should
now be approximately 13.5 to 14.6 volts.
4Switch on as many electrical accessories
(eg the headlights, heated rear window andheater blower) as possible, and check that the
alternator maintains the regulated voltage at
around 13 to 14 volts. The voltage may drop
and then come back up; it may also be
necessary to increase engine speed slightly,
even if the charging system is working
properly.
5If the voltage reading is greater than the
specified charging voltage, renew the voltage
regulator (see Section 13).
6If the voltmeter reading is less than that
specified, the fault may be due to worn
brushes, weak brush springs, a faulty voltage
regulator, a faulty diode, a severed phase
winding, or worn or damaged slip rings. The
brushes and slip rings may be checked (see
Section 13), but if the fault persists, the
alternator should be renewed or taken to an
auto-electrician for testing and repair.
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
- see Section 1.
2Remove the plenum chamber (see Chap-
ter 4).
3Unscrew the nuts to disconnect the wiring
from the alternator (see illustration). If
additional working clearance is required, undo
the right-hand of the three screws securing
the wiring “rail” to the rear of the inlet
manifold.
4Jack up and support the front right-hand
corner of the vehicle. Remove the auxiliary
drivebelt and the engine oil filter - place a wad
of rag to soak up the spilled oil (see Chap-
ter 1). Rather than refit a used filter, you are
advised to drain the engine oil, and then to fit
a new filter and refill the engine with clean oil
on reassembly. Where an engine oil cooler is
fitted, it may prove necessary to remove this
as well, to provide the clearance necessary to
remove the alternator (see Chapter 2, Part A).
5Unscrew the two bolts securing the power
steering system pipes to the right-hand side
of the front suspension subframe. With the
front wheels in the straight-ahead position,
disconnect the right-hand track rod end from
the steering knuckle (see Chapter 10).
6Remove the mounting bolts and nuts (one
12 Alternator-
removal and refitting
11 Charging system- testing
10 Charging system - general
information and precautions
Engine electrical systems 5•5
5
12.3 Disconnecting alternator wiring
procarmanuals.com
Page 141 of 279

24Ford specify the use of their STAR (Self-
Test Automatic Readout) tester; most Ford
dealers should have such equipment, and the
staff trained to use it effectively. The only
alternatives are as follows:
(a) To obtain one of those proprietary readers
which can interpret EEC-IV three-digit
codes - at present, such readers are too
expensive for the DIY enthusiast, but are
becoming more popular with smaller
specialist garages.
(b) To use an analogue voltmeter, whereby
the stored codes are displayed as sweeps
of the voltmeter needle. This option limits
the operator to a read-out of any codes
stored - ie, there is no control of sensors
and/or actuators - but can still be useful in
pinpointing the faulty part of the engine
management system. The display is
interpreted as follows. Each code
(whether fault code or
command/separator) is marked by a
three-to-four second pause - code “538”
would therefore be shown as long (3 to
4 seconds) pause, five fast sweeps of the
needle, slight (1 second) pause, three fast
sweeps, slight pause, eight fast sweeps,
long pause.
(c) Owners without access to such
equipment must take the vehicle to a Ford
dealer, or to an expert who has similar
equipment and the skill to use it.
25Because of the variations in the design of
fault code readers, it is not possible to give
exact details of the sequence of tests; the
manufacturer’s instructions must be followed,
in conjunction with the codes given below.
The following ten paragraphs outline the
procedure to be followed using a version of
the Ford STAR tester, to illustrate the general
principles, as well as notes to guide the owner
using only a voltmeter.
26The vehicle must be prepared by applying
the handbrake, switching off the air
conditioning (where fitted) and any other
electrical loads (lights, heated rear window,
etc), then selecting neutral (manual
transmission) or the “P” position (automatic
transmission). Where the engine is required to
be running, it must be fully warmed-up to
normal operating temperature before the test
is started. Using any adaptors required,
connect the fault code reader to the system
via the (triangular, three-pin) self-test
connector on the right-hand end of the engine
compartment bulkhead (see illustration). If a
voltmeter is being used, connect its positive
lead to the battery positive terminal, and its
negative lead to the self-test connector’s
output terminal, pin 17. Have a pen and paper
ready to write down the codes displayed.
27Set the tester in operation. For the Ford
STAR tester, a display check will be carried
out and the test mode requirements must be
entered. If a voltmeter is being used, connect
a spare length of wire to earth the self-test
connector’s input terminal, pin 48. Be very
careful to ensure that you earth the correctterminal - the one with the white/green wire.
The first part of the test starts, with the
ignition switched on, but with the engine off.
On pressing the “Mem/test” button, the tester
displays “TEST” and the ready code “000”,
followed by a command code “010” - the
accelerator pedal must be fully depressed
within 10 seconds of the command code
appearing, or fault codes “576” or “577” will
appear when they are called up later. If a
voltmeter is being used, code “000” will not
appear (except perhaps as a flicker of the
needle) and “010” will appear as a single
sweep - to ensure correct interpretation of the
display, watch carefully for the interval
between the end of one code and the
beginning of the next, otherwise you will
become confused and misinterpret the read-
out.
28The tester will then display the codes for
any faults in the system at the time of the test.
Each code is repeated once; if no faults are
present, code “111” will be displayed. If a
voltmeter is being used, the pause between
repetitions will vary according to the
equipment in use and the number of faults in
the system, but was found to be
approximately 3 to 4 seconds - it may be
necessary to start again, and to repeat the
read-out until you are familiar with what you
are seeing.
29Next the tester will display code “010”
(now acting as a separator), followed by the
codes for any faults stored in the ECU’s
memory; if no faults were stored, code “111”
will be displayed.
30When prompted by the tester, the
operator must next depress the accelerator
pedal fully; the tester then checks several
actuators. Further test modes include a
“wiggle test” facility, whereby the operator
can check the various connectors as
described in paragraph 19 above (in this case,
any fault will be logged and the appropriate
code will be displayed), a facility for recalling
codes displayed, and a means for clearing the
ECU’s memory at the end of the test
procedure when any faults have been
rectified.
31The next step when using the Ford STAR
tester is to conduct a test with the engine
running. With the tester set in operation (see
paragraph 26 above) the engine is started and
allowed to idle. On pressing the “Mem/test”
button, the tester displays “TEST”, followed
by one of two codes, as follows.
32If warning code “998” appears, followed
by the appropriate fault code, switch off and
check as indicated the coolant temperature
sensor, the intake air temperature sensor, the
air mass meter, the throttle potentiometer
and/or their related circuits, then restart the
test procedure.
33If command code “020” appears, carry
out the following procedure within ten
seconds:
(a) Depress the brake pedal fully.
(b) Turn the steering to full-lock (either way)and centre it again, to produce a signal
from the power steering pressure switch -
if no signal is sent, fault code “521” will
be displayed.
(c) If automatic transmission is fitted, switch
the overdrive cancel button on and off,
then do the same for the
“Economy/Sport” mode switch.
(d) Wait for separator code “010” to be
displayed, then within 10 seconds,
depress the accelerator pedal fully,
increasing engine speed rapidly above
3000 rpm - release the pedal.
34Any faults found in the system will be
logged and displayed. Each code is repeated
once; if no faults are present, code “111” will
be displayed.
35When the codes have been displayed for
all faults logged, the ECU enters its “Service
Adjustment Programme”, as follows:
(a) The programme lasts for 2 minutes.
(b) The idle speed control valve is
deactivated, and the idle speed is set to
its pre-programmed (unregulated) value. If
the appropriate equipment is connected,
the base idle speed can be checked
(note, however, that it is not adjustable).
(c) The ignition timing can be checked if a
timing light is connected (note, however,
that it is not adjustable).
(d) Pressing the accelerator pedal fully at any
time during this period will execute a
cylinder balance test. Each injector in turn
is switched off, and the corresponding
decrease in engine speed is logged -
code “090” will be displayed if the test is
successful.
(e) At the end of the 2 minutes, the
completion of the programme is shown
by the engine speed briefly rising, then
returning to normal idling speed as
the idle speed control valve is
reactivated.
36As with the engine-off test, further test
modes include a “wiggle test” facility,
whereby the operator can check the various
connectors as described in paragraph 19
above (in this case, any fault will be logged
and the appropriate code will be displayed), a
facility for recalling codes displayed, and a
means for clearing the ECU’s memory at the
end of the test procedure when any faults
have been rectified. If equipment other than
the Ford STAR tester is used, the ECU’s
memory can be cleared by disconnecting the
battery - if this is not done, the code will
reappear with any other codes in the event of
subsequent trouble, but remember that other
systems with memory (such as the clock and
audio equipment) will also be affected. Should
it become necessary to disconnect the
battery during work on any other part of the
vehicle, first check to see if any fault codes
have been logged.
37Given overleaf are the possible codes,
their meanings, and where relevant, the action
to be taken as a result of a code being
displayed.
Emissions control systems 6•7
6
procarmanuals.com
Page 144 of 279

Ignition timing and base idle
speed check
Note:The following procedure is a check only,
essentially of the ECU. Both the ignition timing
and the base idle speed are controlled by the
ECU. The ignition timing is not adjustable at
all; the base idle speed is set in production,
and should not be altered.
38If the fault code read-out (with any checks
resulting from it) has not eliminated the fault,
the next step is to check the ECU’s control of
the ignition timing and the base idle speed.
This task requires the use of a Ford STAR
tester (a proprietary fault code reader can be
used only if it is capable of inducing the ECU
to enter its “Service Adjustment Programme”),
coupled with an accurate tachometer and a
good-quality timing light. Without this
equipment, the task is not possible; the
vehicle must be taken to a Ford dealer for
attention.
39To make the check, apply the handbrake,
switch off the air conditioning (where fitted)
and any other electrical loads (lights, heated
rear window, etc), then select neutral (manual
transmission) or the “P” position (automatic
transmission). Start the engine, and warm it
up to normal operating temperature. The
radiator electric cooling fan must be running
continuously while the check is made; this
should be activated by the ECU, when
prompted by the tester. Switch off the engine,
and connect the test equipment as directed
by the manufacturer - refer to paragraph 26
above for details of STAR tester connection.
40Raise and support the front of the vehicle
securely, and remove the auxiliary drivebelt
cover (see Chapter 1). Emphasise the two
pairs of notches in the inner and outer rims of
the crankshaft pulley, using white paint. Note
that an ignition timing reference mark is not
provided on the pulley - in the normal
direction of crankshaft rotation (clockwise,
seen from the right-hand side of the vehicle)
the first pair of notches are irrelevant to the
vehicles covered in this manual, while the
second pair indicate Top Dead Centre (TDC)
when aligned with the rear edge of the raised
mark on the sump; when checking the ignition
timing, therefore, the (rear edge of the) sumpmark should appear just before the TDC
notches (see Part A of Chapter 2, Section 4,
for further information if required).
41Start the engine and allow it to idle. Work
through the engine-running test procedure
until the ECU enters its “Service Adjustment
Programme” - see paragraph 35 above.
42Use the timing light to check that the
timing marks appear approximately as
outlined above at idle speed. Do not spend
too much time on this check; if the timing
appears to be incorrect, the system may have
a fault, and a full system test must be carried
out (see below) to establish its cause.
43Using the tachometer, check that the
base idle speed is as given in the
Specifications Section of Chapter 4.
44If the recorded speed differs significantly
from the specified value, check for air leaks,
as described in the preliminary checks
(paragraphs 15 to 18 above), or any other
faults which might cause the discrepancy.
45The base idle speed is set in production
by means of an air bypass screw (located in
the front right-hand corner of the throttle
housing) which controls the amount of air that
is allowed to pass through a bypass passage,
past the throttle valve when it is fully closed in
the idle position; the screw is then sealed with
a white tamperproof plug (see illustration). In
service, the idle speed is controlled by the
ECU, which has the ability to compensate for
engine wear, build-up of dirt in the throttle
housing, and other factors which might
require changes in idle speed. The air bypass
screw setting should not, therefore, be
altered. If any alterations are made, a blue
tamperproof plug must be fitted, and the
engine should be allowed to idle for at least
five minutes on completion, so that the ECU
can re-learn its idle values.
46When both checks have been made and
the “Service Adjustment Programme” is
completed, follow the tester instructions to
return to the fault code read-out, and
establish whether the fault has been cured or
not.
Basic check of ignition system
47If the checks so far have not eliminated
the fault, the next step is to carry out a basic
check of the ignition system components,
using an engine analyser with an oscilloscope
- without such equipment, the only tests
possible are to remove and check each spark
plug in turn, to check the spark plug (HT) lead
connections and resistances, and to check
the connections and resistances of the
ignition coil. Refer to the relevant Sections of
Chapters 1 and 5.
Basic check of fuel system
48If the checks so far have not eliminated
the fault, the next step is to carry out a basic
check of the fuel system components.
49Assuming that the preliminary checks
have established that the fuel pump is
operating correctly, that the fuel filter isunlikely to be blocked, and also that there are
no leaks in the system, the next step is to
check the fuel pressure (see Chapter 4). If this
is correct, check the injectors (see Chapter 4)
and the Positive Crankcase Ventilation system
(see Chapter 1).
System test
50The final element of the Ford testing
procedure is to carry out a system test, using
a break-out box - this is a device that is
connected between the ECU and its electrical
connector, so that the individual circuits
indicated by the fault code read-out can be
tested while connected to the system, if
necessary with the engine running. In the case
of many of the system’s components, this
enables their output voltages to be measured
- a more accurate means of testing.
51In addition to the break-out box and the
adaptors required to connect it, several items
of specialist equipment are needed to
complete these tests. This puts them quite
beyond the scope of many smaller dealers, let
alone the DIY owner; the vehicle should be
taken to a Ford dealer for attention.
Note:This Section is concerned principally
with the sensors which give the ECU the
information it needs to control the various
engine management sub-systems - for further
details of those systems and their other
components, refer to the relevant Chapter of
this manual.
General
ECU (Electronic Control Unit)
1This component is the heart of the entire
engine management system, controlling the
fuel injection, ignition and emissions control
systems. It also controls sub-systems such as
the radiator cooling fan, air conditioning and
automatic transmission, where appropriate.
Refer to Section 2 of this Chapter for an
illustration of how it works.
Air mass meter
2This uses a “hot-wire” system, sending the
ECU a constantly-varying (analogue) voltage
signal corresponding to the mass of air
passing into the engine. Since air mass varies
with temperature (cold air being denser than
warm), measuring air mass provides the ECU
with a very accurate means of determining the
correct amount of fuel required to achieve the
ideal air/fuel mixture ratio.
Crankshaft speed/position sensor
3This is an inductive pulse generator bolted
(in a separate bracket) to the cylinder
block/crankcase, to scan the ridges between
36 holes machined in the inboard (right-hand)
face of the flywheel/driveplate. As each ridge
4 Information sensors -
general information, testing,
removal and refitting
6•10 Emissions control systems
3.45 Throttle housing air bypass screw is
sealed on production with a white
tamperproof plug (arrowed)
procarmanuals.com
Page 178 of 279

Chapter 11 Bodywork and fittings
Body side-trim mouldings and adhesive emblems - removal
and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Bonnet - removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Bonnet lock - removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Bonnet release cable and lever - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Boot lid - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Boot lid lock components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Bumpers - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Central locking system components - testing, removal and refitting . 23
Centre console - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Door - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Door handle and lock components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . 14
Door inner trim panel - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Door window glass - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Door window regulator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Exterior mirror and glass - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Facia - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1Glovebox - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Interior mirror - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Interior trim panels - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Maintenance - bodywork and underframe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Maintenance - upholstery and carpets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Major body damage - repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Minor body damage - repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Overhead console - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Radiator grille - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Seat belts - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Seats - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Sunroof - general information and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Tailgate - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Tailgate lock components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Tailgate support strut - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Wheel arch liner - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Windscreen and fixed windows - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . 24
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Bonnet and tailgate hinges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 18
Boot lid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Front seat mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38 28
Seat belt mounting nuts and bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38 28
Bumper mounting nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
11•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,suitable
for competent DIY
mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
11
The bodyshell and underframe on all
models is of all-steel welded construction,
incorporating progressive crumple zones at
the front and rear, and a rigid centre safety
cell. The bulkhead behind the engine
compartment incorporates crash grooves
which determine its energy-absorption
characteristics, and special beams to prevent
the intrusion of the front wheels into the
passenger compartment during a serious
accident. All passenger doors incorporate
side impact bars.
All sheet metal surfaces which are prone tocorrosion are galvanized. The painting
process includes a base colour which closely
matches the final topcoat, so that any stone
damage is not noticeable.
Hatchback, Saloon and Estate versions are
available. The front section of the vehicle up to
the “B” pillar is identical on all models.
Automatic seat belts are fitted to all models,
and the front seat belt stalks are mounted on
automatic tensioners (also known as
“grabbers”) (see illustration). In the event of a
serious front impact, a spring mass sensor
releases a coil spring which pulls the stalk
buckle downwards and tensions the seat belt.
It is not possible to reset the tensioner once
fired, and it must therefore be renewed.
In the UK, central locking is standard on all
1 General information
1.4 Automatic seat belt tensioner
1 Coil spring 3 Spring mass sensor
2 Lever system
procarmanuals.com
Page 179 of 279

models (see illustration). In other countries, it
is available on certain models only. Where
double-locking is fitted, the lock mechanism
is disconnected (when the system is in use)
from the interior door handles, making it
impossible to open any of the doors or the
tailgate/bootlid from inside the vehicle. This
means that, even if a thief should break a side
window, he will not be able to open the door
using the interior handle. Models with the
double-locking system are fitted with a
control module located beneath the facia on
the right-hand side. In the event of a serious
accident, a crash sensor unlocks all doors if
they were previously locked.
Many of the procedures in this Chapter
require the battery to be disconnected. Refer
to Chapter 5, Section 1 first.
The general condition of a vehicle’s
bodywork is the one thing that significantly
affects its value. Maintenance is easy, but
needs to be regular. Neglect, particularly after
minor damage, can lead quickly to further
deterioration and costly repair bills. It is
important also to keep watch on those parts
of the vehicle not immediately visible, for
instance the underside, inside all the wheel
arches, and the lower part of the engine
compartment.
The basic maintenance routine for the
bodywork is washing - preferably with a lot of
water, from a hose. This will remove all the
loose solids which may have stuck to the
vehicle. It is important to flush these off in
such a way as to prevent grit from scratching
the finish. The wheel arches and underframe
need washing in the same way, to remove any
accumulated mud, which will retain moisture
and tend to encourage rust. Paradoxically
enough, the best time to clean the underframe
and wheel arches is in wet weather, when the
mud is thoroughly wet and soft. In very wet
weather, the underframe is usually cleaned of
large accumulations automatically, and this is
a good time for inspection.
Periodically, except on vehicles with a wax-
based underbody protective coating, it is a
good idea to have the whole of the
underframe of the vehicle steam-cleaned,
engine compartment included, so that a
thorough inspection can be carried out to see
what minor repairs and renovations are
necessary. Steam-cleaning is available at
many garages, and is necessary for the
removal of the accumulation of oily grime,
which sometimes is allowed to become thick
in certain areas. If steam-cleaning facilities are
not available, there are some excellent grease
solvents available which can be brush-
applied; the dirt can then be simply hosed off.
Note that these methods should not be used
on vehicles with wax-based underbodyprotective coating, or the coating will be
removed. Such vehicles should be inspected
annually, preferably just prior to Winter, when
the underbody should be washed down, and
any damage to the wax coating repaired.
Ideally, a completely fresh coat should be
applied. It would also be worth considering
the use of such wax-based protection for
injection into door panels, sills, box sections,
etc, as an additional safeguard against rust
damage, where such protection is not
provided by the vehicle manufacturer.
After washing paintwork, wipe off with a
chamois leather to give an unspotted clear
finish. A coat of clear protective wax polish
will give added protection against chemical
pollutants in the air. If the paintwork sheenhas dulled or oxidised, use a cleaner/polisher
combination to restore the brilliance of the
shine. This requires a little effort, but such
dulling is usually caused because regular
washing has been neglected. Care needs to
be taken with metallic paintwork, as special
non-abrasive cleaner/polisher is required to
avoid damage to the finish. Always check that
the door and ventilator opening drain holes
and pipes are completely clear, so that water
can be drained out. Brightwork should be
treated in the same way as paintwork.
Windscreens and windows can be kept clear
of the smeary film which often appears, by the
use of proprietary glass cleaner. Never use
any form of wax or other body or chromium
polish on glass.
2 Maintenance -
bodywork and underframe
11•2 Bodywork and fittings
1.5 Central locking component locations
1 Indicator light
2 Buzzer
3 Central locking module4 Infra-red receiver
5 Lock motor
6 Set/reset switch7 Ajar switch
8 Infra-red transmitter
procarmanuals.com