1993 CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM change time
[x] Cancel search: change timePage 1767 of 2438

shutter. The switch plate contains the distributor
pick-up which is a Hall Effect device and magnet.
The shutter blades rotate through the distributor
pick-up. As the shutter blades pass through the pick-
up, they interrupt the magnetic field. The Hall effect
device in the pick-up senses the change in the mag-
netic field and switches on and off (which creates
pulses), generating the input signal to the PCM. The
PCM calculates engine speed through the number of
pulses generated.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP)
SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The PCM supplies 5 volts to the MAP sensor. The
MAP sensor converts intake manifold pressure into
voltage. The PCM monitors the MAP sensor output
voltage. As vacuum increases, MAP sensor voltage
decreases proportionately. Also, as vacuum decreases,
MAP sensor voltage increases proportionately. During cranking, before the engine starts running,
the PCM determines atmospheric air pressure from
the MAP sensor voltage. While the engine operates,
the PCM determines intake manifold pressure from
the MAP sensor voltage. Based on MAP sensor voltage and inputs from
other sensors, the PCM adjusts spark advance and
the air/fuel mixture. The MAP sensor mounts on the dash panel (Fig. 5).
A vacuum hose connects the sensor to the throttle
body.
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (O2SENSOR)ÐPCM
INPUT
The O2sensor is located in the exhaust manifold
and provides an input voltage to the PCM. The input
tells the PCM the oxygen content of the exhaust gas
(Fig. 6). The PCM uses the information to fine tune
the air-fuel ratio by adjusting injector pulse width. The O
2sensor produces voltages from 0 to 1 volt,
depending upon the oxygen content of the exhaust
gas. When a large amount of oxygen is present
(caused by a lean air-fuel mixture), the sensor pro-
duces a low voltage. When there is a lesser amount
present (rich air-fuel mixture), it produces a higher
voltage. By monitoring the oxygen content and con-
verting it to electrical voltage, the sensor acts as a
rich-lean switch. The oxygen sensor is equipped with a heating ele-
ment that keeps the sensor at proper operating tem-
perature during all operating modes. Maintaining
correct sensor temperature at all times allows the
system to enter into closed loop operation sooner.
Also, it allows the system to remain in closed loop
operation during periods of extended idle. In Closed Loop operation the PCM monitors the O
2
sensor input (along with other inputs) and adjusts
the injector pulse width accordingly. During Open
Loop operation the PCM ignores the O
2sensor input.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width based on a pre-
programmed (fixed) oxygen sensor input value and
inputs from other sensors.
SPEED CONTROLÐPCM INPUT
The speed control system provides four separate
voltages (inputs) to the PCM. The voltages corre-
spond to the On/Off, Set, and Resume. The speed control ON voltage informs the PCM
that the speed control system has been activated.
The speed control SET voltage informs the PCM that
a fixed vehicle speed has been selected. The speed
control RESUME voltage indicates the previous fixed
speed is requested. The speed control OFF voltage
tells the PCM that the speed control system has de-
activated. Refer to Group 8H for further speed con-
trol information.
Fig. 5 Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Location
Fig. 6 Heated Oxygen Sensor
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 27
Page 1768 of 2438

TRANSAXLE PARK/NEUTRAL SWITCHÐPCM
INPUT
The park/neutral switch is located on the auto-
matic transaxle housing (Fig. 7). Manual transaxles
do not use park neutral switches. The switch pro-
vides an input to the PCM. The input indicates
whether the automatic transaxle is in Park, Neutral,
or a drive gear selection. This input is used to deter-
mine idle speed (varying with gear selection), fuel in-
jector pulse width, and ignition timing advance. The
park neutral switch is sometimes referred to as the
neutral safety switch.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS)ÐPCM INPUT
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is mounted on
the throttle body and connected to the throttle blade
shaft (Fig. 8). The TPS is a variable resistor. The
sensor provides an input signal (voltage) to the PCM
representing throttle blade position. As the position
of the throttle blade changes, the resistance of the
TPS changes.
The PCM supplies approximately 5 volts to the
TPS. The TPS output voltage (input signal to the
PCM) represents the throttle blade position. The
PCM receives an input signal voltage from the TPS
varying in an approximate range of from 1 volt at
minimum throttle opening (idle) to 4 volts at wide open throttle. Along with inputs from other sensors,
the PCM uses the TPS input to determine current
engine operating conditions. The PCM adjusts fuel
injector pulse width and ignition timing based on
these inputs.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The vehicle speed sensor is located in the transaxle
extension housing (Fig. 9). The sensor input is used
by the PCM to determine vehicle speed and distance
traveled.
The speed sensor generates 8 pulses per sensor rev-
olution. These signals, along with a closed throttle
signal from the TPS, determine if a closed throttle
deceleration or normal idle condition (vehicle
stopped) exists. Under deceleration conditions, the
PCM adjusts the idle air control motor to maintain a
desired MAP value. Under idle conditions, the PCM
adjusts the idle air control motor to maintain a de-
sired engine speed.
AIR CONDITIONING (A/C) CLUTCH RELAYÐPCM
OUTPUT
The PCM operates the air conditioning clutch relay
ground circuit. The radiator fan relay supplies bat-
tery power to the solenoid side of the A/C clutch re-
lay. The air conditioning clutch relay will not
energize unless the radiator fan relay energizes. The
PCM energizes the radiator fan relay when the air
conditioning or defrost switch is put in the ON posi-
tion and the low pressure and high pressure switches
close. With the engine operating, the PCM cycles the air
conditioning clutch on and off when the A/C switch
closes with the blower motor switch in the on posi-
tion. When the PCM senses low idle speeds or wide
open throttle through the throttle position sensor, it
de-energizes the A/C clutch relay. The relay contacts
open, preventing air conditioning clutch engagement.
Fig. 7 Park/Neutral Switch
Fig. 8 Throttle Position Sensor
Fig. 9 Vehicle Distance (Speed) SensorÐTypical
14 - 28 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1772 of 2438

TACHOMETERÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies engine RPM to the instrument
panel tachometer. Refer to Group 8 for tachometer
information.
MODES OF OPERATION
As input signals to the PCM change, the PCM
adjusts its response to the output devices. For example,
the PCM must calculate a different injector pulse
width and ignition timing for idle than it does for wide
open throttle (WOT). There are several different modes
of operation that determine how the PCM responds to
the various input signals. There are two different areas of operation, OPEN
LOOP and CLOSED LOOP. During OPEN LOOP modes, the PCM receives input
signals and responds according to preset PCM pro-
gramming. Input from the oxygen (O
2) sensor is not
monitored during OPEN LOOP modes. During CLOSED LOOP modes, the PCM does moni-
tor the oxygen (O
2) sensor input. This input tells the
PCM if the calculated injector pulse width results in an
air-fuel ratio of 14.7 to 1. By monitoring the exhaust
oxygen content, the can PCM fine tune injector pulse
width for optimum fuel economy and low emissions. The single point fuel injection system has the follow-
ing modes of operation:
² Ignition switch ON - Zero RPM
² Engine start-up
² Engine warm-up
² Cruise (Idle)
² Acceleration
² Deceleration
² Wide Open Throttle
² Ignition switch OFF
The engine start-up (cranking), engine warm-up, and
wide open throttle modes are OPEN LOOP modes. The
acceleration, deceleration, and cruise modes, with the
engine at operating temperature are CLOSED
LOOP modes (under most operating conditions).
IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE
When the single point fuel injection system is acti-
vated by the ignition switch, the following actions
occur:
² The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure from
the MAP sensor input to calculate basic fuel strategy.
² The PCM monitors the coolant temperature sensor
and throttle position sensor inputs. The PCM modifies
fuel strategy based on these inputs. When the key is in the ON position and the engine is
not running, the (ASD) and fuel pump relays are not
energized. Therefore, battery voltage is not supplied to
the fuel pump, ignition coil, fuel injector or oxygen
sensor heating element. ENGINE START-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. The following actions
occur when the starter motor is engaged. If the PCM receives a distributor signal it energizes
the auto shutdown (ASD) relay and fuel pump relay to
supply battery voltage to the fuel injector, ignition coil
and oxygen sensor heating element. If the PCM does
not receive a distributor input, it de-energizes the ASD
and fuel pump relays after approximately one second. When the engine idles within 664 RPM of the target
RPM, the PCM compares the current MAP value with
the atmospheric pressure value it received during the
Ignition Switch On (Zero RPM) Mode. If a minimum
difference between the two is not detected, a MAP
sensor fault is set into memory. Once the ASD relay and fuel pump relay have ener-
gized, the PCM:
² Supplies a ground path to the injector. The injector
is pulsed four times per engine revolution instead of
the normal two pulses per revolution.
² Determines injector pulse width based on coolant
temperature, MAP sensor input, throttle position, and
the number of engine revolutions since cranking was
initiated.
² Monitors the coolant temperature sensor, distribu-
tor pick-up, MAP sensor, and throttle position sensor to
determine correct ignition timing.
ENGINE WARM-UP MODE
This is a OPEN LOOP mode. The following inputs
are received by the PCM:
² coolant temperature
² manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
² engine speed (distributor pick-up)
² throttle position
² A/C switch
² battery voltage
The PCM provides a ground path for the injector to
precisely control injector pulse width (by switching the
ground on and off) and fires the injector twice per
engine revolution. The PCM regulates ignition timing.
It also adjusts engine idle speed through the idle air
control motor.
CRUISE OR IDLE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature this is
a CLOSED LOOP mode. During cruising speed and at
idle the following inputs are received by the PCM:
² coolant temperature
² manifold absolute pressure
² engine speed
² throttle position
² exhaust gas oxygen content
² A/C control positions
² battery voltage
14 - 32 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1798 of 2438

A/C clutch relay. To compensate for increased engine
load, the PCM also adjusts idle speed to a scheduled
RPM.
BATTERY VOLTAGEÐPCM INPUT
The powertrain control module (PCM) monitors the
battery voltage input to determine fuel injector pulse
width and generator field control. If battery voltage
is low, the PCM increases injector pulse width to
compensate.
BRAKE SWITCHÐPCM INPUT
When the brake switch activates, the powertrain
control module (PCM) receives an input indicating
that the brakes are being applied. After receiving the
input, the PCM vents the speed control servo. Vent-
ing the servo turns the speed control system off.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSORÐPCM
INPUT
The coolant temperature sensor is installed behind
the thermostat housing and ignition coil in the ther-
mostat housing (hot box). The PCM supplies 5 volts
to the coolant temperature sensor. The sensor pro-
vides an input voltage to the PCM (Fig. 3). As cool-
ant temperature varies, the coolant temperature
sensor resistance changes resulting in a different in-
put voltage to the PCM. The PCM demands slightly richer air-fuel mixtures
and higher idle speeds until the engine reaches nor-
mal operating temperature. This sensor is also used for cooling fan control.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The camshaft position sensor (distributor pick-up)
supplies engine speed and the injector sync signal to
the powertrain control module (PCM). The sensor is
a Hall Effect device (Fig. 4). A shutter (sometimes referred to as an interrupter)
is attached to the distributor shaft. The shutter con-
tains four blades, one per engine cylinder. A switch plate is mounted to the distributor housing above the
shutter. The switch plate contains the camshaft posi-
tion sensor (distributor pick-up) through which the
shutter blades rotate. As the shutter blades pass
through the pick-up, they interrupt the magnetic
field. The Hall effect device in the pick-up senses the
change in the magnetic field and switches on and off
(which creates pulses), generating the input signal to
the PCM. The PCM calculates engine speed through
the number of pulses generated. One of the shutter blades has a window cut into it.
The window tells the PCM which injector to energize.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP)
SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies 5
volts to the MAP sensor. The MAP sensor converts
intake manifold pressure into voltage. The PCM
monitors the MAP sensor output voltage. As vacuum
increases, MAP sensor voltage decreases proportion-
ately. Also, as vacuum decreases, MAP sensor volt-
age increases proportionately. During cranking, before the engine starts running,
the PCM determines atmospheric air pressure from
the MAP sensor voltage. While the engine operates,
the PCM determines intake manifold pressure from
the MAP sensor voltage. Based on MAP sensor volt-
age and inputs from other sensors, the PCM adjusts
spark advance and the air/fuel mixture. The MAP sensor mounts on the dash panel inside
the engine compartment (Fig. 5). A vacuum hose con-
nects the sensor to the throttle body.
Fig. 3 Coolant Temperature Sensor
Fig. 4 Camshaft Position Sensor (Distributor Pick-Up)
14 - 58 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1800 of 2438

In Closed Loop operation the PCM monitors the O2
sensor input (along with other inputs) and adjusts
the injector pulse width accordingly. During Open
Loop operation the PCM ignores the O
2sensor input.
In Open Loop, the PCM adjusts injector pulse width
based on a preprogrammed (fixed) oxygen sensor in-
put value and other inputs.
SPEED CONTROLÐPCM INPUT
The speed control system provides four separate
voltages (inputs) to the PCM. The voltages corre-
spond to the On/Off, Set, and Resume. The speed control ON voltage informs the PCM
that the speed control system has been activated.
The speed control SET voltage informs the PCM that
a fixed vehicle speed has been selected. The speed
control RESUME voltage indicates the previous fixed
speed is requested. The speed control OFF voltage
tells the PCM that the speed control system has de-
activated. Refer to Group 8H for further speed con-
trol information.
TRANSAXLE PARK/NEUTRAL SWITCHÐPCM
INPUT
The park/neutral switch is located on the auto-
matic transaxle housing (Fig. 8). Manual transaxles
do not use park/neutral switches. The switch pro-
vides an input to the PCM. The input indicates if the
automatic transaxle is in Park, Neutral, or a drive
gear selection. The input is used to determine idle
speed (varying with gear selection), fuel injector
pulse width, and ignition timing advance. The park
neutral switch is sometimes referred to as the neu-
tral safety switch.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS)ÐPCM INPUT
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is mounted on
the throttle body and connected to the throttle blade
shaft (Fig. 9). The TPS is a variable resistor. The
sensor provides the PCM with an input signal (volt-
age) representing throttle blade position. As the po-
sition of the throttle blade changes, the resistance of
the TPS changes. The PCM supplies approximately 5 volts to the
TPS. The TPS output voltage (input signal to the PCM) represents the throttle blade position. The
PCM receives an input signal voltage from the TPS
varying in an approximate range of from 1 volt at
minimum throttle opening (idle) to 4 volts at wide
open throttle. Along with inputs from other sensors,
the PCM uses the TPS input to determine current
engine operating conditions. The PCM adjusts fuel
injector pulse width and ignition timing based on
these inputs.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The vehicle speed sensor (Fig. 10) is located in the
transaxle extension housing. The sensor input is
used by the PCM to determine vehicle speed and dis-
tance traveled.
The vehicle speed sensor generates 8 pulses per
sensor revolution. These signals, along with a closed
throttle signal from the TPS, determine if a closed
throttle deceleration or normal idle condition (vehicle
stopped) exists. Under deceleration conditions, the
PCM adjusts the idle air control motor to maintain a
Fig. 8 Park Neutral Switch
Fig. 9 Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) and Idle Air Control Motor
Fig. 10 Vehicle Speed Sensor
14 - 60 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1824 of 2438
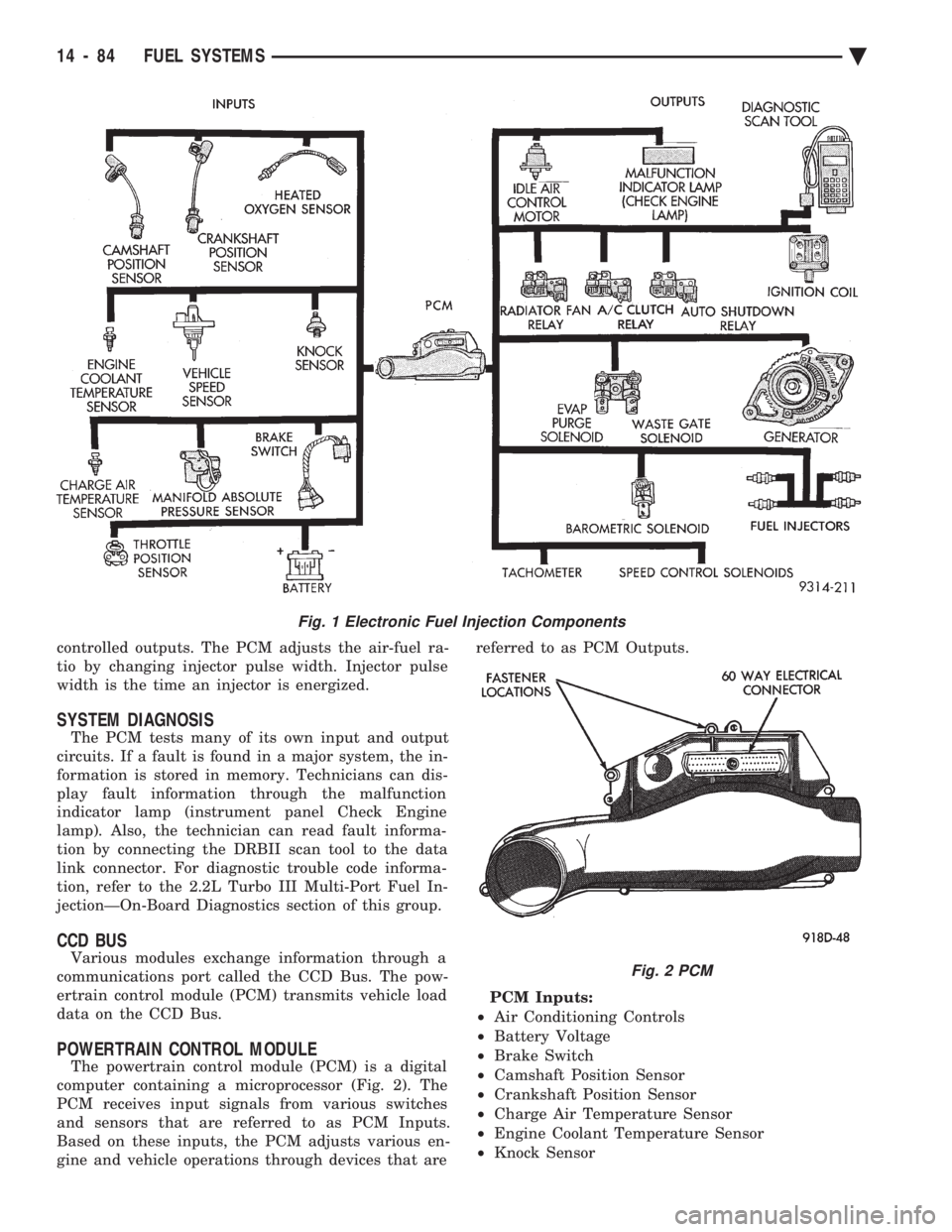
controlled outputs. The PCM adjusts the air-fuel ra-
tio by changing injector pulse width. Injector pulse
width is the time an injector is energized.
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
The PCM tests many of its own input and output
circuits. If a fault is found in a major system, the in-
formation is stored in memory. Technicians can dis-
play fault information through the malfunction
indicator lamp (instrument panel Check Engine
lamp). Also, the technician can read fault informa-
tion by connecting the DRBII scan tool to the data
link connector. For diagnostic trouble code informa-
tion, refer to the 2.2L Turbo III Multi-Port Fuel In-
jectionÐOn-Board Diagnostics section of this group.
CCD BUS
Various modules exchange information through a
communications port called the CCD Bus. The pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) transmits vehicle load
data on the CCD Bus.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
The powertrain control module (PCM) is a digital
computer containing a microprocessor (Fig. 2). The
PCM receives input signals from various switches
and sensors that are referred to as PCM Inputs.
Based on these inputs, the PCM adjusts various en-
gine and vehicle operations through devices that are referred to as PCM Outputs.
PCM Inputs:
² Air Conditioning Controls
² Battery Voltage
² Brake Switch
² Camshaft Position Sensor
² Crankshaft Position Sensor
² Charge Air Temperature Sensor
² Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
² Knock Sensor
Fig. 1 Electronic Fuel Injection Components
Fig. 2 PCM
14 - 84 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1825 of 2438

² Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
² Oxygen Sensor
² SCI Receive
² Speed Control System Controls
² Throttle Position Sensor
² Vehicle Speed Sensor
PCM Outputs:
² Air Conditioning Clutch Relay
² Generator Field
² Idle Air Control Motor
² Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay
² Barometric Read Solenoid
² Canister Purge Solenoid
² Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine Lamp)
² Data Link Connector
² Fuel Injectors
² Ignition Coil
² Radiator Fan Relay
² Speed Control Solenoids
² Tachometer Output
² Wastegate Solenoid
Based on inputs it receives, the PCM adjusts fuel
injector pulse width, idle speed, ignition spark ad-
vance, ignition coil dwell and canister purge opera-
tion. The PCM regulates operation of the cooling fan,
A/C and speed control systems. The PCM changes
generator charge rate by adjusting the generator
field. The PCM adjusts injector pulse width (air-fuel ra-
tio) based on the following inputs.
² battery voltage
² engine coolant temperature
² exhaust gas content
² engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
² manifold absolute pressure
² throttle position
The PCM adjusts ignition timing based on the fol-
lowing inputs.
² engine coolant temperature
² knock sensor
² engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
² manifold absolute pressure
² throttle position
The Automatic Shut Down (ASD) and Fuel Pump
relays are mounted externally, but turned on and off
by the PCM through the same circuit. The camshaft position sensor and crankshaft posi-
tion sensor signals are sent to the PCM. If the PCM
does not receive both signals within approximately
one second of engine cranking, it deactivates the
ASD relay and fuel pump relay. When these relays
are deactivated, power is shut off to the fuel injector,
ignition coil, oxygen sensor heating element and fuel
pump. The PCM contains a voltage converter that
changes battery voltage to a regulated 8.0 volts. The
8.0 volts power the camshaft position sensor, crank- shaft position sensor and vehicle speed sensor. The
PCM also provides a 5.0 volts supply for the coolant
temperature sensor, manifold absolute pressure sen-
sor and throttle position sensor.
AIR CONDITIONING SWITCH SENSEÐPCM INPUT
When the air conditioning or defrost switch is put
in the ON position and the low pressure and high
pressure switches are closed, the PCM receives an in-
put for air conditioning. After receiving this input,
the PCM activates the A/C compressor clutch by
grounding the A/C clutch relay. The PCM also ad-
justs idle speed to a scheduled RPM to compensate
for increased engine load.
BATTERY VOLTAGEÐPCM INPUT
The PCM monitors the battery voltage input to de-
termine fuel injector pulse width and generator field
control. If battery voltage is low the PCM will in-
crease injector pulse width (period of time that the
injector is energized).
BRAKE SWITCHÐPCM INPUT
When the brake switch is activated, the PCM re-
ceives an input indicating that the brakes are being
applied. After receiving this input, the PCM vents
the speed control servo. Venting the servo turns the
speed control system off. The brake switch is
mounted on the brake pedal support bracket.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM INPUT
Fuel injection synchronization and cylinder identi-
fication are provided through the camshaft position
sensor (Fig. 3). The sensor generates pulses. The
pulse are the input sent to the PCM. The PCM inter-
prets the camshaft position sensor input along with
the crankshaft position sensor input to determine
crankshaft position. The PCM uses crankshaft posi-
tion sensor input to determine injector sequence and
ignition timing.
Fig. 3 Camshaft Sensor
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 85
Page 1829 of 2438
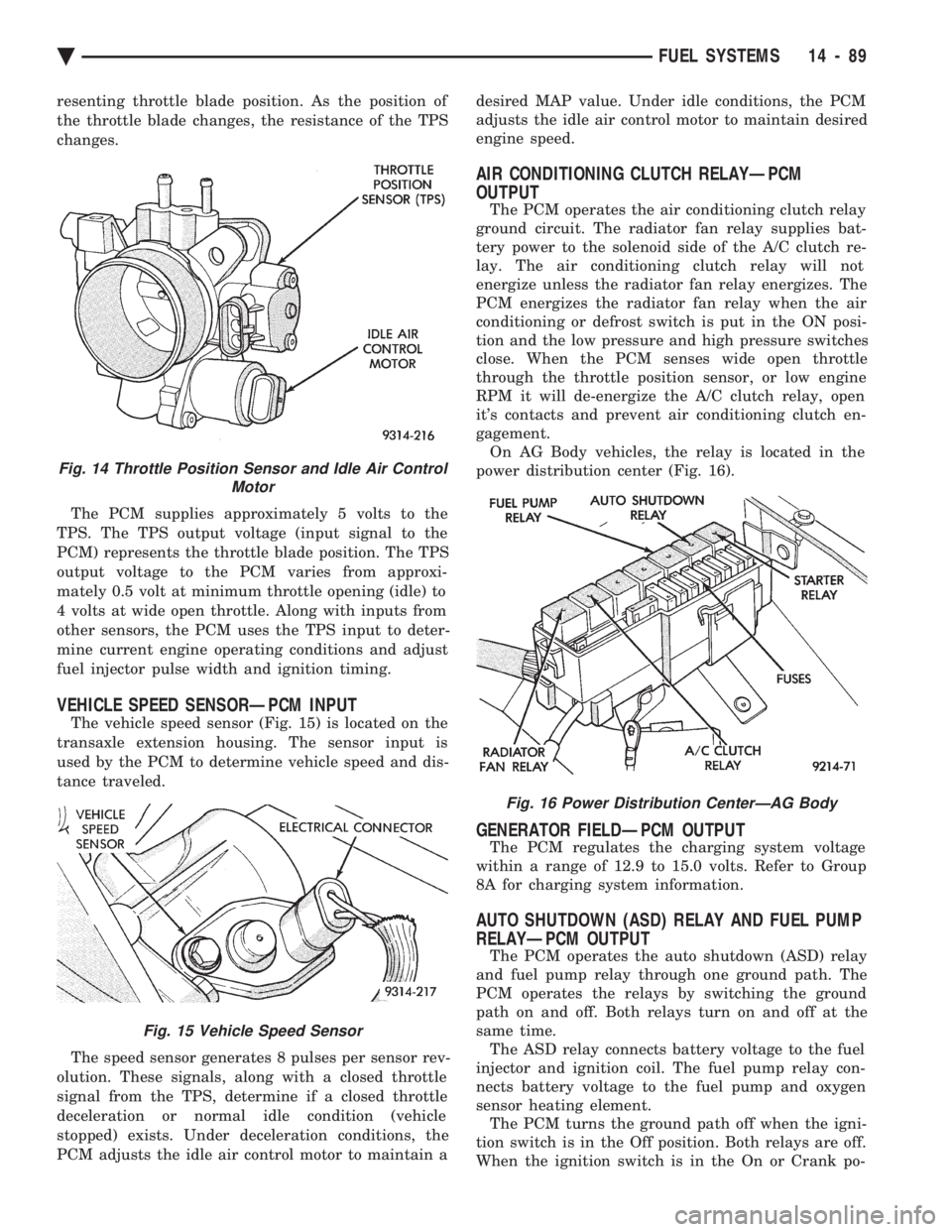
resenting throttle blade position. As the position of
the throttle blade changes, the resistance of the TPS
changes. The PCM supplies approximately 5 volts to the
TPS. The TPS output voltage (input signal to the
PCM) represents the throttle blade position. The TPS
output voltage to the PCM varies from approxi-
mately 0.5 volt at minimum throttle opening (idle) to
4 volts at wide open throttle. Along with inputs from
other sensors, the PCM uses the TPS input to deter-
mine current engine operating conditions and adjust
fuel injector pulse width and ignition timing.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The vehicle speed sensor (Fig. 15) is located on the
transaxle extension housing. The sensor input is
used by the PCM to determine vehicle speed and dis-
tance traveled.
The speed sensor generates 8 pulses per sensor rev-
olution. These signals, along with a closed throttle
signal from the TPS, determine if a closed throttle
deceleration or normal idle condition (vehicle
stopped) exists. Under deceleration conditions, the
PCM adjusts the idle air control motor to maintain a desired MAP value. Under idle conditions, the PCM
adjusts the idle air control motor to maintain desired
engine speed.
AIR CONDITIONING CLUTCH RELAYÐPCM
OUTPUT
The PCM operates the air conditioning clutch relay
ground circuit. The radiator fan relay supplies bat-
tery power to the solenoid side of the A/C clutch re-
lay. The air conditioning clutch relay will not
energize unless the radiator fan relay energizes. The
PCM energizes the radiator fan relay when the air
conditioning or defrost switch is put in the ON posi-
tion and the low pressure and high pressure switches
close. When the PCM senses wide open throttle
through the throttle position sensor, or low engine
RPM it will de-energize the A/C clutch relay, open
it's contacts and prevent air conditioning clutch en-
gagement. On AG Body vehicles, the relay is located in the
power distribution center (Fig. 16).
GENERATOR FIELDÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM regulates the charging system voltage
within a range of 12.9 to 15.0 volts. Refer to Group
8A for charging system information.
AUTO SHUTDOWN (ASD) RELAY AND FUEL PUMP
RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM operates the auto shutdown (ASD) relay
and fuel pump relay through one ground path. The
PCM operates the relays by switching the ground
path on and off. Both relays turn on and off at the
same time. The ASD relay connects battery voltage to the fuel
injector and ignition coil. The fuel pump relay con-
nects battery voltage to the fuel pump and oxygen
sensor heating element. The PCM turns the ground path off when the igni-
tion switch is in the Off position. Both relays are off.
When the ignition switch is in the On or Crank po-
Fig. 14 Throttle Position Sensor and Idle Air Control Motor
Fig. 15 Vehicle Speed Sensor
Fig. 16 Power Distribution CenterÐAG Body
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 89