1993 CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM relay
[x] Cancel search: relayPage 1779 of 2438
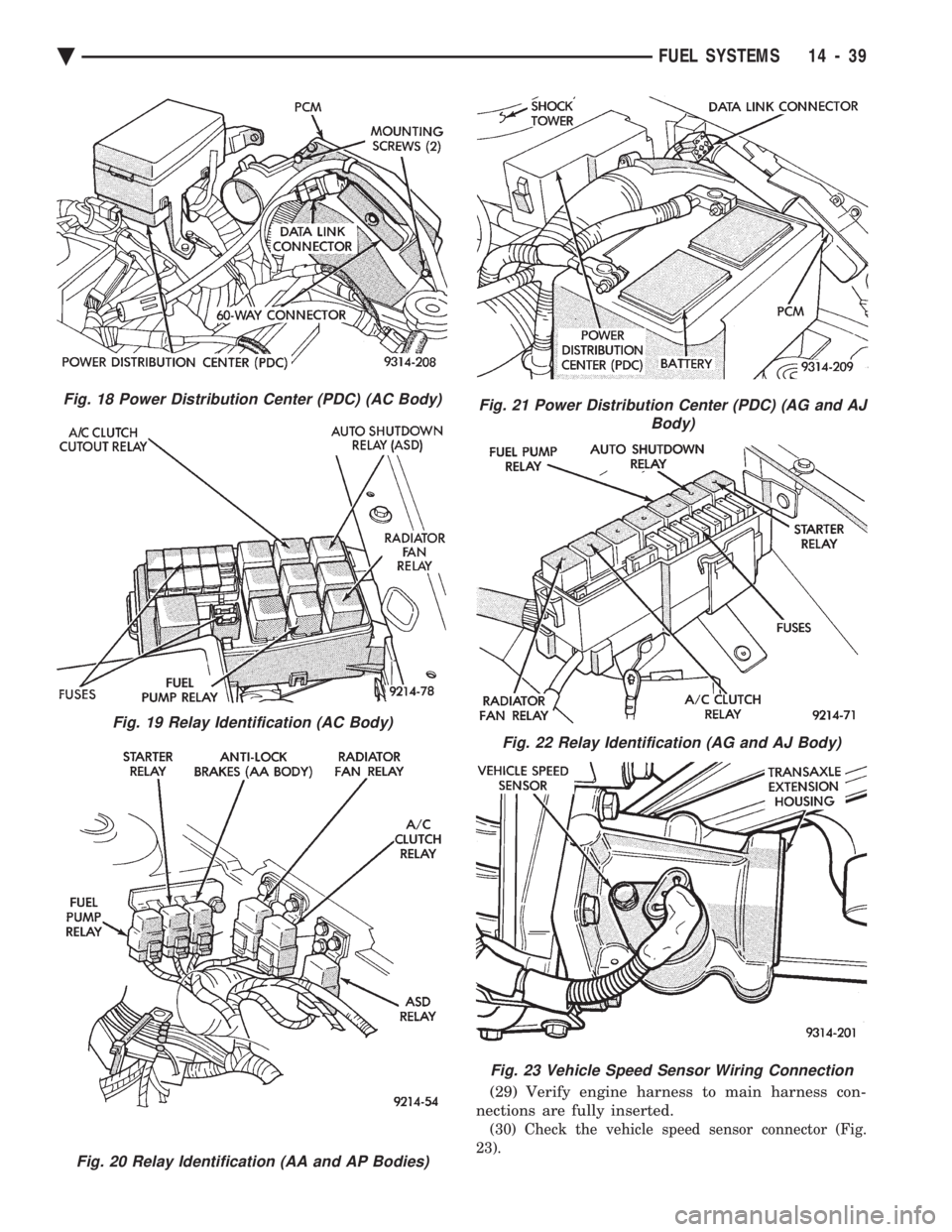
(29) Verify engine harness to main harness con-
nections are fully inserted.
(30) Check the vehicle speed sensor connector (Fig.
23).
Fig. 18 Power Distribution Center (PDC) (AC Body)
Fig. 19 Relay Identification (AC Body)
Fig. 20 Relay Identification (AA and AP Bodies)
Fig. 21 Power Distribution Center (PDC) (AG and AJ Body)
Fig. 22 Relay Identification (AG and AJ Body)
Fig. 23 Vehicle Speed Sensor Wiring Connection
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 39
Page 1785 of 2438

SYSTEMS TEST
WARNING: APPLY PARKING BRAKE AND/OR
BLOCK WHEELS BEFORE PERFORMING A TEST
WITH THE ENGINE OPERATING.
OBTAINING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
(1) Connect DRBII scan tool to the data link con-
nector located in the engine compartment near the
powertrain control module (PCM). (2) Start the engine if possible, cycle the transaxle
selector and the A/Cswitch if applicable. Shut off
the engine. (3) Turn the ignition switch on, access Read Fault
Screen. Record all the fault messages shown on the
DRBII scan tool. Observe the malfunction indicator
lamp (check engine lamp on the instrument panel).
The lamp should light for 3 seconds then go out (bulb
check).
STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs used by the powertrain control
module (PCM) have only two recognized states,
HIGH and LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot
recognize the difference between a selected switch po-
sition versus an open circuit, a short circuit, or a de-
fective switch. If the change is displayed, it can be
assumed that the entire switch circuit to the PCM is
functional. From the state display screen access ei-
ther State Display Inputs and Outputs or State Dis-
play Sensors.
STATE DISPLAY INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the State Display screen. Then access Inputs and
Outputs. The following is a list of the engine control
system functions accessible through the Inputs and
Outputs screen. Park/Neutral Switch (automatic transaxle only)
Speed Control Resume
Brake Switch
Speed Control On/Off
Speed Control Set
A/C Switch Sense
S/C (Speed Control) Vent Solenoid
S/C (Speed Control) Vacuum Solenoid
Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid (3 speed auto-
matic transaxle)
A/C Clutch Relay
EGR Solenoid
Auto Shutdown Relay
Radiator Fan Relay
Purge Solenoid
Malfunction Indicator (Check Engine) Lamp
STATE DISPLAY SENSORS
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the State Display screen. Then access Sensor
Display. The following is a list of the engine control
system functions accessible through the Sensor Dis-
play screen. Oxygen Sensor Signal
Coolant Temperature
Coolant Temp Sensor
Throttle Position
Minimum Throttle
Battery Voltage
MAP Sensor Reading
Idle Air Control Motor Position
Added Adaptive Fuel
Adaptive Fuel Factor
Barometric Pressure
Min Airflow Idl Spd
Engine Speed
Fault #1 Key-On Info
Module Spark Advance
Speed Control Target
Fault #2 Key-On Info
Fault #3 Key-On Info
Speed Control Status
Charging System Goal
Theft Alarm Status
Speed Control Switch Voltage
Map Sensor Voltage
Vehicle Speed
Oxygen Sensor State
MAP Gauge Reading
Throttle Opening (percentage)
Total Spark Advance
CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST MODE
The circuit actuation test mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices which the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) cannot internally rec-
ognize. The PCM can attempt to activate these
outputs and allow an observer to verify proper oper-
ation. Most of the tests provide an audible or visual
indication of device operation (click of relay contacts,
spray fuel, etc.). With the exception of an intermit-
tent condition, if a device functions properly during
its test, it can be assumed that the device, its associ-
ated wiring, and its driver circuit are in working or-
der.
OBTAINING CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the Actuators screen. The following is a list of
the engine control system functions accessible
through Actuators screens. Stop All Tests
Ignition Coil #1
Fuel Injector #1
Idle Air Control Motor Open/Close
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 45
Page 1786 of 2438

Radiator Fan Relay
A/C Clutch Relay
Auto Shutdown Relay
Purge Solenoid
S/C Servo Solenoids
Generator Field
Tachometer Output
Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid (3 speed auto-
matic transaxle only)
EGR Solenoid
All Solenoids/Relays
ASD Fuel System Test
Speed Control Vacuum Solenoid
Speed Control Vent Solenoid
THROTTLE BODY MINIMUM AIR FLOW CHECK
PROCEDURE
(1) Connect DRBII scan tool.
(2) Remove air cleaner assembly. Plug the heated
air door vacuum hose. (3) Warm engine in Park or Neutral until the cool-
ing fan has cycled on and off at least once. (4) Hook-up timing check device and tachometer.
(5) Disconnect the coolant temperature sensor and
set basic timing to 12ÉBTDC 62ÉBTDC.
(6) Shut off engine. Reconnect coolant temperature
sensor. (7) Disconnect the PCV valve hose from the intake
manifold nipple. (8) Attach Air Metering Fitting #6457 (Fig. 4) to
the intake manifold PCV nipple. (9) Restart the engine, allow engine to idle for at
least one minute. (10) Using the DRBII scan tool, Access Min Air-
flow Idle Spd in the sensor read test mode. (11) The following will then occur:
² Idle air control motor will fully close.
² Idle spark advance will become fixed.
² Idle fuel will be provided at a set value.
² Engine RPM will be displayed on DRBII scan tool.
(12) Check idle RPM with tachometer. If idle RPM is within the specifications listed below, then the
throttle body minimum air flow is set correctly.
If idle RPM is not within specification replace
throttle body. (13) Shut off engine.
(14) Remove Special Tool number 6457 from in-
take manifold PCV nipple. Reinstall the PCV valve
hose. (15) Remove DRBII scan tool.
(16) Reinstall air cleaner assembly. Reinstall
heated air door vacuum hose. (17) Disconnect timing check device and tachome-
ter.
IGNITION TIMING PROCEDURE
Refer to Group 8D Ignition System
60-WAY PCM WIRING CONNECTOR
Refer to the powertrain control module (PCM) wir-
ing connector descriptions for information regarding
wire colors and cavity numbers (Fig. 5).
Fig. 4 Air Metering Fitting
IDLE SPECIFICATIONS
14 - 46 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1790 of 2438

(5) Remove throttle cable. If equipped, remove the
speed control and transaxle kickdown cables. (6) Remove return spring.
(7) Loosen fuel tube clamp on valve cover (Fig. 4).
(8) Wipe quick connect fittings to remove any dirt.
Remove fuel intake and return tubes. Refer to Fuel
Hoses, Clamps and Quick Connect Fittings in the
Fuel Delivery Section of this Group. Place a shop
towel under the connections to absorb any fuel spilled. (9) Remove throttle body mounting screws and lift
throttle body from vehicle. Remove throttle body gas-
ket from intake manifold.
INSTALLATION
(1) Using a new gasket, install throttle body and
tighten mounting screws to 20 N Im (175 in. lbs.)
torque. (2) Lubricate the ends of the fuel supply and return
tubes with clean 30 weight oil. Connect fuel lines to
quick connect fittings. Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps
and Quick Connect Fittings in the Fuel Delivery
Section of this Group . After the fuel tubes are
connected to the fittings, pull on the tubes to ensure
that they are fully inserted and locked into position. (3) Tighten the fuel tube clamp on the valve cover.
(4) Install return spring.
(5) Install throttle cable. If equipped, install kick-
down and speed control cables. (6) Install wiring connectors and vacuum hoses.
(7) Install air cleaner.
(8) Reconnect negative battery cable.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test, the
Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized for
either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or until the
ignition switch is turned to the Off position. (9) With the ignition key in ON position, access the
DRBII scan tool ASD Fuel System Test to pressurize
the fuel system. Check for leaks.
FUEL FITTING
REMOVAL
(1) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(2) Perform Fuel System Pressure Release proce-
dure. (3) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(4) Loosen fuel tube clamp on valve cover.
(5) Wipe any dirt from around quick connect fittings.
(Fig. 5) Place a shop towel under the connections to
catch any spilled fuel. Remove fuel tubes from quick
connect fittings. Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps and
Quick Connect Fittings in the Fuel Delivery Sec-
tion of this Group .
(6) Remove each fitting from throttle body and note
inlet diameter. Remove copper washers.
INSTALLATION
(1) Replace copper washers with new washers.
(2) Install fuel fittings in proper ports and tighten to
20 N Im (175 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Lubricate ends of the fuel tubes with 30 weight
oil. Insert the tubes into the quick connect fittings.
Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps and Quick Connect
Fittings in the Fuel Delivery Section of this
Group . After the fuel tubes are connected to the
fittings, pull on the tubes to ensure that they are fully
inserted and locked into position. (4) Tighten fuel tube clamp on valve cover.
(5) Reconnect negative battery cable.
Fig. 5 Servicing Fuel Fitting
Fig. 4 Fuel Line Clamp
14 - 50 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1791 of 2438

CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized
for either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or un-
til the ignition switch is turned to the Off position. (6) With the ignition key in ON position, access
the DRBII scan tool ASD Fuel System Test to pres-
surize the fuel system. Check for leaks. (7) Reinstall air cleaner assembly.
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
The fuel pressure regulator is mounted on top of
the throttle body (Fig. 6).
REMOVAL
(1) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(2) Perform Fuel System Pressure Release proce-
dure. (3) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(4) Remove pressure regulator mounting screws
(Fig. 6).
WARNING: PLACE A SHOP TOWEL AROUND FUEL
INLET CHAMBER TO CONTAIN ANY FUEL REMAIN-
ING IN THE SYSTEM.
(5) Pull pressure regulator from the throttle body.
(6) Carefully remove O-ring from pressure regula-
tor and remove gasket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place new gasket on pressure regulator. Care-
fully install new O-ring. (2) Position pressure regulator on throttle body.
Press regulator into place and install mounting
screws. Tighten screws to 5 N Im (40 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect negative cable to battery.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized
for either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or un-
til the ignition switch is turned to the Off position. (4) With the ignition key in ON position, access
the DRBII scan tool ASD Fuel System Test to pres-
surize the fuel system. Check for leaks. (5) Reinstall air cleaner assembly.
FUEL INJECTOR
The fuel injector is installed in the top of the throt-
tle body. The injector is covered by a cap.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(2) Perform Fuel System Pressure Release proce-
dure. (3) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(4) Remove injector cap holddown screw (Torx-
head). (5) With two small screwdrivers, lift the top off the
injector using the slots provided (Fig. 7).
(6) Using a small screwdriver placed in the hole in
the front of the electrical connector, gently pry the
injector from the pod (Fig. 8).
Fig. 6 Servicing Fuel Pressure Regulator
Fig. 7 Removing Injector Cap
Fig. 8 Removing Fuel Injector
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 51
Page 1792 of 2438

(7) Ensure the injector lower O-ring has been re-
moved from the pod (Fig. 9).
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply a light coating of clean engine oil on the
O-rings. (2) Place assembly in the pod. Align the injector
wiring terminals with the injector cap fastener hole
(Fig. 10).
(3) Install injector cap with locating notch aligned
with the locating lobe on the injector (Fig. 11). (4) Push down on the cap to ensure a good seal.
(5) Rotate the cap and injector to line up the at-
tachment hole (Fig. 12).
(6) Install injector cap holddown screw (torx-head
screw). Tighten screw to 4-5 N Im (35-45 in. lbs.) torque.
(7) Connect negative cable to battery.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized
for either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or un-
til the ignition switch is turned to the Off position. (8) With the ignition key in ON position, access
the DRBII scan tool ASD Fuel System Test to pres-
surize the fuel system. Check for leaks. (9) Reinstall the air cleaner assembly.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove air cleaner.
(3) Disconnect harness connector from throttle po-
sition sensor (Fig. 13). (4) Remove throttle position sensor mounting
screws. (5) Remove throttle position sensor from throttle
shaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install throttle position sensor to throttle body,
position toward the front of the vehicle. Tighten
screws to 2 N Im (20 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect 3 way connector at throttle position
sensor.
Fig. 9 Servicing Fuel Injector
Fig. 10 Fuel Injector Installation
Fig. 11 Installing Fuel Injector Cap
Fig. 12 Fuel Injector Installed
14 - 52 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1795 of 2438

(2) Remove sensor using Tool C-4907 (Fig. 21).
Slightly tightening the sensor can ease removal. When the sensor is removed, the exhaust manifold
threads must be cleaned with an 18 mm X 1.5 + 6E
tap. If the same sensor is to be reinstalled, the sensor
threads must be coated with an anti-seize compound
such as Loctite 771-64 or equivalent. New sensors
are packaged with compound on the threads and do
not require additional compound. The sensor must be
tightened to 27 N Im (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
2.5L FLEXIBLE FUEL MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTIONÐSYSTEM OPERATION
INDEX
page page
Air Conditioning (A/C) Clutch RelayÐPCM Output.61
Air Conditioning Switch SenseÐPCM Input ..... 57
Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay and Fuel Pump RelayÐPCM Output ..................... 61
Battery VoltageÐPCM Input ................ 58
Brake SwitchÐPCM Input .................. 58
Camshaft Position SensorÐPCM Input ........ 58
CCD BUS .............................. 57
Data Link ConnectorÐPCM Output ........... 62
Duty Cycle Evap Purge SolenoidÐPCM Output . 61
Engine Coolant Temperature SensorÐPCM Input . 58
Fuel InjectorÐPCM Output ................. 62
Fuel Injectors and Fuel Rail Assembly ......... 65
Fuel Pressure Regulator ................... 65
Fuel Supply Circuit ....................... 65
General Information ....................... 55
Generator FieldÐPCM Output ............... 62
Heated Oxygen Sensor (O
2Sensor)ÐPCM Input . 59
Identifying Flexible Fuel Components .......... 55
Idle Air Control MotorÐPCM Output .......... 62 Ignition CoilÐPCM Output
.................. 62
Malfunction Indicator (Check Engine) LampÐPCM Output ............................... 62
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) SensorÐPCM Input ................................ 58
Methanol Concentration SensorÐPCM Input .... 59
Modes of Operation ....................... 63
Powertrain Control Module ................. 57
Radiator Fan RelayÐPCM Output ............ 63
Speed Control SolenoidsÐPCM Output ........ 63
Speed ControlÐPCM Input ................. 60
System Diagnosis ........................ 56
System Operation ........................ 56
TachometerÐPCM Output .................. 63
Throttle Body ............................ 65
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)ÐPCM Input ..... 60
Torque Converter Clutch SolenoidÐPCM Output . 63
Transaxle Park/Neutral SwitchÐPCM Input ..... 60
Vehicle Speed SensorÐPCM Input ........... 60
GENERAL INFORMATION
In this model year Chrysler began producing AA-
Body vehicles designed to operate on a mixture of
gasoline and methanol. These automobiles are re-
ferred to as Flexible Fuel vehicles. Fuel system com-
ponents designed for use in flexible fuel vehicles are
referred to as Methanol Compatible. Flexible fuel vehicles can operate on a mixture of
up to 85 percent methanol, 15 percent unleaded gas-
oline. These vehicles also operate on mixtures con-
taining a lower percentage of methanol or just pure
unleaded gasoline.
IDENTIFYING FLEXIBLE FUEL COMPONENTS
Flexible Fuel vehicles have unique methanol com-
patible fuel system components. Chrysler identifies
methanol compatible components that could be phys-
ically interchanged with gasoline only parts by color-
ing them green or applying a green label or tag to
them. Even though they may appear physically iden- tical, components for gasoline only AA-body vehicles
must not be used on flexible fuel vehicles.
FLEXIBLE FUEL COMPONENTS
The fuel system of flexible fuel AA-body vehicles
have the following unique methanol compatible com-
ponents.
² Duty Cycle EVAP Purge Solenoid
² Fuel pump module
² Fuel level sensor
² Fuel gauge (gauge cluster).
² Fuel tank
² Fuel pressure regulator (including O-rings)
² Fuel rail
² Fuel injectors (including O-rings)
² Fuel tubes
² Fuel filter
² EVAP canister
² Fuel filler cap
² Fuel filler tube
Fig. 21 Oxygen Sensor Socket
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 55
Page 1797 of 2438

The second method of reading diagnostic trouble
codes uses the DRBII scan tool. For diagnostic trou-
ble code information, refer to the On-Board Diagnos-
tics section in this group.
CCD BUS
Various modules exchange information through a
communications port called the CCD Bus. The pow-
ertrain control module transmits vehicle load data on
the CCD Bus.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
The powertrain control module (PCM) is a digital
computer containing a microprocessor (Fig. 2). The
PCM receives input signals from various switches
and sensors referred to as Powertrain Control Mod-
ule Inputs. Based on these inputs, the PCM adjusts
various engine and vehicle operations through de-
vices referred to as Powertrain Control Module Out-
puts.
PCM Inputs:
² Air Conditioning Controls
² Battery Voltage
² Brake Switch
² Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
² Camshaft Position Sensor (Distributor Pick-up)
² Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
² Methanol Concentration Sensor
² Oxygen Sensor
² SCI Receive
² Speed Control System Controls
² Throttle Position Sensor
² Park/Neutral Switch (automatic transaxle)
² Vehicle Speed Sensor
PCM Outputs:
² Air Conditioning Clutch Relay
² Generator Field
² Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay
² Duty Cycle EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid
² Data Link (Diagnostic) Connector ²
Fuel Injectors
² Idle Air Control Motor
² Ignition Coil
² Malfunction Indicator (Check Engine) Lamp
² Radiator Fan Relay
² Speed Control Solenoids
² Tachometer Output
² Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
Based on inputs it receives, the PCM adjusts fuel
injector pulse width, idle speed, ignition spark ad-
vance, ignition coil dwell and canister purge opera-
tion. The PCM regulates operation of the radiator
fan, A/C and speed control systems. Also, the PCM
changes generator charge rate by adjusting the gen-
erator field. The PCM adjusts injector pulse width (air-fuel ra-
tio) based on the following inputs.
² Battery voltage
² Coolant temperature
² Exhaust gas content
² Engine speed
² Manifold absolute pressure
² Methanol percentage of fuel
² Throttle position
The PCM adjusts ignition timing based on the fol-
lowing inputs.
² Coolant temperature
² Engine speed
² Manifold absolute pressure
² Methanol percentage of fuel
² Throttle position
The auto shutdown (ASD) and fuel pump relays are
mounted externally. The PCM turns both relays on
and off through the same circuit. The camshaft position sensor (distributor pick-up)
sends a signal to the PCM. If the PCM does not re-
ceive a camshaft position sensor signal within ap-
proximately one second of engine cranking, it
deactivates the ASD and fuel pump relays. When
these relays deactivate, they shut off power to the
fuel injectors, fuel pump, ignition coil, methanol con-
centration sensor and oxygen sensor heater element. The PCM contains a voltage converter that
changes battery voltage to a regulated 8.0 volts to
power the distributor pick-up methanol concentration
sensor and vehicle speed sensor. The PCM also pro-
vides a 5.0 volts supply for the engine coolant tem-
perature sensor, manifold absolute pressure sensor
and throttle position sensor.
AIR CONDITIONING SWITCH SENSEÐPCM INPUT
When the operator puts the A/C or defrost switch
in the ON position and the low pressure and high
pressure switches close, the PCM receives an input.
The input indicates the operator selected air condi-
tioning. After receiving this input, the PCM acti-
vates the A/C compressor clutch by grounding the
Fig. 2 Powertrain Control Module
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 57