1993 CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM tire type
[x] Cancel search: tire typePage 53 of 2438

should be above ADD mark. Add fluid only if level is
below ADD mark on dipstick when transaxle is
warm.The automatic transaxle does not require periodic
maintenance when used for general transportation. If
the vehicle is subjected to severe service conditions,
the automatic transaxle will require fluid/filter
change and band adjustments every 24 000 km
(15,000 miles). For additional information, refer to
Severe Service paragraph and Lubrication and Main-
tenance Schedules in General Information section of
this group. The fluid and filter should be changed
when water contamination is suspected. If fluid has
foamy or milky appearance, it is probably contami-
nated. If the fluid appears brown or dark and a foul
odor is apparent, the fluid is burned, transaxle re-
quires maintenance or service. A circular magnet lo-
cated in the transaxle pan, collects metallic particles
circulating in the oil. For proper diagnostic and ser-
vice procedures, refer to Group 21, Automatic Tran-
saxle.
SELECTING AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID
Chrysler Corporation recommends Mopar ATF Plus
(automatic transmission fluid type 7176) be used to
add to or replace automatic transaxle fluid. If ATF
Plus is not available use Mopar Dexron II tAuto-
matic Transmission Fluid or equivalent.
DRIVE SHAFT CV AND TRIPOD JOINT BOOTS
The front drive shaft constant velocity and tripod
joint boots (Fig. 5) should be inspected when other
under vehicle service is performed. Inspect boots for
cracking, tears, leaks or other defects. If service re-
pair is required, refer to Group 2, Suspension.
FRONT WHEEL BEARINGS
The front wheel bearings are permanently sealed,
requiring no lubrication. For proper diagnostic and
service procedures refer to Group 2, Suspension.
TIRES
The tires should be inspected at every engine oil
change for proper inflation and condition. The tires
should be rotated at the distance intervals described
in the Lubrication and Maintenance Schedules of the
General Information section in this group. For tire
inflation specifications refer to the Owner's Manual.
A Tire Inflation sticker is located in the driver door
opening. For proper diagnostic procedures, see Group
22, Wheels and Tires.Fig. 2 3-speed Automatic Transaxle Fill hole
Fig. 3 4-speed Automatic Transaxle Fill tube
Fig. 4 Automatic Transaxle DipstickÐTypical
Fig. 5 Drive Shaft Boots
Ä LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 17
Page 63 of 2438

FRONT SUSPENSION SERVICE PROCEDURES INDEX
page page
Ball Joints .............................. 13
Hub and Bearing Assembly ................. 20
Knuckle (Front Suspension) ................. 16
Lower Control Arm ....................... 10
Lower Control Arm Pivot Bushings ........... 11 Shock Absorbers (Strut Damper)
............. 10
Strut Damper Assembly ..................... 7
Suspension Coil Springs .................... 9
Sway Bar .............................. 14
Wheel Alignment .......................... 5
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
Front wheel alignment is the proper adjustment of
all interrelated front suspension angles. These angles
are what affects the running and steering of the
front wheels of the vehicle. The method of checking front alignment will vary
depending on the type of equipment being used. The
instructions furnished by the manufacturer of the
equipment should always be followed. With the ex-
ception that the alignment specifications recom-
mended by Chrysler Corporation be used. There are six basic factors which are the founda-
tion to front wheel alignment. These are height,
caster, camber, toe-in, steering axis inclination and
toe-out on turns. Of the six basic factors only camber
and toe in are mechanically adjustable (Fig. 1)
CAUTION: Do not attempt to modify any suspen-
sion or steering components by heating or bending
of the component.
Wheel alignment adjustments and checks should be
made in the following sequence. (1) Camber
(2) Toe
Camber is the number of degrees the top of the
wheel is tilted inward or outward from true vertical.
Inward tilt is negative camber. Outward tilt is posi-
tive camber. Excessive camber is a tire wear factor: negative
camber causes wear on the inside of the tire, while
positive camber causes wear to the outside. Toe
is measured in degrees or inches and is the
distance the front edges of the tires are closer (or far-
ther apart) than the rear edges. See Front Wheel
Drive Specifications for Toesettings.
PRE-ALIGNMENT
Before any attempt is made to change or correct
the wheel alignment factors. The following inspection
and necessary corrections must be made on those
parts which influence the steering of the vehicle. (1) Check and inflate tires to recommended pres-
sure. All tires should be the same size and in good
condition and have approximately the same wear.
Note type of tread wear which will aid in diagnosing,
see Wheels and Tires, Group 22. (2) Check front wheel and tire assembly for radial
runout. (3) Inspect lower ball joints and all steering link-
age for looseness. (4) Check for broken or sagged front and rear
springs. Front suspension must only be checked after the
vehicle has had the following checked or adjusted.
Tires set to recommended pressures, full tank of fuel,
no passenger or luggage compartment load and is on
a level floor or alignment rack. Just prior to each alignment reading. The vehicle
should be bounced (rear first, then front) by grasping
bumper at center and jouncing each end an equal
number of times. Always release bumpers at bottom
of down cycle.
Ä SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS 2 - 5
Page 89 of 2438
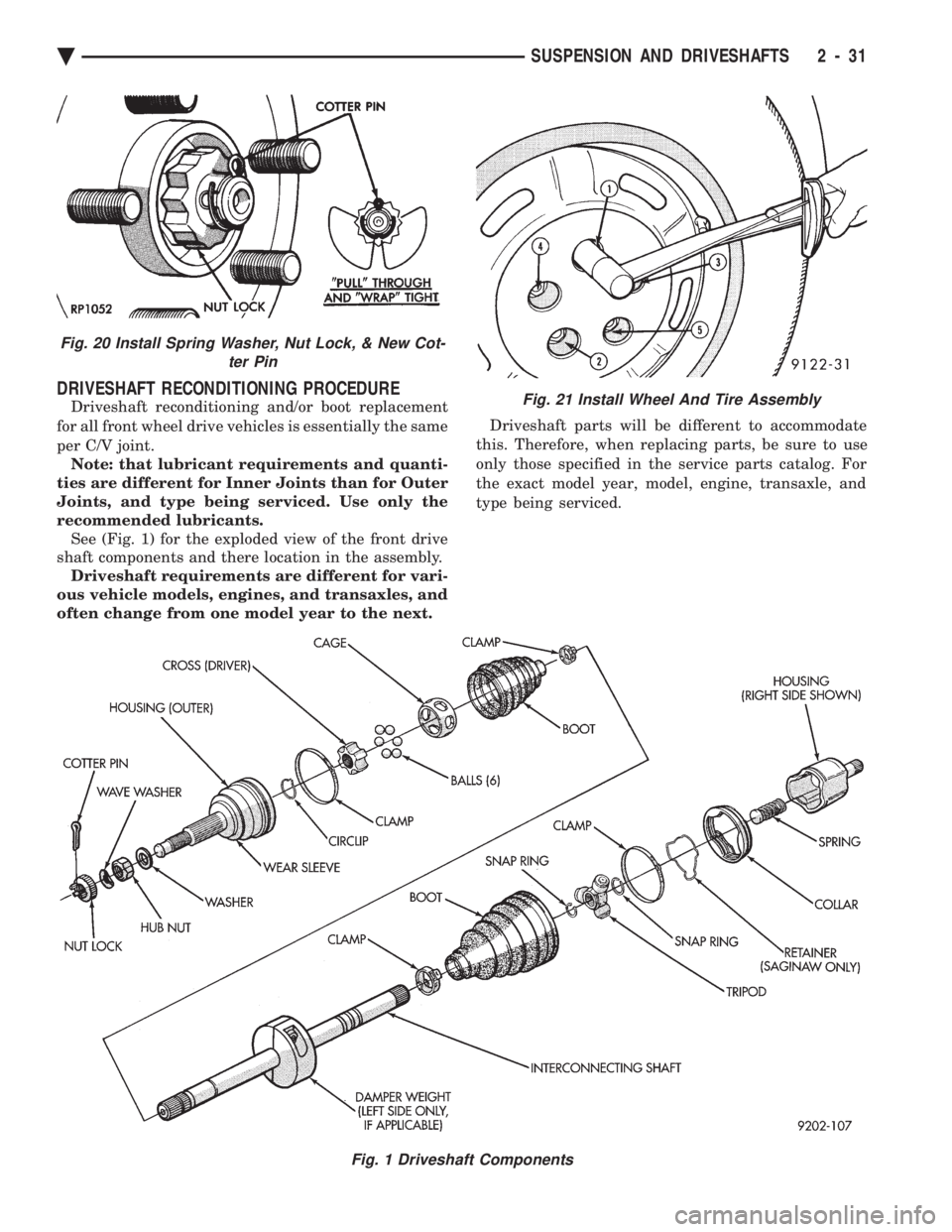
DRIVESHAFT RECONDITIONING PROCEDURE
Driveshaft reconditioning and/or boot replacement
for all front wheel drive vehicles is essentially the same
per C/V joint. Note: that lubricant requirements and quanti-
ties are different for Inner Joints than for Outer
Joints, and type being serviced. Use only the
recommended lubricants. See (Fig. 1) for the exploded view of the front drive
shaft components and there location in the assembly. Driveshaft requirements are different for vari-
ous vehicle models, engines, and transaxles, and
often change from one model year to the next. Driveshaft parts will be different to accommodate
this. Therefore, when replacing parts, be sure to use
only those specified in the service parts catalog. For
the exact model year, model, engine, transaxle, and
type being serviced.
Fig. 1 Driveshaft Components
Fig. 21 Install Wheel And Tire Assembly
Fig. 20 Install Spring Washer, Nut Lock, & New Cot- ter Pin
Ä SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS 2 - 31
Page 108 of 2438
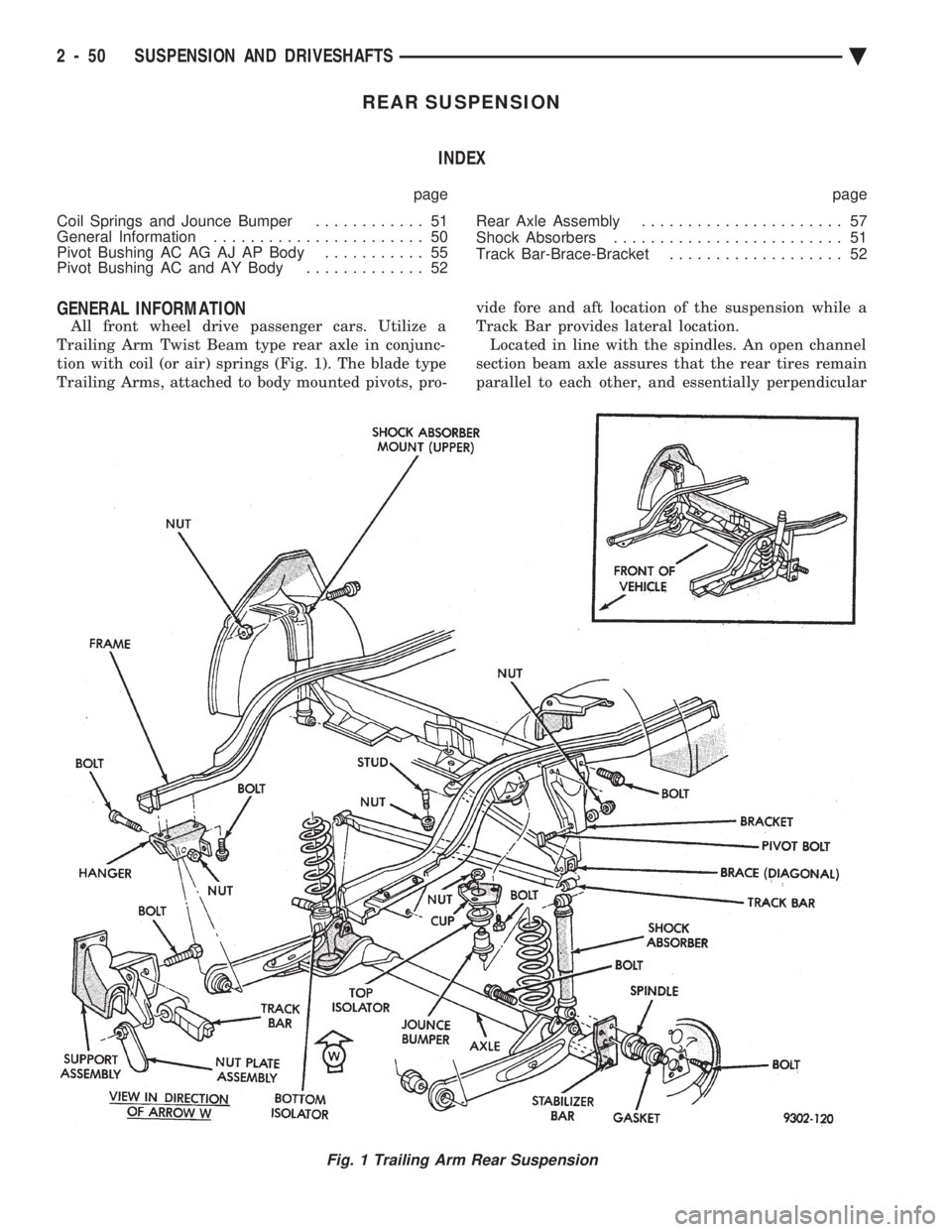
REAR SUSPENSION INDEX
page page
Coil Springs and Jounce Bumper ............ 51
General Information ....................... 50
Pivot Bushing AC AG AJ AP Body ........... 55
Pivot Bushing AC and AY Body ............. 52 Rear Axle Assembly
...................... 57
Shock Absorbers ......................... 51
Track Bar-Brace-Bracket ................... 52
GENERAL INFORMATION
All front wheel drive passenger cars. Utilize a
Trailing Arm Twist Beam type rear axle in conjunc-
tion with coil (or air) springs (Fig. 1). The blade type
Trailing Arms, attached to body mounted pivots, pro- vide fore and aft location of the suspension while a
Track Bar provides lateral location. Located in line with the spindles. An open channel
section beam axle assures that the rear tires remain
parallel to each other, and essentially perpendicular
Fig. 1 Trailing Arm Rear Suspension
2 - 50 SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS Ä
Page 161 of 2438

BRAKE HOSE AND TUBING
INSPECTION OF BRAKE HOSE AND TUBING
Flexible rubber hose is used at both front brakes and
at the rear axle. Inspection of brake hoses should be
performed whenever the brake system is serviced and
every 7,500 miles or 12 months, whichever comes first
(every engine oil change). Inspect hydraulic brake
hoses for severe surface cracking, scuffing, or worn
spots. Should the fabric casing of the rubber hose be
exposed due to cracks or abrasions in the rubber hose
cover, the hose should be replaced immediately. Even-
tual deterioration of the hose can take place with
possible burst failure. Faulty installation can cause
twisting and wheel, tire or chassis interference. The steel brake tubing should be inspected periodi-
cally for evidence of physical damage or contact with
moving or hot components.
INSTALLATION OF BRAKE HOSE
Always use factory recommended brake hose to en-
sure quality, correct length and superior fatigue life.
Care should be taken to make sure that the tube and
hose mating surfaces are clean and free from nicks and
burrs. Front right and left side hoses are not
interchangeable. Connections should be correct and properly made.
Use new copper seal washers on all connections using
Banjo Bolts and tighten all fittings to their specified
torques. The flexible front hydraulic brake hose should al-
ways be installed on the vehicle by first attaching the
Banjo connector to the caliper assembly. Then bolt the
intermediate hose bracket to the strut assembly allow-
ing the bracket to position the hose to prevent twisting.
Attach the hose to the body bracket and steel brake
tubing. Tighten all fittings to specified torque. The
body bracket and hose end are keyed so that they will
only fit one way. Install rear brake hoses first to the trailing arm
tubes and then to the floor pan tubes. Minimize hose
twisting. Vehicles equipped with rear disc brakes have
brake hoses attached to the caliper on each side. The
brake hose should be first attached by the Banjo bolt to
the caliper and then secured to the hose bracket with
the retaining clip. The attach the steel brake tubing to
the hose fitting.
REPAIR AND INSTALLATION OF BRAKE TUB- ING
Only double wall 4.75mm (3/16 in.) steel tubing
should be used for replacement. Care should be taken
when replacing brake tubing, to be sure the proper
bending and flaring tools and procedures are used, to
avoid kinking. Do not route the tubes against sharp edges, moving components or into hot areas. All
tubes should be properly attached with recommended
retaining clips.
TYPES OF TUBING FLARES
Two different tubing flares (Fig. 13) are used on 93
M.Y. vehicles. On some ABS brake systems the tub-
ing connections made to the hydraulic assembly use
an ISO flare. All other ABS brake system compo-
nent, tubing connections are made using a double in-
verted flare. On non-ABS brake systems all
component tubing connections use only the double in-
verted flare. No ISO flares are used.
CAUTION: ALWAYS USE THE PROPER FLARING
TOOL AND PROCEDURE, FOR THE TYPE OF
BRAKE SYSTEM THAT IS BEING SERVICED TO IN-
SURE THE INTEGRITY OF THE HYDRAULIC SYS-
TEM.
TO REPAIR OR FLARE TUBING
Using Tubing Cutter, Special Tool C-3478-A or
equivalent, cut off damaged seat or tubing (Fig. 14).
Ream out any burrs or rough edges showing on in-
side of tubing (Fig. 15). This will make the ends of
tubing square (Fig. 15) and ensure better seating of
flared end tubing. PLACE TUBE NUT ON TUB-
ING BEFORE FLARING THE TUBING.
DOUBLE INVERTED TUBING FLARES.
To make a double inverted tubing flare (Fig. 13 &
16). Open handles of Flaring Tool, Special Tool
C-4047 or equivalent. Then rotate jaws of tool until
the mating jaws of tubing size are centered between
vertical posts on tool. Slowly close handles with tub-
Fig. 13 Identifying Hydraulic Brake Tubing Flares
Ä BRAKES 5 - 11
Page 184 of 2438

SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
WARNING: DUST AND DIRT ON BRAKE PARTS
GENERATED DURING THE NORMAL USE AND
WEAR OF MOTOR VEHICLE BRAKE SYSTEMS CAN
CONTAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS. BREATHING EXCES-
SIVE CONCENTRATIONS OF ASBESTOS FIBERS
CAN CAUSE SERIOUS BODILY HARM, SUCH AS
ASBESTOSIS AND CANCER. EXTREME CARE
SHOULD BE EXERCISED WHILE SERVICING
BRAKE ASSEMBLIES OR COMPONENTS. DO NOT CLEAN BRAKE ASSEMBLIES OR COM-
PONENTS WITH COMPRESSED AIR OR BY DRY
BRUSHING; USE A VACUUM CLEANER SPECIFI-
CALLY RECOMMENDED FOR USE WITH ASBES-
TOS FIBERS. IF A SUITABLE VACUUM CLEANER IS
NOT AVAILABLE, CLEANING SHOULD BE DONE
WET USING A WATER DAMPENED CLOTH. DO NOT CREATE DUST BY SANDING, GRINDING,
AND/OR SHAVING BRAKE LININGS OR PADS UN-
LESS SUCH OPERATION IS DONE WHILE USING
PROPERLY EXHAUST VENTILATED EQUIPMENT. DISPOSE OF ALL DUST AND DIRT SUSPECTED
TO CONTAIN ANY ASBESTOS FIBERS IN SEALED
BAGS OR CONTAINERS TO MINIMIZE DUST EXPO-
SURE TO YOURSELF AND OTHERS. FOLLOW ALL RECOMMENDED PRACTICES PRE-
SCRIBED BY THE OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND
HEALTH ADMINISTRATION AND THE ENVIRONMEN-
TAL PROTECTION AGENCY. FOR THE HANDLING,
PROCESSING, AND DISPOSITION OF DUST OR DIRT
WHICH MAY CONTAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS. IT IS RECOMMENDED NOT TO BREATH ANY TYPE
OF BRAKE LINING MATERIAL DUST EVEN ASBES-
TOS FREE, DUE TO THE FIBROUS NATURE OF THE
MATERIALS BEING USED.
Grease or any other foreign material must be kept off
caliper assembly, surfaces of braking disc and external
surfaces of hub, during service procedures. Handling of the braking disc and caliper. Should be
done in such a way as to avoid deformation of the disc
and scratching or nicking of the brake linings. If inspection reveals that the square sectioned cali-
per piston seal is worn or damaged, it should be
replaced immediately. During removal and installation of a wheel and tire
assembly, use care not to strike the caliper. Before vehicle is moved after any brake service
work, be sure to obtain a firm brake pedal.
5 - 34 BRAKES Ä
Page 195 of 2438

REAR DISC BRAKES INDEX
page page
Assembling Rear Disc Brake Caliper .......... 49
Brake Shoe Removal ..................... 46
Cleaning and Inspection ................... 49
Disassembling Rear Caliper Assembly ......... 48 General Information
....................... 45
Lining Wear ............................. 45
Service Precautions ....................... 46
GENERAL INFORMATION
The rear disc brakes are similar to front disc
brakes, however, there are several distinctive fea-
tures that require different service procedures. This
single piston, floating caliper rear disc brake assem-
bly includes a hub assembly, adapter, braking disc
(rotor), caliper, shoes and linings. The parking brake
system on all vehicles equipped with rear disc
brakes. Consists of a small duo-servo drum brake
mounted to the caliper adapter. The drum brake
shoes expand out against a braking surface (hat sec-
tion) on the inside area of the braking disk (rotor). The AC and AY body vehicles are equipped with a
caliper assembly that has a 36 mm (1.42 inch) piston,
and utilizes a 14 inch solid braking disc (rotor). The AA body vehicle are equipped with a caliper
assembly that uses a 34 mm (1.34 inch) piston. The
AA body uses the same 14 inch solid braking disc
(rotor) as on the AC and AY applications. Also avail-
able on the AA body is a caliper assembly with a 36
mm (1.42 inch) piston, with a 15 inch vented braking
disc (rotor). The AG AJ and AP body vehicles are also equipped
with different size caliper pistons depending on the size and type of braking disk used on the vehicle.
The 14 9solid braking disk (rotor) applications use a
34 mm (1.34 inch) piston, and the 15 9vented braking
disk (rotor) applications use a 36 mm (1.42 inch) pis-
ton. The caliper assembly on all applications float on
rubber bushings using internal metal sleeves which
are attached to the adapter using threaded guide pin
bolts. The adapter is mounted to the rear axle of the ve-
hicle and is used to mount the brake shoes and actu-
ating cables for the parking brake system. The
adapter also mounts the rear caliper assembly to the
vehicle. The adapter has two machined abutments
which are used to position and align the caliper and
brake shoes for movement for and aft (Fig. 1)
LINING WEAR
To check the amount of lining wear, remove the
wheel and tire assemblies. If a visual inspection does
not adequately determine the condition of the lining,
Fig. 1 Rear Disc Brake Assembly
Ä BRAKES 5 - 45
Page 196 of 2438

removal will be necessary. Remove the shoe and lin-
ing assemblies (see Brake Shoe Removal).Combined shoe and lining thickness should be
measured at the thinnest part of the assembly. When a shoe and lining assembly is worn to a
thickness of approximately 7.0 mm (9/32 inch) it
should be replaced. Replace both shoe assemblies (inboard and out-
board) on both wheels whenever shoe assemblies on
either side are replaced. If a shoe assembly does not require replacement.
Reinstall it, making sure each shoe assembly is re-
turned to its original position on the wheel of the ve-
hicle from which it was removed. (See Brake Shoe
Installation).
SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
WARNING: DUST AND DIRT ON BRAKE PARTS
GENERATED DURING THE NORMAL USE AND
WEAR OF MOTOR VEHICLE BRAKE SYSTEMS CAN
CONTAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS. BREATHING EXCES-
SIVE CONCENTRATIONS OF ASBESTOS FIBERS
CAN CAUSE SERIOUS BODILY HARM, SUCH AS
ASBESTOSIS AND CANCER. EXTREME CARE
SHOULD BE EXERCISED WHILE SERVICING
BRAKE ASSEMBLIES OR COMPONENTS. DO NOT CLEAN BRAKE ASSEMBLIES OR COM-
PONENTS WITH COMPRESSED AIR OR BY DRY
BRUSHING; USE A VACUUM CLEANER SPECIFI-
CALLY RECOMMENDED FOR USE WITH ASBES-
TOS FIBERS. IF A SUITABLE VACUUM CLEANER IS
NOT AVAILABLE, CLEANING SHOULD BE DONE
WET USING A WATER DAMPENED CLOTH. DO NOT CREATE DUST BY SANDING, GRINDIN-
G,AND/OR SHAVING BRAKE LININGS OR PADS
UNLESS SUCH OPERATION IS DONE WHILE USING
PROPERLY EXHAUST VENTILATED EQUIPMENT. DISPOSE OF ALL DUST AND DIRT SUSPECTED
TO CONTAIN ANY ASBESTOS FIBERS IN SEALED
BAGS OR CONTAINERS TO MINIMIZE DUST EXPO-
SURE TO YOURSELF AND OTHERS. FOLLOW ALL RECOMMENDED PRACTICES PRE-
SCRIBED BY THE OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND
HEALTH ADMINISTRATION AND THE ENVIRON-
MENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY. FOR THE HAN-
DLING, PROCESSING, AND DISPOSITION OF DUST
OR DIRT WHICH MAY CONTAIN ASBESTOS FI-
BERS. IT IS RECOMMENDED NOT TO BREATH ANY
TYPE OF BRAKE LINING MATERIAL DUST EVEN
ASBESTOS FREE, DUE TO THE FIBROUS NATURE
OF THE MATERIALS BEING USED.
Grease or any other foreign material must be kept
off the caliper assembly, surfaces of the braking disc
and external surfaces of the hub, during service pro-
cedures. Handling the braking disc and caliper should be done
in such a way as to avoid deformation of the disc and
scratching or nicking the brake linings (pads). During removal and installation of a wheel and tire
assembly, use care not to strike the caliper. Before vehicle is moved after any brake service
work, be sure to obtain a firm brake pedal.
BRAKE SHOE REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on jackstands or centered on a
hoist. (2) Remove rear wheel and tire assemblies.
(3) Remove caliper attaching bolts (Fig. 2).
(4) Lift caliper away from adapter rails (Fig. 3).
(5) Remove outboard shoe. By prying the shoe re-
taining clip over the raised area on the caliper. Then
slide the shoe down and off the caliper (Fig. 4). (6) Pull inboard shoe away from piston, until the
retaining clip is free from the cavity in the piston. (Fig.
5).
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
Check for piston seal leaks (brake fluid in and
around boot area and inboard lining) and for any
ruptures of piston dust boot. If the boot is damaged, or
fluid leak is visible, disassemble caliper assembly and
install a new seal and boot (and piston if scored). Refer
to procedure titled Disc Brake Caliper Disassembly.
BRAKE SHOE INSTALLATION
(1) Retract piston.
If the originally removed brake shoe assem-
blies are to be replaced back on vehicle. Be sure
Fig. 2 Removing Caliper Attaching Bolts
5 - 46 BRAKES Ä