1993 CHEVROLET DYNASTY warning
[x] Cancel search: warningPage 136 of 2438

(3) Check solenoid to volume canister joint.
² Front strut to solenoid valve connection.
² Rear spring to solenoid valve connection.
(4) Check air line for ruptures, cuts, splits or heat
damage. Use a soap and water solution or a liquid de-
veloped for leak detection.
SYSTEM OPERATION
ENGINE RUN OPERATION
The system will compensate for load
addition/removal when.
² The trunk and all doors are closed.
² The engine speed exceeds 600 R.P.M.
² Throttle angle is less than 65 degrees.
² The brake is not applied.
² You are not cornering above 10 mph.
² There is not a charging system problem with the
vehicle.
ENGINE OFF OPERATION
After passengers/load is removed from the vehicle
the system will correct the vehicle attitude after:
² The trunk and all doors are closed.
² The ignition switch is in the OFF position.
Opening the a door or trunk wakes up the body
computer and the air suspension module. The air
suspension system is now capable of leveling, if
required.
LONG TERM IGNITION OFF OPERATION
The system is capable of one an additional leveling
cycle. After 2 continuous hours of ignition key off and
no door open or trunk open activities. This feature is
implemented to eliminate possible ice freeze-up be-
tween the tire and the inner fender shield.
SYSTEM OPERATION INHIBITORS
The air suspension system is inhibited when:
² The trunk is open.
² A door(s) is/are open.
² The brake pedal is engaged.
² The throttle is at the wide open position.
² The charging system fails.
The maximum compressor pump or exhaust
time is 3 minutes.
SYSTEM FAILURES
Vehicles equipped with air suspension and overhead
console. Will alert the driver of an air suspension
system malfunction. A warning Check Air Suspension
will appear on the overhead console screen.
SAFETY CONCERNS
WARNING: REAR AIR SPRINGS MUST BE DEFLATED
BEFORE BEING REMOVED FROM THE VEHICLE.
WARNING: OPEN TRUNK, OR DOOR(S) OR REMOVE
GROUND STRAP FROM BATTERY BEFORE HOIST-
ING OR JACKING A VEHICLE DURING MECHANICAL
REPAIRS.
WARNING: IF THE VEHICLE NEEDS SERVICE OR
REPAIR OF THE REAR SHOCK ABSORBERS OR
REAR AXLE PIVOT BUSHINGS. THE REAR AIR
SPRINGS MUST HAVE THE AIR PRESSURE RE-
MOVED BEFORE THE VEHICLE CAN BE SERVICED
SAFELY.
SHIPPING MODE
(1) Removing shipping height signal for customer
use.
² Use DRB II tester and 1991 Chassis (Air Suspen-
sion) service cartridge.
² Follow DRB II requirements to cancel shipping
height message in the body computer.
² Connect the Ignition Off Draw (I.O.D.) circuit.
The connection of the IOD circuit will cancel
the Shipping height signal. (2) Return to shipping height.
² Set shipping command in the body computer using
the DRB II and the 1991 Chassis (Air suspension)
service cartridge.
² Disconnect the I.O.D. connector.
DIAGNOSIS
INITIAL DIAGNOSTIC CHECK
(1) Check for blown or missing fuses.
Fig. 9 Compressor Current Draw Test
2 - 78 SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS Ä
Page 144 of 2438
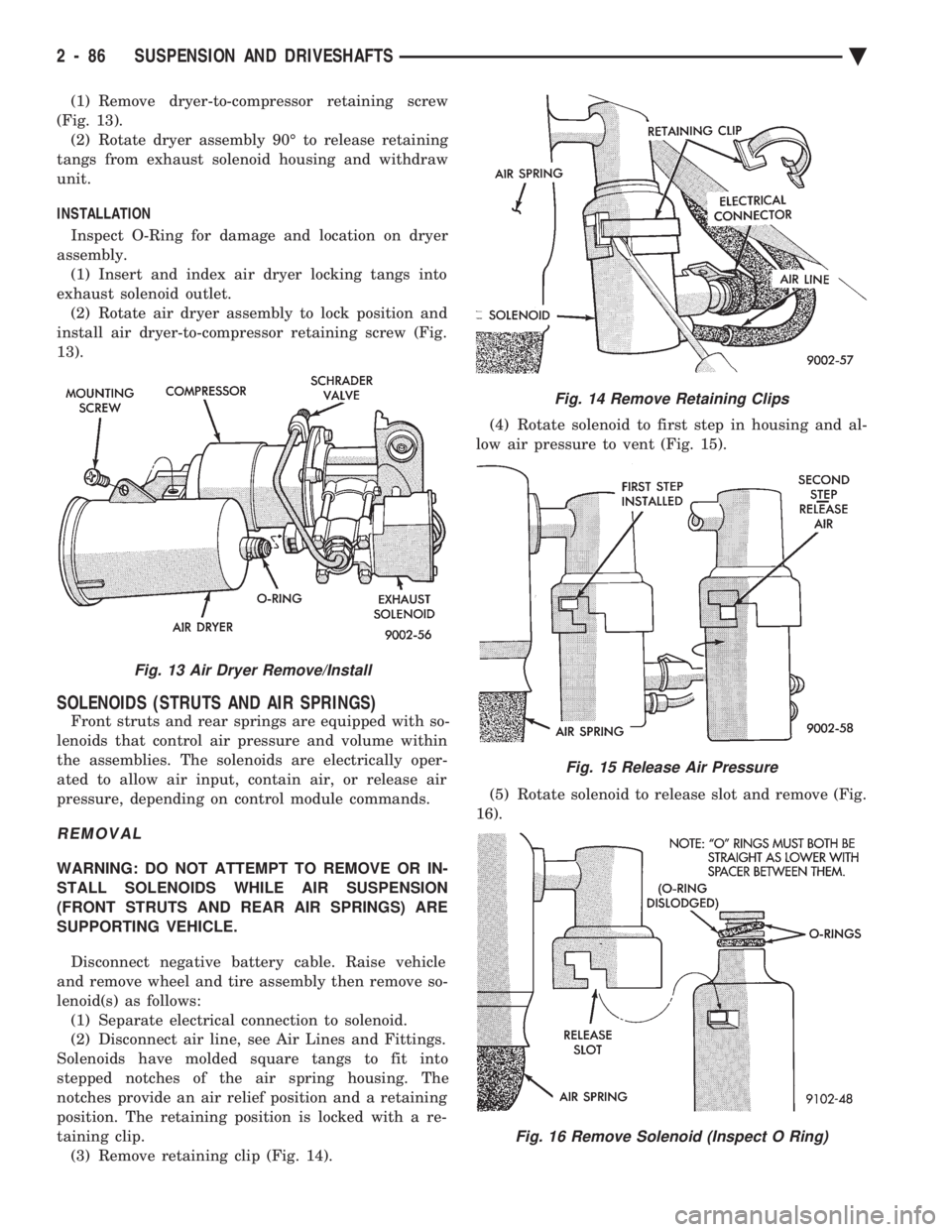
(1) Remove dryer-to-compressor retaining screw
(Fig. 13). (2) Rotate dryer assembly 90É to release retaining
tangs from exhaust solenoid housing and withdraw
unit.
INSTALLATION
Inspect O-Ring for damage and location on dryer
assembly. (1) Insert and index air dryer locking tangs into
exhaust solenoid outlet. (2) Rotate air dryer assembly to lock position and
install air dryer-to-compressor retaining screw (Fig.
13).
SOLENOIDS (STRUTS AND AIR SPRINGS)
Front struts and rear springs are equipped with so-
lenoids that control air pressure and volume within
the assemblies. The solenoids are electrically oper-
ated to allow air input, contain air, or release air
pressure, depending on control module commands.
REMOVAL
WARNING: DO NOT ATTEMPT TO REMOVE OR IN-
STALL SOLENOIDS WHILE AIR SUSPENSION
(FRONT STRUTS AND REAR AIR SPRINGS) ARE
SUPPORTING VEHICLE.
Disconnect negative battery cable. Raise vehicle
and remove wheel and tire assembly then remove so-
lenoid(s) as follows: (1) Separate electrical connection to solenoid.
(2) Disconnect air line, see Air Lines and Fittings.
Solenoids have molded square tangs to fit into
stepped notches of the air spring housing. The
notches provide an air relief position and a retaining
position. The retaining position is locked with a re-
taining clip. (3) Remove retaining clip (Fig. 14). (4) Rotate solenoid to first step in housing and al-
low air pressure to vent (Fig. 15).
(5) Rotate solenoid to release slot and remove (Fig.
16).
Fig. 13 Air Dryer Remove/Install
Fig. 14 Remove Retaining Clips
Fig. 15 Release Air Pressure
Fig. 16 Remove Solenoid (Inspect O Ring)
2 - 86 SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS Ä
Page 151 of 2438

BRAKES
CONTENTS
page page
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEMÐBENDIX ANTI-LOCK 10 AC/Y BODY ............. 72
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEMÐBENDIX ANTI-LOCK 6 AA,AG,AJ,AP BODY ....... 113
BRAKE DISC (ROTOR) ................... 53
BRAKE SUPPORT ASSEMBLY ............. 25
FRONT DISC BRAKES ................... 31
GENERAL INFORMATION .................. 1
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM CONTROL VALVES . . . 26
KELSEY HAYES DOUBLE PIN FAMILY CALIPER ............................ 35 KELSEY HAYES DOUBLE PIN NON-FAMILY
CALIPER ............................ 38
MASTER CYLINDER ..................... 66
PARKING BRAKES ...................... 57
POWER BRAKES ....................... 68
REAR DISC BRAKES .................... 45
REAR WHEEL DRUM BRAKES ............ 18
SERVICE ADJUSTMENTS .................. 4
WHEEL BEARINGS ...................... 70
WHEEL CYLINDERS ..................... 23
GENERAL INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references may be made to
a particular vehicle by letter or number designation.
A chart showing the break down of these designa-
tions is included in the Introduction Section at the
front of this service manual. Standard brake equipment consists of:
² Double pin floating caliper disc front brakes.
² Rear automatic adjusting drum brakes.
² Differential valve with a brake warning switch.
² Master cylinder.
² Vacuum power booster.
² Double pin floating caliper rear disc brakes are
available on some models. The Bendix Anti-Lock 10 braking system, uses the
standard power brake system caliper assemblies,
braking discs, pedal assembly, brake lines and hoses.
The unique parts of the Bendix Anti-Lock 10 braking
system consists of the following components. Propor-
tioning valves, wheel speed sensors, tone wheels,
electronic control unit, modulator assembly and hy-
draulic assembly. These components replace the con-
ventional master cylinder and power booster. The
components will be described in detail in the Bendix
Anti-Lock 10 brake section in this group of the ser-
vice manual. The Bendix Anti-Lock 6 braking system, uses the
following standard brake system components. Master
cylinder, power booster, caliper assemblies, braking
discs, pedal assembly, brake lines and hoses. The
unique parts of the Bendix Anti-Lock 6 braking sys-
tem consists of the following components. Modulator
assembly, unique proportioning valves, wheel speed
sensors, tone wheels, and electronic control unit.
These components will be described in detail in the
Bendix Anti-Lock 6 brake section in this group of the
service manual. The front disc brake shoes have semi-metallic lin-
ings. The hydraulic brake system (Fig .123and4)is
diagonally split on both the Non-ABS and ABS brak-
ing system. With the left front and right rear brakes
on one hydraulic system and the right front and left
rear on the other. The Non-ABS and ABS brake system may use dif-
ferent types of brake line fittings and tubing flares.
The Non-ABS brake system uses double wall tubing
flares and fittings at all tubing joint locations. Some
ABS brake systems use both ISO style tubing flares
and double wall tubing flares and corresponding fit-
tings at different joint locations. See (Figs . 2 3 and 4)
for specific joint locations and type of tubing flare. The front disc brakes consist of two different types
of caliper assemblies. A double pin Kelsey-Hayes cal-
iper (family caliper) with a bolt-on adapter attached
to the steering knuckle. Or a double pin Kelsey-
Hayes caliper (non-family caliper) which mounts di-
rectly to rails on the steering knuckle. The non-
family caliper is only used on the AY Body
(Imperials).
CAUTION: Caliper pistons, boots and seals for the
different caliper assemblies used on the front and
rear disc brake assemblies are not interchangeable.
Misusage could result in a complete brake system
failure. Be sure that the parts are replaced with the
correct replacement parts, refer to the parts book
for the type and model year of the vehicle being
worked on.
The master cylinder is anodized, lightweight alu-
minum, with a bore size of 24.0mm, 21.0mm or 7/8
inch.
Ä BRAKES 5 - 1
Page 168 of 2438

REAR WHEEL DRUM BRAKES INDEX
page page
Brake Drum Refacing ..................... 21
Brake Shoe Assemblies ................... 19 Description
............................. 18
Service Procedures ....................... 18
DESCRIPTION
Rear wheel drum brakes (Fig .2&3)aretwoshoe,
internal expanding type with an automatic adjuster
screw assembly that is activated each time the
brakes are applied. The automatic adjuster screw is
located directly below the wheel cylinder as shown in
figure (Fig .2&3).
WARNING: DUST AND DIRT ON BRAKE PARTS
GENERATED DURING THE NORMAL USE AND
WEAR OF MOTOR VEHICLE BRAKE SYSTEMS MAY
CONTAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS. BREATHING EXCES-
SIVE CONCENTRATIONS OF ASBESTOS FIBERS
CAN CAUSE SERIOUS BODILY HARM, SUCH AS
ASBESTOSIS AND CANCER. EXTREME CARE
SHOULD BE EXERCISED WHILE SERVICING
BRAKE ASSEMBLIES OR COMPONENTS. DO NOT CLEAN BRAKE ASSEMBLIES OR COM-
PONENTS WITH COMPRESSED AIR OR BY DRY
BRUSHING; USE A VACUUM CLEANER SPECIFI-
CALLY RECOMMENDED FOR USE WITH ASBES-
TOS FIBERS. IF A SUITABLE VACUUM CLEANER IS
NOT AVAILABLE, CLEANING SHOULD BE DONE
WET USING A WATER DAMPENED CLOTH. DO NOT CREATE DUST BY SANDING, GRINDING,
AND/OR SHAVING BRAKE LININGS OR PADS UN-
LESS SUCH OPERATION IS DONE WHILE USING
PROPERLY EXHAUST VENTILATED EQUIPMENT. DISPOSE OF ALL DUST AND DIRT SUSPECTED
TO CONTAIN ANY ASBESTOS FIBERS IN SEALED
BAGS OR CONTAINERS TO MINIMIZE DUST EXPO-
SURE TO YOURSELF AND OTHERS. FOLLOW ALL RECOMMENDED PRACTICES PRE-
SCRIBED BY THE OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND
HEALTH ADMINISTRATION AND THE ENVIRON-
MENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY. FOR THE HAN-
DLING, PROCESSING, AND DISPOSITION OF DUST
OR DIRT WHICH MAY CONTAIN ASBESTOS FI-
BERS. IT IS RECOMMENDED NOT TO BREATH ANY
TYPE OF BRAKE LINING MATERIAL DUST EVEN
ASBESTOS FREE, DUE TO THE FIBROUS NATURE
OF THE MATERIALS BEING USED.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
REAR BRAKE DRUM REMOVAL
If the rear brake drum is difficult to remove, fur-
ther clearance can be obtained by backing off the
brake automatic adjuster screw. Remove rubber plug
from the top of the support plate and rotate the au-
tomatic adjuster screw assembly with an upward mo-
tion, using the Brake Adjuster, Special Tool C-3784. See adjusting rear service brakes in the Service
Adjustments section in this group of the service man-
ual for the specific adjustment procedure. Remove wheel bearing grease cap (Fig. 1).
Remove cotter pin, nut lock, retaining nut, thrust
washer and outer bearing cone (Fig. 1). Remove brake drum and hub and bearing assembly
from the rear spindle (Fig. 1). Inspect brake linings for wear, shoe alignment and
contamination.
BRAKE DRUM INSTALLATION
Install brake drum and hub and bearing assembly
on rear spindle. Install outer wheel bearing, thrust washer and nut.
Tighten wheel bearing adjusting nut to 27 to 34
N Im (240 to 300 in. lbs.) torque while rotating hub.
This seats the bearings. Back off adjusting nut 1/4 turn (90É) then tighten
adjusting nut finger tight. Position lock on nut with one pair of slots in-line
with cotter pin hole. Install cotter pin.
Fig. 1 Brake Drum and Hub Assembly
5 - 18 BRAKES Ä
Page 176 of 2438

HYDRAULIC SYSTEM CONTROL VALVES INDEX
page page
ABS Brake Proportioning Valve Operation ...... 27
General Information ....................... 26
Hydraulic System Service Procedures ......... 27 Non-ABS Proportioning Unit Operation
........ 26
Pressure Differential Warning Light Switch ...... 26
Testing ABS Proportioning Valves ............ 29
GENERAL INFORMATION
Most models not equipped with an Anti-Lock brak-
ing system have a combination hydraulic system con-
trol valve in the brake hydraulic system (Fig. 1). The
valve is attached to the frame rail below the master
cylinder.
The control valve assembly combines a warning
switch with a dual proportioning valve (Fig. 2) Proportioning valves balance front to rear braking
by controlling at a given ratio, the increase in rear
system hydraulic pressure above a preset level. Un-
der light pedal application, the valve allows full hy-
draulic pressure to the rear brakes. There is only one valve assembly in each vehicle,
see Valve Application Chart. During any service pro-
cedures identify valve assemblies by part number as
well as split point (PSI) and slope.
PRESSURE DIFFERENTIAL WARNING LIGHT
SWITCH
The hydraulic brake system, on non-ABS vehicles,
is split diagonally. The left front and right rear
brakes are part of one system. And the right front and left rear are part of another. Both systems are
routed through, but hydraulically separated by a Pres-
sure Differential Switch. The function of the Pressure
Differential Switch is to alert the driver of a malfunc-
tion in the brake system. If hydraulic pressure is lost in one system, the
warning light switch will activate a red light on the
instrument panel, when the brake pedal is depressed.
At this point the brakes require service. However, since
the brake systems are split diagonally the vehicle will
retain 50% of its stopping capability in the event of a
failure in either half. The warning light switch is the latching type. It
will automatically center itself after the repair is
made and the brake pedal is depressed. The instrument panel bulb can be checked each time
the ignition switch is turned to the start position or the
parking brake is set.
NON-ABS PROPORTIONING UNIT OPERATION
The proportioning valve section operates by trans-
mitting full input pressure to the rear brakes up to a
certain point. This is called the split point. Beyond this
point it reduces the amount of pressure increase to the
rear brakes according to a certain ratio. On light pedal applications equal brake pressure will
be transmitted to the front and rear brakes. On heavier
pedal applications the pressure transmitted
Fig. 1 Brake Combination Valve And Warning Switch Location
Fig. 2 Switch and Valve Assembly
5 - 26 BRAKES Ä
Page 177 of 2438

to the rear will be lower than the front brakes. This will
prevent premature rear wheel lock-up and skid. If
hydraulic pressure is lost in one half of the diagonally
split system, the operation of the proportioning valve
in the remaining half is not effected.
ABS BRAKE PROPORTIONING VALVE OPERATION
On vehicles using the ABS braking system, screw in
proportioning valves are used in place of the conven-
tional differential pressure/proportioning valve. Each rear brake circuit has its own screw-in propor-
tioning valve which is attached to the rear brake outlet
ports of the hydraulic assembly. These valves limit
brake pressure to the rear brakes after a certain
pressure is reached. This improves front to rear brake
balance during normal braking.
Screw in proportioning valves can be identified by
the numbers stamped on the body of the valve. The
first digit represents the slope, the second digit repre-
sents the split (cut-in) point, and the arrow represents
the flow direction of the valve. Be sure that the
numbers listed on the replacement valve are the
same as on the valve that is being removed. See
(Fig. 3) for detail of the valve identification.
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURES
BRAKE WARNING SYSTEM
CHECKING BRAKE WARNING SWITCH UNIT
The Red Brake Warning light will come on when
the parking brake is applied with the ignition key
turned ON. The same light will also illuminate
should one of the two service brake hydraulic sys-
tems fail.
CAUTION:Make sure air does not enter the hydrau-
lic system during this test procedure. See bleeding
without a pressure bleeder at the beginning of this
section for master cylinder fluid level checking pro-
cedures.
To test the service brake warning system lamp.
Raise the vehicle on a hoist and open a wheel cylin-
der bleeder while a helper depresses the brake pedal
and observes the warning light. If the light fails to light, inspect for a burned out
bulb, disconnected socket, or a broken or discon-
nected wire at the switch. If the bulb is not burned
out and the wire continuity is uninterrupted. Check
the service brake warning switch operation with a
test lamp between the switch terminal and a known
good ground. Be sure to fill master cylinder and
bleed brake system after correction has been made, if
necessary.
PROPORTIONING VALVES
TESTING PROPORTIONING VALVE UNIT
If premature rear wheel skid occurs on hard brake
application, it could be an indication that a malfunc-
tion has occurred with the proportioning valve unit. The proportioning valve is designed with two sep-
arate systems. One half controls the right rear
brake, and the other half controls the left rear brake.
Therefore, a road test to determine which rear brake
slides first is essential.
RIGHT REAR WHEEL SLIDES FIRST To test the proportioning valve when the right rear
wheel slides first, leave the front brakes connected to
the valve, proceed as follows: (1) Install one gauge and (TEE) of set C-4007-A
between the brake line from the master cylinder sec-
ondary port and the brake valve assembly. (2) Install the second gauge of set C-4007-A to the
right rear brake outlet port (Fig. 4). Using an
adapter tube, made from a short piece of brake tube
and (2) 3/8 x 24 tube nuts. Connect the hose to the
valve. Bleed the hose and gauge. (3) Have a helper exert pressure on the brake
pedal (holding pressure) to get a reading on the valve
inlet gauge and check the reading on the outlet
Fig. 3 ABS PROPORTIONING VALVE IDENTIFICA- TION
Ä BRAKES 5 - 27
Page 181 of 2438

FRONT DISC BRAKES INDEX
page page
General Information ....................... 31
Service Precautions ....................... 34 Shoe and Lining Wear
.................... 33
GENERAL INFORMATION
The single piston, floating caliper disc brake as-
sembly (Fig. 1 and 2) consists of:
² The driving hub
² Braking disc (rotor)
² Caliper assembly
² Shoes and linings
² Adapter for mounting the caliper assembly to the
steering knuckle WARNING: THE PISTONS THAT ARE USED
IN THE 2 DIFFERENT CALIPER ASSEMBLIES
ARE UNIQUE TO THE CALIPER THEY ARE
USED IN. THE DIMENSIONS OF THESE PIS-
TONS ARE DIFFERENT, DO NOT INTER-
CHANGE THE CALIPER PISTONS.
IMPROPER USE COULD CAUSE A COM-
PLETE FAILURE OF THE BRAKE SYSTEM. The double pin Kelsey-Hayes Family Caliper, is
mounted to the adapter using bushings, sleeves and
2 through bolts threaded into the adapter (Fig. 3 and
5). The adapter is then mounted to the steering
knuckle using 2 attaching bolts. The double pin Kelsey-Hayes Non-Family Caliper,
is mounted directly to the steering knuckle of the ve-
hicle using bushings, sleeves and 2 through bolts (Fig. 4). The adapter is not used on the vehicles
equipped with the Non-Family caliper assembly.
Two machined abutments on the caliper mounting
adapter or steering knuckle, (Fig. 3 and 4) position
the caliper fore and aft. The guide pin bolts, sleeves
and bushings control the float, side to side movement
of the caliper. The piston seal, is designed to pull the
piston back into the bore of the caliper when the
brake pedal is released. This maintains proper brake
shoe to rotor clearance (Fig. 6). Vehicles equipped with Kelsey-Hayes double pin
family calipers, have 1 anti-rattle clip attached to
the top of the adapter (Fig. 1). All of the braking force is taken up directly by the
adapter or the steering knuckle depending on the
type of caliper assembly the vehicle is equipped with. The caliper is a one piece casting with the inboard
side containing a single piston cylinder bore. The front disc brake caliper phenolic piston is 2 dif-
ferent sizes depending on the vehicle that the caliper
assembly is used on. The AC, AG & AY body use a
60 mm piston, and the AA, AP, AG & AJ body use a
54 mm piston.
Fig. 1 Front Disc Brake Assembly (Family Caliper Typical)
Ä BRAKES 5 - 31
Page 184 of 2438

SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
WARNING: DUST AND DIRT ON BRAKE PARTS
GENERATED DURING THE NORMAL USE AND
WEAR OF MOTOR VEHICLE BRAKE SYSTEMS CAN
CONTAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS. BREATHING EXCES-
SIVE CONCENTRATIONS OF ASBESTOS FIBERS
CAN CAUSE SERIOUS BODILY HARM, SUCH AS
ASBESTOSIS AND CANCER. EXTREME CARE
SHOULD BE EXERCISED WHILE SERVICING
BRAKE ASSEMBLIES OR COMPONENTS. DO NOT CLEAN BRAKE ASSEMBLIES OR COM-
PONENTS WITH COMPRESSED AIR OR BY DRY
BRUSHING; USE A VACUUM CLEANER SPECIFI-
CALLY RECOMMENDED FOR USE WITH ASBES-
TOS FIBERS. IF A SUITABLE VACUUM CLEANER IS
NOT AVAILABLE, CLEANING SHOULD BE DONE
WET USING A WATER DAMPENED CLOTH. DO NOT CREATE DUST BY SANDING, GRINDING,
AND/OR SHAVING BRAKE LININGS OR PADS UN-
LESS SUCH OPERATION IS DONE WHILE USING
PROPERLY EXHAUST VENTILATED EQUIPMENT. DISPOSE OF ALL DUST AND DIRT SUSPECTED
TO CONTAIN ANY ASBESTOS FIBERS IN SEALED
BAGS OR CONTAINERS TO MINIMIZE DUST EXPO-
SURE TO YOURSELF AND OTHERS. FOLLOW ALL RECOMMENDED PRACTICES PRE-
SCRIBED BY THE OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND
HEALTH ADMINISTRATION AND THE ENVIRONMEN-
TAL PROTECTION AGENCY. FOR THE HANDLING,
PROCESSING, AND DISPOSITION OF DUST OR DIRT
WHICH MAY CONTAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS. IT IS RECOMMENDED NOT TO BREATH ANY TYPE
OF BRAKE LINING MATERIAL DUST EVEN ASBES-
TOS FREE, DUE TO THE FIBROUS NATURE OF THE
MATERIALS BEING USED.
Grease or any other foreign material must be kept off
caliper assembly, surfaces of braking disc and external
surfaces of hub, during service procedures. Handling of the braking disc and caliper. Should be
done in such a way as to avoid deformation of the disc
and scratching or nicking of the brake linings. If inspection reveals that the square sectioned cali-
per piston seal is worn or damaged, it should be
replaced immediately. During removal and installation of a wheel and tire
assembly, use care not to strike the caliper. Before vehicle is moved after any brake service
work, be sure to obtain a firm brake pedal.
5 - 34 BRAKES Ä