1993 CHEVROLET DYNASTY boot
[x] Cancel search: bootPage 99 of 2438
(8) Insert balls into raceway by tilting cage and in-
ner race assembly (Fig. 7). (9) Fasten boot to shaft. See Boots Install.
(10) On G.K.N. units insert the new circlip, pro-
vided with kit in shaft groove. Do not over expand
or twist circlip during assembly (Fig. 8). The S.S.G.
unit has a reusable circlip retainer that is an inte-
gral part of driver assembly.
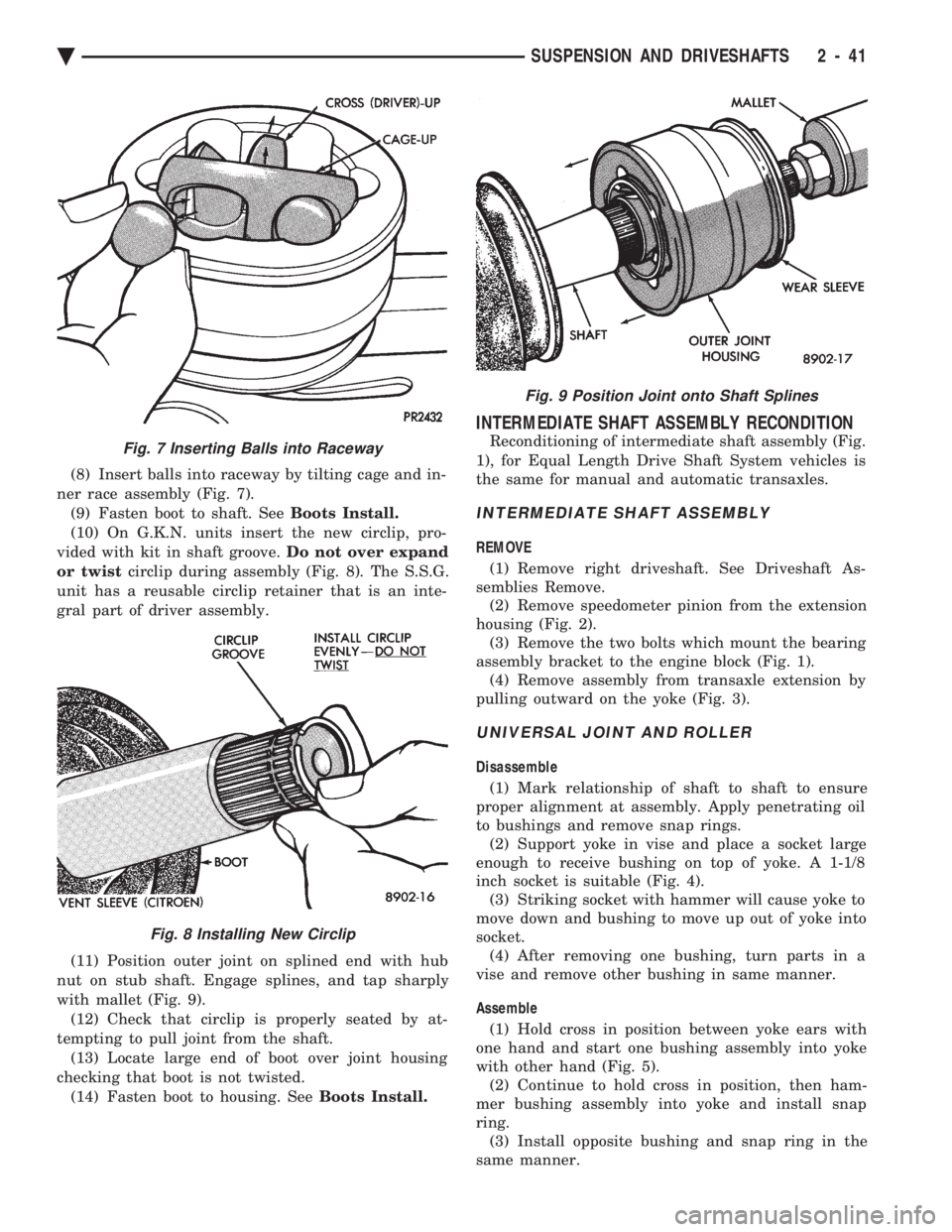
(11) Position outer joint on splined end with hub
nut on stub shaft. Engage splines, and tap sharply
with mallet (Fig. 9). (12) Check that circlip is properly seated by at-
tempting to pull joint from the shaft. (13) Locate large end of boot over joint housing
checking that boot is not twisted. (14) Fasten boot to housing. See Boots Install.
INTERMEDIATE SHAFT ASSEMBLY RECONDITION
Reconditioning of intermediate shaft assembly (Fig.
1), for Equal Length Drive Shaft System vehicles is
the same for manual and automatic transaxles.
INTERMEDIATE SHAFT ASSEMBLY
REMOVE
(1) Remove right driveshaft. See Driveshaft As-
semblies Remove. (2) Remove speedometer pinion from the extension
housing (Fig. 2). (3) Remove the two bolts which mount the bearing
assembly bracket to the engine block (Fig. 1). (4) Remove assembly from transaxle extension by
pulling outward on the yoke (Fig. 3).
UNIVERSAL JOINT AND ROLLER
Disassemble
(1) Mark relationship of shaft to shaft to ensure
proper alignment at assembly. Apply penetrating oil
to bushings and remove snap rings. (2) Support yoke in vise and place a socket large
enough to receive bushing on top of yoke. A 1-1/8
inch socket is suitable (Fig. 4). (3) Striking socket with hammer will cause yoke to
move down and bushing to move up out of yoke into
socket. (4) After removing one bushing, turn parts in a
vise and remove other bushing in same manner.
Assemble (1) Hold cross in position between yoke ears with
one hand and start one bushing assembly into yoke
with other hand (Fig. 5). (2) Continue to hold cross in position, then ham-
mer bushing assembly into yoke and install snap
ring. (3) Install opposite bushing and snap ring in the
same manner.
Fig. 7 Inserting Balls into Raceway
Fig. 8 Installing New Circlip
Fig. 9 Position Joint onto Shaft Splines
Ä SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS 2 - 41
Page 102 of 2438

(3) Swing the bracket into position on the engine and
loosely install the screws through the slotted holes. (4) Push the intermediate shaft assembly into the
transaxle as far as it can travel. Hold the assembly in
this position and tighten the screws (bracket to engine
block) to 54 N Im (40 ft. lbs.) torque. This will ensure
full seal engagement between the journal on the
intermediate shaft and the seal in the transaxle
extension. (5) Distribute a liberal amount of grease in side
spline and pilot bore on bearing end of intermediate
shaft. Use MOPAR Multi-Purpose Lubricant, or
equivalent. (6) Install speedometer pinion (Fig. 9).
(7) Install right driveshaft. See Driveshaft Assem-
blies Install.
C/V JOINT BOOTS Handling and Cleaning
It is vitally important during anyservice procedures
requiring boot handling. That care be taken not to
puncture or tear the boot by over tightening clamps,
misuse of tool(s) or pinching the boot. Pinching can
occur by rotating the C/V joints (especially the tripod)
beyond normal working angles.
The driveshaft boots are not compatible with oil, gaso-
line, or cleaning solvents. Care must be taken that boots
never come in contact with any of these liquids. The only
acceptable cleaning agent for driveshaft boots is
soap and water. After washing, boot must be thor-
oughly rinsed and dried before reusing.
BOOTS INSPECT
Noticeable amounts of grease on areas adjacent to or
on the exterior of the C/V joint boot. Is the first
indication that a boot is punctured, torn or that a
clamp has loosened. When a C/V joint is removed for
servicing of the joint. The boot should be properly
cleaned and inspected for cracks, tears and scuffed
areas on interior surfaces. If any of these conditions
exist, boot replacement is recommended.
BOOTS INSTALL
THE HARD PLASTIC BOOTS REQUIRE APPROXI-
MATELY 100TIMES THE CLAMPING FORCE OF THE
RUBBER BOOT. THE CLAMPS USED ON THE RUB-
BER BOOTS DO NOT HAVE THE TYPE OF LOAD
CAPACITY REQUIRED. TO SEAL THE HARD PLASTIC
BOOTS AND SHOULD NOT BE USED FOR THIS PUR-
POSE.
Rubber boots appear only on the inner joints of
certain driveshafts.
Fig. 9 Install Speedometer PinionFig. 1 C/V Joint Boot Positioning G.K.N.
Fig. 8 Installing Intermediate Shaft Assembly
2 - 44 SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS Ä
Page 103 of 2438

Rubber boots must be serviced with the strap and
buckle clamp. Use the Clamp Installer, Special Tool
C-4653. Proceed with the boot installation as follows: (1) Slide the small end of the boot over the shaft.
Position the boot to the edge of the locating mark or
groove, whichever is appropriate (Fig. 1). (2) Install the C/V joint. See Inner or Outer C/V
Joint Assemble. (3) Slide the large diameter of the boot into the lo-
cating groove (Fig. 6). (4) Wrap binding strap around boot twice, PLUS
63 mm (2-1/2 inches) (Fig. 2).
(5) Pass the strap through the buckle and fold it
back about 29 mm (1-1/8 inches) on the inside of the
buckle (Fig. 3).
(6) Put the strap around the boot with the eye of
the buckle toward you (Fig. 4). Wrap the strip
around the boot once and pass it through the buckle,
then wrap it around a second time also passing it
through the buckle. (7) Fold the strip back slightly to prevent it from
slipping backwards (Fig. 5). (8) Open the tool all the way and place strip in
narrow slot approximately 13 mm (1/2 inch) from
buckle (Fig. 6).
Fig. 2 Measure & Cut Binding Strap
Fig. 3 Install Buckle on Strap
Fig. 4 Wrap Strap (through Buckle Eye) Twice
Fig. 5 Fold Strap Lightly to Keep Position
Fig. 6 Open Tool, Position Strap in Narrow Slot 1/2 Inch from Buckle
Ä SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS 2 - 45
Page 105 of 2438
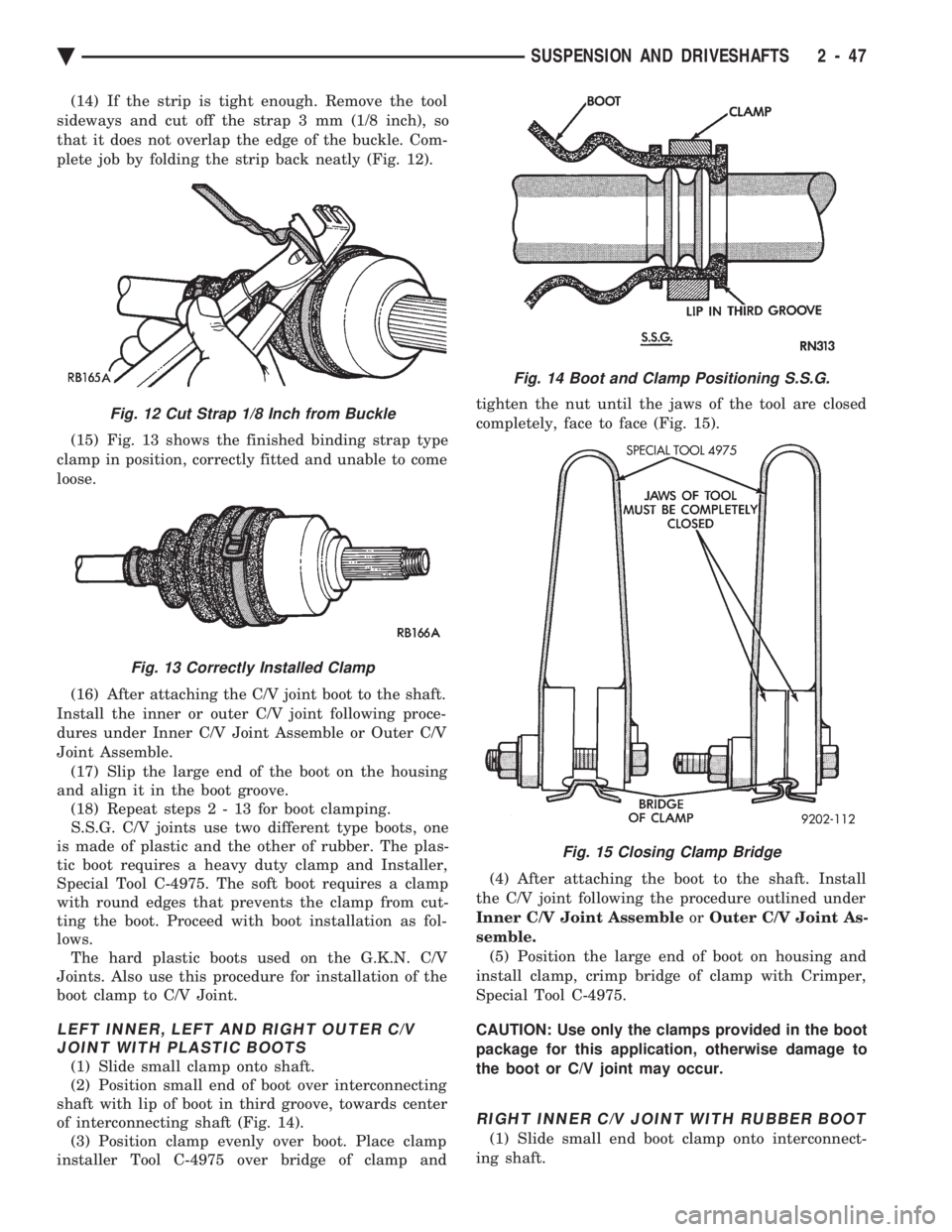
(14) If the strip is tight enough. Remove the tool
sideways and cut off the strap 3 mm (1/8 inch), so
that it does not overlap the edge of the buckle. Com-
plete job by folding the strip back neatly (Fig. 12).
(15) Fig. 13 shows the finished binding strap type
clamp in position, correctly fitted and unable to come
loose.
(16) After attaching the C/V joint boot to the shaft.
Install the inner or outer C/V joint following proce-
dures under Inner C/V Joint Assemble or Outer C/V
Joint Assemble. (17) Slip the large end of the boot on the housing
and align it in the boot groove. (18) Repeat step s2-13forboot clamping.
S.S.G. C/V joints use two different type boots, one
is made of plastic and the other of rubber. The plas-
tic boot requires a heavy duty clamp and Installer,
Special Tool C-4975. The soft boot requires a clamp
with round edges that prevents the clamp from cut-
ting the boot. Proceed with boot installation as fol-
lows. The hard plastic boots used on the G.K.N. C/V
Joints. Also use this procedure for installation of the
boot clamp to C/V Joint.
LEFT INNER, LEFT AND RIGHT OUTER C/V JOINT WITH PLASTIC BOOTS
(1) Slide small clamp onto shaft.
(2) Position small end of boot over interconnecting
shaft with lip of boot in third groove, towards center
of interconnecting shaft (Fig. 14). (3) Position clamp evenly over boot. Place clamp
installer Tool C-4975 over bridge of clamp and tighten the nut until the jaws of the tool are closed
completely, face to face (Fig. 15).
(4) After attaching the boot to the shaft. Install
the C/V joint following the procedure outlined under
Inner C/V Joint Assemble orOuter C/V Joint As-
semble. (5) Position the large end of boot on housing and
install clamp, crimp bridge of clamp with Crimper,
Special Tool C-4975.
CAUTION: Use only the clamps provided in the boot
package for this application, otherwise damage to
the boot or C/V joint may occur.
RIGHT INNER C/V JOINT WITH RUBBER BOOT
(1) Slide small end boot clamp onto interconnect-
ing shaft.
Fig. 12 Cut Strap 1/8 Inch from Buckle
Fig. 13 Correctly Installed Clamp
Fig. 14 Boot and Clamp Positioning S.S.G.
Fig. 15 Closing Clamp Bridge
Ä SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS 2 - 47
Page 106 of 2438

(2) Install boot onto interconnecting shaft, position
boot on the flat between the locating shoulders (Fig. 16).
(3) Position clamp on boot and crimp bridge of
clamp with Crimper Special Tool C-4124.
(4) Install the C/V Joint following the procedure
outlined under Inner C/V Joint Assemble .
(5) Position the large end of boot on housing and
install clamp, crimp bridge of clamp with Crimper,
Special Tool C-4124.
CAUTION: During any service procedures where
knuckle and driveshaft are separated, thoroughly
clean seal and wear sleeve with suitable solvent
and lubricate BOTH components at assembly. Do
not allow solvent to contact boot.
Lubricate wear sleeve (and seal) with Mopar Multi-
Purpose Lubricant, or equivalent, as follows: Wear Sleeve: Apply a full circumference 6 mm
(1/4 inch) bead of lubricant to seal contact area. See
(Fig. 11), Driveshaft Assemblies Install. Seal: Fill lip to housing cavity (full circumference)
and wet seal lip with lubricant.
S.S.G INNER C/V JOINT LARGE CLAMP (MANUAL TRANS ONLY)
(1) Install small clamp and inner C/V joint housing
according to the procedures outlined in this manual. (2) Position the boot over the outer C/V joint.
(3) Slide the large band clamp over the boot and
position it evenly in the groove on the inner C/V
joint boot. (Fig. 17). (4) Use Clamp Locking Tool Snap-On YA3050 or
equivalent shown in (Fig. 18) to install the clamp on
the boot. (5) Place the prongs of the clamp locking tool in
the holes on the clamp and squeeze together until
the two ends meet (Fig. 18).
DAMPER WEIGHTS
Damper weights are used on the left driveshaft as-
semblies of all front wheel drive vehicles (Fig. 19).
These weights are attached to the interconnecting
shaft and are available as a separate service part. They should be removed from the driveshaft assem-
bly during driveshaft positioning specification proce-
dures. When the weights are attached between the
locating shoulders, tighten the fasteners to the fol-
lowing specifications:
² S.S.G. Ð 28 N Im (21 ft. lbs.)
² G.K.N. Ð 30 N Im (23 ft. lbs.)DRIVESHAFT POSITIONING SPECIFICATIONS
Front wheel drive vehicles have engine mounts with
slotted holes allowing for side to side positioning of the
engine. If the vertical bolts on right or left upper engine
Fig. 16 Right Inner C/V Joint S.S.G.
Fig. 17 Boot Clamp Installed
Fig. 18 Locking Boot Clamp
2 - 48 SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS Ä
Page 107 of 2438

mount have been loosened for any reason, or if vehicle
has experienced front structural damage, driveshaft
lengths must be checked and corrected, if required. A
shorter than required driveshaft length can result in ob-
jectionable noise. A longer than required driveshaft
length may result in potential damage.
Use of the following procedure will ensure satisfac-
tory driveshaft engagement under all normal vehicle
operating conditions. (1) The vehicle must be completely assembled.
Front wheels must be properly aligned and in the
straight ahead position. The vehicle must be in a po-
sition so that the full weight of the body is distrib-
uted to all four tires. A platform hoist, or front end
alignment rack, is recommended.
(2) Using a tape measure or other suitable measuring
device. Measure the direct distance from the inner edge of the outboard boot to the inner edge of the inboard
boot on both driveshafts. This measurement must be
taken at the bottom (six o'clock position) of the drive-
shafts (Fig. 1).
Note that the required dimension varies with car-line,
engine, transaxle, and driveshaft manufacturer (Fig. 2).
(3) If the lengths of both shafts are within the
range specified, no further action is required. If either left or right driveshaft length is not
within the specified range. Refer to Group 09, Engine
Removal and Installation to properly position engine
according to specified driveshaft lengths.
(4) If proper driveshaft lengths cannot be achieved
within the travel limits available in the slotted engine
mounts. Check for any condition that could effect the
side to side position of the measurement locations (e.g.,
engine support brackets, siderail alignment, etc.).
(5) After ensuring proper driveshaft lengths the
transmission shift linkage must be adjusted to en-
sure proper operation. Refer to Transaxle, Group 21.
Fig. 2 Driveshaft Identification and Dimensions
Fig. 19 Left Driveshaft with Damper Weight
Fig. 1 Driveshaft Positioning
Ä SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS 2 - 49
Page 151 of 2438

BRAKES
CONTENTS
page page
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEMÐBENDIX ANTI-LOCK 10 AC/Y BODY ............. 72
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEMÐBENDIX ANTI-LOCK 6 AA,AG,AJ,AP BODY ....... 113
BRAKE DISC (ROTOR) ................... 53
BRAKE SUPPORT ASSEMBLY ............. 25
FRONT DISC BRAKES ................... 31
GENERAL INFORMATION .................. 1
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM CONTROL VALVES . . . 26
KELSEY HAYES DOUBLE PIN FAMILY CALIPER ............................ 35 KELSEY HAYES DOUBLE PIN NON-FAMILY
CALIPER ............................ 38
MASTER CYLINDER ..................... 66
PARKING BRAKES ...................... 57
POWER BRAKES ....................... 68
REAR DISC BRAKES .................... 45
REAR WHEEL DRUM BRAKES ............ 18
SERVICE ADJUSTMENTS .................. 4
WHEEL BEARINGS ...................... 70
WHEEL CYLINDERS ..................... 23
GENERAL INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references may be made to
a particular vehicle by letter or number designation.
A chart showing the break down of these designa-
tions is included in the Introduction Section at the
front of this service manual. Standard brake equipment consists of:
² Double pin floating caliper disc front brakes.
² Rear automatic adjusting drum brakes.
² Differential valve with a brake warning switch.
² Master cylinder.
² Vacuum power booster.
² Double pin floating caliper rear disc brakes are
available on some models. The Bendix Anti-Lock 10 braking system, uses the
standard power brake system caliper assemblies,
braking discs, pedal assembly, brake lines and hoses.
The unique parts of the Bendix Anti-Lock 10 braking
system consists of the following components. Propor-
tioning valves, wheel speed sensors, tone wheels,
electronic control unit, modulator assembly and hy-
draulic assembly. These components replace the con-
ventional master cylinder and power booster. The
components will be described in detail in the Bendix
Anti-Lock 10 brake section in this group of the ser-
vice manual. The Bendix Anti-Lock 6 braking system, uses the
following standard brake system components. Master
cylinder, power booster, caliper assemblies, braking
discs, pedal assembly, brake lines and hoses. The
unique parts of the Bendix Anti-Lock 6 braking sys-
tem consists of the following components. Modulator
assembly, unique proportioning valves, wheel speed
sensors, tone wheels, and electronic control unit.
These components will be described in detail in the
Bendix Anti-Lock 6 brake section in this group of the
service manual. The front disc brake shoes have semi-metallic lin-
ings. The hydraulic brake system (Fig .123and4)is
diagonally split on both the Non-ABS and ABS brak-
ing system. With the left front and right rear brakes
on one hydraulic system and the right front and left
rear on the other. The Non-ABS and ABS brake system may use dif-
ferent types of brake line fittings and tubing flares.
The Non-ABS brake system uses double wall tubing
flares and fittings at all tubing joint locations. Some
ABS brake systems use both ISO style tubing flares
and double wall tubing flares and corresponding fit-
tings at different joint locations. See (Figs . 2 3 and 4)
for specific joint locations and type of tubing flare. The front disc brakes consist of two different types
of caliper assemblies. A double pin Kelsey-Hayes cal-
iper (family caliper) with a bolt-on adapter attached
to the steering knuckle. Or a double pin Kelsey-
Hayes caliper (non-family caliper) which mounts di-
rectly to rails on the steering knuckle. The non-
family caliper is only used on the AY Body
(Imperials).
CAUTION: Caliper pistons, boots and seals for the
different caliper assemblies used on the front and
rear disc brake assemblies are not interchangeable.
Misusage could result in a complete brake system
failure. Be sure that the parts are replaced with the
correct replacement parts, refer to the parts book
for the type and model year of the vehicle being
worked on.
The master cylinder is anodized, lightweight alu-
minum, with a bore size of 24.0mm, 21.0mm or 7/8
inch.
Ä BRAKES 5 - 1
Page 169 of 2438
Install grease cap and wheel and tire assemblies.
Tighten wheel stud nuts to 115 N Im (85 ft. lbs.)
torque on all models. Install wheel covers.
BRAKE SHOE ASSEMBLIES
Three brake shoe assemblies are used on the front
wheel drive passenger cars. Vehicles will have axle
sets of either 200 or 220 mm Kelsey Hayes (Fig. 2),
or Varga (Fig. 3). Varga brake shoes are HANDED
for right or left side. Except for brake shoe to support plate, park brake
lever retention and automatic adjuster positioning
guide buttons, service procedures for either assembly
are essentially the same.REMOVAL
Remove automatic adjuster spring and lever (Fig.
4).
Rotate the automatic adjuster screw assembly so
that each shoe assembly moves out far enough to be
free from the wheel cylinder boots (Fig. 5).
Disconnect the parking brake cable from the park-
ing brake lever (Fig. 6).
Fig. 2 Kelsey Hayes 200 And 220 (Left) Rear Wheel Brake
Fig. 3 Varga (Left) Rear Wheel Brake
Fig. 4 Remove or Install Adjuster Lever Spring
Fig. 5 Expand or Retract Adjuster Screw
Ä BRAKES 5 - 19