1993 CHEVROLET DYNASTY service
[x] Cancel search: servicePage 352 of 2438
SERVICE PROCEDURES INDEX
page page
Automatic Transmission Oil Coolers .......... 23
Coolant ................................ 14
Coolant Recovery System (CRS) ............. 17
Cooling System Drain, Clean, Flush and Refill . . 15
Electric Fan Motor ........................ 22
Engine Thermostats ....................... 13
Fan Shroud ............................. 23 Fans
.................................. 21
Radiator Hoses .......................... 21
Radiator Pressure Cap .................... 18
Radiators ............................... 18
Testing System for Leaks .................. 17
Water Pumps ........................... 10
WATER PUMPS
A quick test to tell whether or not the pump is
working is to see if the heater warms properly. A
defective pump will not be able to circulate heated
coolant through the long heater hose. The water pump on all models can be replaced
without discharging the air conditioning system.
WATER PUMPÐ2.2/2.5L ENGINE
The 2.2/2.5L engine water pump has a diecast alu-
minum body and housing with a stamped steel impel-
ler. The 2.2/2.5L pump uses an O-ring gasket between
body and housing. The assembly bolts directly to the
block. Cylinder block to water pump sealing is provided
by a rubber O-ring.
REMOVAL (1) Drain cooling system. Refer to Draining Cooling
System in this group. (2) If equipped with air conditioning, see Solid
Mount Accessory Bracket in (Standard Service Proce-
dures) Group 9, Engine: (a) Remove air conditioning compressor and gen-
erator from solid mount bracket and set aside.It is
not necessary to discharge the a/c system. (b) Remove solid mount bracket.
(3) If the vehicle is not equipped with air condi-
tioning, remove generator and mounting bracket. (4) Disconnect lower radiator and heater hoses
from pump. (5) Remove water pump attaching screws to engine
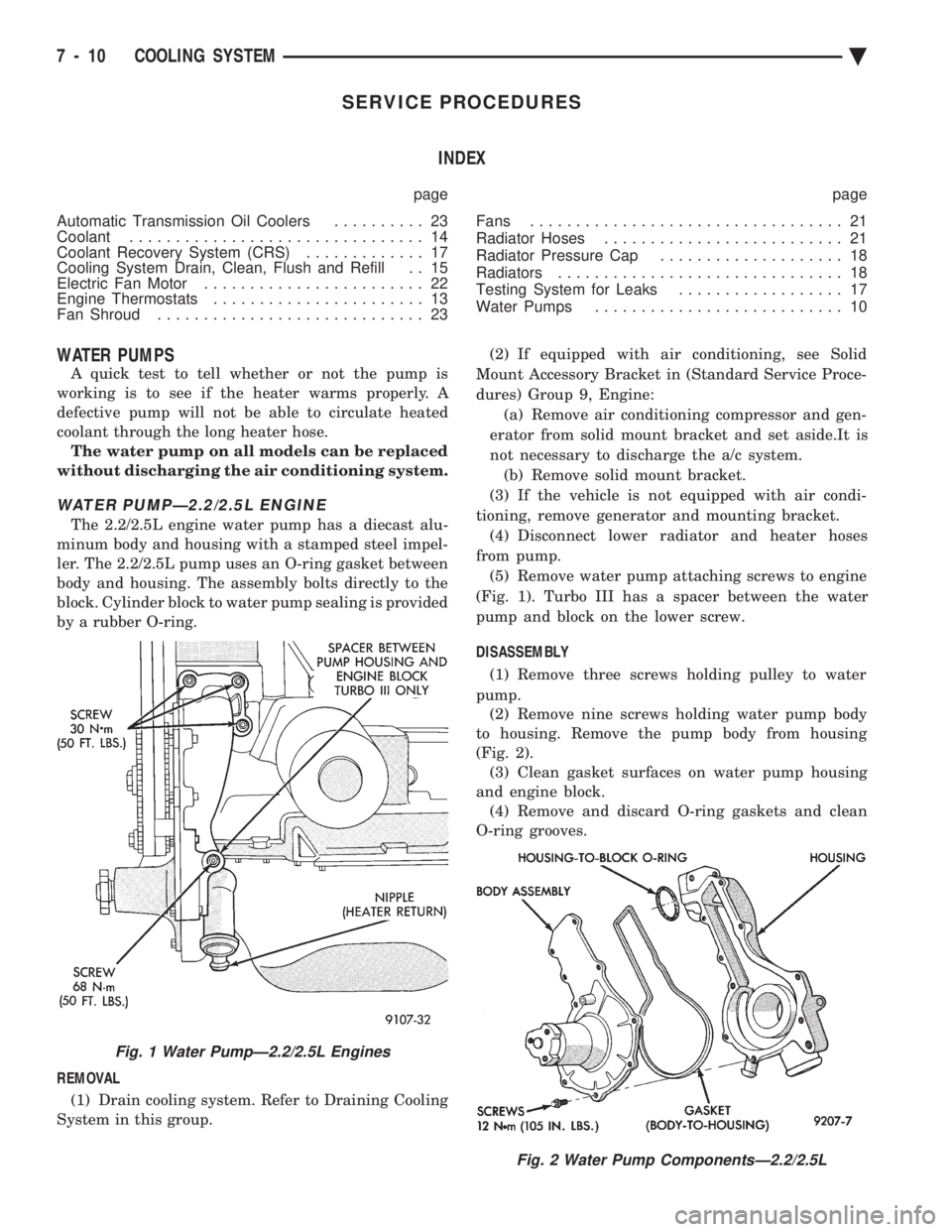
(Fig. 1). Turbo III has a spacer between the water
pump and block on the lower screw.
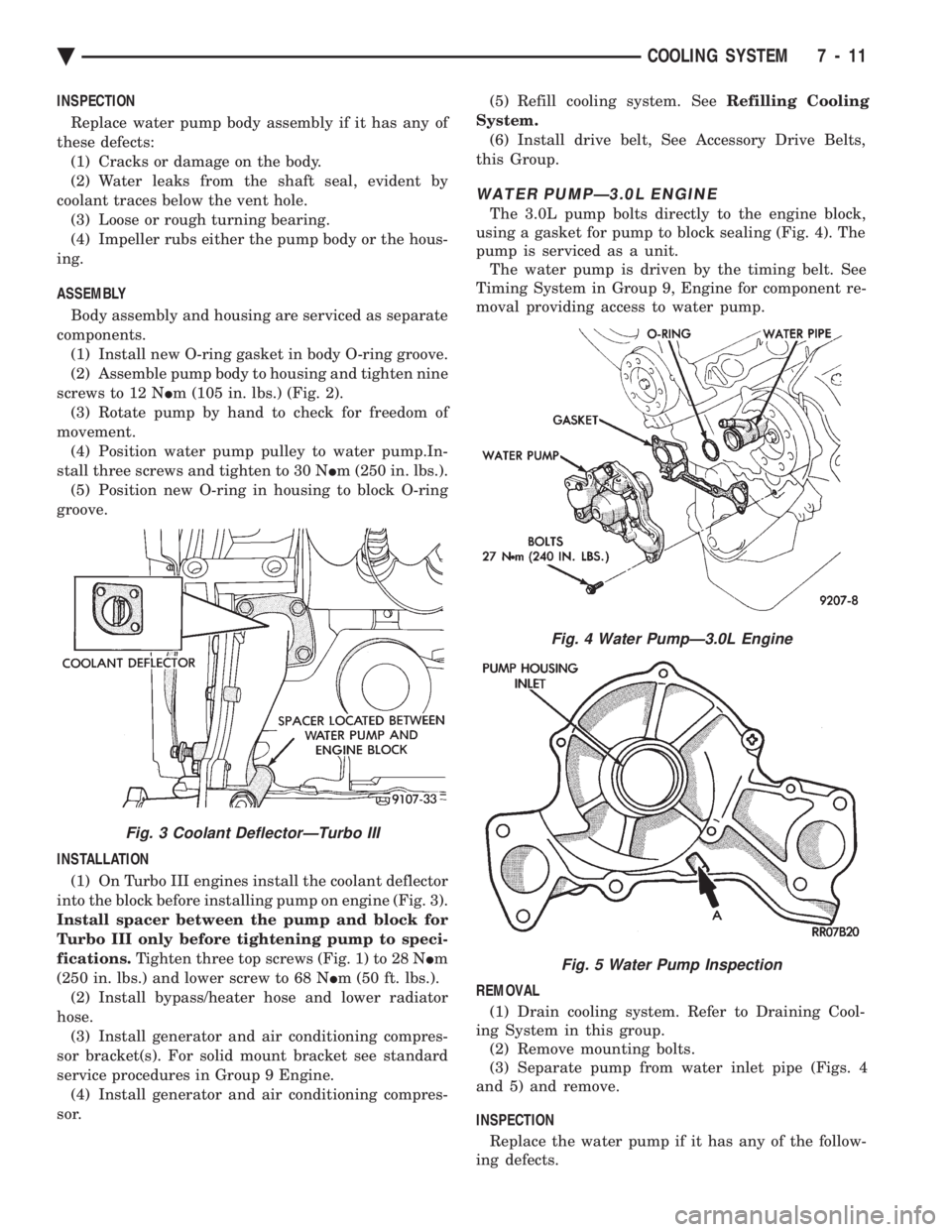
DISASSEMBLY (1) Remove three screws holding pulley to water
pump. (2) Remove nine screws holding water pump body
to housing. Remove the pump body from housing
(Fig. 2). (3) Clean gasket surfaces on water pump housing
and engine block. (4) Remove and discard O-ring gaskets and clean
O-ring grooves.
Fig. 2 Water Pump ComponentsÐ2.2/2.5L
Fig. 1 Water PumpÐ2.2/2.5L Engines
7 - 10 COOLING SYSTEM Ä
Page 353 of 2438
INSPECTION Replace water pump body assembly if it has any of
these defects: (1) Cracks or damage on the body.
(2) Water leaks from the shaft seal, evident by
coolant traces below the vent hole. (3) Loose or rough turning bearing.
(4) Impeller rubs either the pump body or the hous-
ing.
ASSEMBLY
Body assembly and housing are serviced as separate
components. (1) Install new O-ring gasket in body O-ring groove.
(2) Assemble pump body to housing and tighten nine
screws to 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.) (Fig. 2).
(3) Rotate pump by hand to check for freedom of
movement. (4) Position water pump pulley to water pump.In-
stall three screws and tighten to 30 N Im (250 in. lbs.).
(5) Position new O-ring in housing to block O-ring
groove.
INSTALLATION (1) On Turbo III engines install the coolant deflector
into the block before installing pump on engine (Fig. 3).
Install spacer between the pump and block for
Turbo III only before tightening pump to speci-
fications. Tighten three top screws (Fig. 1) to 28 N Im
(250 in. lbs.) and lower screw to 68 N Im (50 ft. lbs.).
(2) Install bypass/heater hose and lower radiator
hose. (3) Install generator and air conditioning compres-
sor bracket(s). For solid mount bracket see standard
service procedures in Group 9 Engine. (4) Install generator and air conditioning compres-
sor. (5) Refill cooling system. See
Refilling Cooling
System. (6) Install drive belt, See Accessory Drive Belts,
this Group.
WATER PUMPÐ3.0L ENGINE
The 3.0L pump bolts directly to the engine block,
using a gasket for pump to block sealing (Fig. 4). The
pump is serviced as a unit. The water pump is driven by the timing belt. See
Timing System in Group 9, Engine for component re-
moval providing access to water pump.
REMOVAL (1) Drain cooling system. Refer to Draining Cool-
ing System in this group. (2) Remove mounting bolts.
(3) Separate pump from water inlet pipe (Figs. 4
and 5) and remove.
INSPECTION Replace the water pump if it has any of the follow-
ing defects.
Fig. 4 Water PumpÐ3.0L Engine
Fig. 5 Water Pump Inspection
Fig. 3 Coolant DeflectorÐTurbo III
Ä COOLING SYSTEM 7 - 11
Page 357 of 2438

-37ÉC (-35ÉF) to -59ÉC (-50ÉF). If it looses color or
becomes contaminated, drain, flush, and replace with
fresh properly mixed solution.
SERVICE
Coolant should be changed at 52,500 miles or three
years, whichever occurs first, then every two years or
30,000 miles.
ROUTINE LEVEL CHECK
Do not remove radiator cap for routine coolant
level inspections. The coolant reserve system provides a quick visual
method for determining the coolant level without re-
moving the radiator cap. Simply observe, with the
engine idling and warmed up to normal operating
temperature, that the level of the coolant in the reserve
tank (Figs. 5 and 6) is between the minimum and
maximum marks.
ADDING ADDITIONAL COOLANT
The radiator cap should not be removed. When
additional coolant is needed to maintain this level, it
should be added to the coolant reserve tank. Use only
50/50 concentration of ethylene glycol type antifreeze
and water.
SERVICE COOLANT LEVEL
The cooling system is closed and designed to main-
tain coolant level to the top of the radiator. When servicing requires a coolant level check in the
radiator, the engine must be offand notunder pres-
sure. Drain several ounces of coolant from the radiator
drain cock while observing the Coolant Recovery Sys-
tem (CRS) Tank. Coolant level in the CRS tank should
drop slightly. Then remove the radiator cap. The radia-
tor should be full to the top. If not, and the coolant level
in the CRS tank is at the MIN mark there is a air leak
in the CRS system. Check hose or hose connections to
the CRS tank, radiator filler neck or the pressure cap
seal to the radiator filler neck for leaks.
LOW COOLANT LEVEL AERATION
Low coolant level in a cross flow radiator will equal-
ize in both tanks with engine off. With engine at
running operating temperature the high pressure inlet
tank runs full and the low pressure outlet tank drops.
If this level drops below the top of the transmission oil
cooler, air will be sucked into the water pump:
² Transmission oil will become hotter.
² High reading shown on the temperature gauge.
² Air in the coolant will also cause loss of flow through
the heater.
² Exhaust gas leaks into the coolant can also cause the
same problems.
DEAERATION
Air can only be removed from the system by gather-
ing under the pressure cap. On the next heat up it will
be pushed past the pressure cap into the CRS tank by
thermal expansion of the coolant. It then escapes to the
atmosphere in the CRS tank and is replaced with solid
coolant on cool down.
COOLING SYSTEM DRAIN, CLEAN, FLUSH AND
REFILL
Drain, flush, and fill the cooling system at the
mileage or time intervals specified in the Maintenance
Schedule in this Group. If the solution is dirty or rusty
or contains a considerable amount of sediment, clean
and flush with a reliable cooling system cleaner. Care
should be taken in disposing of the used engine coolant
from your vehicle. Check governmental regulations for
disposal of used engine coolant.
DRAINING
To drain cooling system move temperature selector
for heater to full heat with engine running (to provide
vacuum for actuation). Without removing radiator
pressure cap and with system not under pres-
sure, Shut engine off and open draincock. The coolant
reserve tank (Fig. 5) should empty first, then remove
radiator pressure cap. (if not, see Testing Cooling
System for leaks). To vent 2.2/2.5L engines remove the
plug above thermostat housing (Fig. 1). For Turbo III
engines remove coolant temperature sensor in the
thermostat housing (Fig. 2). For 3.3L /3.8L engine
remove the engine temperature sending unit (Fig. 3).
Removal of a plug or other component is required
because the thermostat has no air vent and prevents
air flow through it. This allows the coolant to drain
from the engine block.
Fig. 1 Thermostat Housing Drain/Fill PlugÐ2.2/2.5L Engines
Ä COOLING SYSTEM 7 - 15
Page 359 of 2438

TESTING SYSTEM FOR LEAKS
With engine not running, wipe the radiator filler
neck sealing seat clean. The radiator should be full. Attach a radiator pressure tester to the radiator, as
shown in (Fig. 4) and apply 104 kPa (15 psi) pres-
sure. If the pressure drops more than 2 psi in 2 min-
utes inspect all points for external leaks. All hoses, radiator and heater, should be moved
while at 15 psi since some leaks occur while driving
due to engine rock, etc.
If there are no external leaks after the gauge dial
shows a drop in pressure, detach the tester. Start en-
gine and run the engine to normal operating temper-
ature in order to open the thermostat and allow the
coolant to expand. Re-attach the tester. If the needle
on the dial fluctuates it indicates a combustion leak,
usually a head gasket leak.
WARNING: WITH TOOL IN PLACE PRESSURE
BUILDS UP FAST. ANY EXCESSIVE AMOUNT OF
PRESSURE BUILT UP BY CONTINUOUS ENGINE
OPERATION MUST BE RELEASED TO A SAFE
PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRESSURE TO
EXCEED 138 KPA (20 PSI).
If the needle on the dial does not fluctuate, race
the engine a few times. If an abnormal amount of
coolant or steam is emitted from the tail pipe, it may
indicate a faulty head gasket, cracked engine block
or cylinder head. There may be internal leaks which can be deter-
mined by removing the oil dip-stick. If water glob-
ules appear intermixed with the oil it will indicate a internal leak in the engine. If there is an internal
leak, the engine must be disassembled for repair.
COOLANT RECOVERY SYSTEM (CRS)
This system works in conjunction with the radiator
pressure cap to utilize thermal expansion and con-
traction of the coolant to keep the coolant free of
trapped air. It provides a volume for expansion and
contraction, provides a convenient and safe method
for checking coolant level and adjusting level at at-
mospheric pressure without removing the radiator
pressure cap. It also provides some reserve coolant to
cover minor leaks and evaporation or boiling losses.
All vehicles are equipped with this system (Figs. 5
and 6).
See Coolant Level Check Service, Deaeration and
Pressure Cap sections for operation and service. Ve-
hicles equipped with the electric monitor system use
a level sensor in the CRS tank, see Group 8E Elec-
trical for service.
Fig. 4 Pressure Testing Cooling System
Fig. 5 Coolant Recovery System Typical
Fig. 6 Coolant Recovery SystemÐAC-AY Models
Ä COOLING SYSTEM 7 - 17
Page 360 of 2438

RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP
Radiators are equipped with a pressure cap which
releases pressure at some point within a range of
97-124 kPa (14-18 psi) (Fig. 7). The system will operate at higher than atmospheric
pressure which raises the coolant boiling point allow-
ing increased radiator cooling capacity. There is also a vent valve in the center of the cap that
allows a small coolant flow to the CRS tank. If valve is
stuck shut, the radiator hoses will be collapsed
on cool down. Clean the vent valve (Fig. 7) to
ensure proper sealing when boiling point is
reached.
There is also a gasket in the cap to seal to the top of
the filler neck so that vacuum can be maintained for
drawing coolant back into the radiator from the coolant
reserve system tank.
RADIATOR CAP TO FILLER NECK SEAL PRES- SURE RELIEF CHECK
The pressure cap upper gasket (seal) pressure relief
can be checked by removing the overflow hose at the
radiator filler neck nipple (Fig. 7). Attach the Radiator
Pressure Tool to the filler neck nipple and pump air
into the radiator. Pressure cap upper gasket should
relieve at 69-124 kPa (10-18 psi) and hold pressure at
55 kPa (8 psi) minimum.
WARNING: THE WARNING WORDS DO NOT OPEN
HOT ON THE RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP IS A
SAFETY PRECAUTION. WHEN HOT, PRESSURE
BUILDS UP IN COOLING SYSTEM. TO PREVENT
SCALDING OR INJURY, THE RADIATOR CAP
SHOULD NOT BE REMOVED WHILE THE SYSTEM IS
HOT AND/OR UNDER PRESSURE.
There is no need to remove the radiator cap at any
time except for the following purposes:
(1) Check and adjust antifreeze freeze point.
(2) Refill system with new antifreeze.
(3) Conducting service procedures.
(4) Checking for vacuum leaks.
WARNING: IF VEHICLE HAS BEEN RUN RECENTLY,
WAIT 15 MINUTES BEFORE REMOVING CAP. THEN PLACE A SHOP TOWEL OVER THE CAP AND WITH-
OUT PUSHING DOWN ROTATE IT COUNTER-
CLOCKWISE TO THE FIRST STOP. ALLOW FLUIDS
TO ESCAPE THROUGH THE OVERFLOW TUBE AND
WHEN THE SYSTEM STOPS PUSHING COOLANT
AND STEAM INTO THE CRS TANK AND PRESSURE
DROPS PUSH DOWN AND REMOVE THE CAP COM-
PLETELY. SQUEEZING THE RADIATOR INLET HOSE
WITH A SHOP TOWEL (TO CHECK PRESSURE) BE-
FORE AND AFTER TURNING TO THE FIRST STOP IS
RECOMMENDED.
PRESSURE TESTING RADIATOR CAPS
Dip the pressure cap in water, clean any deposits off
the vent valve or its seat and apply cap to end of
Radiator Pressure Tool. Working the plunger, bring the
pressure to 104 kPa (15 psi) on the gauge. If the
pressure cap fails to hold pressure of at least 97 kPa
(14 psi) replace cap. See CAUTION
If the pressure cap tests properly while positioned on
Radiator Pressure Tool, but will not hold pressure or
vacuum when positioned on the radiator. Inspect the
radiator filler neck and cap top gasket for irregularities
that may prevent the cap from sealing properly.
CAUTION: Radiator Pressure Tool is very sensitive to
small air leaks which will not cause cooling system
problems. A pressure cap that does not have a
history of coolant loss should not be replaced just
because it leaks slowly when tested with this tool.
Add water to the tool. Turn tool upside down and
recheck pressure cap to confirm that cap is bad.
INSPECTION
Hold the cap in hand, right side up(Fig. 7). The
vent valve at the bottom of the cap should open. If the
rubber gasket has swollen and prevents the valve from
opening, replace the cap. Hold the cleaned cap in hand upside down.If any
light can be seen between vent valve and rubber
gasket, replace cap. Do not use a replacement cap
that has a spring to hold the vent shut. Replacement cap must be of the type designed for
coolant reserve systems. This design assures coolant
return to radiator.
RADIATORS
The radiators are crossflow types (horizontal tubes)
with design features that provide greater strength as
well as sufficient heat transfer capabilities to keep the
engine satisfactorily cooled.
CAUTION: Plastic tanks, while stronger then brass
are subject to damage by impact, such as wrenches.
Fig. 7 Radiator Pressure Cap Filler Neck
7 - 18 COOLING SYSTEM Ä
Page 361 of 2438

RADIATOR DRAINCOCK SERVICE
REMOVAL (1) Turn the drain cock stem counterclockwise to
unscrew the stem. When the stem is unscrewed to
the end of the threads, pull the stem (Fig. 10) from
the radiator tank.
INSTALLATION (1) Push the draincock assembly body into the
tank opening until it snaps into place. (2) Tighten the draincock stem by turning clock-
wise to 2.0-2.7 N Im (18-25 in. lbs.) torque.
RADIATOR COOLANT FLOW CHECK
To determine whether coolant is flowing through
the cooling system, use the following procedure: (1) If engine is cold, idle engine until normal oper-
ating temperature is reached. Then feel the upper ra-
diator hose. If it is hot, coolant is circulating.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE RADIATOR PRES-
SURE CAP WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM
COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
Fig. 9 Cooling ModuleÐTypical
Fig. 8 Pressure Testing Radiator Cap
Fig. 10 Draincock AssemblyÐTypical
Ä COOLING SYSTEM 7 - 19
Page 373 of 2438

BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS
CONTENTS
page page
BATTERY TEST PROCEDURES ON-VEHICLE . . 3
FAULT CODESÐON BOARD DIAGNOSTICS . . 23
GENERAL INFORMATION .................. 1
GENERATOR TEST PROCEDURES ON VEHICLE.19 IGNITION OFF DRAW (IOD)
............... 9
SPECIFICATIONS ....................... 28
STARTER TEST PROCEDURES ON VEHICLE . 11
GENERAL INFORMATION
² For Battery, Starter or Generator replacement re-
fer to Group 8B, Battery/Starter/Generator Service.
This Group 8A will cover diagnostics only. The Battery, Starting, and Charging Systems oper-
ate with one another, and must be thoroughly tested
as a complete system. To enable the vehicle to start
and charge properly, it must have a battery that will
perform to specifications. The starter motor, genera-
tor, wiring, and electronics also must perform within
specifications. Group 8A will cover Starting (Fig. 1)
and Charging System (Fig. 2) diagnostic procedures.
These will be covered from the most basic conven-
tional methods to On Board Diagnostics (OBD) built
into the vehicle's electronics. The need for conven-
tional testing equipment has not been eliminated by
the introduction of OBD. Frequent use of an amme-
ter, volt/ohmmeter, battery charger, carbon pile rheo-
stat (load tester), and 12 volt (low wattage) test light
will be required. All front wheel drive vehicles are equipped with
OBD and all OBD sensing systems are monitored by
the Powertrain Control Module. The Powertrain Con-
trol module will store in electronic memory, any de-
tectable failure within the monitored circuits. It will
retain this information for a period of 50 engine
starts, then erase the memory if the failure does not
reoccur during that period. This also will translate a
monitored failure as a FAULT CODE when a read-
out command is given. A readout command can be
made by turning the ignition switch to ON-OFF-ON-
OFF-ON without starting the engine. The Malfunc-
tion Indicator (CHECK ENGINE) Lamp on the
instrument cluster will flash in preset sequences to
show Fault Codes. However, the Malfunction Indica-
tor (Check Engine) Lamp cannot express fault codes
for all failures. Fault codes are easier to obtain and
more complete with the use of Diagnostic Tool (DRB
II). This tool is plugged into the diagnostic connector located in the engine compartment (Fig. 2). Refer to
the instructions provided with the (DRB II) tool be-
ing used. For numbered Fault Codes pertaining to compo-
nents within this Group, refer to Failure CodesÐOn
Board Diagnostics in Group 8A. For other Fault
Codes which, do not pertaining to this Group 8A, re-
fer to Group 14, Fuel System, On Board Diagnostics.
Fig. 1 Starting System Components
Ä BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS 8A - 1
Page 375 of 2438

BATTERY TEST PROCEDURES ON-VEHICLE INDEX
page page
Battery Charging .......................... 7
Battery Load Test ......................... 6
Battery Open Circuit Voltage Test ............. 4
Causes of Battery Discharging ............... 4 General Information
........................ 3
State of Charge Tests ...................... 4
Test Indicator ............................ 3
GENERAL INFORMATION
The battery stores, stabilizes, and produces electri-
cal current to operate various electrical systems in
the vehicle. The determination of whether a battery
is good or bad is made by the battery's ability to ac-
cept a charge. It also must produce high amperage
current output over an extended period to be able to
start the vehicle. The capability of the battery to
store electrical current comes from a chemical reac-
tion. This reaction takes place between the sulfuric
acid solution electrolyte and the lead +/- plates in
each cell of the battery. As the battery discharges,
the plates react with the acid from the electrolyte.
When the charging system charges the battery, the
water is converted to sulfuric acid in the battery. The
amount of acid, specific gravity in the electrolyte can
be measured with a hydrometer. The factory in-
stalled battery is equipped with a built in hydrome-
ter as a test indicator (Figs. 3, 4 and 5) to help in
determining the battery's state of charge. The factory
installed battery also is sealed. Water cannot and
should not be added.
The battery is vented to release gases that is cre-
ated when the battery is being charged and dis-
charged. The battery top, posts, and terminals should
be cleaned when other under hood maintenance is
performed (Fig. 3).
WARNING: DO NOT ASSIST BOOST, CHARGE, ADD
WATER, OR LOAD TEST BATTERY WHEN ELEC- TROLYTE LEVEL IS BELOW THE TOP OF THE
PLATES. PERSONAL INJURY MAY OCCUR.
When the electrolyte level is below the top of the
plates a yellow or bright color indicator in sight glass
(Figs. 4 and 5), the battery must be replaced. Refer
to Test Indicator. The battery must be completely
charged with a green color in sight glass. The top,
posts, and terminals should be properly cleaned be-
fore diagnostic procedures are performed. Also refer
to Group 8B, Battery/Starter/Generator Service.
TEST INDICATOR
The test indicator a hydrometer is viewed through
a sight glass, it is built into the top of battery case
(Figs. 3, 4 and 5). This provides visual information
for battery testing. The test indicator sight glass is to
be used with diagnostic procedures described in this
Group.
Fig. 3 Battery Construction and Test Indicator
Fig. 4 Built in Test Indicator
Fig. 5 Test Indicator Sight Glass
Ä BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS 8A - 3