1991 MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE overheating
[x] Cancel search: overheatingPage 45 of 1216

LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE - Maintenance ServiceO:lllO.AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Inspect fluid
I~~+v~!1. Drive until the fluid temperature reaches the usual
temperature
[70-80°C (160- 18O”F)l.2. Place vehicle on level floor.
3.Move selector lever sequentially to every position to fill
torque converter and hydraulic
circuitwith fluid, then
place lever in“N” Neutral position. This operation is
necessary to be sure that fluid level check is accurate.
4.Before removing dipstick, wipe all dirt from area arounddipstick. Then take out the dipstick and check the
condition of the fluid.
The transaxle should be overhauled under the following
conditions.l If there is a “burning” odor.
l If the fluid color has become noticeably blacker.
l If there is a noticeably great amount of metal
particles in the fluid.
5.Check to see if fluid level is in “HOT” range on dipstick.If fluid level is low, add ATF until level reaches “HOT”
range.Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows pump to take in air along with fluid. Airtrapped in hydraulic circuit forms bubbles which make
fluid spongy. Therefore, pressures will be erratic.
Improper filling can also raise fluid level too high. Whentransaxle has too much fluid, gears churn up foam and
cause same conditions which occur with low fluid level,resulting in accelerated deterioration of ATF.
transmission fluid.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating, fluid
oxidation, which can interfere with normal valve, clutch,and servo operation. Foaming can also result in fluid
escaping from transaxle vent where it may be mistakenfor a leak.
6. Be sure to examine fluid on dipstick closely.lO.AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Change fluid)
Drain the fluid and check whether there is any evidence of
contamination.
Replenish with new fluid after the cause of any contamina-tion has been corrected.
(1) Remove drain plugs to let fluid drain.
(2) Remove the oil pan.
(3) Check the oil filter for clogging and damage and replaceif necessary.
(4) Clean the inside of oil pan and 5 magnets.
(5) Attach the five magnets to the concave part of the oil
(6)
Elan both gasket surfaces of transaxle case and oil
pan.(7) Install oil pan with new gasket and tighten oil pan bolts
to
IO-12 Nm (7.5-8.5 ft.lbs.1(8) Tighten drain plug with gasket to
30-35 Nm (22-25
ftlbs.).
Page 872 of 1216

21-178AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Troubleshooting
09P0010Fluid level must be
within this range.09PoOll
0”
Two302
DIAGNOSIS AND TEST
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION1. Drive until the fluid temperature reaches the usual tem-
perature
[70-80°C (160- 18O”F)I.2. Place vehicle on level floor.
3. Move selector lever sequentially to every position to fill
torque converter and hydraulic circuit with fluid, then place
lever in “N” Neutral position. This operation is necessary tobe sure that fluid level check is accurate.
4. Before removing dipstick, wipe all dirt from area around
dipstick. Then take out the dipstick and check the conditionof the fluid.
The transaxle should be overhauled under the following
conditions.l If there is a “burning” odor.
l If the fluid color has become noticeably blacker.
lIf there is a noticeably great amount of metal particles inthe fluid.
5.Check to see if fluid level is in “HOT” range on dipstick. If
fluid level is low, add automatic transaxle fluid until level
reaches “HOT” range.
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions because itallows pump to take in air along with fluid. Air trapped in
hydraulic circuit forms bubbles which make fluid spongy.
Therefore, pressures will be erratic.
Improper filling can also raise fluid level too high. When
transaxle has too much fluid, gears churn up foam and
cause same conditions which occur with low fluid level,
resulting in accelerated deterioration of automatic transaxle
fluid.In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating, fluid
oxidation, which can interfere with normal valve, clutch,
and servo operation. Foaming can also result in fluid
escaping from transaxle vent where it may be mistaken for
a leak.
6. Be sure to examine fluid on dipstick closely.
CONTROL CABLE
Whether control cable is properly adjusted can be confirmed bychecking whether inhibitor switch is performing well.
1. Apply parking brakes and service brakes securely.
2. Place selector lever to “R” range.
3. Set ignition key to “ST” position.
4. Slowly move the selector lever upward until it clicks as it
fits in notch of “P” range. If starter motor operates when
lever makes a click, “P” position is correct.
5.Then slowly move selector lever to “N” range by the same
procedure as in foregoing paragraph. If starter motor
operates when selector lever fits in “N”, “N” position is
correct.6. Also check to be sure the vehicle doesn’t begin to move
and the lever doesn’t stop between P-R-N-D.
7. The control cable is properly adjusted if, as described
above, the starter motor starts at both the “P” range and
the “N” range.
Page 903 of 1216

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - service Adjustment Procedures21-209
09Pooi awith this range.
09POOll
TWO382
SERVICE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURESN21FB6E
TRANSAXLE FLUID LEVEL INSPECTION1. Drive until the fluid temperature reaches the usual tem-
perature
[70-80°C (160- 18O”F)I.2. Place vehicle on level floor.
3. Move selector lever sequentially to every position to fill
torque converter and hydraulic circuit with fluid, then place
lever in “N” Neutral position.
4. Before removing dipstick, wipe all dirt from area around
dipstick. Then take out the dipstick and check the conditionof the fluid.
The transaxle should be overhauled under the following
conditions.l If there is a “burning” odor.
l If the fluid color has become noticeably blacker.
lIf there is a noticeably great amount of metal particles inthe fluid.
5.Check to see if fluid level is in “HOT” range on dipstick. If
fluid level is low, add automatic transaxle fluid until level
reaches “HOT” range.
Transaxle fluid: MOPAR ATF PLUS (Automatic trans-
mission fluid type 7176) or Dia ATF SPor equivalent
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
becaljse it
allows pump to take in air along with fluid. Air trapped in
hydraulic circuit forms bubbles which make fluid spongy.
Therefore, pressures will be erratic, causing delayed shift,
slippy clutch and brakes, etc.
Improper filling can also raise fluid level too high. When
transaxle has too much fluid, gears churn up foam and
cause the same conditions which occur with low fluid level,
resulting in accelerated deterioration of automatic transaxle
fluid.In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating, fluid
oxidation, which can interfere with normal valve, clutch,
and servo operation.Foaming can also result in fluid
escaping from transaxle vent where it may be mistaken for
a leak.6. Be sure to examine fluid on dipstick closely.
TRANSAXLE FLUID REPLACEMENTN21FCBAaRefer to GROUP O-Maintenance Service.
TRANSFER OIL LEVEL INSPECTIONNZlFXAATransfer oil level inspection is the same as for the manual
transaxle transfer.
Refer to GROUP
22-Service Adjustment Procedures.
TRANSFER OIL REPLACEMENTNZlFYAFaTransfer oil replacement is the same as for manual transaxle
transfer.Refer to GROUP
22-Service Adjustment Procedures.
Page 1057 of 1216

BODY - Troubleshooting23-13
OPERATION
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS
-.l If the inside lock knobs of the doors are placedin the LOCK (or UNLOCK) position, the switch inthe door lock actuator will be “OFF” (or “ON”),
and the output transistor will be “ON” for 0.5
second according to the timer function in the
door lock control unit (or theft-alarm control unit).As a result, the LOCK side (or UNLOCK side) of
the door lock relay will be “ON”, operating the
actuators of all of the doors.
NOTE
The door lock actuator contains a PTC thermistor
to prevent damage caused by overheating of the
motor. If the central door lock is frequently used,the actuator may temporarily fail to operate. If it
returns to normal in a few minutes, it is not
defective.
1.
2.One of the door lock actuators fails to operate.
l Check the door actuator which fails to
operate.Cannot be placed in the LOCK or UNLOCK
position by the inside lock knob on either driver’s
or front passenger’s seat side.0 Check the switch in the actuator.0 Check the door lock control unit (or
theft-alarm control unit).
DOOR LOCK CONTROL UNIT (OR THEFT-ALARM CONTROL UNIT) TERMINAL VOLTAGE (Connector
Connected)
TerminalSignal nameConditionTerminalNo.voltage1 or
5”’Door lock relayThe moment the inside lock knob is0.5 vs2
activation signal
pressed down (approx. 0.5 sec.)
NormallySystem voltage2 or 19”’
(Driver’s seat side) insideWhen the inside lock knob is placedSystem voltage
door lock knob signalin the “LOCK” position
When the inside lock knob is placedov
in the “UNLOCK” position3 or
4”’Door lock relayThe moment the inside lock knob is0.5 v2
activation signalpulled up (approx. 0.5 sec.)
NormallySystem voltage4 or 20”’
(Passenger’s seat side)When the inside lock knob is placedSystem voltage
inside door lock knob signalin the “LOCK” position
When the inside lock knob is placedovin the “UNLOCK” position5 or
12*’Power supplyAlwaysSystem voltage6 or
7(11)*’GroundAlwaysov
NOTE*I: Vehicles with theft-alarm system.
*2:Because of the internal resistance of the output transistor, the normal terminal voltage is 0.5 V. If it is 0 V, an open orshort circuit in the harness is suspected.
Page 1156 of 1216

24-12 HEATERS AND AIR CONDITIONING - Service Adjustment Procedures
------__--210 2352,100 Pressure
(30) (33)(299) 2&
kPa(psi)2OPOO14(3) If the sight glass is clear and the magnetic clutch is
disengaged; the clutch is faulty or, the system is out of
refrigerant. Perform low pressure switch test to determine
condition. Check low pressure switch, and clutch coil for
electrical continuity.
(4) If the sight glass shows foam or bubbles, the system could
be low on charge. Occasional foam or bubbles are normal
when the ambient temperature is above
43°C (110°F) or
below
21°C (70°F).Adjust the engine speed to 1,500 rpm. Block the air-flow
thru the condenser to increase the compressor discharge
pressure to 1,422 to 1,520
kPa (206 to 220 psi). If sight
glass still shows bubbles or foam, system charge level is
low.The refrigerant system will not be low on charge unless
there is a leak. Find and repair the leak. If the leak can be
repaired without discharging the system an oil level check
is not necessary. Use the procedure for correcting low
refrigerant level found in the Refrigerant System Service
Procedure Section.DUAL PRESSURE SWITCH
The dual-pressure switch is a combination of the low-pressureswitch (for checking the quantity of refrigerant) and the,
high-pressure switch (for prevention of overheating); it is
installed on the tube, and, when the pressure becomes
approximately 210 kPa (30 psi) or lower, the compressor stops,thus preventing the compressor from being damaged by heat.
When the pressure reaches 2,700
kPa (384 psi) or higher, the
compressor stops, thus preventing overheating. There is
generally no necessity for inspection; if, however, an unusual
condition, such as non-operation of the compressor is encoun-tered, check by following the procedures below.
(1) Check for continuity of the dual-pressure switch.
NOTEIf the air temperature drops to
0°C (32°F) or lower during
cold weather, the air conditioner will not operate (no
continuity).(2) If there is an insufficient amount of refrigerant, check the
refrigerant amount by looking through the sight glass of thereceiver; supply refrigerant if necessary.
(Refer to P.24-21.)
Page 1157 of 1216
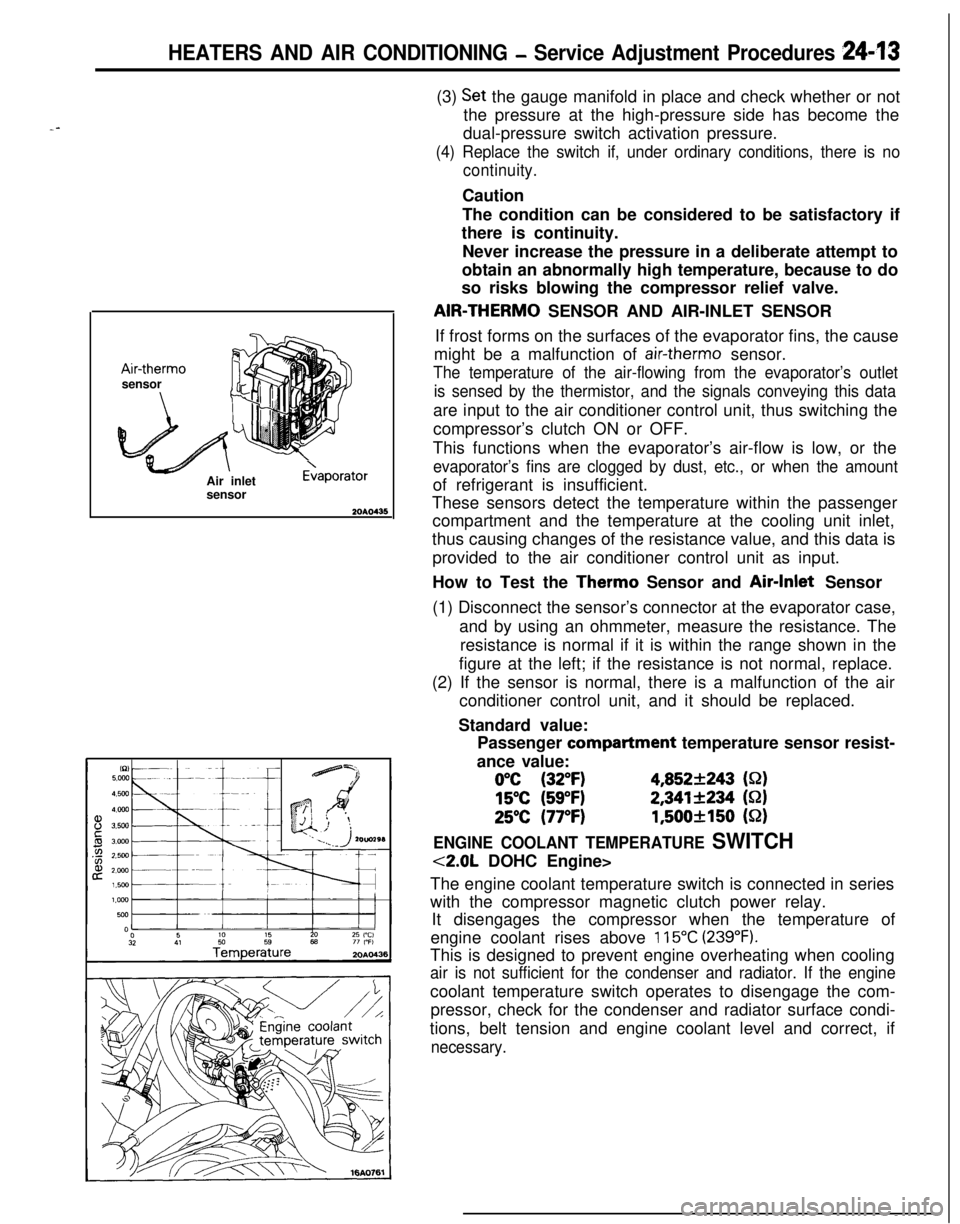
HEATERS AND AIR CONDITIONING - Service Adjustment Procedures 249*I3
--Air-therm0
sensor
Air inlet
sensor
E>aporator(3)
Set the gauge manifold in place and check whether or not
the pressure at the high-pressure side has become the
dual-pressure switch activation pressure.
(4) Replace the switch if, under ordinary conditions, there is no
continuity.Caution
The condition can be considered to be satisfactory if
there is continuity.
Never increase the pressure in a deliberate attempt to
obtain an abnormally high temperature, because to do
so risks blowing the compressor relief valve.AIR-THERM0 SENSOR AND AIR-INLET SENSOR
If frost forms on the surfaces of the evaporator fins, the cause
might be a malfunction of
air-therm0 sensor.
The temperature of the air-flowing from the evaporator’s outlet
is sensed by the thermistor, and the signals conveying this dataare input to the air conditioner control unit, thus switching the
compressor’s clutch ON or OFF.
This functions when the evaporator’s air-flow is low, or the
evaporator’s fins are clogged by dust, etc., or when the amountof refrigerant is insufficient.
These sensors detect the temperature within the passenger
compartment and the temperature at the cooling unit inlet,
thus causing changes of the resistance value, and this data is
provided to the air conditioner control unit as input.
How to Test the Therm0 Sensor and Air-Inlet Sensor
(1) Disconnect the sensor’s connector at the evaporator case,
and by using an ohmmeter, measure the resistance. The
resistance is normal if it is within the range shown in the
figure at the left; if the resistance is not normal, replace.
(2) If the sensor is normal, there is a malfunction of the air
conditioner control unit, and it should be replaced.
Standard value:
Passenger compartment temperature sensor resist-
ance value:
0°C (32°F)4,852+243 (S-2)
15°C (59°F)2,341+234 (S-2)
25°C (77°F)1,500+150 (52)
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SWITCH
<2.0L DOHC Engine>
The engine coolant temperature switch is connected in series
with the compressor magnetic clutch power relay.
It disengages the compressor when the temperature of
engine coolant rises above
115°C (239°F).This is designed to prevent engine overheating when cooling
air is not sufficient for the condenser and radiator. If the enginecoolant temperature switch operates to disengage the com-
pressor, check for the condenser and radiator surface condi-
tions, belt tension and engine coolant level and correct, if
necessary.
Page 1216 of 1216
25-20Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System/EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS - ‘catalytic Converter(5) Measure the resistance between the terminals
of- the
Q [at 20°C (68OF)l
6EM0188
AIR-FUEL RATIO CONTROL (MPI) SYSTEM &CAD
lTo inspect the air-fuel ratio control (MPI) system, refer to
GROUP 14 FUEL SYSTEM-Service Adjustment Proce-
dures.
lFor detailed information concerning the illumination patternof the malfunction-indicator light and other aspects of the
self-diagnosis function,refer to GROUP 14 FUEL
SYSTEM-Self Diagnosis.
CATALYTIC CONVERTERN25lCBHa
INSPECTION.
Inspect for damage, cracking or deterioration. Replace if faulty.
Caution1. Operation of any type, including
idjing, should be
avoided if engine misfiring occurs. Under this conditionthe exhaust system will operate at abnormally ‘high
temperature, which may cause damage to
the”Catalystor underbody parts of the vehicle.
2.Alteration or deterioration of ignition or fuel system, or
any type of operating condition which results in enghtemisfiring must be corrected to avoid overheating the
catalytic converters.
3. Proper maintenance and tune up according to manu-
facturer’s specifications should be made to correct the
conditions as soon as possible.