1991 FORD FESTIVA overheating
[x] Cancel search: overheatingPage 250 of 454
Back To Article
GENERAL INFORMATION
T ROUBLE SHOOT ING
* PLEASE READ THIS FIRST *
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
TUNE-UP TROUBLE SHOOTING NOTE:T his article is generic in nature and all inform ation does not apply to all vehicles. For vehicle specific
inform ation, see the appropriate articles in the ENGINE PERFORMANCE category.
NOTE:T his article is generic in nature and all inform ation does not apply to all vehicles. For vehicle specific
inform ation, see the appropriate articles in the ENGINE PERFORMANCE category.
Problem & Possible CauseAction
Carbon Fouled Plugs
C l o gge d Air Fil t e rReplace Air Filter
Incorrect Idle SpeedReset Idle Speed
Faulty Ignition WiringReplace Ignition Wiring
Sticky Valves/Worn Valve SealCheck Valve Train
Fuel Injection OperationCheck Fuel Injection
Wet/Oil Fouled Plugs
Worn Rings/PistonsOverhaul/Replace Engine
Excessive Cylinder WearOverhaul/Replace Engine
Plug Gap Bridged
Combustion Chamber Carbon DepositsClean Combustion
Chamber
Blistered Electrode
Engine OverheatingCheck Cooling System
Loose Spark PlugsClean/Torque Plugs
Over-Advanced TimingReset Timing
Wrong Plug Heat RangeInstall Correct Plug
Melted Electrodes
Incorrect TimingReset Timing
Burned ValvesReplace Valves
Engine OverheatingCheck Cooling System
Wrong Plug Heat RangeInstall Correct Plug
Engine Won't Start
Loose ConnectionsCheck Connections
No PowerCheck Fuses/Battery
Loose/Worn Timing Belt/Chain/GearsCheck Belt/Chain/Gears
Engine Runs Rough
Leaky/Clogged Fuel InjectorsRepair Fuel Injectors
Leaky/Clogged Fuel LinesRepair Fuel Lines
Clogged Fuel FilterReplace Fuel Filter
Incorrect TimingReset Timing/Check
Advance
Faulty Plugs/WiresReplace Plugs/Wires
Uneven CompressionOverhaul/Replace Engine
Poor Acceleration
Incorrect Ignition TimingReset Timing
Leaky ValvesCheck Compression
Component Failure
Spark ArcingReplace Faulty Part
Defective Pick-Up CoilReplace Pick-Up Coil
Defective Ignition CoilReplace Ignition Coil
Defective Control UnitReplace Control Unit
Ignition Diagnosis By Scope Pattern
All Firing Lines Abnormally High
Retarded Ignition TimingReset Ignition Timing
Lean Air/Fuel MixtureAdjust Fuel Mixture
High Secondary ResistanceRepair Secondary
Ign it io n
All Firing Lines Abnormally Low
Rich Air/Fuel MixtureAdjust Air/Fuel Mixture
Arcing Coil WireReplace Coil Wire
Cracked CoilReplace Coil
Low Coil OutputReplace Coil
Low CompressionCheck/Repair Engine
Page 1 of 3 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION TROUBLE SHOOTING
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 251 of 454

FUEL INJECTION TROUBLE SHOOTING
Se ve r a l High F ir in g Lin e s
Fuel Mixture UnbalancedCheck Fuel System
EGR Valve Stuck OpenClean/Replace EGR
Valve
High Plug Wire ResistanceReplace Plug Wire
Cracked/Broken PlugsReplace Plugs
Intake Vacuum LeakRepair Leak
Several Low Firing Lines
Fuel Mixture UnbalancedAdjust Fuel Mixture
Plug Wires ArcingReplace Plug Wires
Cracked Coil ArcingReplace Coil
Uneven CompressionCheck/Repair Engine
Faulty Spark PlugsReplace Plugs
Cylinders Not Firing
Cracked Distributor CapReplace Cap
Shorted Plug WiresReplace Plug Wires
Mechanical Engine FaultCheck/Repair Engine
Spark Plugs FouledReplace Plugs
Carbon Track in Distributor CapReplace Cap
Hard Starting
Defective Ignition Coil(s)Replace Coil(s)
Fouled Spark PlugsReplace Plugs
Incorrect TimingReset Ignition Timing
NOTE:T his article is generic in nature and all inform ation does not apply to all vehicles. For vehicle specific
inform ation, see the appropriate articles in the ENGINE PERFORMANCE category.
Problem & Possible CauseAction
Cold Start Valve InoperativeTest Cold Start Valve
Poor Vacuum/Electrical ConnectionRepair Connections
Contaminated FuelTest Fuel for Water/Alcohol
Bad Fuel Pump Relay/CircuitTest Relay/Wiring
Battery Voltage LowCharge/Test Battery
Low Fuel PressureTest Press. Regulator/Pump
No Distributor Reference PulseRepair Ignition System
Coolant Temp. Sensor DefectiveTest Temp. Sensor/Circuit
No Power To InjectorsCheck Injector Fuse/Relay
Hard Starting
Defective Idle Air Control (IAC)Test IAC and Circuit
EGR Valve OpenTest EGR Valve/Control
Circuit
Restricted Fuel LinesInspect/Replace Fuel Lines
Poor MAP Sensor SignalTest MAP Sensor/Circuit
Engine Stalls During Parking ManeuverCheck P.S. Press. Switch
Rough Idle
Dirty Fuel InjectorsClean/Replace Injectors
Poor MAP Sensor SignalTest MAP Sensor/Circuit
Intermittent Fuel Injector OperationCheck Harness Connectors
Erratic Vehicle Speed Sensor InputsHarness Too Close to Plug
Wires
Poor O2 Sensor SignalTest O2 Sensor/Circuit
Faulty PCV SystemCheck PCV Valve and
Hoses
Poor Acceleration
Weak Fuel PumpReplace Fuel Pump
Dirty Fuel InjectorsClean/Replace Injectors
Excessive Intake Valve DepositsClean Intake System
Poor High Speed Operation
Low Fuel Pump VolumeFaulty Fuel Pump/Filter
Poor MAP Sensor SignalTest Speed Sensor/Circuit
Acceleration Ping/Knock
Faulty EGR SystemCheck EGR Valve and
Hoses
Poor Knock Sensor SignalTest Knock Sensor/Circuit
Poor Baro Sensor SignalTest Baro Sensor/Circuit
Improper Ignition TimingAdjust Timing
Engine OverheatingCheck Cooling System
Poor Quality FuelUse Different Fuel
Carbon Build-UpDecarbon Engine
Page 2 of 3 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION TROUBLE SHOOTING
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 286 of 454
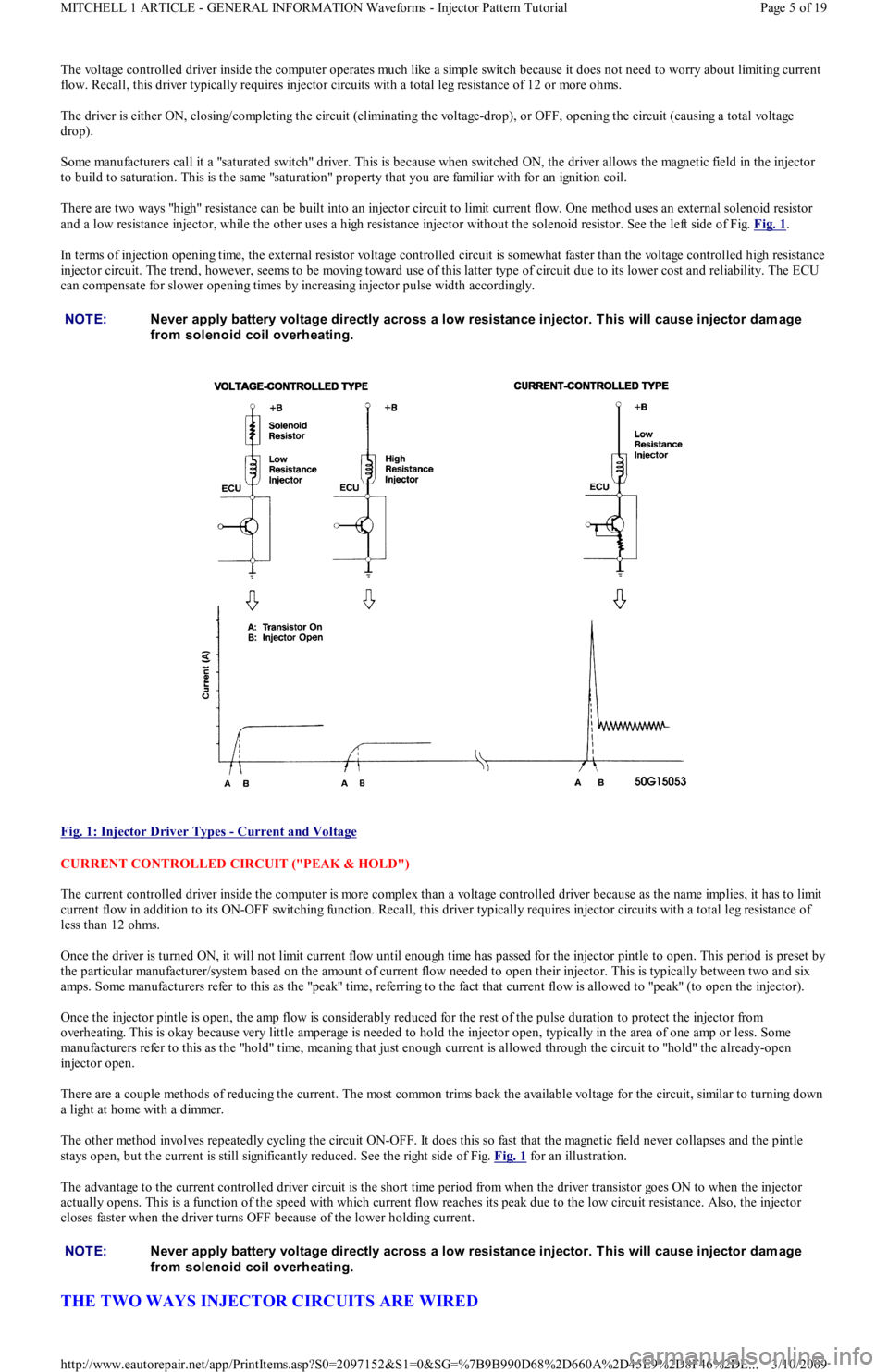
The voltage controlled driver inside the computer operates much like a simple switch because it does not need to worry about limiting current
flow. Recall, this driver typically requires injector circuits with a total leg resistance of 12 or more ohms.
The driver is either ON, closing/completing the circuit (eliminating the voltage-drop), or OFF, opening the circuit (causing a total voltage
drop).
Some manufacturers call it a "saturated switch" driver. This is because when switched ON, the driver allows the magnetic field in the injector
to build to saturation. This is the same "saturation" property that you are familiar with for an ignition coil.
There are two ways "high" resistance can be built into an injector circuit to limit current flow. One method uses an external solenoid resistor
and a low resistance injector, while the other uses a high resistance injector without the solenoid resistor. See the left side of Fig. Fig. 1
.
In terms of injection opening time, the external resistor voltage controlled circuit is somewhat faster than the voltage controlled high resistance
injector circuit. The trend, however, seems to be moving toward use of this latter type of circuit due to its lower cost and reliability. The ECU
can compensate for slower opening times by increasing injector pulse width accordingly.
Fig. 1: Injector Driver Types
- Current and Voltage
CURRENT CONTROLLED CIRCUIT ("PEAK & HOLD")
The current controlled driver inside the computer is more complex than a voltage controlled driver because as the name implies, it has to limit
current flow in addition to its ON-OFF switching function. Recall, this driver typically requires injector circuits with a total leg resistance of
less than 12 ohms.
Once the driver is turned ON, it will not limit current flow until enough time has passed for the injector pintle to open. This period is preset by
the particular manufacturer/system based on the amount of current flow needed to open their injector. This is typically between two and six
amps. Some manufacturers refer to this as the "peak" time, referring to the fact that current flow is allowed to "peak" (to open the injector).
Once the injector pintle is open, the amp flow is considerably reduced for the rest of the pulse duration to protect the injector from
overheating. This is okay because very little amperage is needed to hold the injector open, typically in the area of one amp or less. Some
manufacturers refer to this as the "hold" time, meaning that just enough current is allowed through the circuit to "hold" the already-open
injector open.
There are a couple methods of reducing the current. The most common trims back the available voltage for the circuit, similar to turning down
a light at home with a dimmer.
The other method involves repeatedly cycling the circuit ON-OFF. It does this so fast that the magnetic field never collapses and the pintle
stays open, but the current is still significantly reduced. See the right side of Fig. Fig. 1
for an illustration.
The advantage to the current controlled driver circuit is the short time period from when the driver transistor goes ON to when the injector
actually opens. This is a function of the speed with which current flow reaches its peak due to the low circuit resistance. Also, the injector
closes faster when the driver turns OFF because of the lower holding current.
THE TWO WAYS INJECTOR CIRCUITS ARE WIRED
NOTE:Never apply battery voltage directly across a low resistance injector. T his will cause injector dam age
from solenoid coil overheating.
NOTE:Never apply battery voltage directly across a low resistance injector. T his will cause injector dam age
from solenoid coil overheating.
Page 5 of 19 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Waveforms - Injector Pattern Tutorial
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 439 of 454
1. Inspect wiring and components for shorts, corrosion, overheating, loose connections, or any other damage. Check 10-amp METER fu se.
Disconnect downshift solenoid.
2. With key off, voltage measured at Black/Blue wire should be zero volts. With key on and accelerator pedal fully depressed, voltage
should be greater than 10 volts. If Black/Blue wire is okay, remove downshift solenoid.
3. Apply battery voltage to downshift solenoid connector and ground case. Control rod should move freely when solenoid case is
grounded. If control rod does not move freely, replace downshift solenoid.
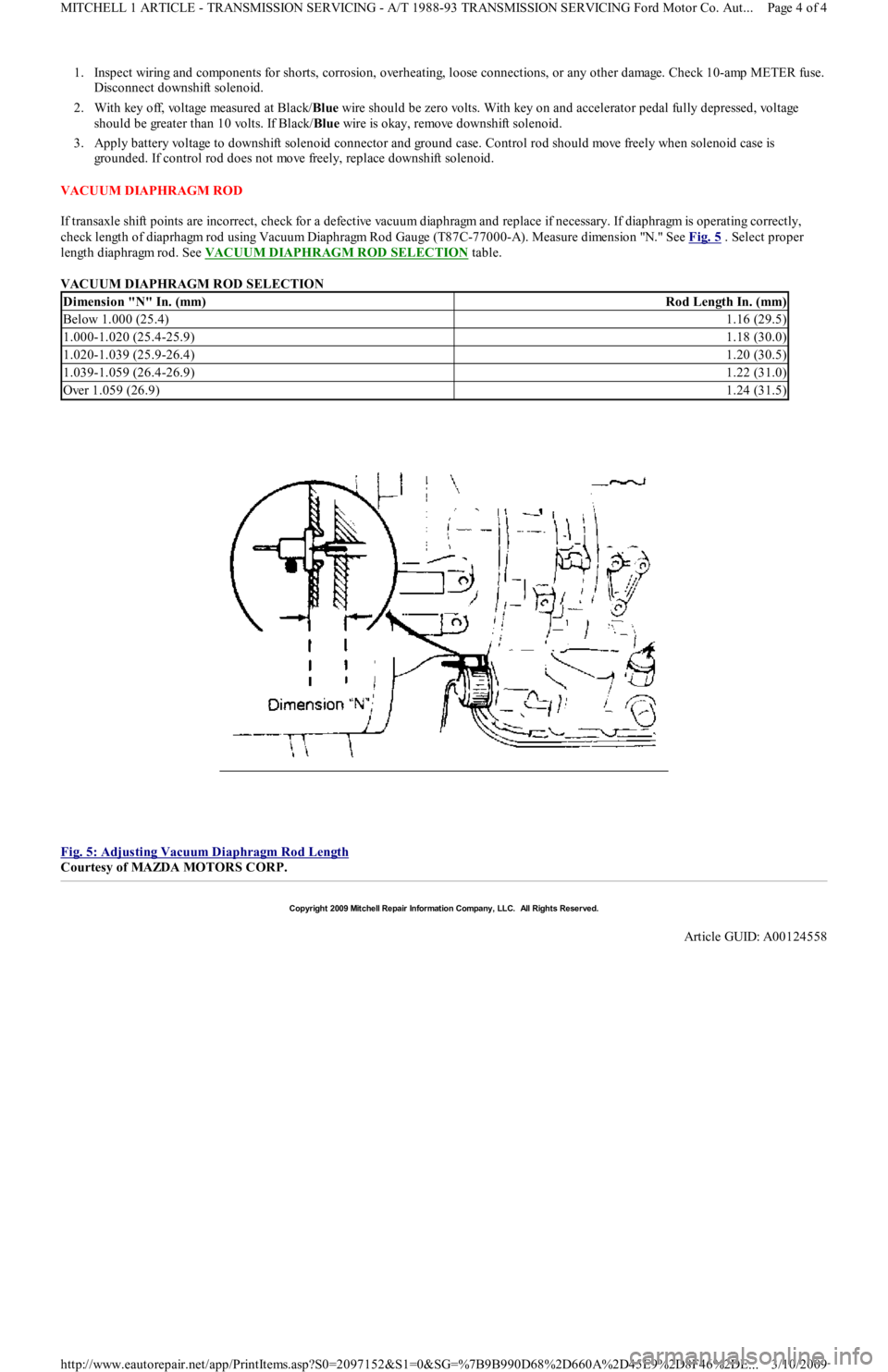
VACUUM DIAPHRAGM ROD
If transaxle shift points are incorrect, check for a defective vacuum diaphragm and replace if necessary. If diaphragm is operating correctly,
check length of diaprhagm rod using Vacuum Diaphragm Rod Gauge (T87C-77000-A). Measure dimension "N." See Fig. 5
. Select proper
length diaphragm rod. See VACUUM DIAPHRAGM ROD SELECTION
table.
VACUUM DIAPHRAGM ROD SELECTION
Fig. 5: Adjusting Vacuum Diaphragm Rod Length
Courtesy of MAZDA MOTORS CORP.
Dimension "N" In. (mm)Rod Length In. (mm)
Below 1.000 (25.4)1.16 (29.5)
1.000-1.020 (25.4-25.9)1.18 (30.0)
1.020-1.039 (25.9-26.4)1.20 (30.5)
1.039-1.059 (26.4-26.9)1.22 (31.0)
Over 1.059 (26.9)1.24 (31.5)
Copyr ight 2009 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
Article GUID: A00124558
Page 4 of 4 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - TRANSMISSION SERVICING - A/T 1988-93 TRANSMISSION SERVICING Ford Motor Co. Aut
...
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...