1990 MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: oil pressurePage 240 of 391

_-
21-16AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - General InformationAUTOMATIC
TRANSAXLE
GENERAL INFQRMATIONRzlBBACF4A22 automatic transaxles with different shift pattern are introduced to match engine output characteristics.
These F4A22 automatic transaxles are transaxles of KM1 70 Type II series and each is a two-mode
electronically controlled automatic transaxle with shift patterns of two modes.
SPECIFICATIONS
Items
Transaxle modelTorque convertor
Me
Stall torque ratio
TransaxleType
Gear ratio
1 St
2nd
3rd4th
ReversePrimary reduction ratio
Differential gear ratio
Friction elements
Number of front clutch discs
Number of rear clutch discs
Number of end clutch discs
Number of low/reverse brake discs
Number of
kickdown brake bandControl system
Manual control system
Shift pattern type
Solenoid yalve operationShift control
(2)
Pressure control
Damper clutch controlDiagnosis
Indication method
Number of diagnosis items
Speedometer gear ratio
ATFOil quantityliter
(qts.)
Specifications-4A22-2-MPAl3element, 1 -stage,
2-phase with damper clutch
2.17l-speed forward, l-speed reverse
2.846
1.581
1
.ooo
3.685
2.176
1.125
3.611V&N-D-2-L (lever type) with overdrive switch
Two-mode electronic-hydraulic control type
ON-OFF controlDuty control
Duty control
Indication with
LEDs
24
29136
MOPAR ATF PLUS (AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIOI
FLUID TYPE 7176VAutomatic Transmission Fluid“DEXRON” or “DEXRON II”
\I6.1
(6.4)J
Page 246 of 391

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Torque Converter
TORQUE CONVERTER
Lock
ring
I
Damper
F
clutch-
B-.Turbine
.AA
/:ront cover
h,Impeller
AStartorWhen damper clutch is
I\When damper
aInput shaftactivated
clutch isactivated
175202The torque-converter is composed of the impeller
(rear cover), turbine,
stator, damper clutch, one-way
clutch, front cover, etc.Furthermore. the torque-converter cannot be dis-
assembled because the outer circumference of the
shell
(front cover and rear cover) is sealed by
welding.
Because the torque-converter is coupled to the
engine’s crankshaft (via the drive plate). the shell
(front cover and impeller) always turns in the same
way when the engine is running.
As a result, the oil pump is also caused to rotate (by
the hub welded to the center part of the rear of the
shell) at the same speed as the engine.
The boss at the front part of the shell is inserted in
the hole at the rear part of the crankshaft. thus
providing support of the torque-converter.
A facing like that attached to the transaxle’s clutch
disc is attached to the damper clutch, and the
damper clutch and the turbine are connected by the
tabs (of the lock ring on the outer circumference of
the turbine shell) that fit into the groove on the outer
circumference of the damper clutch.
The torque-converter actuation hydraulic pressure,at the damper clutch activation area, passes be-
tween the torque-converter’s hub and the reaction
shaft, and enters the torque-converter.
When this happens, the hydraulic pressure acts
upon the A part (between the damper clutch and the
turbine), with the result that the damper clutch is
pressed against the front cover, and the damper
clutch, with a slight slip (as described later) becom-
es connected.
In this manner, the amount of slippage of the
torque-convener is reduced, without a damper
spring, to far below at even the low-speed level,
thus making a practical improvement of fuel con-
sumption.
At the damper clutch non-activation area, because
the torque-converter actuation hydraulic pressure
passes through the input shaft oil passage
-1enters the torque-converter from the
B part &-tween the damper clutch and the front cover). the
damper clutch moves away from the front
cover,thus releasing the damper clutch.
In this condition, operation is as an ordinary torque-
converter.
Page 250 of 391

21-26AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Transaxle Mechanism
REAR CLUTCH
Wave sprmgRear clutch retainer
Clutch reaction piateClutch pressure plate
I1rao2l5Rear clutch is of the multiple disc type, and is
composed of a rear clutch retainer, disc, plates, and
a piston. When the piston is actuated by the oil
pressure, the multiple disc clutch is connected,
conveying driving force from the input shaft to the
forward sun gear in the planetary gear set. The rear
clutch is always actuated when the shift is in first,
second and third gears.
INumber of clutch discsI.3I
1 Number of clutch piates1 2 I-
I Number of reaction plates
I
1 1
I Number of pressure plates’I 1 I
PistonO.D.mm (in.)121 (4.761
I.D.mm (in.)36 (1.42)
POWER FLOW
Rear clutch
Rear clutch hubRear clutch retainer
Forward sun gear,
IInput shaftRear clutch retainerRear clutchRear clutch hubForward sun gear
Page 266 of 391
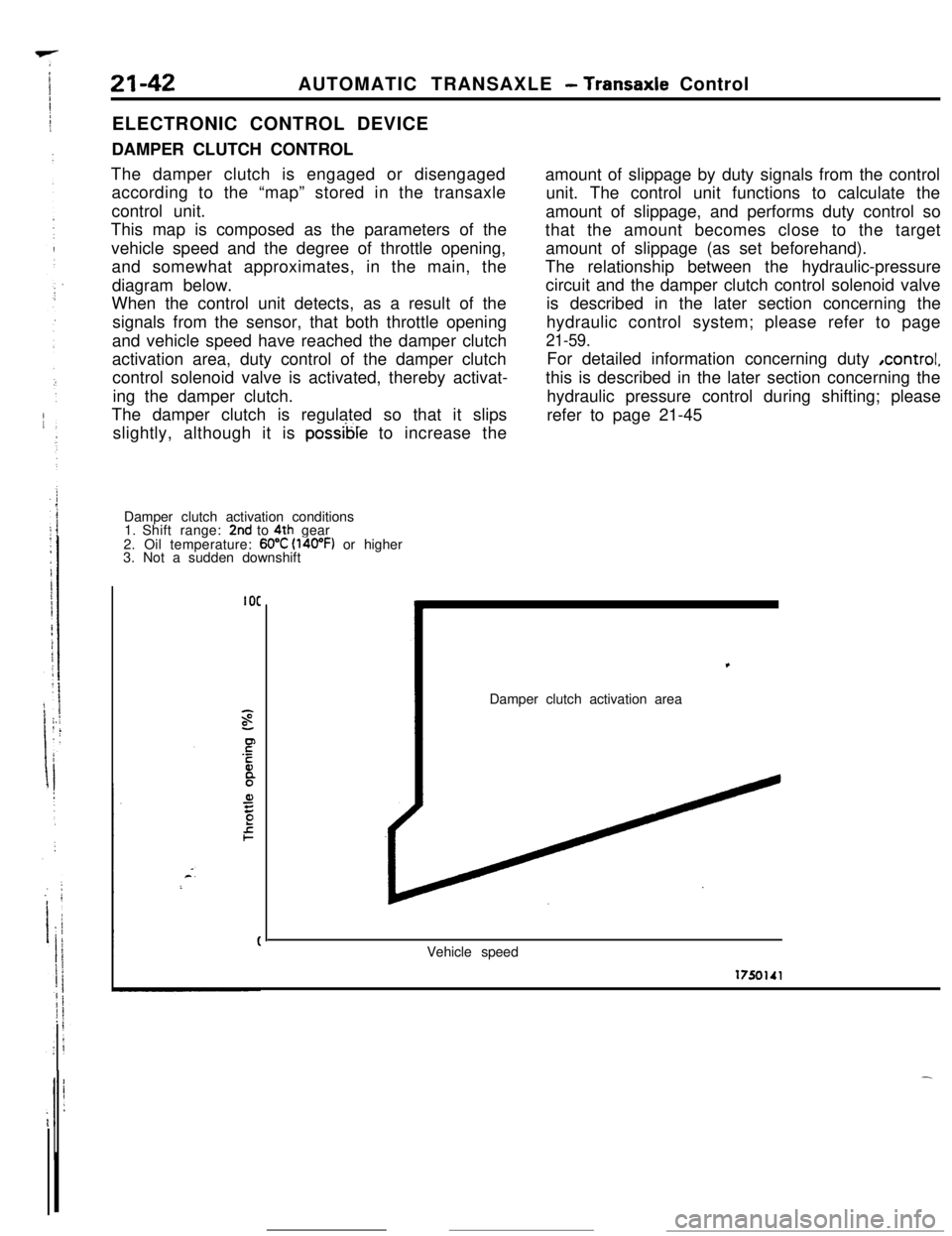
21-42AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Transaxle Control
ELECTRONIC CONTROL DEVICE
DAMPER CLUTCH CONTROL
The damper clutch is engaged or disengaged
according to the “map” stored in the transaxle
control unit.
This map is composed as the parameters of the
vehicle speed and the degree of throttle opening,
and somewhat approximates, in the main, the
diagram below.
When the control unit detects, as a result of the
signals from the sensor, that both throttle opening
and vehicle speed have reached the damper clutch
activation area, duty control of the damper clutch
control solenoid valve is activated, thereby activat-
ing the damper clutch.
The damper clutch is regulated so that it slips
slightly, although it is
possible to increase the
Damper clutch activation conditions
1. Shift range:
2nd to 4th gear
2. Oil temperature: 60°C (l4oOF) or higher
3. Not a sudden downshift
IOCamount of slippage by duty signals from the control
unit. The control unit functions to calculate the
amount of slippage, and performs duty control so
that the amount becomes close to the target
amount of slippage (as set beforehand).
The relationship between the hydraulic-pressure
circuit and the damper clutch control solenoid valve
is described in the later section concerning the
hydraulic control system; please refer to page
21-59.For detailed information concerning duty ,control,
this is described in the later section concerning the
hydraulic pressure control during shifting; please
refer to page 21-45,
Damper clutch activation area
Vehicle speed
Page 269 of 391
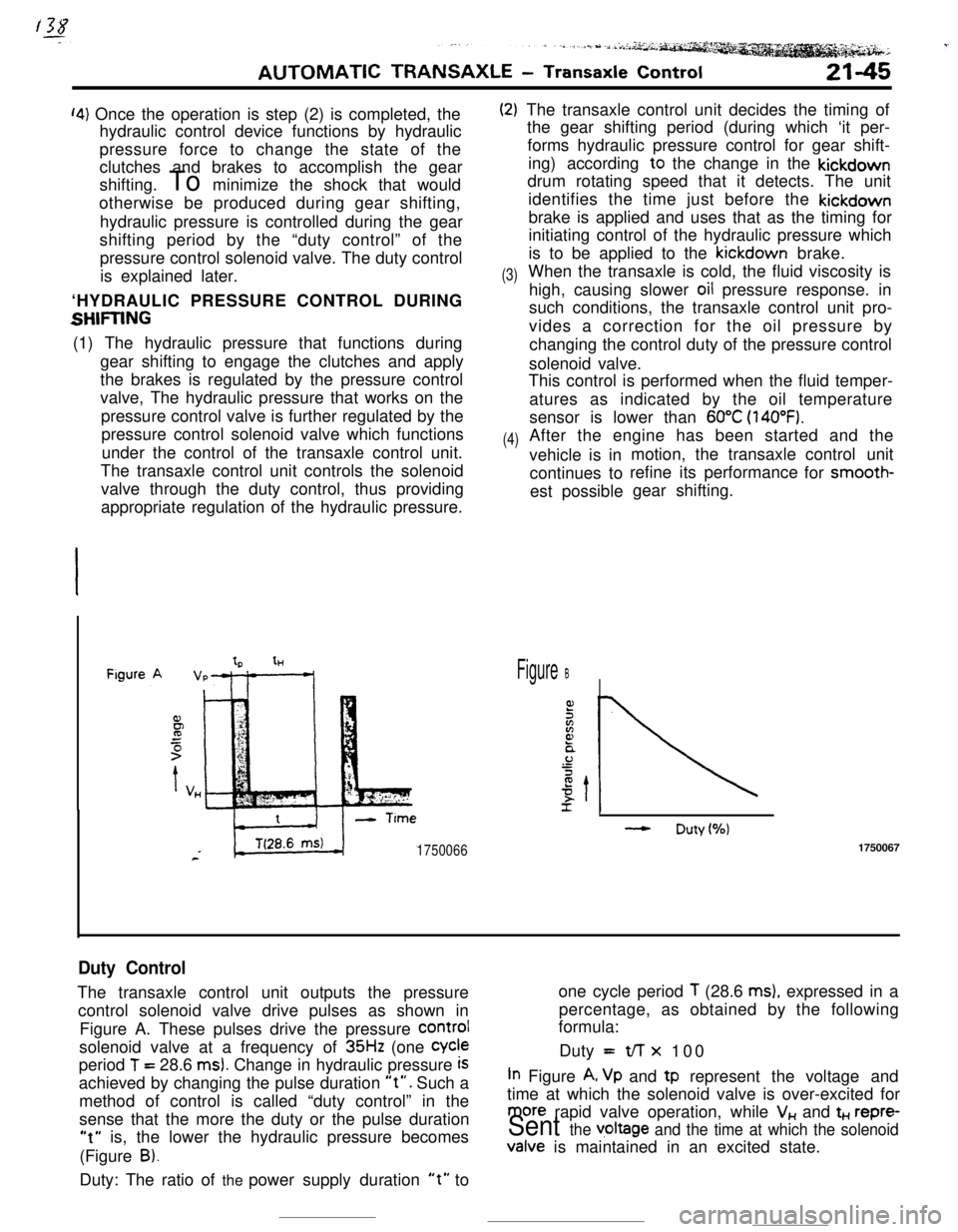
‘4) Once the operation is step (2) is completed, the
hydraulic control device functions by hydraulic
pressure force to change the state of the
clutches and brakes to accomplish the gear
shifting. To minimize the shock that would
otherwise be produced during gear shifting,
hydraulic pressure is controlled during the gear
shifting period by the “duty control” of the
pressure control solenoid valve. The duty control
is explained later.
‘HYDRAULIC PRESSURE CONTROL DURING
SHFIING(1) The hydraulic pressure that functions during
gear shifting to engage the clutches and apply
the brakes is regulated by the pressure control
valve, The hydraulic pressure that works on the
pressure control valve is further regulated by the
pressure control solenoid valve which functions
under the control of the transaxle control unit.
The transaxle control unit controls the solenoid
valve through the duty control, thus providing
appropriate regulation of the hydraulic pressure.
(2)
(3)
(4)The transaxle control unit decides the timing of
the gear shifting period (during which ‘it per-
forms hydraulic pressure control for gear shift-
ing) according to the change in the kickdown
drum rotating speed that it detects. The unit
identifies the time just before the kickdown
brake is applied and uses that as the timing for
initiating control of the hydraulic pressure which
is to be applied to the kickdown brake.
When the transaxle is cold, the fluid viscosity is
high, causing slower oil pressure response. in
such conditions, the transaxle control unit pro-
vides a correction for the oil pressure by
changing the control duty of the pressure control
solenoid valve.
This control is performed when the fluid temper-
atures as indicated by the oil temperature
sensor is lower than
60°C (140°F).After the engine has been started and the
vehicle is inmotion, the transaxle
continues torefine its performance
est possiblegear shifting.control unit
for smooth-
tHFigure B
- Duty(%)
17500661750067
Duty ControlThe transaxle control unit outputs the pressureone cycle period
T (28.6 ms), expressed in a
control solenoid valve drive pulses as shown inpercentage, as obtained by the following
formula:
Figure A. These pulses drive the pressure
COrmIsolenoid valve at a frequency of
35Hz (one Cycleperiod
T = 28.6 ms). Change in hydraulic pressure iSDuty =t/-r x 100
achieved by changing the pulse duration
“t”. Such aIn Figure A, Vp and tp represent the voltage and
method of control is called “duty control” in thetime at which the solenoid valve is over-excited for
sense that the more the duty or the pulse duration
more rapid valve operation, while V,, and t+., repre-
“t” is, the lower the hydraulic pressure becomesSent the v,oltage and the time at which the solenoid(Figure
B).Valve is maintained in an excited state.
Duty: The ratio of the power supply duration
“t” to
Page 271 of 391
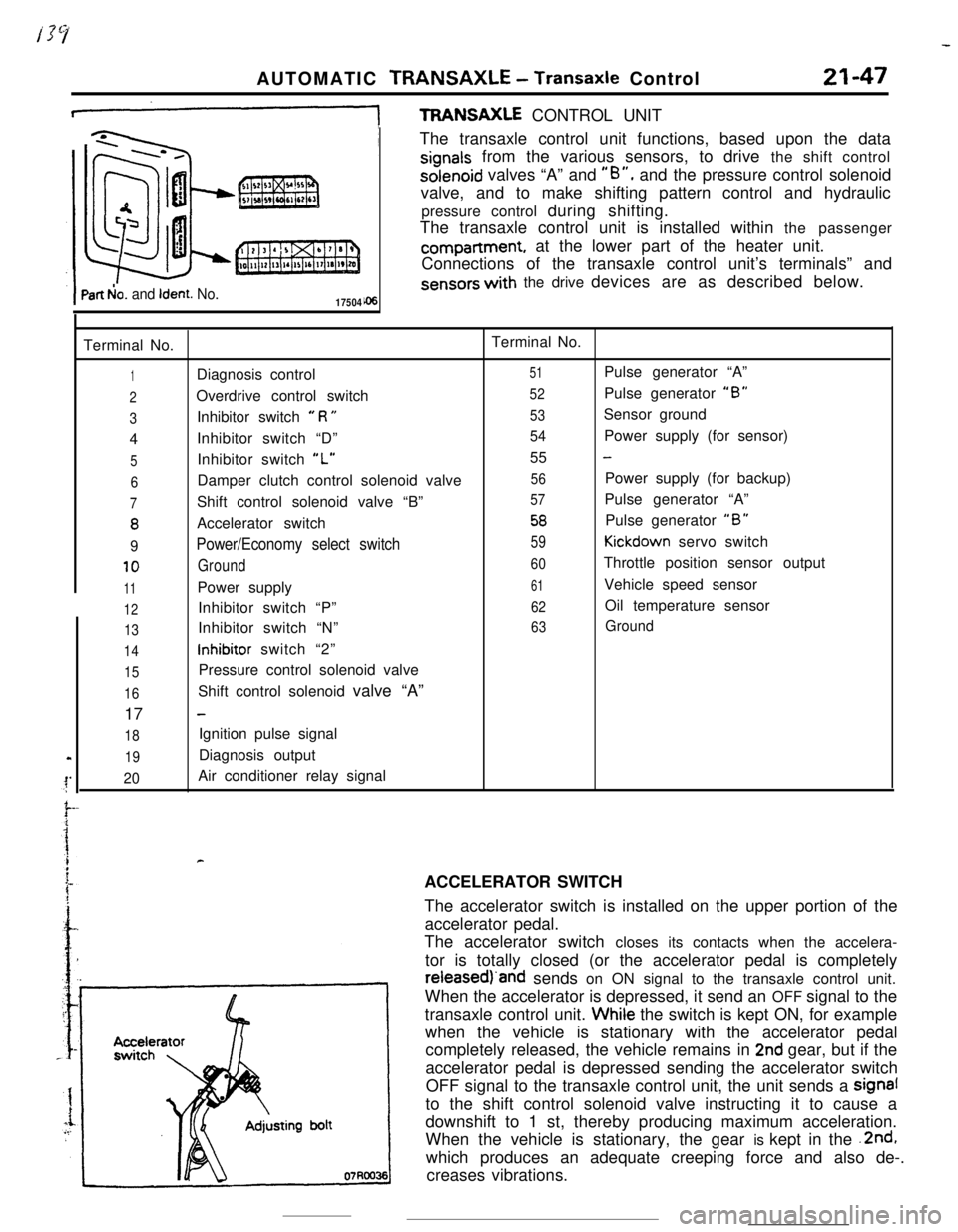
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Transaxle Control21-47
+TFWNSAXLE CONTROL UNIT
Part b!o. and Ident. No.17504The transaxle control unit functions, based upon the data
signals from the various sensors, to drive the shift controlsolenoid valves “A” and
“B”, and the pressure control solenoid
valve, and to make shifting pattern control and hydraulic
pressure control during shifting.
The transaxle control unit is installed within the passengercompartment, at the lower part of the heater unit.
Connections of the transaxle control unit’s terminals” and
sensors with the drive devices are as described below.
Terminal No.Terminal No.
1Diagnosis control51Pulse generator “A”
2Overdrive control switch52Pulse generator “B”
3Inhibitor switch e R U53Sensor ground
4Inhibitor switch “D”
54Power supply (for sensor)
5Inhibitor switch “L”55 -
6Damper clutch control solenoid valve56Power supply (for backup)
7Shift control solenoid valve “B”57Pulse generator “A”
8Accelerator switch58Pulse generator “B”
9Power/Economy select switch59Kickdown servo switch
10Ground60Throttle position sensor output
11Power supply61Vehicle speed sensor
12Inhibitor switch “P”62Oil temperature sensor
13Inhibitor switch “N”63Ground
14inhibitor switch “2”
15Pressure control solenoid valve
16Shift control solenoid valve “A”
17
-
18Ignition pulse signal
19Diagnosis output
20Air conditioner relay signal
rACCELERATOR SWITCH
The accelerator switch is installed on the upper portion of the
accelerator pedal.
The accelerator switch closes its contacts when the accelera-
tor is totally closed (or the accelerator pedal is completelyreieasedj‘and sends on ON signal to the transaxle control unit.
When the accelerator is depressed, it send an OFF signal to the
transaxle control unit. Whiie the switch is kept ON, for example
when the vehicle is stationary with the accelerator pedal
completely released, the vehicle remains in
2nd gear, but if the
accelerator pedal is depressed sending the accelerator switch
OFF signal to the transaxle control unit, the unit sends a signal
to the shift control solenoid valve instructing it to cause a
downshift to 1 st, thereby producing maximum acceleration.
When the vehicle is stationary, the gear is kept in the .2nd,
which produces an adequate creeping force and also de-.
creases vibrations.
Page 272 of 391
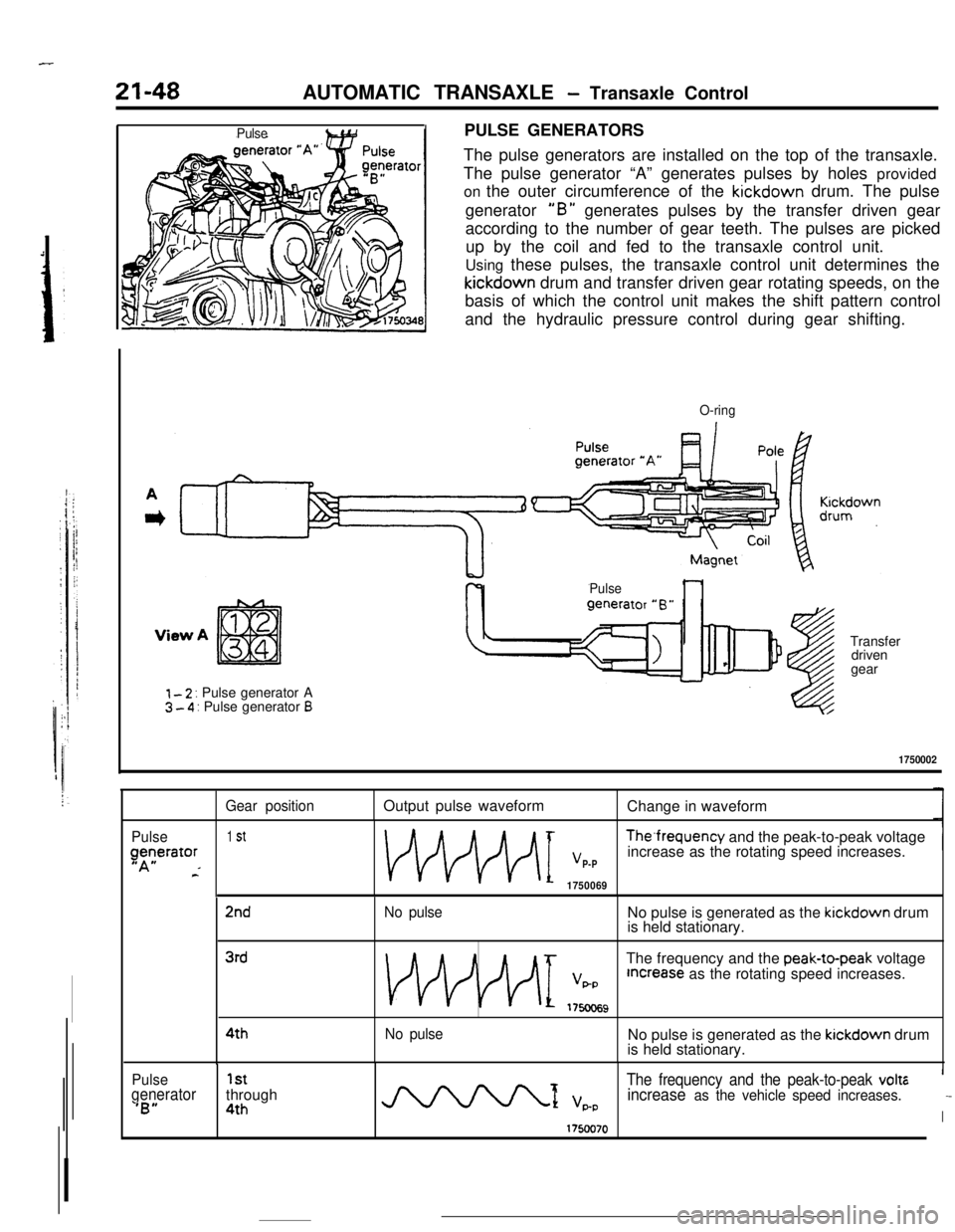
21-48AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Transaxle Control
PulsePULSE GENERATORS
The pulse generators are installed on the top of the transaxle.
The pulse generator “A” generates pulses by holes provided
on the outer circumference of the kickdown drum. The pulse
generator
“B” generates pulses by the transfer driven gear
according to the number of gear teeth. The pulses are picked
up by the coil and fed to the transaxle control unit.
Using these pulses, the transaxle control unit determines thekickdown drum and transfer driven gear rotating speeds, on the
basis of which the control unit makes the shift pattern control
and the hydraulic pressure control during gear shifting.
O-ring
Pulse
View ATransfer
driven
gear
I - 2 : Pulse generator A3 - 4 : Pulse generator B
1750002
Gear positionOutput pulse waveform
Change in waveform
Pulse1 St
Tcerator-FThe‘frequency and the peak-to-peak voltageVP-Pincrease as the rotating speed increases.
1750069
2ndNo pulseNo pulse is generated as the kickdown drum
is held stationary.
3rdThe frequency and the peak-to-peak voltage
VF+PIncrease as the rotating speed increases.
175oc69
4thNo pulseNo pulse is generated as the kickdown drum
is held stationary.
Pulse1st
generator‘B”through4th-1 VP-P
The frequency and the peak-to-peak volt6’
increase as the vehicle speed increases.
I
-
Page 279 of 391

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Transaxle Control21-55HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYSTEM
Reaction shaft
support
BushingThe hydraulic control system consists of an oil pump which
generates hydraulic pressure for the system, and valves and
solenoid valves to control the pressure or switch the oil
passages. The valves and solenoid valves are all built in the
valve body.
OIL PUMPOil pump generates the pressure for supplying oil to the torque
converter, for lubricating frictional parts of the planetary gear
set and the overrunning clutch, etc., and for activating the
hydraulic control system.
The pump is of the inner-teeth engaging involute gear type. It
always generates the oil pressure when the engine is running
since the drive gear
is driven by 2 pawls of the pump drive hub
welded at the center of the torque converter shell.