1990 MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE fuel pressure
[x] Cancel search: fuel pressurePage 119 of 391
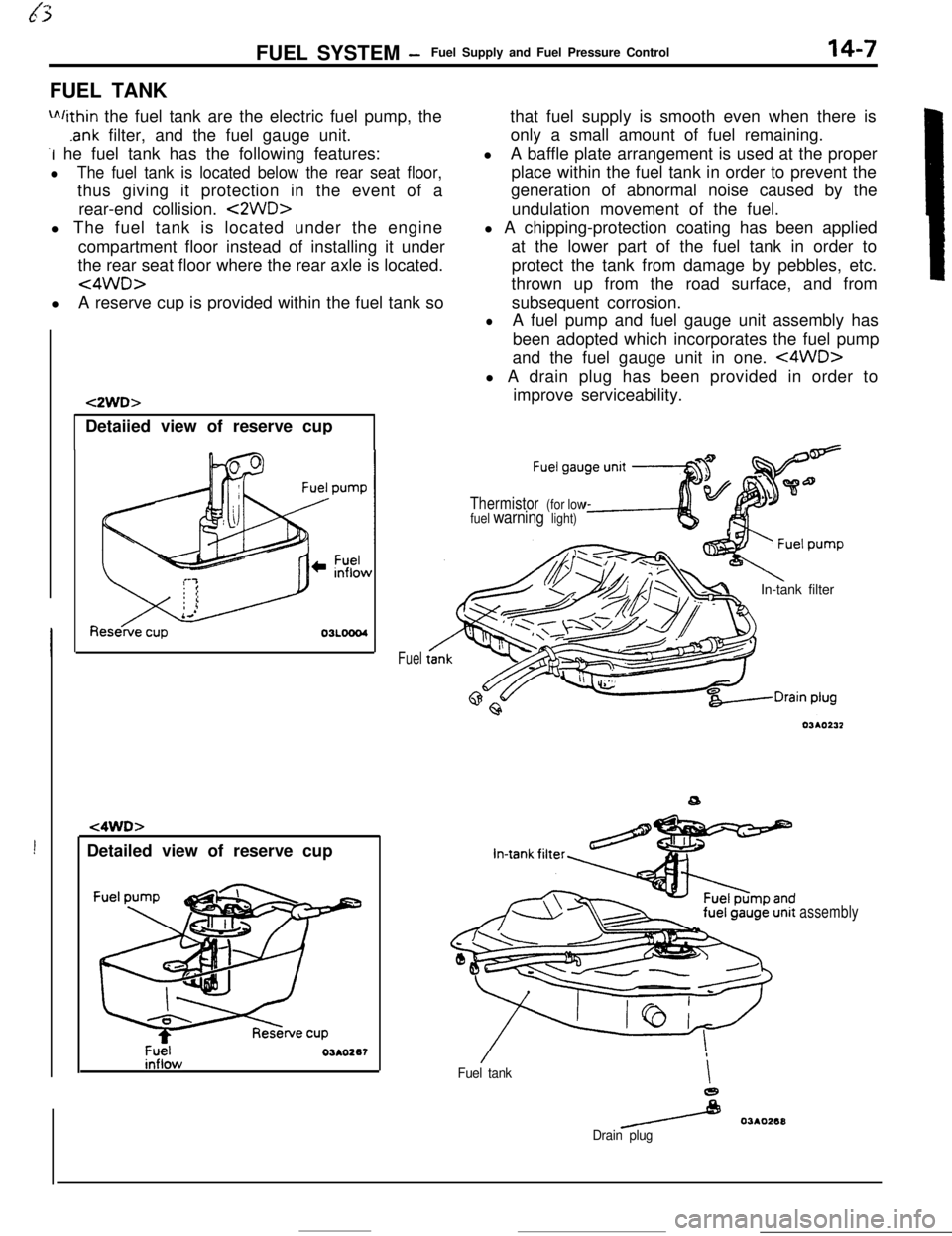
FUEL SYSTEM -Fuel Supply and Fuel Pressure Control14-7FUEL TANK
m/ithin the fuel tank are the electric fuel pump, the
.ank filter, and the fuel gauge unit.
-I he fuel tank has the following features:
lThe fuel tank is located below the rear seat floor,thus giving it protection in the event of a
rear-end collision.
<2WD>l The fuel tank is located under the engine
compartment floor instead of installing it under
the rear seat floor where the rear axle is located.
<4WD>lA reserve cup is provided within the fuel tank so
!Detailed view of reserve cup
t2WD>Detaiied view of reserve cup
t4WD>
Fuel03AO267
Fuelthat fuel supply is smooth even when there is
only a small amount of fuel remaining.
lA baffle plate arrangement is used at the proper
place within the fuel tank in order to prevent the
generation of abnormal noise caused by the
undulation movement of the fuel.
l A chipping-protection coating has been applied
at the lower part of the fuel tank in order to
protect the tank from damage by pebbles, etc.
thrown up from the road surface, and from
subsequent corrosion.
lA fuel pump and fuel gauge unit assembly has
been adopted which incorporates the fuel pump
and the fuel gauge unit in one.
<4WD>l A drain plug has been provided in order to
improve serviceability.
Thermistor (for low
fuel warning light)In-tank filter
Fuel tankI
e
/ 03AO268
Drain plug
assembly
Page 120 of 391

14-8
rFUEL SYSTEM
-Fuel Supply and Fuel Pressure Control
FUEL PUMP
This fuel pump is known as the in-tank type becauseit is located within the fuel tank itself, surrounded by
the fuel. For this reason, the pump operation noise
is well insulated, and it has excellent resistance to
vapor-locks.This type of pump is also called the “wet type”
because even its internal parts are in contact with
the fuel. With a construction that is the unification of
a ferrite-type DC motor and an impeller-type pump,
the pump itself is composed of the impeller, which
is driven by the motor, as well as the casing and the
cover. There are, in addition, a relief valve (a safety
valve for protection of the fuel-pressure circuit) and
a check valve (to maintain residual pressure).
The electric fuel pump has the following features:
l It has greater discharge pressure
mechanical-type fuel pump, as wellthan a
as lessdischarge pulsation.
lIt has a lower level of operation sound that the
electromagnetic type (Bendix type) of fuelpump.
PRESSURE-SUPPLY OF FUEL
When the impeller is caused to rotate by the motor,
a pressure differential develops at the upper. and
lower parts of the impeller, caused by the grooves in
the circumference of the impeller.
When this happens, a whirlpool effect is generated
within the fuel pump, causing the fuel pressure to
become higher, thereby causing the fuel to be
expelled from the pump chamber and to pass
through the motor, opening the check valve, and to
be discharged from the discharge port.
Discharge port
4Check!nRelief valve
DC mo
-lllll1 I/
Circum-ferential
flow pumr
II’ f-Pump
casing
J
Pumpcovert
lntakler 03R0071REWEF VALVE
If for some reason, such as an abnormal condition at the
_discharge side, the fuel were not to be discharged, the fuel
pressure within the fuel pump would become abnormally high.
Thus, when the pressure within the fuel pump reaches
450-600 kPa (64-85 psi), the relief valve opens and the
pressure escapes, so that, the fuel line pressure does not
increase to the regulated level or above.
CHECK VALVE
When the pump stops, the check valve is closed by spring
force, so that there is high pressure remaining within the fuel
line.By in this way maintaining a high pressure within the fuel line,
the restarting of the engine becomes easier, and vapor-locks at
high temperature are prevented.
-
-_..I
-~
Page 121 of 391
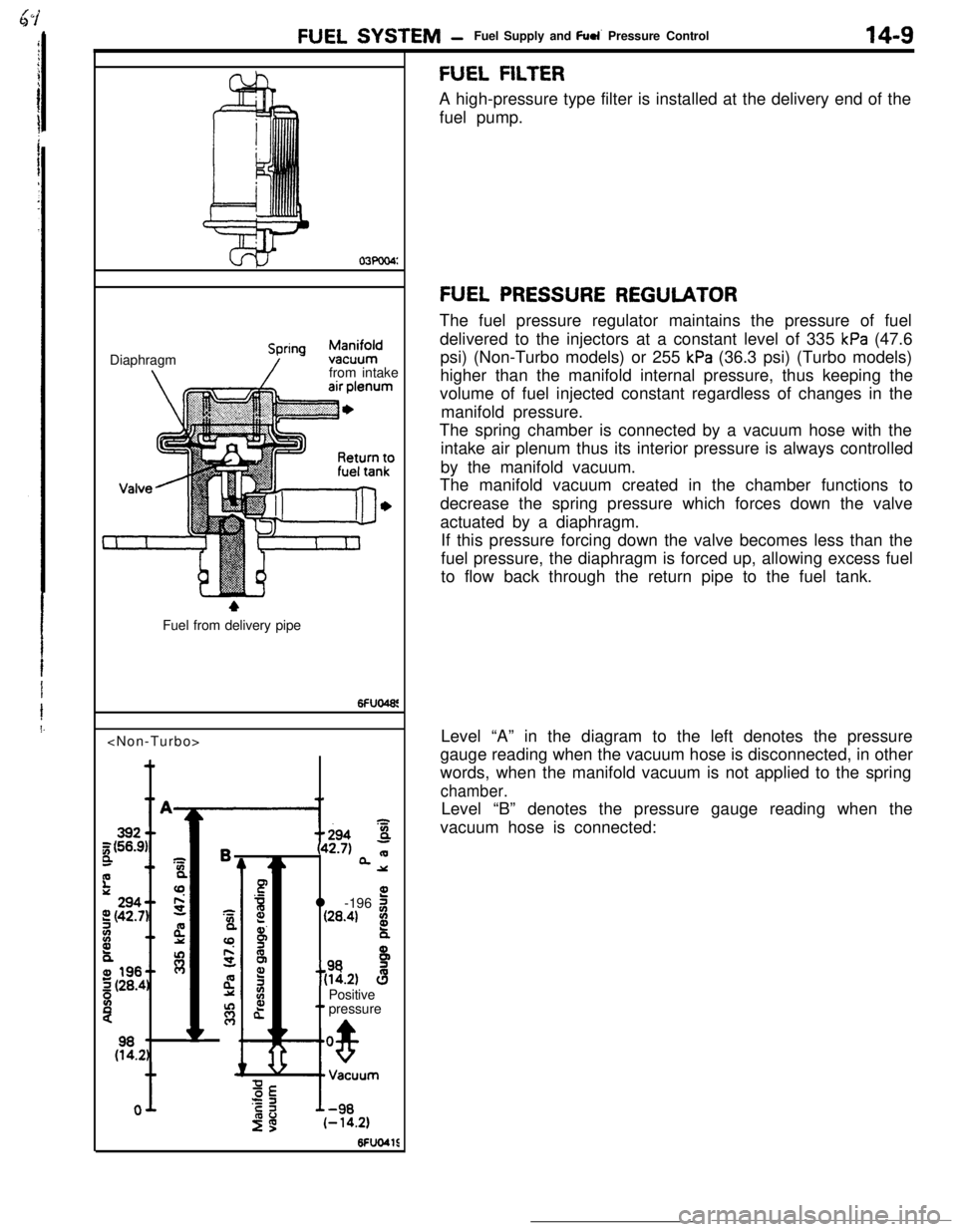
FUEL SYSTEM -Fuel Supply and Fuel Pressure Control14-9
03Poo4:Diaphragm
from intake
4Fuel from delivery pipe
4m
B(42.7)QQ
2
sl -196 2
(26.4) g
t
$!a d
9
0)Positive5 z‘. pressure
(E.2)
w
FUEL FILTERA high-pressure type filter is installed at the delivery end of the
fuel pump.
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATORThe fuel pressure regulator maintains the pressure of fuel
delivered to the injectors at a constant level of 335
kPa (47.6
psi) (Non-Turbo models) or 255
kPa (36.3 psi) (Turbo models)
higher than the manifold internal pressure, thus keeping the
volume of fuel injected constant regardless of changes in the
manifold pressure.
The spring chamber is connected by a vacuum hose with the
intake air plenum thus its interior pressure is always controlled
by the manifold vacuum.
The manifold vacuum created in the chamber functions to
decrease the spring pressure which forces down the valve
actuated by a diaphragm.
If this pressure forcing down the valve becomes less than the
fuel pressure, the diaphragm is forced up, allowing excess fuel
to flow back through the return pipe to the fuel tank.
Level “A” in the diagram to the left denotes the pressure
gauge reading when the vacuum hose is disconnected, in other
words, when the manifold vacuum is not applied to the spring
chamber.Level “B” denotes the pressure gauge reading when the
vacuum hose is connected:
Page 122 of 391

14-10
INJECTORFUEL SYSTEM
-Fuel Supply and Fuel Pressure Control
Intake port
lelivelYPipte
,FilterSpringAn injector is mounted on each of the four intake ports of the
cylinder head.
The injector is activated by electric current controlled by the
engine control unit.Wh-en current flows through the solenoid coil, the plunger and
needle valve, which form a single unit are magnetically
attracted, causing the injector nozzle to open and fuel to be
injected.When the current is interrupted, the plunger and needle valve
are pushed back by the spring, closing the injector nozzle.
Page 123 of 391

FUEL SYSTEM -Fuel Supply and Fuel Pressure Control
FUEL-PRESSURE CONTROL VALVE
14-11To fuel
-
Fuel-pressureregulatorFuel-pressurecontrol valve
Intake-airEnginecontrol
unit
Usually, the negative pressure (vacuum) of the
intake manifold is applied to the fuel-pressure
regulator, and, because the fuel pressure is thus
held at a fixed constant level relative to the pressure
within the intake manifold, the amount to fuel
injected is regulated so as to be proportional to the
injectors’ actuation time. If, however, the engine
coolant-temperature and the intake air temperature
are high when then engine is started, the engine
control unit sends a flow of current to the fuel-
pressure control valve, with the result that outside
air (atmospheric) pressure acts upon the fuel-
pressure regulator.
0Fuel ump
1chec terminal 1!Fuel pumpAs a result. the
fuel pressure is increased and the
generation of fuel vapors caused by high tem-
perature is suppressed, thereby maintaining idling
stability immediately after restarting under
high-temperature conditions.
Note that there is a return to the usual fuel pressure
level after two minutes or more have passed after
starting is completed.
In addition, the circuitry of the fuel-pressure control
valve. is interrupted, thus controlling so that the fuel
pressure corresponds to supercharging pressure,
under high-load driving conditions (during super-
charged driving by the turbocharger).
FU,EL PUMP CHECK TERMINAL
This terminal is for directly driving the fuel pump.
By applying the battery voltage directly to this terminal, you can
check fuel pump operation or check fuel leaks from the
fuel
line.
__. - ---
Page 126 of 391

14-14
.._~- ---.FUEL SYSTEM
- Sensors
SENSORSRlUGENERAL DESCRIPTION
The types and functions of the sensors are as listedsend corresponding signals to the engine control
below. These sensors detect engine conditions and
unit.
SENSORSFUNCTION
AIR FLOW SENSOR
fSenses the intake arr volume with a Karman vortex flow meter.
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSORSenses the Intake air temperature (temperature of air at
the point of entry into the air cleaner).I
BAROMETRIC PRESSURE
SENSORISenses the barometric pressure faltrtude) wrth a
semiconductor diffusion type pressure sensor.
$;;OOf;T TEMPERATURESenses the engine coolant tern
THROTTLE
POSITISenses the throttle
tI
IDLE POSITION SWITCHSenses whether or not the accelerator pedal is being
operated with a contact switch.
Senses the top dead center on compression stroke of
NO. 1 and No. 4 cylinders with an LED and photo diode pair.
CRANK ANGLE SENSORSenses the crank angle of each cylinder with an LED
and photo diodepair.
T
OXYGEN SENSORSenses
actrvation of the air con
POWER STEERING OIL
PRESSURE SWITCHc-lSenses the power steering ‘load with a contact switch.
IGNITION SWITCHSenses ON/OFF
posrtion of the ignition switch.I
Senses engine cranking.
,
IGNITION TIMING
ADJUSTMENT TERMINALWhen this terminal is shorted, the ignition timing and idle
speed control servo is set in the adjustrng mode by the enginecontrol unit.
INHIBITOR SWITCHSenses the *P” and “N” positthe automatic transaxle.Senses.
by pieto-electric element,. cylinder block
vibrations that occur when there ISengineknocking.
CONTROL RELAY
(Fuel pump drive signal)
lFnorne ianitron sianal!Senses ignrtton coil prIman/ voltage.
Page 127 of 391

FUEL SYSTEM - Sensors
AIR FLOW SENSOR
IAir
0
Power supplyAir flow sensor(from control relay)
r-- Amplifier Few
L+--J Vortex ITo throttle
bodyEngine control unit
>- Power supply
e5 volts
6FUO493
EC1537
Karman vortex
(1) Slow air flow
6FUO423
(2) Fast air flow
6Fuo42rThe air flow sensor for measuring the volume of engine intake
air uses the Karman vortex phenomenon to detect the air flow
rate. The air flow rate detected in this way is sent to the engine
control unit as data on intake air volume.
Using this signal and the engine rpm signal, the engine control
unit makes computations to determine the basic injection
timing.
A barometric pressure sensor and an intake air temperature
sensor are installed on the air flow sensor.
The air flow sensor consists of the following parts:
l Rectifier:
Rectifies the flow of intake air admitted through the air
cleaner.l Vortex generating column:
Serves to generate Karman vortices.
l Transmitter:
Transmits ultrasonic waves.
l Receiver:
Receives ultrasonic waves.
l Amplifier:
Generates ultrasonic waves.
l Modulator:
Converts ultrasonic waves that have been received into
electric pulses.
l Acoustic material
Karman Vortex
When a triangular column is placed in an air stream, regularly
spaced vortices are generated downstream alternately on
either side of the column. These vortices are called
“Karman
vortices”.The number of vortices generated is proportional to a
cloSedegree to the volume of air flow in a given time; the higher the
flow speed, the more vortices are generated.
Page 130 of 391
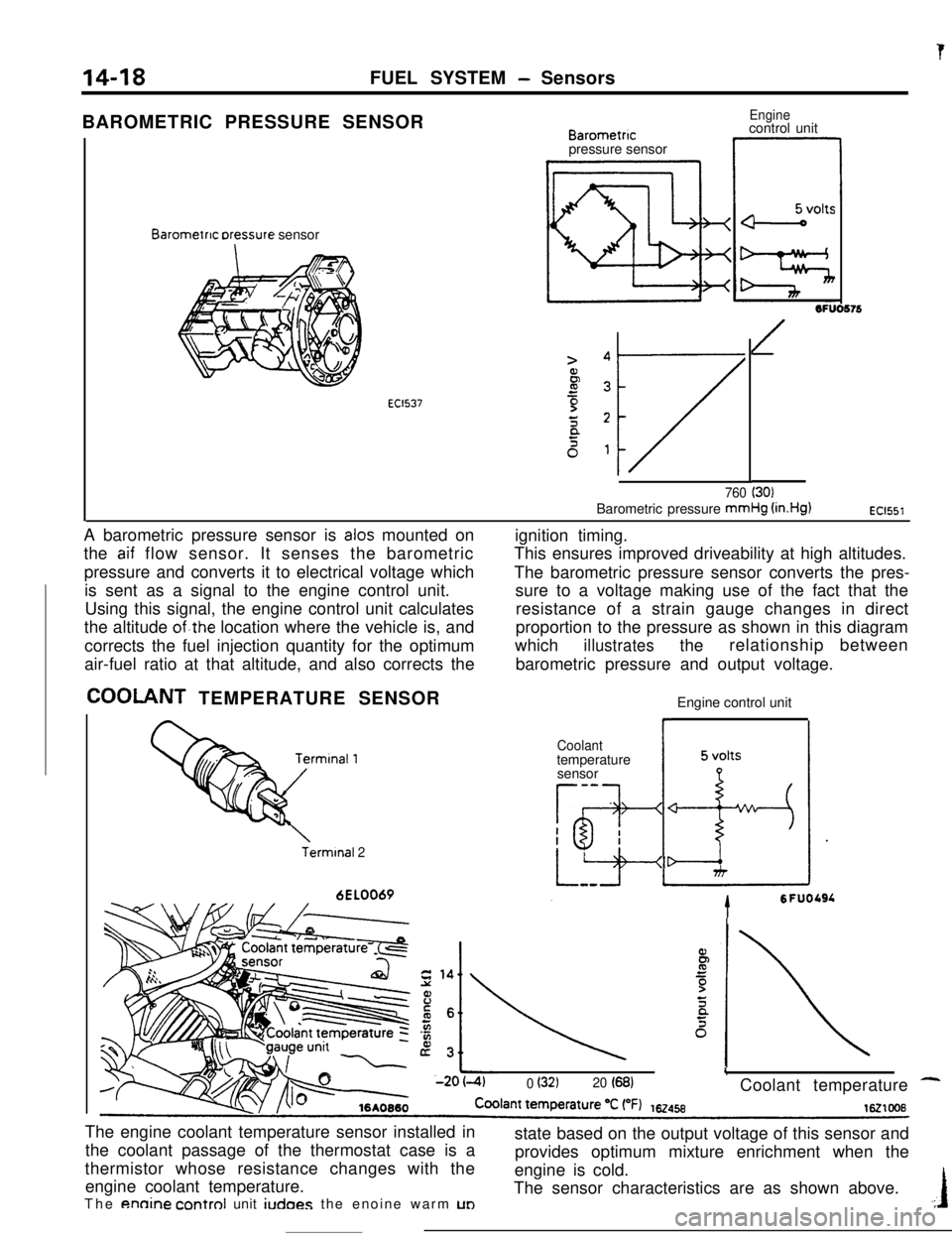
14-18FUEL SYSTEM - Sensors
tBAROMETRIC PRESSURE SENSOR
Barometnc rxessure sensor
EC1537
Barometncpressure sensor
Enginecontrol unit
1OFUO576
/
760 (30)Barometric pressure mmHg
(in.Hg)EC1551A barometric pressure sensor is
alas mounted on
the
aif flow sensor. It senses the barometric
pressure and converts it to electrical voltage which
is sent as a signal to the engine control unit.
Using this signal, the engine control unit calculates
the altitude
of.the location where the vehicle is, and
corrects the fuel injection quantity for the optimum
air-fuel ratio at that altitude, and also corrects the
COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Terminal 26EL0069ignition timing.
This ensures improved driveability at high altitudes.
The barometric pressure sensor converts the pres-
sure to a voltage making use of the fact that the
resistance of a strain gauge changes in direct
proportion to the pressure as shown in this diagram
which
illustratestherelationship between
barometric pressure and output voltage.
Engine control unit
Coolanttemperature
sensor
-a
Tg-I
h-esI
*
LizIdr
tSFUOLSL
L0 (32120 (68)Coolant temperature -The engine coolant temperature sensor installed in
the coolant passage of the thermostat case is a
thermistor whose resistance changes with the
engine coolant temperature.
The
annine control unit iudoes the enoine warm UDstate based on the output voltage of this sensor and
provides optimum mixture enrichment when the
engine is cold.
The sensor characteristics are as shown above..:I