1988 OPEL CALIBRA coolant
[x] Cancel search: coolantPage 194 of 525

pitting. If evident, the cylinder head and all
bearing caps must be renewed as a matched
set, as there is no provision for refacing if the
bearing caps cannot be renewed individually.
8The camshaft(s) should show no marks or
scoring on the journal or cam lobe surfaces. if
evident, renew the camshaft(s).
9It is advisable to renew the camshaft front
oil seal(s) as a matter of course. Prise the old
seal(s) from the front of the camshaft(s) and
discard them.
Refitting
10Begin refitting by liberally coating the
contact faces of the hydraulic valve lifters and
the camshaft(s) with molybdenum disulphide
paste.
11Coat the mating faces of the front and
rear bearing caps with sealing compound and
refit the bearing caps in their original positions
as noted during removal.
12Tighten the camshaft bearing cap nuts to
the specified torque in half-turn stages, as
when loosening the nuts. Note that when
refitting the exhaust camshaft, the two smaller
rear bearing cap securing nuts should be
tightened after all the main camshaft bearing
cap nuts have been tightened. Note also that
the two smaller nuts should be tightened to a
lower torque wrench setting than the main
nuts.
13Turn the camshaft until the locating peg
for the camshaft sprocket is uppermost, then
lubricate the lips of a rear camshaft front oil
seal with a little grease, and fit the oil seal,
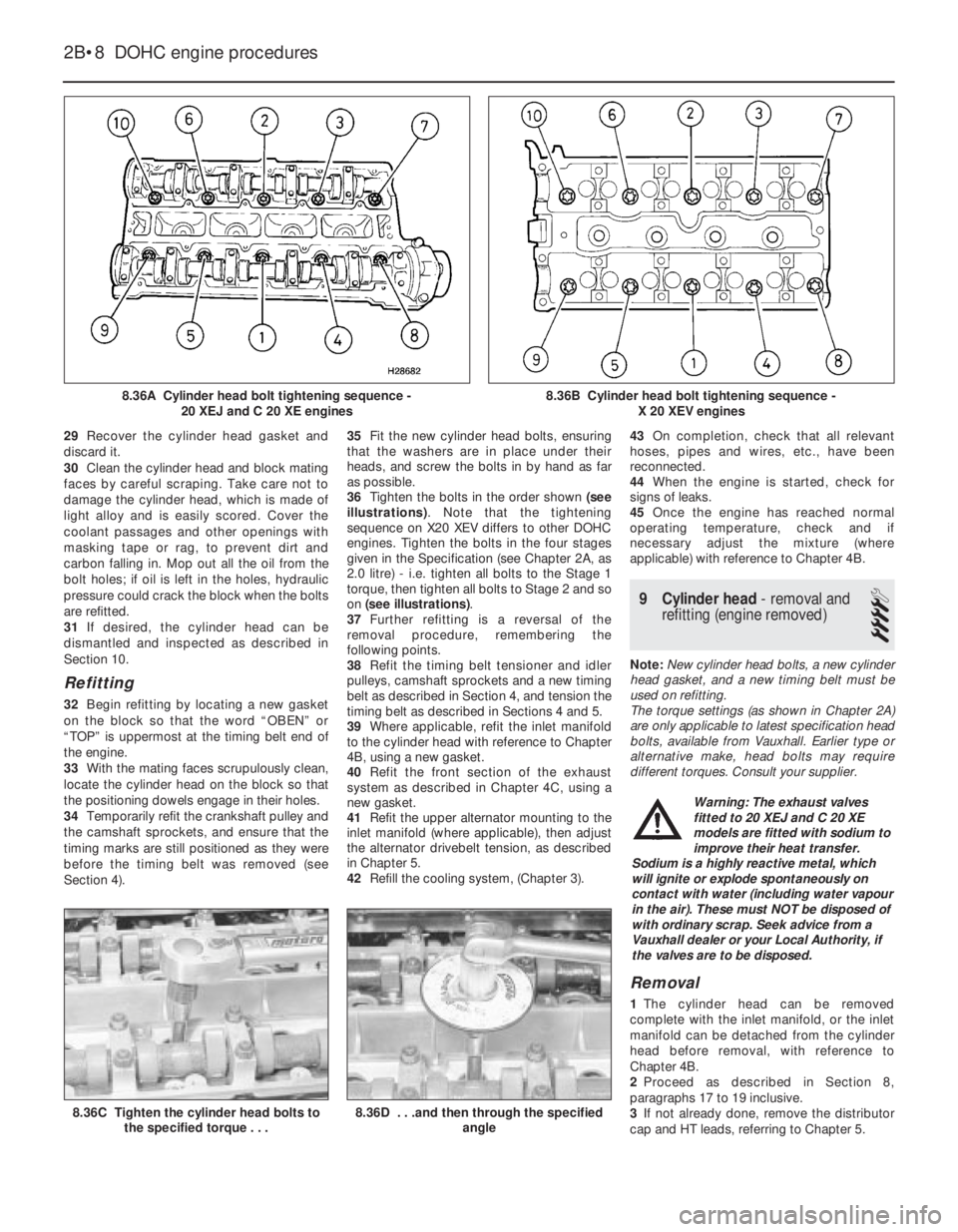
using a tube or socket of similar diameter with
a washer and the camshaft sprocket bolt.
Screw the camshaft sprocket bolt into the end
of the camshaft to draw the oil seal into
position on its shoulder.
14Repeat the procedure for the remaining
camshaft.
15Refit the distributor with reference to
Chapter 5. Fit a new timing belt and the
camshaft sprockets, then adjust the timing
belt as described in Section 4 or 5, as
applicable.
8Cylinder head -removal and
refitting (engine in vehicle)
4
Note: The engine must be cold when the
cylinder head is removed. Do not remove the
cylinder head from a hot engine. New cylinder
head bolts, a new cylinder head gasket and a
new timing belt must be used on refitting.
The torque settings (as shown in Chapter 2A)
are only applicable to latest specification head
bolts, available from Vauxhall. Earlier type or
alternative make, head bolts may require
different torques. Consult your supplier
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Drain the cooling system, as described in
Chapter 3.3Remove the front section of the exhaust
system, as described in Chapter 4C.
4The cylinder head can be removed
complete with the inlet manifold, or the inlet
manifold can be detached from the cylinder
head before removal, with reference to
Chapter 4B. If no work is to be carried out on
the inlet manifold, it can be unbolted from the
cylinder head and supported to one side out
of the way, thus avoiding the need to
disconnect the relevant hoses, pipes and
wiring.
5If the cylinder head is to be removed
complete with the inlet manifold, disconnect
all relevant hoses, pipes and wiring from the
inlet manifold and associated components,
referring to Chapter 4B, and unbolt the
manifold support bracket from the manifold.
Loosen the alternator mountings with
reference to Chapter 5, then unbolt the upper
alternator mounting from the inlet manifold.
6If the inlet manifold is to be left in the engine
compartment, continue as follows, otherwise
go on to paragraph 17.
7Disconnect the wiring plug from the airflow
meter, and the breather hose from the air box
on the throttle body. Disconnect the air
cleaner trunking and remove the airflow
meter/air box assembly from the throttle
body. Refer to Chapter 4B if necessary.
8Disconnect the end of the throttle cable
from the throttle valve lever, then unbolt the
throttle cable support bracket and remove it
from the inlet manifold.
9Unscrew the two earth lead securing nuts
from the fuel rail (one at each end of the rail)
and disconnect the three earth leads.
10Disconnect the wiring plug from the
throttle position switch.
11Pull up on the wiring harness housing, and
disconnect the wiring plugs from the fuel
injectors by compressing the retaining clips.
Move the wiring harness housing to one side.
12Disconnect the two breather hoses from
the rear of the camshaft cover.
13Loosen the alternator mountings, with
reference to Chapter 5, then unbolt the upper
alternator mounting from the inlet manifold.
14Unbolt the manifold support bracket from
the manifold.15Make a final check to ensure that all
necessary hoses, pipes and wires have been
disconnected, then unscrew the securing nuts
and lift the inlet manifold from the cylinder
head. Ensure that the manifold is properly
supported, taking care not to strain any of the
hoses, pipes and wires, etc., which are still
connected.
16Recover the manifold gasket from the
cylinder head.
17Remove the timing belt, camshaft
sprockets, and timing belt tensioner and idler
pulleys, as described in Section 4.
18Unscrew the upper and middle studs for
the timing belt outer cover screws. Note that
the upper stud simply unscrews from the
cylinder head, but the middle stud is secured
by a bolt.
19Unscrew the two upper rear timing belt
cover securing bolts from the cylinder head.
20Remove the distributor cap and HT leads
with reference to Chapter 5.
21Disconnect the distributor wiring plug.
22Disconnect the coolant hose from the
left-hand end of the cylinder head.
23Unscrew the bolt securing the crankcase
breather tube bracket to the end of the
cylinder head.
24Disconnect the radiator top hose from the
thermostat housing, and disconnect the
wiring plugs from the temperature gauge
sender and the coolant temperature sensor
(both situated in the thermostat housing).
25Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant hoses, pipes and wires have been
disconnected.
26On X20 XEV models, remove the
camshaft, as described in Section 7.
27Using a Torx socket, and working in the
order shown (see illustrations), loosen all the
cylinder head bolts by a quarter of a turn, then
loosen all the bolts by half a turn, and finally
loosen and remove the bolts. Recover the
washers. Note that the loosening sequence
on X20 XEV differs to other DOHC engines.
28Lift the cylinder head from the cylinder
block. If necessary, tap the cylinder head
gently with a soft-faced mallet to free it from
the block, but do not lever at the mating
faces. Note that the cylinder head is located
on dowels.
DOHC engine procedures 2B•7
8.27B Cylinder head bolt loosening
sequence - (X 20 XEV engines)8.27A Cylinder head bolt loosening
sequence - (20 XEJ and C 20 XE engines)
2B
Page 195 of 525
29Recover the cylinder head gasket and
discard it.
30Clean the cylinder head and block mating
faces by careful scraping. Take care not to
damage the cylinder head, which is made of
light alloy and is easily scored. Cover the
coolant passages and other openings with
masking tape or rag, to prevent dirt and
carbon falling in. Mop out all the oil from the
bolt holes; if oil is left in the holes, hydraulic
pressure could crack the block when the bolts
are refitted.
31If desired, the cylinder head can be
dismantled and inspected as described in
Section 10.
Refitting
32Begin refitting by locating a new gasket
on the block so that the word “OBEN” or
“TOP” is uppermost at the timing belt end of
the engine.
33With the mating faces scrupulously clean,
locate the cylinder head on the block so that
the positioning dowels engage in their holes.
34Temporarily refit the crankshaft pulley and
the camshaft sprockets, and ensure that the
timing marks are still positioned as they were
before the timing belt was removed (see
Section 4).35Fit the new cylinder head bolts, ensuring
that the washers are in place under their
heads, and screw the bolts in by hand as far
as possible.
36Tighten the bolts in the order shown (see
illustrations). Note that the tightening
sequence on X20 XEV differs to other DOHC
engines. Tighten the bolts in the four stages
given in the Specification (see Chapter 2A, as
2.0 litre) - i.e. tighten all bolts to the Stage 1
torque, then tighten all bolts to Stage 2 and so
on (see illustrations).
37Further refitting is a reversal of the
removal procedure, remembering the
following points.
38Refit the timing belt tensioner and idler
pulleys, camshaft sprockets and a new timing
belt as described in Section 4, and tension the
timing belt as described in Sections 4 and 5.
39Where applicable, refit the inlet manifold
to the cylinder head with reference to Chapter
4B, using a new gasket.
40Refit the front section of the exhaust
system as described in Chapter 4C, using a
new gasket.
41Refit the upper alternator mounting to the
inlet manifold (where applicable), then adjust
the alternator drivebelt tension, as described
in Chapter 5.
42Refill the cooling system, (Chapter 3).43On completion, check that all relevant
hoses, pipes and wires, etc., have been
reconnected.
44When the engine is started, check for
signs of leaks.
45Once the engine has reached normal
operating temperature, check and if
necessary adjust the mixture (where
applicable) with reference to Chapter 4B.
9Cylinder head -removal and
refitting (engine removed)
4
Note: New cylinder head bolts, a new cylinder
head gasket, and a new timing belt must be
used on refitting.
The torque settings (as shown in Chapter 2A)
are only applicable to latest specification head
bolts, available from Vauxhall. Earlier type or
alternative make, head bolts may require
different torques. Consult your supplier.
Removal
1The cylinder head can be removed
complete with the inlet manifold, or the inlet
manifold can be detached from the cylinder
head before removal, with reference to
Chapter 4B.
2Proceed as described in Section 8,
paragraphs 17 to 19 inclusive.
3If not already done, remove the distributor
cap and HT leads, referring to Chapter 5.
2B•8DOHC engine procedures
8.36A Cylinder head bolt tightening sequence -
20 XEJ and C 20 XE engines
8.36C Tighten the cylinder head bolts to
the specified torque . . .8.36D . . .and then through the specified
angle
8.36B Cylinder head bolt tightening sequence -
X 20 XEV engines
Warning: The exhaust valves
fitted to 20 XEJ and C 20 XE
models are fitted with sodium to
improve their heat transfer.
Sodium is a highly reactive metal, which
will ignite or explode spontaneously on
contact with water (including water vapour
in the air). These must NOT be disposed of
with ordinary scrap. Seek advice from a
Vauxhall dealer or your Local Authority, if
the valves are to be disposed.
Page 203 of 525

Torque wrench settings (continued)Nmlbf ft
Big-end bearing cap: *
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3526
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 45º
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 15º
Camshaft housing cover to housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Camshaft pulley to camshaft . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4533
Camshaft thrust plate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Coolant outlet to thermostat housing:
C 16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Coolant pump to cylinder block:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C 16 NZ2) (M6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre (M8) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Crankshaft sensor wheel:
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1310
Cylinder head to cylinder block: *
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2):
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 60º
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 60º
Stage 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 60º
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 90º
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 90º
Stage 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 90º
Drivebelt (ribbed) pulley/timing belt drive to crankshaft: *
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2):
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5541
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 45º
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 15º
Drivebelt pulley to timing belt drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
Drivebelt (ribbed) tensioner to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
Drivebelt (ribbed) tensioner to support:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1813
Engine bracket to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6044
Engine bracket to transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6044
Engine mounting bracket to engine bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6044
Engine mounting to engine mounting bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6548
Engine mounting to front axle housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4030
Engine mounting to power steering pump support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6044
Engine mounting to side member . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6548
Exhaust manifold to cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2216
Exhaust pipe to manifold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Flexplate to crankshaft . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6044
Flywheel to crankshaft: *
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2):
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3526
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 30º
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 15º
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6548
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 30º
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 15º
Front timing belt cover to rear cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Fuel pump to camshaft housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1813
Guide sleeve, release bearing to transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2216
Heat shield sleeves to cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3022
Inlet manifold to cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2216
Knock sensor to cylinder block (X16 SZ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1310
Main bearing cap: *
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5037
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 45º
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 15º
Oil filter to oil pump/cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
2A•6SOHC engine procedures
Page 204 of 525

Oil pick-up pipe bracket to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Oil pick-up pipe to oil pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Oil pipes to radiator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2216
Oil pressure switch to oil pump:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3022
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4030
Oil pressure relief valve to oil pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3022
Oil pump cover to oil pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Oil pump to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Oxygen sensor to exhaust manifold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3022
Power steering pump bracket to support:
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1813
Power steering pump to support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Right engine mounting to subframe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6548
Shackle to alternator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Spark plugs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Starter to cylinder block (M10) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4533
Starter to cylinder block (M12) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6044
Sump:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1511
Sump drain plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5541
Support to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3526
Temperature sender to cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
Thermostat housing:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .107
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1511
Timing belt tensioner to oil pump:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5541
Timing belt cover to oil pump/camshaft housing:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .129
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Timing belt drive gear to crankshaft:
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13096
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by between 40º to 50º
Transmission to engine (M10) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4533
Transmission to engine (M12) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6044
1General description
General
The engine is of four-cylinder, in-line single
or double overhead camshaft type (depending
on model), mounted transversely at the front
of the vehicle.
The crankshaft runs in five shell-type
bearings, and the centre bearing incorporates
a thrust bearing shell to control crankshaft
endfloat.
The connecting rods are attached to the
crankshaft by horizontally split shell-type
big-end bearings. On single overhead
camshaft (SOHC) models, the pistons are
attached to the connecting rods by gudgeon
pins, which are an interference fit in the
connecting rod small-end bore. The
aluminium alloy pistons are fitted with three
piston rings: two compression rings and an oil
control ring.
The camshaft on SOHC engines is driven
from the crankshaft by a toothed composite
rubber belt. Each cylinder has two valves (oneinlet and one exhaust), operated through
rocker arms that are supported at their pivot
ends by hydraulic self-adjusting valve lifters
(tappets).
The inlet and exhaust valves are each
closed by a single valve spring, and operate in
guides pressed into the cylinder head.
A gear-type oil pump is located in a housing
attached to the front of the cylinder block, and
is driven directly from the crankshaft. A
full-flow type oil filter is fitted.
The distributor is driven directly from the
end of the camshaft. On carburettor models,
the mechanical fuel pump is operated from
the front end of the camshaft. The coolant
pump is located at the front of the cylinder
block, and is driven by the timing belt.
Chapter 2A describes the SOHC engine
repair procedures. Many repairs and specifi-
cations to the DOHC engine are similar to the
2.0 litre SOHC. However where they differ,
details can be found in Chapter 2B.
Engine identification codes -
general
Before ordering spare parts, or carrying out
any repair or overhaul operations on the
engine, it is essential to identify the exactengine type being worked on. Later engines,
although outwardly similar in appearance,
often have significant differences in repair
procedures, even though they may be of the
same displacement and model year.
The following sub-Sections in this Chapter
are mainly specific to engine type, as will be
noted from the sub-Section headings. Check
the engine identification code first, which is
located on a horizontal surface on the exhaust
manifold side of the cylinder block, at the
distributor end. On later engines, the code is
on the cylinder block-to-transmission flange,
next to the engine oil dipstick.
2Crankcase ventilation
system - description and
maintenance
2
Description
1A crankcase ventilation system is fitted to
all models, but the systems differ in detail
depending on the model concerned.
2Oil fumes and blow-by gases (combustion
gases that have passed by the piston rings)
are drawn from the crankcase into the area of
SOHC engine procedures 2A•7
2A
Page 205 of 525

the cylinder head above the camshaft(s)
through a hose. From here the gases are
drawn into the inlet manifold/throttle body (as
applicable) and/or the air box on the
carburettor (where applicable), where they are
re-burnt with fresh air/fuel mixture, hence
reducing harmful exhaust emissions.
Maintenance
3Certain models have a mesh filter inside the
camshaft cover, which should be cleaned in
paraffin if clogging is evident (see
illustration).
4On high mileage vehicles, particularly when
regularly used for short journeys, a jelly-like
deposit may be evident inside the crankcase
ventilation system hoses. If excessive
deposits are present, the relevant hose(s)
should be removed and cleaned.
5Periodically inspect the system hoses for
security and damage, and renew as
necessary. Note that damaged or loose hoses
can cause various engine running problems
that can be difficult to trace.
6The crankcase breather/dipstick tube can
be unbolted from the cylinder block after
disconnecting the hose. Use a new gasket
when refitting.
3Compression test -
description
3
Description
1If engine performance is poor, or if misfiring
occurs which cannot be attributed to the
ignition or fuel system, a compression test
can provide diagnostic clues. If the test is
performed regularly, it can give warning of
trouble on a high mileage engine before any
other symptoms become apparent.
2The engine must be at operating
temperature, the battery must be fully
charged, and the spark plugs must be
removed. The help of an assistant will also be
required.
3Disable the ignition system by
disconnecting the coil LT (“+15”) wire. Fit the
compression tester to No 1 cylinder spark
plug hole.4Have the assistant hold the throttle wide
open and crank the engine on the starter.
Record the highest reading obtained on the
compression tester.
5Repeat the test on the remaining cylinders,
recording the pressure developed in each.
6The difference in pressure between any two
cylinders should be no more than 1.0 bar
(14.5 lbf/in2). If the pressure in any cylinder is
low, pour a teaspoonful of clean engine oil
into the spark plug hole, and repeat the test.
7If the addition of oil temporarily improves
the compression pressure, this indicates that
cylinder bore or piston ring wear was
responsible for the pressure loss. No
improvement suggests that leaking or burnt
valves, or a blown head gasket may be to
blame.
8A low reading from two adjacent cylinders
is almost certainly due to the head gasket
leaking between them.
9On completion of the test, refit the spark
plugs and reconnect the coil LT wire.
4Major operations possible
with the engine in the vehicle
1The following operations may be carried out
without removing the engine from the vehicle:
a)Removal and refitting of oil pressure relief
valve (see Section 30)
b)Removal and refitting of timing belt and
sprockets
c)Removal and refitting of camshaft housing
(SOHC engines)
d)Removal and refitting of camshaft(s)
e)Removal and refitting of cylinder head
f)Removal and refitting of sump
g)Removal and refitting of oil pump
h)Removal and refitting of
piston/connecting rod assemblies
i)Removal and refitting of flywheel
j)Renewal of crankshaft front oil seal
k)Removal and refitting of
engine/transmission mountings
Note: It is possible to renew the crankshaft
rear oil seal with the engine in the vehicle, but
this requires the use of special tools, and is a
difficult operation, due to the lack of working
space. For this reason, this operation is
described with the engine removed from the
vehicle.
5Major operations requiring
engine removal
The engine must be removed from the
vehicle to carry out the following operations:
a)Renewal of the crankshaft main bearings
b)Removal and refitting of the crankshaft
c)Renewal of crankshaft rear oil seal
6Method of engine removal
The engine may be removed either on its
own, or together with the transmission. Unless
work is also necessary on the transmission, it
is recommended that the engine is removed
on its own. In either case, the engine or
engine/transmission assembly must be lifted
out through the top of the engine
compartment, using a hoist and lifting tackle.
7Engine - removal and refitting,
(leaving transmission in car)
4
Note: A hoist and lifting tackle will be required
for this operation.If the torque converter is
removed (even partially) from the transmission,
a considerable amount of the fluid inside it will
leak out. To prevent this, when prising the
engine from the transmission and removing it,
be careful to keep the torque converter
pressed firmly into the transmission. If the
transmission is to be removed for some time,
retain the torque converter by bolting a strip of
metal across the bellhousing mating surface.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the bonnet (Chapter 11).
3Apply the handbrake, then jack up the front
of the vehicle, and support securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”).
4Drain the cooling system, remove the
radiator and transmission fluid cooler hoses
(automatic models), as described in Chapter 3.
5Drain the engine oil as described in Chapter 1,
remove the oil filter and discard, safely.
6Remove the air cleaner (or air cleaner
cover), the air cleaner trunking, and the air
box from the carburettor or throttle body (as
applicable), referring to Chapter 4A or 4B, if
necessary. On carburettor models,
disconnect the hot air hose from the exhaust
manifold hot air shroud and the air cleaner,
and remove the hose. On automatic models,
disconnect additional wiring, hoses, etc., from
the carburettor, as described in Chapter 4A.
7Remove the alternator, as described in
Chapter 5.
8On models with power steering, remove the
hydraulic pump, as described in Chapter 10.
9Disconnect the brake servo vacuum hose
from the inlet manifold.
10Disconnect the throttle cable from the
throttle lever and the bracket on the
carburettor or inlet manifold, as applicable.
11On carburettor models, disconnect the
coolant hoses from the automatic choke
housing, and disconnect the wiring from the
automatic choke heater and the choke
pull-down solenoid (see illustrations). Also
disconnect the air box vacuum pipe from the
carburettor.
2A•8SOHC engine procedures
2.3 Crankcase ventilation filter removed
from camshaft cover -
1.6 litre engine
Page 206 of 525
12Disconnect the pressure sensor vacuum
pipe from the carburettor (see illustration).
13Remove the coolant hose(s) from the inlet
manifold and/or throttle body, as applicable.
14Disconnect the fuel hoses from the fuel
pump and vapour separator on carburettor
models or from the fuel pipes at the
right-hand side of the engine compartment on
other models. Be prepared for fuel spillage,
and take adequate fire precautions. Plug the
open ends of the pipes and hoses, to prevent
dirt ingress and further fuel leakage (see
illustrations).
15Disconnect all relevant wiring connections
and plugs, and remove the fuel injection
wiring harness. Pull up on the wiring harness
housing, and compress the wiring plug
retaining clips to release the harness housing
from the fuel injectors (see illustration).16Disconnect the heater coolant hoses from
the coolant gallery at the rear of the cylinder
block.
17Disconnect the wiring from the following
components (where applicable):
a)Starter motor
b)Distributor (note HT lead positions)
c)Oil pressure switch
d)Oil temperature switch
e)TDC sensor
f)Oil level sensor
g)Knock sensor
h)Coolant temperature sensor
i)Temperature gauge sender
18Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant hoses, pipes and wires have been
disconnected, and that they are positioned
clear of the engine.
19Remove the front section of the exhaust
system, as described in Chapter 4C.
20Unbolt and remove the bellhousing cover
plate (see illustration).
21Remove the clutch (if applicable), as
described in Chapter 6. On automatic models,
use chalk or a felt-tip pen to mark the
relationship of the torque converter to the
flexplate before unbolting the torque converter.
Refer to note at the beginning of this Section
and to Chapter 7B for further information.
22Remove the crankshaft pulley. Some
pulleys are secured by four bolts, which must
be unscrewed using an Allen key or hexagon
bit. Unscrew each of the three bolts in turn
and remove them. On other engines, the
pulley is secured by a single bolt, which alsosecures the crankshaft sprocket. On manual
transmission models, if the engine is in the
vehicle, the crankshaft can be prevented from
turning by having an assistant engage first
gear and depress the brake pedal.
Alternatively, the flywheel (or flexplate, on
automatics), ring gear teeth can be jammed,
through the bellhousing cover aperture using
a large screwdriver, or similar tool. Access to
the crankshaft pulley is most easily obtained
through the right-hand wheel arch, after
removing the roadwheel.
23Attach a hoist and lifting gear to the
engine lifting brackets on the cylinder head,
and support the weight of the engine.
24Unscrew and remove two of the three
upper engine-to-transmission bolts,
accessible from the engine compartment,
leaving one fastened for safety.
25Unbolt the right-hand engine mounting
from the body and from the cylinder block,
and withdraw the mounting bracket.
26Unscrew and remove the four lower
engine-to-transmission bolts.
27Support the transmission using a trolley
jack and interposed block of wood. Remove
the last upper transmission bolt.
28Manipulate the engine as necessary to
separate it from the transmission. Note that
the transmission locates on dowels in the
cylinder block.
29Carefully raise the hoist, and lift the
engine from the vehicle, taking care not to
damage any of the surrounding components
in the engine compartment.
SOHC engine procedures 2A•9
7.12 Disconnect the pressure sensor
vacuum pipe from the carburettor -
1.6 litre model
7.20 Removing the transmission
bellhousing cover plate7.15 Removing the fuel injection wiring
harness -
2.0 litre SOHC model7.14B Fuel hose-to-pipe connections at
right-hand side of engine compartment -
2.0 litre SOHC model
7.14A Disconnecting a fuel hose from the
fuel pump - 1.6 litre model
7.11B . . .and disconnect the choke
heater/pull-down solenoid wiring plug -
1.6 litre model7.11A Disconnect the coolant hoses from
the automatic choke housing . . .
2A
Page 210 of 525
a)Inlet and exhaust manifolds (where
applicable)
b)Starter motor
c)Rear coolant gallery and hoses
d)Oil pressure switch
e)Oil temperature switch (where applicable)
f)Oil level sensor (where applicable)
g)Knock sensor (where applicable)
h)TDC sensor (where applicable)
i)Distributor components
j)Fuel pump (where applicable)
k)Thermostat/housing (N 16 NZ2, 1.8 and
2.0 litre models)
l)Power steering pump and mounting
bracket (where applicable)
m)Alternator mounting bracket
n)Engine lifting brackets
o)Dipstick/crankcase breather tube
p)Inlet manifold mounting bracket (where
applicable)
13To ensure maximum life, with minimum
trouble, from a rebuilt engine, not only must
everything be correctly assembled, but it must
also be spotlessly clean. All oilways and
coolant passages must be clear, and all
washers must be fitted in their original
positions. Oil all bearings and other moving
surfaces thoroughly with clean engine oil
during assembly.
14Before assembly begins, renew any bolts
or studs with damaged threads.
15Obtain a torque wrench, an angle-torque
gauge, sockets and bits, an oil can, clean
lint-free rag, and a set of engine gaskets and
oil seals, together with a new oil filter.16If they have been removed, new cylinder
head bolts, flywheel bolts, big-end bearing
cap bolts and main bearing cap bolts will also
be required.
17On completion of reassembly, refit the
applicable ancillary components listed in
paragraph 12.
18Follow procedure shown in Section 37.
11Timing belt and sprockets
(without automatic tensioner) -
removal, refitting and adjustment
3
Note: A two-legged puller may be required to
remove the crankshaft sprocket on N 16 NZ2,
1.8 and 2.0 litre models.Some of the later 1.4
and 1.6 litre engines, identifiable by the
squared-off top surfaces of the timing belt
covers, are fitted with spring-loaded auto-matic timing belt tensioners to ensure correct
belt tensioning on assembly.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2On models with power steering, remove the
pump drivebelt, see Chapters 1 and 10.
3Remove the alternator drivebelt, as
described in Chapter 5.
4On C 16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models,
disconnect the wiring from the temperature
gauge sender.
5Release the securing clips (or hexagon-
headed screws, if fitted), and remove the main
outer timing belt cover, then unclip the smaller
outer timing belt cover from the coolant pump.
Where applicable, three screws retain the lower
(small) outer cover to the rear cover, the fourth
secures the tensioner (see illustrations).
6On 1.6 litre models with power steering,
remove the power steering pump, as
described in Chapter 10.
7Turn the crankshaft using a socket or
spanner on the crankshaft sprocket bolt, until
the timing mark on the camshaft sprocket is
aligned with the notch in the rear timing belt
cover, and the notch in the crankshaft pulley
is aligned with the pointer on the rear timing
belt cover (see illustrations). Note that on 1.4
litre engine there are two notches in the
crankshaft pulley, representing 5°and 10°
BTDC, and the 10°BTDC notch should be
aligned with the pointer (see illustration).
8Loosen the three coolant pump securing
bolts (see illustration), and turn the pump to
relieve the tension in the timing belt, then slide
the belt from the camshaft sprocket.
SOHC engine procedures 2A•13
11.5C Timing belt lower (small) outer
cover screws (A), tensioner screw (B),
ignition timing fixed reference mark (C)
11.8 Loosening a coolant pump securing
bolt - 2.0 litre engine11.7C Crankshaft pulley 10°BTDC notch
aligned with pointer on rear timing belt
cover - 1.4 litre engine11.7B . . .and notch in crankshaft pulley
aligned with pointer on rear timing belt
cover - 2.0 litre engine
11.7A Camshaft sprocket TDC mark
aligned with notch in rear timing belt
cover . . .
11.5B . . .and the smaller cover from the
coolant pump - 2.0 litre engine11.5A Remove the main outer timing belt
cover . . .
2A
Page 211 of 525

9The crankshaft pulley must now be
removed. On 1.4 and 1.6 litre engines (except
C 16 NZ2), the pulley is secured by a single
bolt, which also secures the crankshaft
sprocket. On C 16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre
engines, the pulley is secured by four bolts,
which must be unscrewed using an Allen key
or hexagon bit. On manual transmission
models, if the engine is in the vehicle, the
crankshaft can be prevented from turning by
having an assistant engage first gear and
depress the brake pedal. Alternatively, the
flywheel ring gear teeth can be jammed using
a large screwdriver or similar tool.
10With the crankshaft pulley removed, the
timing belt can be withdrawn.
11If desired, the sprockets and the rear
timing belt cover can be removed as follows,
otherwise go on to paragraph 23.
12To remove the camshaft sprocket, firstdisconnect the breather hose(s) from the
camshaft cover, then unscrew the securing
bolts noting the locations of the HT lead
brackets and any other wiring brackets, and
remove the camshaft cover.
13Recover the gasket. Prevent the camshaft
from turning by holding it with a spanner on
the flats provided between No’s 3 and 4
camshaft lobes, and unscrew the camshaft
sprocket bolt.
14Withdraw the sprocket from the end of the
camshaft.
15To remove the crankshaft sprocket on 1.4
and 1.6 litre engines (except C 16 NZ2), if
necessary, remove the lower securing bolts
from the main rear timing belt cover and use
two large screwdrivers behind the cover to
lever off the sprocket. Remove the Woodruff
key if it is loose.
16To remove the crankshaft sprocket on C
16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre engines, it will benecessary to prevent the crankshaft from
turning, as described in paragraph 9. Take
care when unscrewing the sprocket bolt, as it
is very tight. If necessary, use a two-legged
puller to remove the sprocket. Recover the
Woodruff key and the thrustwasher from the
end of the crankshaft.
17To remove the main rear timing belt cover
on C 16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models
disconnect the TDC sensor wiring plug and
unclip the wiring from the belt cover. Then
unscrew the two upper securing bolts and the
lower securing bolt(s) (one in the case of C 16
NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre engines, two on other
SOHC engines). Withdraw the cover,
manipulating it from the smaller rear belt
cover on the coolant pump (see illustrations).
18If desired, the smaller rear belt cover can
be removed from the coolant pump, after
unscrewing the securing bolt (see
illustration), by rotating it to disengage it from
the retaining flange on the pump.
Refitting
19Refit the rear timing belt cover(s) using a
reversal of the removal procedure, and
ensuring that the main cover engages correctly
with the smaller cover on the coolant pump.
20On C 16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre engines,
refit the thrustwasher and the Woodruff key to
the end of the crankshaft. Then refit the
crankshaft sprocket, and tighten the securing
bolt to the specified torque in the two stages
given in the Specifications. Ensure that the
washer is in place under the bolt head, and
prevent the crankshaft from turning as during
removal (see illustrations).
2A•14SOHC engine procedures
11.17A Loosening the main rear timing
belt cover lower securing bolt -
2.0 litre engine11.18 Unscrewing the coolant pump rear
belt cover securing bolt - 2.0 litre engine
11.20E Tighten the bolt to the specified
torque . . .11.20D . . .and the washer and bolt11.20C . . .the crankshaft sprocket . . .
11.20B . . . the Woodruff key . . .11.20A Refit the thrustwasher . . .
11.17B Main rear timing belt cover lower
securing bolts (arrowed) - 1.6 SV engine