1988 OPEL CALIBRA oil temperature
[x] Cancel search: oil temperaturePage 235 of 525

8Radiator -inspection and
cleaning
2
1If the radiator has been removed due to
suspected blockage, reverse-flush it as
described in Section 3.
2Clean dirt and debris from the radiator fins,
using an air jet or a soft brush. Take care, as
the fins are easily damaged and are sharp.
3If necessary, a radiator specialist can
perform a “flow test” on the radiator, to
establish whether an internal blockage exists.
4A leaking radiator must be referred to a
specialist for permanent repair. Do not
attempt to weld or solder a leaking radiator,
as damage to the plastic components may
result.
5In an emergency, minor leaks from the
radiator can be cured by using a radiator
sealant.
9Thermostat - removal and
refitting
3
Note: A new O-ring should be used when
refitting the thermostat
1.4 and 1.6 litre models (except
C16 NZ2)
Removal
1Partially drain the cooling system, as
described in Section 2.
2Remove the timing belt and the camshaft
sprocket, as described in Chapters 2A or 2B,
(as applicable).
3Unscrew and remove the two upper bolts
securing the rear timing belt cover to the
cylinder head, and the lower right-hand bolt
securing the cover to the cylinder block.
4Disconnect the coolant hose from the
thermostat housing.
5Pull the rear timing belt cover forwards,
away from the cylinder head, for access to the
two thermostat housing securing bolts.
6Unscrew and remove the two thermostat
housing securing bolts, and lift off the
thermostat housing (see illustration).7Withdraw the thermostat from the cylinder
head, noting that coolant may be released
from the radiator bottom outlet as the
thermostat is withdrawn, even though the
cooling system has been partially drained
(see illustration).
8Remove the sealing ring from the edge of
the thermostat.
9If desired, the thermostat can be tested, as
described in Section 10.
Refitting
10Refitting is a reversal of removal, using a
new sealing ring, and bearing in mind the
following points.
11Refit the camshaft sprocket and timing
belt, and tension the timing belt, as described
in Chapters 2A or 2B.
12Refill the cooling system, (Section 4).
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models
Removal
13Remove the engine undershield, if fitted.
Partially drain the cooling system, as
described in Section 2.
14Disconnect the radiator top hose from the
thermostat cover.
15Unscrew and remove the thermostat
cover securing bolts, and withdraw the cover
complete with thermostat. Recover the O-ring
(see illustrations).
16If desired, the thermostat can be tested,
as described in Section 10.
17Note that if it is necessary to renew the
thermostat, the complete cover and
thermostat must be renewed as an assembly,
as the two cannot be separated.
Refitting
18Refitting is a reversal of removal, but use a
new O-ring, and on completion refill the
cooling system, as described in Section 4.
10Thermostat -testing
2
1A rough test of the thermostat may be
made by suspending it with a piece of string in
a container full of water. Heat the water to
bring it to the boil -the thermostat must open
by the time the water boils. If not, renew it.
2If a thermometer is available, the precise
opening temperature of the thermostat may
be determined, and compared with the figures
given in the Specifications. The opening
temperature is also marked on the thermostat
(see illustration).
3A thermostat that fails to close as the water
cools must also be renewed.
11Coolant pump -removal and
refitting
4
SOHC models
Removal
1If the engine is in the vehicle, drain the
cooling system, as described in Section 2.
2On 1.4 and 1.6 litre models (except C16
NZ2), remove the rear timing belt cover. On
3•4Cooling, heating and ventilation systems
9.6 Remove the thermostat housing . . .9.15A Withdraw the thermostat cover
complete with thermostat . . .
10.2 View of thermostat showing opening
temperature markings - 1.6 litre model
9.15B . . .and recover the O-ring -
2.0 litre SOHC model
9.7 . . .and withdraw the thermostat -
1.6 litre model
Page 236 of 525
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models, remove the
timing belt. Details are as described in
Chapter 2A.
3Remove timing belt tension roller from oil
pump, where applicable.
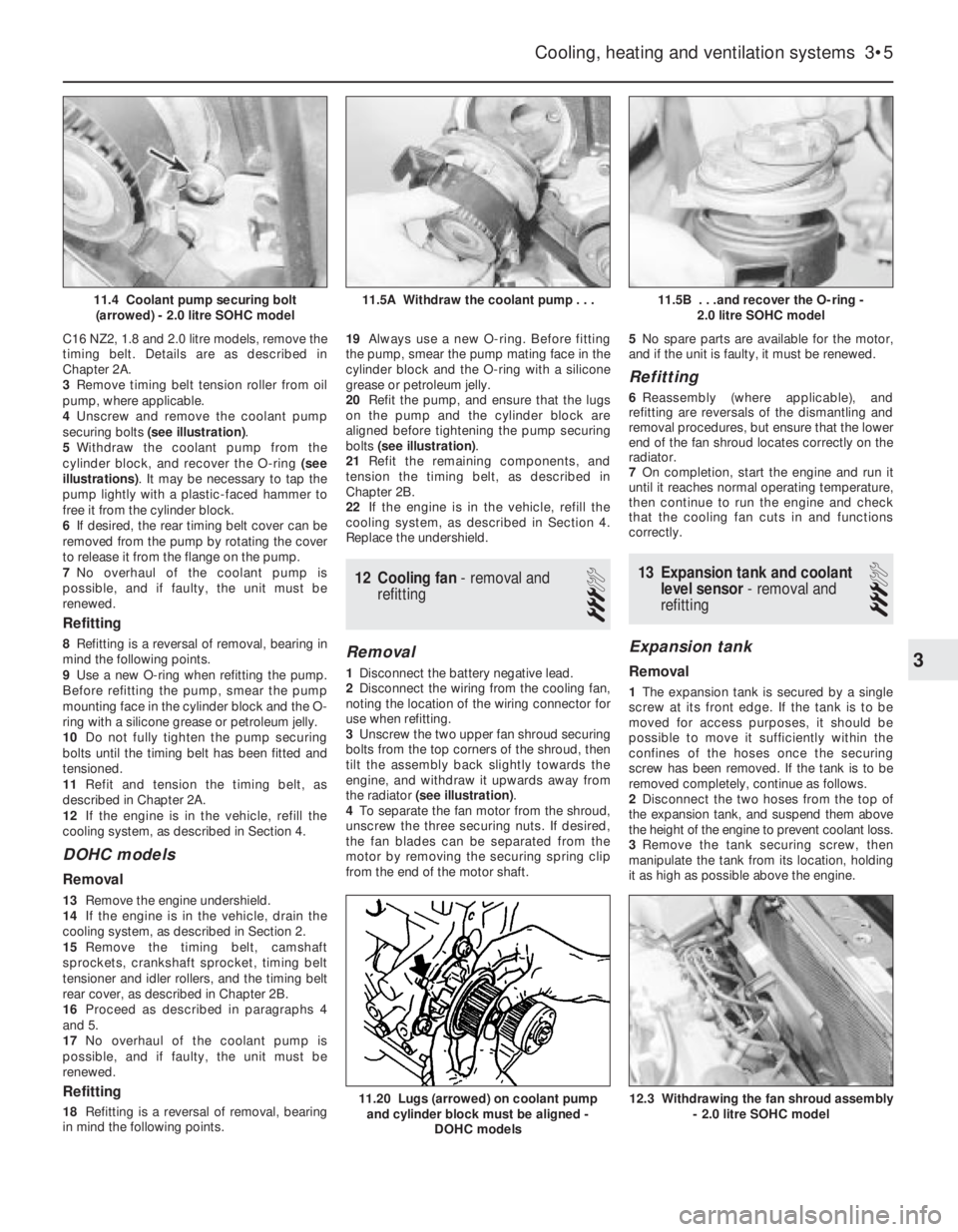
4Unscrew and remove the coolant pump
securing bolts (see illustration).
5Withdraw the coolant pump from the
cylinder block, and recover the O-ring (see
illustrations). It may be necessary to tap the
pump lightly with a plastic-faced hammer to
free it from the cylinder block.
6If desired, the rear timing belt cover can be
removed from the pump by rotating the cover
to release it from the flange on the pump.
7No overhaul of the coolant pump is
possible, and if faulty, the unit must be
renewed.
Refitting
8Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing in
mind the following points.
9Use a new O-ring when refitting the pump.
Before refitting the pump, smear the pump
mounting face in the cylinder block and the O-
ring with a silicone grease or petroleum jelly.
10Do not fully tighten the pump securing
bolts until the timing belt has been fitted and
tensioned.
11Refit and tension the timing belt, as
described in Chapter 2A.
12If the engine is in the vehicle, refill the
cooling system, as described in Section 4.
DOHC models
Removal
13Remove the engine undershield.
14If the engine is in the vehicle, drain the
cooling system, as described in Section 2.
15Remove the timing belt, camshaft
sprockets, crankshaft sprocket, timing belt
tensioner and idler rollers, and the timing belt
rear cover, as described in Chapter 2B.
16Proceed as described in paragraphs 4
and 5.
17No overhaul of the coolant pump is
possible, and if faulty, the unit must be
renewed.
Refitting
18Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points.19Always use a new O-ring. Before fitting
the pump, smear the pump mating face in the
cylinder block and the O-ring with a silicone
grease or petroleum jelly.
20Refit the pump, and ensure that the lugs
on the pump and the cylinder block are
aligned before tightening the pump securing
bolts (see illustration).
21Refit the remaining components, and
tension the timing belt, as described in
Chapter 2B.
22If the engine is in the vehicle, refill the
cooling system, as described in Section 4.
Replace the undershield.
12Cooling fan - removal and
refitting
3
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Disconnect the wiring from the cooling fan,
noting the location of the wiring connector for
use when refitting.
3Unscrew the two upper fan shroud securing
bolts from the top corners of the shroud, then
tilt the assembly back slightly towards the
engine, and withdraw it upwards away from
the radiator (see illustration).
4To separate the fan motor from the shroud,
unscrew the three securing nuts. If desired,
the fan blades can be separated from the
motor by removing the securing spring clip
from the end of the motor shaft.5No spare parts are available for the motor,
and if the unit is faulty, it must be renewed.
Refitting
6Reassembly (where applicable), and
refitting are reversals of the dismantling and
removal procedures, but ensure that the lower
end of the fan shroud locates correctly on the
radiator.
7On completion, start the engine and run it
until it reaches normal operating temperature,
then continue to run the engine and check
that the cooling fan cuts in and functions
correctly.
13Expansion tank and coolant
level sensor -removal and
refitting
3
Expansion tank
Removal
1The expansion tank is secured by a single
screw at its front edge. If the tank is to be
moved for access purposes, it should be
possible to move it sufficiently within the
confines of the hoses once the securing
screw has been removed. If the tank is to be
removed completely, continue as follows.
2Disconnect the two hoses from the top of
the expansion tank, and suspend them above
the height of the engine to prevent coolant loss.
3Remove the tank securing screw, then
manipulate the tank from its location, holding
it as high as possible above the engine.
Cooling, heating and ventilation systems 3•5
11.5B . . .and recover the O-ring -
2.0 litre SOHC model
12.3 Withdrawing the fan shroud assembly
- 2.0 litre SOHC model11.20 Lugs (arrowed) on coolant pump
and cylinder block must be aligned -
DOHC models
11.5A Withdraw the coolant pump . . .11.4 Coolant pump securing bolt
(arrowed) - 2.0 litre SOHC model
3
Page 250 of 525

MOTTest Checks REF•11
MExamine the handbrake mechanism,
checking for frayed or broken cables,
excessive corrosion, or wear or insecurity of
the linkage. Check that the mechanism works
on each relevant wheel, and releases fully,
without binding.
MIt is not possible to test brake efficiency
without special equipment, but a road test can
be carried out later to check that the vehicle
pulls up in a straight line.
Fuel and exhaust systems
MInspect the fuel tank (including the filler
cap), fuel pipes, hoses and unions. All
components must be secure and free from
leaks.
MExamine the exhaust system over its entire
length, checking for any damaged, broken or
missing mountings, security of the retaining
clamps and rust or corrosion.
Wheels and tyres
MExamine the sidewalls and tread area of
each tyre in turn. Check for cuts, tears, lumps,
bulges, separation of the tread, and exposure
of the ply or cord due to wear or damage.
Check that the tyre bead is correctly seated
on the wheel rim, that the valve is sound andproperly seated, and that the wheel is not
distorted or damaged.
MCheck that the tyres are of the correct size
for the vehicle, that they are of the same size
and type on each axle, and that the pressures
are correct.
MCheck the tyre tread depth. The legal
minimum at the time of writing is 1.6 mm over
at least three-quarters of the tread width.
Abnormal tread wear may indicate incorrect
front wheel alignment.
Body corrosion
MCheck the condition of the entire vehicle
structure for signs of corrosion in load-bearing
areas. (These include chassis box sections,
side sills, cross-members, pillars, and all
suspension, steering, braking system and
seat belt mountings and anchorages.) Any
corrosion which has seriously reduced the
thickness of a load-bearing area is likely to
cause the vehicle to fail. In this case
professional repairs are likely to be needed.
MDamage or corrosion which causes sharp
or otherwise dangerous edges to be exposed
will also cause the vehicle to fail.
Petrol models
MHave the engine at normal operating
temperature, and make sure that it is in good
tune (ignition system in good order, air filter
element clean, etc).
MBefore any measurements are carried out,
raise the engine speed to around 2500 rpm,
and hold it at this speed for 20 seconds. Allowthe engine speed to return to idle, and watch
for smoke emissions from the exhaust
tailpipe. If the idle speed is obviously much
too high, or if dense blue or clearly-visible
black smoke comes from the tailpipe for more
than 5 seconds, the vehicle will fail. As a rule
of thumb, blue smoke signifies oil being burnt
(engine wear) while black smoke signifies
unburnt fuel (dirty air cleaner element, or other
carburettor or fuel system fault).
MAn exhaust gas analyser capable of
measuring carbon monoxide (CO) and
hydrocarbons (HC) is now needed. If such an
instrument cannot be hired or borrowed, a
local garage may agree to perform the check
for a small fee.
CO emissions (mixture)
MAt the time of writing, the maximum CO
level at idle is 3.5% for vehicles first used after
August 1986 and 4.5% for older vehicles.
From January 1996 a much tighter limit
(around 0.5%) applies to catalyst-equipped
vehicles first used from August 1992. If the
CO level cannot be reduced far enough to
pass the test (and the fuel and ignition
systems are otherwise in good condition) then
the carburettor is badly worn, or there is some
problem in the fuel injection system or
catalytic converter (as applicable).
HC emissionsMWith the CO emissions within limits, HC
emissions must be no more than 1200 ppm
(parts per million). If the vehicle fails this test
at idle, it can be re-tested at around 2000 rpm;
if the HC level is then 1200 ppm or less, this
counts as a pass.
MExcessive HC emissions can be caused by
oil being burnt, but they are more likely to be
due to unburnt fuel.
Diesel models
MThe only emission test applicable to Diesel
engines is the measuring of exhaust smoke
density. The test involves accelerating the
engine several times to its maximum
unloaded speed.
Note: It is of the utmost importance that the
engine timing belt is in good condition before
the test is carried out.
M
Excessive smoke can be caused by a dirty
air cleaner element. Otherwise, professional
advice may be needed to find the cause.
4Checks carried out on
YOUR VEHICLE’S EXHAUST
EMISSION SYSTEM
REF
Page 253 of 525

MFaulty ignition coil (Chapter 5).
MUneven or low cylinder compressions (Chapter 2A).
MBlocked carburettor jet(s) or internal passages - carburettor
models (Chapter 4A).
MBlocked injector/fuel injection system fault - fuel-injected models
(Chapter 4B).
Engine hesitates on acceleration
MWorn, faulty or incorrectly gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
MVacuum leak at the carburettor/throttle body, inlet manifold or
associated hoses (Chapter 4A or 4B).
MBlocked carburettor jet(s) or internal passages - carburettor
models (Chapter 4A).
MBlocked injector/fuel injection system fault - fuel-injected models
(Chapter 4B).
Engine stalls
MVacuum leak at the carburettor/throttle body, inlet manifold or
associated hoses (Chapter 4A or 4B).
MFuel filter choked (Chapter 1).
MFuel pump faulty, or delivery pressure low (Chapter 4A or 4B).
MFuel tank vent blocked, or fuel pipes restricted (Chapter 4A or 4B).
MBlocked carburettor jet(s) or internal passages - carburettor
models (Chapter 4A).
MBlocked injector/fuel injection system fault - fuel-injected models
(Chapter 4B).
Engine lacks power
MTiming belt incorrectly fitted or tensioned (Chapter 2A or 2B).
MFuel filter choked (Chapter 1).
MFuel pump faulty, or delivery pressure low (Chapter 4A or 4B).
MUneven or low cylinder compressions (Chapter 2A).
MWorn, faulty or incorrectly gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
MVacuum leak at the carburettor/throttle body, inlet manifold or
associated hoses (Chapter 4A or 4B).
MBlocked carburettor jet(s) or internal passages - carburettor
models (Chapter 4A).
MBlocked injector/fuel injection system fault - fuel-injected models
(Chapter 4B).
MBrakes binding (Chapters 1 and 9).
MClutch slipping (Chapter 6).
Engine backfires
MTiming belt incorrectly fitted or tensioned (Chapter 2A or 2B).
MVacuum leak at the carburettor/throttle body, inlet manifold or
associated hoses (Chapter 4A or 4B).
MBlocked carburettor jet(s) or internal passages - carburettor
models (Chapter 4A).
MBlocked injector/fuel injection system fault - fuel-injected models
(Chapter 4B).
Oil pressure warning light illuminated with engine
running
MLow oil level, or incorrect oil grade (Chapter 1).
MFaulty oil pressure warning light switch (Chapter 12).
MWorn engine bearings and/or oil pump (Chapter 2A).
MHigh engine operating temperature (Chapter 3).
MOil pressure relief valve defective (Chapter 2A).
MOil pick-up strainer clogged (Chapter 2A).
Engine runs-on after switching off
MExcessive carbon build-up in engine (Chapter 2A).
MHigh engine operating temperature (Chapter 3).
MFaulty fuel cut-off solenoid - carburettor models (Chapter 4A).
MFuel injection system fault - fuel-injected models (Chapter 4B).
Engine noises
Pre-ignition (pinking) or knocking during acceleration or
under load
MIgnition timing incorrect/ignition system fault (Chapters 1 and 5).
MIncorrect grade of spark plug (Chapter 1).
MIncorrect grade of fuel (Chapter 1).
MVacuum leak at the carburettor/throttle body, inlet manifold or
associated hoses (Chapter 4A or 4B).
MExcessive carbon build-up in engine (Chapter 2A).
MBlocked carburettor jet(s) or internal passages - carburettor
models (Chapter 4A).
MBlocked injector/fuel injection system fault - fuel-injected models
(Chapter 4B).
Whistling or wheezing noises
MLeaking inlet manifold or carburettor/throttle body gasket
(Chapter 4A or 4B).
MLeaking exhaust manifold gasket or pipe-to-manifold joint
(Chapter 4C).
MLeaking vacuum hose (Chapters 4A, 4B, 4C, 5, 9 and 12).
MBlowing cylinder head gasket (Chapter 2A or 2B).
Tapping or rattling noises
MWorn valve gear or camshaft (Chapter 2A or 2B).
MAncillary component fault (coolant pump, alternator, etc.)
(Chapters 3, 5, etc.).
Knocking or thumping noises
MWorn big-end bearings (regular heavy knocking, perhaps less
under load), (Chapter 2A or 2B).
MWorn main bearings (rumbling and knocking, perhaps worsening
under load), (Chapter 2A or 2B).
MPiston slap (most noticeable when cold), (Chapter 2A).
MAncillary component fault (coolant pump, alternator, etc.)
(Chapters 3, 5, etc.).
REF•14Fault Finding
Engine (continued)
Page 254 of 525

Excessive fuel consumption
MAir filter element dirty or clogged (Chapter 1).
MChoke cable incorrectly adjusted, or choke sticking - carburettor
models (Chapter 4A).
MFuel injection system fault - fuel-injected models (Chapter 4B).
MIgnition timing incorrect/ignition system fault (Chapters 1 and 5).
MTyres under-inflated (Chapter 1).
Fuel leakage and/or fuel odour
MDamaged or corroded fuel tank, pipes or connections (Chapter 4A
or 4B).
MCarburettor float chamber flooding (float height incorrect) -
carburettor models (Chapter 4A).
Excessive noise or fumes from exhaust system
MLeaking exhaust system or manifold joints (Chapters 1 and 4C).
MLeaking, corroded or damaged silencers or pipe (Chapters 1 and 4C).
MBroken mountings causing body or suspension contact (Chapter 1).
Pedal travels to floor - no pressure or very little
resistance
MBroken clutch cable (Chapter 6).
MIncorrect clutch cable adjustment (Chapter 6).
MBroken clutch release bearing or fork (Chapter 6).
MBroken diaphragm spring in clutch pressure plate (Chapter 6).
Clutch fails to disengage (unable to select gears).
MIncorrect clutch cable adjustment (Chapter 6).
MClutch disc sticking on transmission input shaft splines (Chapter 6).
MClutch disc sticking to flywheel or pressure plate (Chapter 6).
MFaulty pressure plate assembly (Chapter 6).
MClutch release mechanism worn or incorrectly assembled (Chapter 6).
Clutch slips (engine speed increases, with no
increase in vehicle speed).
MIncorrect clutch cable adjustment (Chapter 6).
MClutch disc linings excessively worn (Chapter 6).MClutch disc linings contaminated with oil or grease (Chapter 6).
MFaulty pressure plate or weak diaphragm spring (Chapter 6).
Judder as clutch is engaged
MClutch disc linings contaminated with oil or grease (Chapter 6).
MClutch disc linings excessively worn (Chapter 6).
MClutch cable sticking or frayed (Chapter 6).
MFaulty or distorted pressure plate or diaphragm spring (Chapter 6).
MWorn or loose engine or transmission mountings (Chapter 2A or 2B).
MClutch disc hub or transmission input shaft splines worn (Chapter 6).
Noise when depressing or releasing clutch pedal
MWorn clutch release bearing (Chapter 6).
MWorn or dry clutch pedal bushes (Chapter 6).
MFaulty pressure plate assembly (Chapter 6).
MPressure plate diaphragm spring broken (Chapter 6).
MBroken clutch disc cushioning springs (Chapter 6).
Fault Finding REF•15
REF
Overheating
MInsufficient coolant in system (Chapter 1).
MThermostat faulty (Chapter 3).
MRadiator core blocked, or grille restricted (Chapter 3).
MElectric cooling fan or thermoswitch faulty (Chapter 3).
MPressure cap faulty (Chapter 3).
MIgnition timing incorrect/ignition system fault (Chapters 1 and 5).
MInaccurate temperature gauge sender unit (Chapter 3).
MAirlock in cooling system (Chapter 1).
Overcooling
MThermostat faulty (Chapter 3).
MInaccurate temperature gauge sender unit (Chapter 3).
External coolant leakage
MDeteriorated or damaged hoses or hose clips (Chapter 1).
MRadiator core or heater matrix leaking (Chapter 3).
MPressure cap faulty (Chapter 3).
MWater pump seal leaking (Chapter 3).
MBoiling due to overheating (Chapter 3).
MCore plug leaking (Chapter 2A).
Internal coolant leakage
MLeaking cylinder head gasket (Chapter 2A or 2B).
MCracked cylinder head or cylinder bore (Chapter 2A or 2B).
Corrosion
MInfrequent draining and flushing (Chapter 1).
MIncorrect coolant mixture or inappropriate coolant type (Chapter 1).
Cooling system
Clutch
Fuel and exhaust systems
Page 260 of 525

Glossary of Technical Terms REF•21
REF
CamshaftA rotating shaft on which a series
of cam lobes operate the valve mechanisms.
The camshaft may be driven by gears, by
sprockets and chain or by sprockets and a
belt.
CanisterA container in an evaporative
emission control system; contains activated
charcoal granules to trap vapours from the
fuel system.
CarburettorA device which mixes fuel with
air in the proper proportions to provide a
desired power output from a spark ignition
internal combustion engine.
CastellatedResembling the parapets along
the top of a castle wall. For example, a
castellated balljoint stud nut.
CastorIn wheel alignment, the backward or
forward tilt of the steering axis. Castor is
positive when the steering axis is inclined
rearward at the top.Catalytic converterA silencer-like device in
the exhaust system which converts certain
pollutants in the exhaust gases into less
harmful substances.
CirclipA ring-shaped clip used to prevent
endwise movement of cylindrical parts and
shafts. An internal circlip is installed in a
groove in a housing; an external circlip fits into
a groove on the outside of a cylindrical piece
such as a shaft.
ClearanceThe amount of space between
two parts. For example, between a piston and
a cylinder, between a bearing and a journal,
etc.
Coil springA spiral of elastic steel found in
various sizes throughout a vehicle, for
example as a springing medium in the
suspension and in the valve train.
CompressionReduction in volume, and
increase in pressure and temperature, of a
gas, caused by squeezing it into a smaller
space.
Compression ratioThe relationship between
cylinder volume when the piston is at top
dead centre and cylinder volume when the
piston is at bottom dead centre.
Constant velocity (CV) jointA type of
universal joint that cancels out vibrations
caused by driving power being transmitted
through an angle.
Core plugA disc or cup-shaped metal device
inserted in a hole in a casting through which
core was removed when the casting was
formed. Also known as a freeze plug or
expansion plug.
CrankcaseThe lower part of the engine
block in which the crankshaft rotates.
CrankshaftThe main rotating member, or
shaft, running the length of the crankcase,
with offset “throws” to which the connecting
rods are attached.Crocodile clipSee Alligator clip
DDiagnostic codeCode numbers obtained by
accessing the diagnostic mode of an engine
management computer. This code can be
used to determine the area in the system
where a malfunction may be located.
Disc brakeA brake design incorporating a
rotating disc onto which brake pads are
squeezed. The resulting friction converts the
energy of a moving vehicle into heat.
Double-overhead cam (DOHC)An engine
that uses two overhead camshafts, usually
one for the intake valves and one for the
exhaust valves.
Drivebelt(s)The belt(s) used to drive
accessories such as the alternator, water
pump, power steering pump, air conditioning
compressor, etc. off the crankshaft pulley.
DriveshaftAny shaft used to transmit
motion. Commonly used when referring to the
axleshafts on a front wheel drive vehicle.
Drum brakeA type of brake using a drum-
shaped metal cylinder attached to the inner
surface of the wheel. When the brake pedal is
pressed, curved brake shoes with friction
linings press against the inside of the drum to
slow or stop the vehicle.
Castellated nut
Catalytic converter
Crankshaft assembly
Carburettor
Canister
Drum brake assembly
Accessory drivebelts
Driveshaft
Page 262 of 525

Glossary of Technical Terms REF•23
JJump startStarting the engine of a vehicle
with a discharged or weak battery by
attaching jump leads from the weak battery to
a charged or helper battery.
LLoad Sensing Proportioning Valve (LSPV)A
brake hydraulic system control valve that
works like a proportioning valve, but also
takes into consideration the amount of weight
carried by the rear axle.
LocknutA nut used to lock an adjustment
nut, or other threaded component, in place.
For example, a locknut is employed to keep
the adjusting nut on the rocker arm in
position.
LockwasherA form of washer designed to
prevent an attaching nut from working loose.
MMacPherson strutA type of front
suspension system devised by Earle
MacPherson at Ford of England. In its original
form, a simple lateral link with the anti-roll bar
creates the lower control arm. A long strut - an
integral coil spring and shock absorber - is
mounted between the body and the steering
knuckle. Many modern so-called MacPherson
strut systems use a conventional lower A-arm
and don’t rely on the anti-roll bar for location.
MultimeterAn electrical test instrument with
the capability to measure voltage, current and
resistance.
NNOxOxides of Nitrogen. A common toxic
pollutant emitted by petrol and diesel engines
at higher temperatures.
OOhmThe unit of electrical resistance. One
volt applied to a resistance of one ohm will
produce a current of one amp.
OhmmeterAn instrument for measuring
electrical resistance.
O-ringA type of sealing ring made of a
special rubber-like material; in use, the O-ring
is compressed into a groove to provide the
sealing action.Overhead cam (ohc) engineAn engine with
the camshaft(s) located on top of the cylinder
head(s).
Overhead valve (ohv) engineAn engine with
the valves located in the cylinder head, but
with the camshaft located in the engine block.
Oxygen sensorA device installed in the
engine exhaust manifold, which senses the
oxygen content in the exhaust and converts
this information into an electric current. Also
called a Lambda sensor.
PPhillips screwA type of screw head having a
cross instead of a slot for a corresponding
type of screwdriver.
PlastigageA thin strip of plastic thread,
available in different sizes, used for measuring
clearances. For example, a strip of Plastigage
is laid across a bearing journal. The parts are
assembled and dismantled; the width of the
crushed strip indicates the clearance between
journal and bearing.
Propeller shaftThe long hollow tube with
universal joints at both ends that carries
power from the transmission to the differential
on front-engined rear wheel drive vehicles.
Proportioning valveA hydraulic control
valve which limits the amount of pressure to
the rear brakes during panic stops to prevent
wheel lock-up.
RRack-and-pinion steeringA steering system
with a pinion gear on the end of the steering
shaft that mates with a rack (think of a geared
wheel opened up and laid flat). When the
steering wheel is turned, the pinion turns,
moving the rack to the left or right. This
movement is transmitted through the track
rods to the steering arms at the wheels.
RadiatorA liquid-to-air heat transfer device
designed to reduce the temperature of the
coolant in an internal combustion engine
cooling system.
RefrigerantAny substance used as a heat
transfer agent in an air-conditioning system.
R-12 has been the principle refrigerant for
many years; recently, however, manufacturers
have begun using R-134a, a non-CFC
substance that is considered less harmful tothe ozone in the upper atmosphere.
Rocker armA lever arm that rocks on a shaft
or pivots on a stud. In an overhead valve
engine, the rocker arm converts the upward
movement of the pushrod into a downward
movement to open a valve.
RotorIn a distributor, the rotating device
inside the cap that connects the centre
electrode and the outer terminals as it turns,
distributing the high voltage from the coil
secondary winding to the proper spark plug.
Also, that part of an alternator which rotates
inside the stator. Also, the rotating assembly
of a turbocharger, including the compressor
wheel, shaft and turbine wheel.
RunoutThe amount of wobble (in-and-out
movement) of a gear or wheel as it’s rotated.
The amount a shaft rotates “out-of-true.” The
out-of-round condition of a rotating part.
SSealantA liquid or paste used to prevent
leakage at a joint. Sometimes used in
conjunction with a gasket.
Sealed beam lampAn older headlight design
which integrates the reflector, lens and
filaments into a hermetically-sealed one-piece
unit. When a filament burns out or the lens
cracks, the entire unit is simply replaced.
Serpentine drivebeltA single, long, wide
accessory drivebelt that’s used on some
newer vehicles to drive all the accessories,
instead of a series of smaller, shorter belts.
Serpentine drivebelts are usually tensioned by
an automatic tensioner.
ShimThin spacer, commonly used to adjust
the clearance or relative positions between
two parts. For example, shims inserted into or
under bucket tappets control valve
clearances. Clearance is adjusted by
changing the thickness of the shim.
Slide hammerA special puller that screws
into or hooks onto a component such as a
shaft or bearing; a heavy sliding handle on the
shaft bottoms against the end of the shaft to
knock the component free.
SprocketA tooth or projection on the
periphery of a wheel, shaped to engage with a
chain or drivebelt. Commonly used to refer to
the sprocket wheel itself.
Starter inhibitor switchOn vehicles with an
O-ring
Serpentine drivebelt
Plastigage
REF
Page 264 of 525

AABS components- 9•2, 9•16
Accelerator cable- 4A•5, 4B•9
Accelerator pedal- 4A•5
Acknowledgements- 0•4
Aerial- 12•17
Air cleaner- 1•3, 1•13, 4A•3, 4B•4
Air box- 4B•5
Air pump/cut off valve- 4C•2
Air temp control- 4B•5
Air vents- 3•8
Airbag- 12•19
Airflow meters- 4B•12
Alternator- 5•5
Alternator V-belt check- 1•12
Anti theft alarm- 12•19
Anti-roll bars- 10•8, 10•13, 10•17
Antifreeze mixture- 0•12, 0•17, 1•2, 3•3
ATF- 0•17, 1•2, 1•11, 7B•3
Automatic choke unit- 4A•9
Automatic transmission- 7B•1 et seq
cooler pipes and hoses - 7B•5
ECU - 7B•5
fault diagnosis - REF•12, REF•16
fluid - 0•17, 1•2, 1•11, 7B•3
kickdown switch - 7B•3
removal and refitting - 7B•6
selector control cable - 7B•4
speed sensors - 7B•6
starter inhibitor switch - 7B•3
temperature sensor - 7B•5
BBattery- 0•6, 0•15, 5•5
Bearings (engine)- 2A•31
Bleeding the brakes- 9•3
Bleeding the power steering- 10•22
Blower motor- 3•7
Body damage- 11•2
Body electrical systems - 12•1 et seq
Bodywork and fittings- 11•1 et seq
Bonnet- 11•4
Bonnet lock/release cable- 11•4
Boot lid- 11•4
Boot lid lock- 11•5
Bores- 2A•33
Brake checks- 1•12,
Braking system- 9•1 et seq
ABS components - 9•2, 9•16
backplate - 9•12
bleeding the brakes - 9•3
brake caliper - 9•8
brake disc - 9•10
brake drum - 9•11
brake fluid pipes and hoses - 9•18
brake lamp switch - 12•5
brake pads - 9•4
brake pedal - 9•21
brake shoes - 9•6
disc shield - 9•13
fault diagnosis - REF•12, REF•17
fluid - 0•13, 0•17handbrake adjustment - 9•18
handbrake cables - 9•19
handbrake lever - 9•20
master cylinder - 9•13
pressure valves - 9•18
vacuum servo unit - 9•15
wheel cylinder - 9•11
Bulbs- 12•2, 12•7, 12•11
Bumpers- 11•11
CCables:
bonnet release - 11•4
clutch - 6•2
handbrake - 9•19
selector automatic transmission - 7B•4
speedometer - 12•18
throttle - 4A•5, 4B•9
Caliper (brake)- 9•8
Camber- 10•1, 10•24
Camshaft- 2A•19, 2B•6
Camshaft housing- 2A•18
Camshaft oil seals- 2A•18
Capacities- 1•2
Carbon canister- 4C•4
Carburettor- 4A•5, 4A•11
Carpets- 11•2
Castor- 10•1, 10•24
Catalytic converter- 4C•3
Central door locking- 12•16
Centre console- 11•18
Cigarette lighter- 12•5
Clock- 12•6
Clutch- 6•1 et seq
cable - 6•2
fault diagnosis - REF•12, REF•15
pedal - 6•3
release bearing - 6•6
removal, inspection and refitting - 6•3
Coil- 5•9
Coil spring (rear)- 10•12, 10•15
Compression test- 2A•8
Computer components- 12•7
Connecting rods- 2A•29
Contents- 0•2
Control units- 4B•16, 7B•5
Conversion factors- REF•2
Coolant- 0•12, 0•17, 1•2, 3•3
Cooling, heating and ventilation systems-
3•1 et seq
blower motor - 3•7
coolant level sensor - 3•5
coolant pump - 3•4
cooling fan - 3•5
draining - 3•2
expansion tank - 3•5
fan switch - 3•6
fault diagnosis - REF•12, REF•15
filling - 3•2
flushing - 3•2
heater control panel - 3•6
heater matrix - 3•7
radiator - 3•3temperature gauge sender - 3•6
thermostat - 3•4
vents - 3•8
Courtesy lamp switch- 12•5
Crankcase ventilation system- 2A•7
Crankshaft- 2A•31
Crankshaft oil seals- 2A•26, 2B•6, 2B•9
Cylinder bores- 2A•33
Cylinder head- 2A•19, 2A•22, 2B•7DDents- 11•2
Depressurising fuel system- 4B•5
Differential bearing oil seal- 7A•3
Dimensions and weights- REF•1
Disc (brake)- 9•10
Distributor- 5•10
Door- 11•6
handle - 11•7
inner trim panel - 11•6
lock key battery - 1•13
mirror - 11•11
Driveshafts- 8•1 et seq
fault diagnosis - REF•12, REF•16
gaiter - 8•4
joint renewal - 8•4
Drum (brake)- 9•11
EEarth fault finding- 12•2
ECU’s - 4B•16, 7B•5
EGR components- 4C•2
Electric windows- 12•15
Electrical fault finding- 12•2
Electrical system (body)- 12•1 et seq
Electrical system- 0•14, 5•2
Electrical system fault diagnosis- REF•12,
REF•18
Electronic control units- 4B•16, 7B•5
Engine:
bearings - 2A•31
camshaft - 2A•19, 2B•6
camshaft housing - 2A•18
camshaft oil seals - 2A•18, 2B•6
codes - 2A•1, 2B•1
compartment - 0•10, 1•5
compression test - 2A•8
connecting rods - 2A•29
crankcase ventilation - 2A•7
crankshaft - 2A•31
crankshaft oil seals - 2A•26, 2B•6, 2B•9
cylinder bores - 2A•33
cylinder head - 2A•19, 2A•22, 2B•7
dismantling - 2A•12
DOHC - 2B•1 et seq
electrical systems - 5•1 et seq
fault diagnosis - REF•12, REF•13
flexplate (automatic transmission) - 2A•26
flywheel - 2A•26
main and big-end bearings - 2A•31
mountings (engine/transmission) - 2A•12,
2B•3
Index REF•25
REF
Note:References throughout this index are in the form - “Chapter number” • “page number”