Page 1283 of 1378

Mismatched tires See WHEEL ALIGNMENT
Broken or sagging spring See SUSPENSION section
Broken torsion bar See SUSPENSION section
Power steering valve not See STEERING section
centered
Front alignment out of See WHEEL ALIGNMENT
tolerance section
Defective wheel bearing See WHEEL BEARINGS in
SUSPENSION section
Uneven sway bar links See SUSPENSION section
Frame bent Check for frame damage
Steering system bushing See STEERING section
worn
������������������\
������������������\
������������������\
������������������\
������������������\
������������������\
������������������\
�������������
Hard Steering Idler arm bushing too tight See STEERING LINKAGE
in STEERING section
Ball joint tight or seized See SUSPENSION section
Steering linkage too tight See STEERING LINKAGE in
STEERING section
Power steering fluid low Add proper amount of
fluid
Power steering drive belt See STEERING section
loose
Power steering pump See STEERING section
defective
Steering gear out of See STEERING section
adjustment
Incorrect wheel alignment See WHEEL ALIGNMENT
Damaged steering gear See STEERING section
Damaged suspension See SUSPENSION section
Bent steering knuckle or See SUSPENSION section
supports
������������������\
������������������\
������������������\
������������������\
������������������\
������������������\
������������������\
�������������
Vehicle Strut rod or control arm See SUSPENSION section
"Wanders" bushing worn
Loose or worn wheel See WHEEL BEARINGS in
bearings SUSPENSION section
Improper tire inflation Check tire pressure
Stabilizer bar missing or See SUSPENSION section
defective
Page 1348 of 1378
WHEEL A LIG NM EN T S PEC IF IC ATIO NS & P R O CED URES
�
1988 J e ep C hero ke e
1988 Wheel Alignment
INTRODUCTION
PRE-ALIGNMENT
VEHICLE CHECKS
Prior to making wheel alignment adjustments, check and
adjust the following items:
1) Tire pressure must be inflated to manufacturers
recommended specifications.Tires should be equal in size and type.
Runout must not be excessive. Tires and wheels should be in balance.
2) Wheel bearings must be properly adjusted. Steering
linkage and suspension must not have excessive wear and/or looseness.
Check for wear in tie rod ends and ball joints.
3) Steering gear box must not have excessive play. Check and
adjust to manufacturer's specifications.
4) Vehicle must be at correct ride height with full fuel
load and spare tire in vehicle. No extra load should be on vehicle.
5) Vehicle must be level with floor and with suspension
settled. Jounce front and rear of vehicle several times and allow it
to settle to normal ride height.
6) Ensure steering wheel spokes are centered with front
wheels in straight-ahead position, correct by shortening one tie rod
adjusting sleeve and lengthening opposite sleeve equal amounts.
7) Ensure wheel lug nuts are tightened to torque
specifications.
DESCRIPTION
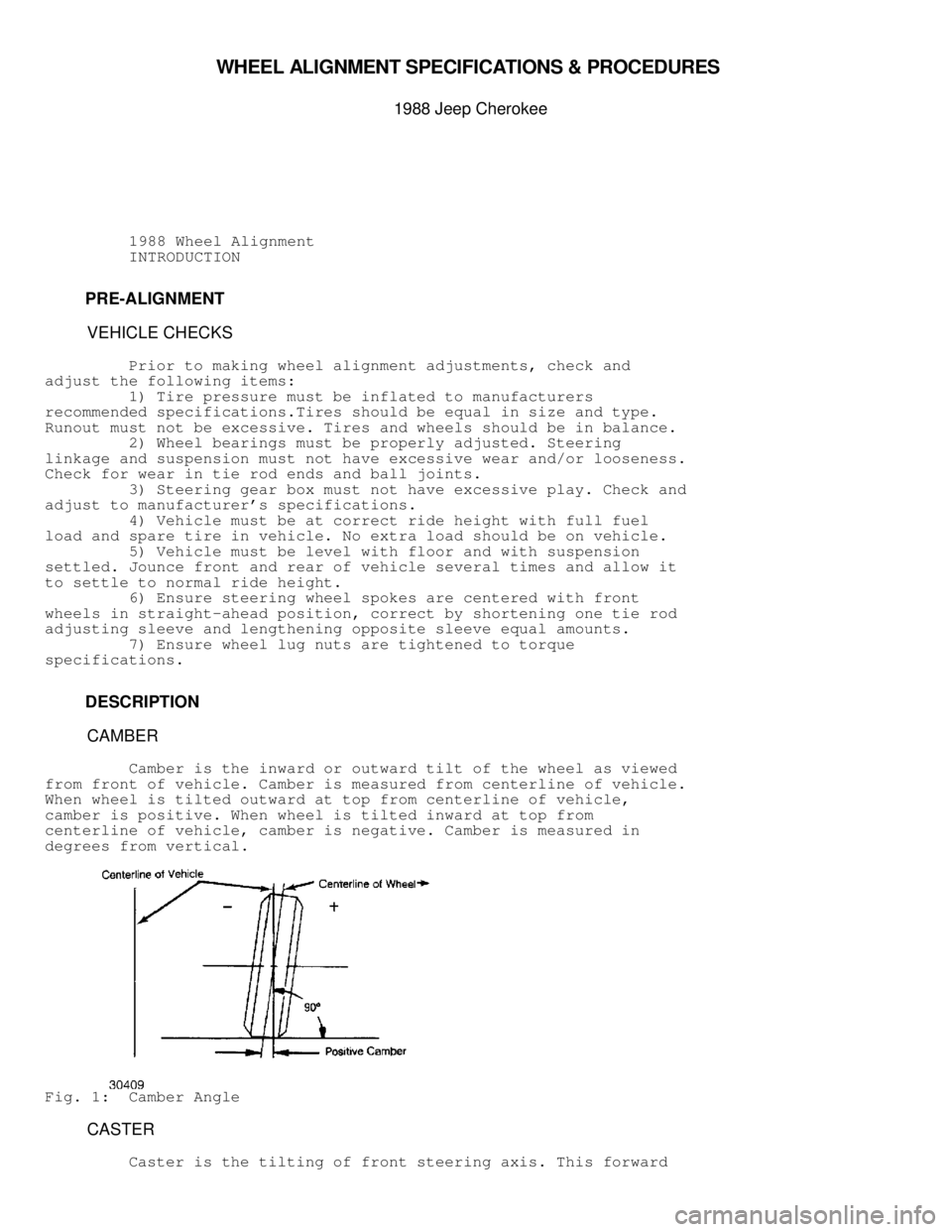
CAMBER
Camber is the inward or outward tilt of the wheel as viewed
from front of vehicle. Camber is measured from centerline of vehicle.
When wheel is tilted outward at top from centerline of vehicle,
camber is positive. When wheel is tilted inward at top from
centerline of vehicle, camber is negative. Camber is measured in
degrees from vertical.
Fig. 1: Camber Angle
CASTER
Caster is the tilting of front steering axis. This forward
Page 1353 of 1378

ALIGNMENT SPECIFICATIONS
WHEEL ALIGNMENT SPECIFICATIONS TABLE������������������\
������������������\
������������������\
������������������\
������������������\
������������������\
�����������
Application Specification
Cherokee, Comanche,
Wrangler & Wagoneer
Ride Height in Inches ........................... .....
Adjustment Procedures ........................... .....
Camber in Degrees (Fraction) .............. -1/2 to 1/2
Camber in Degrees (Decimal) ............. -0.50 to 0.50
Caster in Degrees (Fraction) ................... 7 to 8
Caster in Degrees (Decimal) ................ 7.0 to 8.0
Toe-In in Inches (Fraction) .............. 1/32 to 1/32
Toe-In in Inches (Decimal) ............. 0.031 to 0.031
Toe-In in Degrees (Fraction) ............. 1/16 to 1/16
Toe-In in Degrees (Decimal) ............ 0.063 to 0.063
Toe-Out on Turns
Inner .......................................... NS
Outer .......................................... NS
Steering Axis Inclination (SAI) ................ 8 1/2
�
Grand Wagoneer
Ride Height in Inches ........................... .....
Adjustment Procedures ........................... .....
Camber in Degrees (Fraction)................... 0 to 1/2
Camber in Degrees (Decimal) .................. 0 to 0.5
Caster in Degrees (Fraction) ................... 4 to 5
Caster in Degrees (Decimal) ................ 4.0 to 5.0
Toe-In in Inches (Fraction) .............. 3/64 to 3/32
Toe-In in Inches (Decimal) ............. 0.047 to 0.094
Toe-In in Degrees (Fraction) ............. 3/32 to 3/16
Toe-In in Degrees (Decimal) ............ 0.094 to 0.188
Toe-Out on Turns
Inner .......................................... NS
Outer .......................................... NS
Steering Axis Inclination (SAI) ................ 8 1/2
�
NS - Information not available from manufacturer.������������������\
������������������\
������������������\
������������������\
������������������\
������������������\
���������
RIDING HEIGHT SPECIFICATIONS
Inflate tires to proper air pressure. Specifications can be
found on door pillar or in glove box. Cargo compartment must by
empty. Fuel tank should be full. Bounce vehicle up and down to
normalize ride height. Ride height specifications in regard to setting
camber and caster are not provided by the manufacturer.
Page 1354 of 1378
\003
WHEEL A LIG NM EN T T H EO RY/O PER ATIO N
�
1988 J e ep C hero ke e
GENERAL INFORMATION
Wheel Alignment Theory & Operation
ALL MODELS
* PLEASE READ THIS FIRST *
NOTE: This article is intended for general information purposes
only. This information may not apply to all makes and models.
PRE-ALIGNMENT INSTRUCTIONS
GENERAL ALIGNMENT CHECKS
Before adjusting wheel alignment, check the following:
* Each axle uses tires of same construction and tread style,
equal in tread wear and overall diameter. Verify that radial
and axial runout is not excessive. Inflation should be at
manufacturer's specifications.
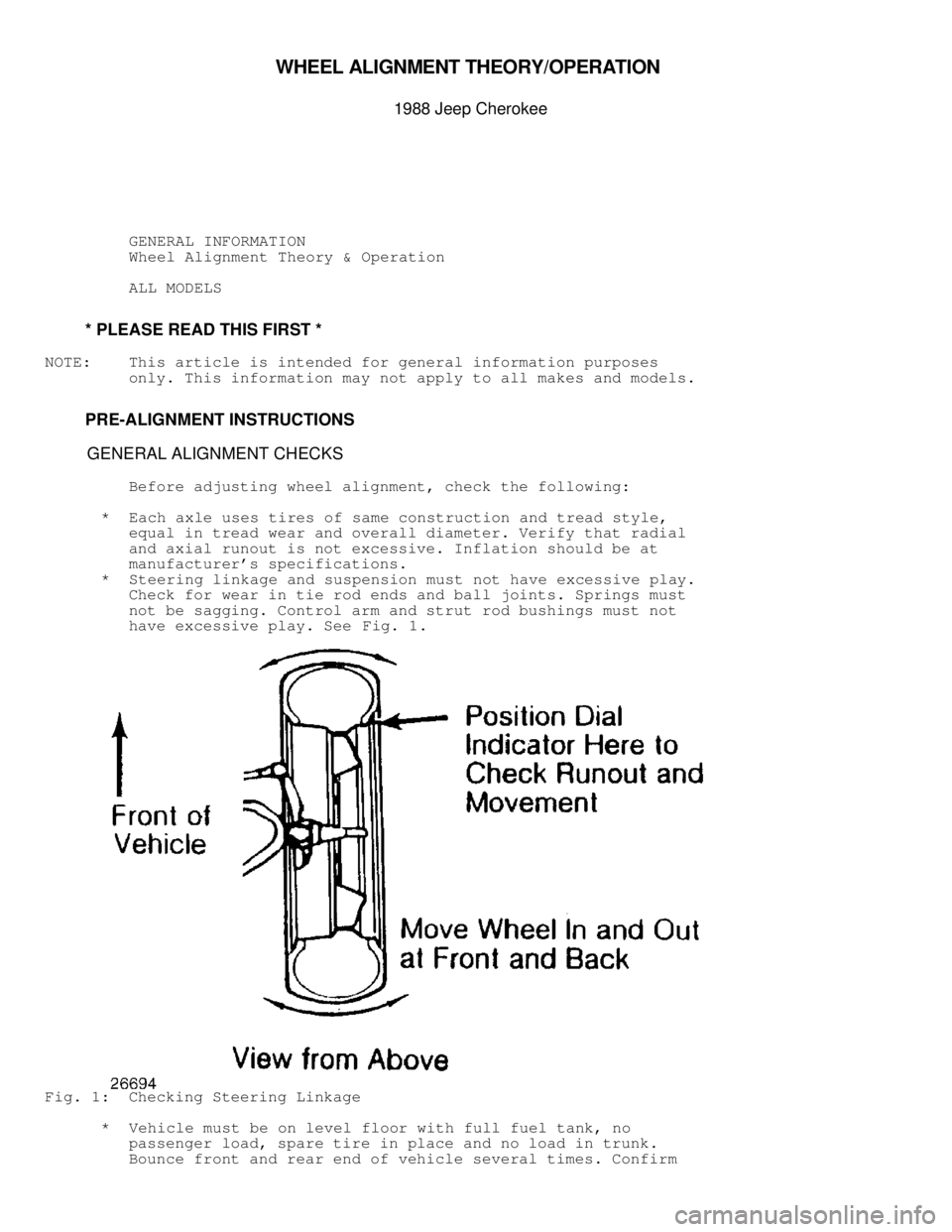
* Steering linkage and suspension must not have excessive play.
Check for wear in tie rod ends and ball joints. Springs must
not be sagging. Control arm and strut rod bushings must not
have excessive play. See Fig. 1.
Fig. 1: Checking Steering Linkage
* Vehicle must be on level floor with full fuel tank, no
passenger load, spare tire in place and no load in trunk.
Bounce front and rear end of vehicle several times. Confirm
Page:
< prev 1-8 9-16 17-24