1983 FIAT UNO drain bolt
[x] Cancel search: drain boltPage 221 of 303

require maintenance other than general
inspection for wear in the linkage joints. If
excessive wear is found in any of the joints, they
can be individually detached and renewed.
13Access to the control rods is eased by
detaching and lowering the exhaust system
from the exhaust manifold.
14If a new adjustable control rod is to be
fitted, remove the original rod as a unit, but do
not alter its adjustment for length. The new
rod can then (if required) be set to the same
length as the original in order to maintain the
original setting. Do so by loosening off the
locknut and turning the balljoint as required;
ensure that the angle of the joint is correct
before tightening the locknut.
15Access to the gear lever/main connecting
rod joint from above is made by prising back
the gear lever gaiter from the centre console.
Access from underneath can be made by
raising and supporting the car on axle stands.
Working from the underside of the lever, undo
the retaining nuts and remove the inspection
plate from the floor (photos).
16Any adjustment to the gear linkage should
be entrusted to a FIAT dealer.
Transmission -
removal and refitting#
17The transmission can be removed
together with the engine and then separated
as described in Section 7, or on its own (as
described below), leaving the engine in
position in the car. Before starting to remove
the transmission, it should be noted that
suitable equipment will be required to support
the engine during this procedure.
18Disconnect the battery negative lead.
19Remove the bonnet as described in
Chapter 12.
20Refer to Section 11 in this Chapter for
details and detach the clutch operating
cylinder together with its mounting bracket
from the top of the transmission, but do not
disconnect the hydraulic fluid hose from the
cylinder connection. Leave the cylinder
attached to the bracket. Tie the cylinder and
bracket up to support them out of the way.
21Reaching down between the transmission
and the bulkhead, unscrew the knurled
retaining nut and withdraw the speedometer
cable from the transmission.
22Remove the front roadwheel trims, then
loosen off the front wheel retaining bolts.
Raise the vehicle and support it on axle
stands at a suitable height to allow working
underneath and eventual transmission
removal from under the front end.
23Drain the transmission oil as described
previously in this Section.
24Disconnect and remove the starter motor
(photos).
25Detach the reversing light switch lead
connector.
26Undo the retaining bolt and detach the
earth lead from the rear end of the
transmission (see photo 7C.33). Refit the bolt
once the lead has been disconnected.
13•96 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
12B.15B Access cover to gear lever lower
connection to rod on the 1372 cc engine
Fig. 13.92 Exploded view of the gear selector and control road assembly components
fitted to 1372 cc models (Sec 12)
12B.15A Gear lever connection to the main
connecting rod on the 1372 cc engine
Fig. 13.91 Exploded view of the gear selector lever, rod and linkage components on
1372 cc models (Sec 12)
Page 222 of 303

27The engine must now be supported at its
left-hand end. If the engine/transmission lift
bracket is unbolted it can be attached at
another suitable position on the engine and
the lift sling/tool attached to it, but take care
not to attach it to a weak fixing point.
28The engine will need to be supported
using an engine lift beam/support bar of the
type shown in Fig. 13.93. A strong wood or
metal beam resting on blocks in the front wing
drain channels will suffice, or alternatively use
an engine lift hoist and sling.
29Refer to Section 13 in this Chapter and
Section 2 in Chapter 7 for details and remove
the front driveshaft each side.
30Prise back the tabs of the retaining
washers, then undo the retaining nuts and
detach the exhaust downpipe from the
manifold. Detach the exhaust mounting
bracket (where applicable) and lower the
exhaust to allow access to the gearchange
linkages.
31Disconnect the gearchange control and
selector link rod balljoints (photo). Do not alter
their lengths or the adjustment setting will be
affected.
32Using a small diameter pin punch, drive the
retaining pins from the retaining clips which
secure the left-hand side underwing shield.
Prise free the clips and detach the shield.
33Undo the retaining bolts and remove the
lower cover plate from the flywheel housing
(photo).
34Position a trolley jack under the
transmission with an interposed block ofwood to protect the casing and spread the
load. Raise the jack to support the weight of
the transmission.
35Check that the weight of the engine is
securely supported, then unbolt and detach
the front engine mounting unit, then the rear
engine mounting unit.
36Unscrew and remove the remaining bolts
securing the transmission to the engine. As
they are removed, note the position of any
brackets or additional fixings secured by
these bolts (photo).
37Check around the transmission to ensure
that all fixings are detached from it and out of
the way, then carefully pull the transmission
free from the engine dowel pins. If possible
engage the aid of an assistant to help in
guiding or lowering the unit as it is removed.
As the unit is withdrawn from the engine, take
care not to place any strain on the input shaft.
Once the input shaft is clear of the clutch, the
transmission can be lowered and manoeuvred
from underneath the car. If available, lower the
unit onto a suitable crawler board to ease its
withdrawal from under the front end of the car.
38Dismantling and overhaul of this
transmission is not recommended. If the
transmission has covered a high mileage it is
likely that several internal components are in
need of renewal. The cumulative cost of
renewing all worn and defective components
will almost certainly make overhaul
uneconomical when compared with the cost
of a new or service exchange transmission
from a FIAT dealer or transmission specialist.39Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure, but note the following special
points.
a) Ensure that the engine and transmission
mating surfaces and the dowel pins are
clean and that all clutch components are
in good condition.
b) Apply a thin smear of molybdenum
disulphide grease to the splines of the
input shaft. Do not over-lubricate though
or the grease may work its way onto the
clutch friction surfaces and cause clutch
slip.
c) Raise the transmission so that it is in-line
with the engine, engage the end of the
input shaft into the clutch driven plate hub
and align the splines of each to enable the
transmission to be pushed home. It may
well be necessary to turn the flywheel a
fraction so that the splines align for
re-engagement
d) Do not fully tighten the engine and
transmission retaining bolts until all are
attached.
e) Tighten all retaining bolts and nuts of the
specified torque wrench settings (where
given).
f) Refer to Section 13 in this Chapter for
details on refitting the driveshafts.
g) Refill the transmission with the specified
quantity and grade of oil before lowering
the car to the ground (see paragraph 11).
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•97
Fig. 13.93 FIAT lift beam/support bar in
place to support the weight of the engine.
Inset shows lift hook engagement point -
1372 cc models (Sec 12)
12B.24B . . . and retaining bolts (arrowed)
on the 1372 cc ie engine12B.24A Starter motor electrical
connection . . .
12B.36 Transmission upper retaining bolts.
Note bracket under the left-hand bolt12B.33 Lower cover plate and retaining
bolts (arrowed)12B.31 Gear control and selector link rod
joints
13
Page 224 of 303
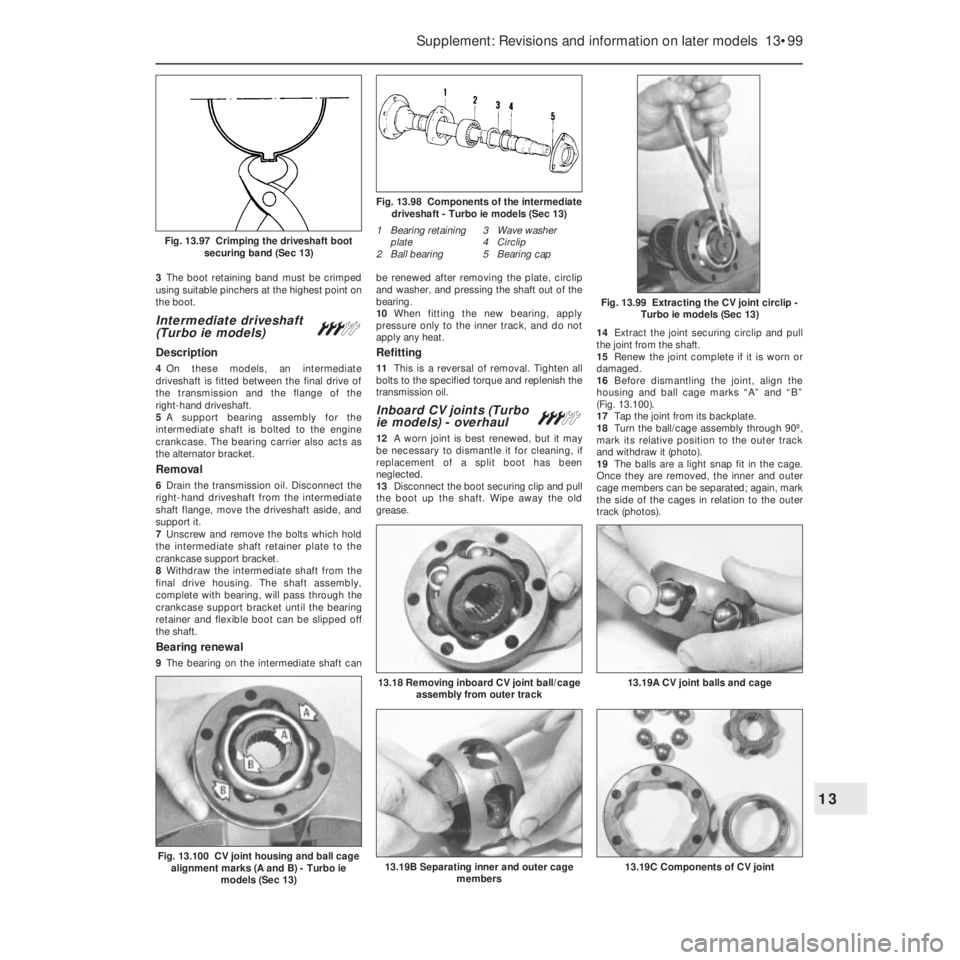
3The boot retaining band must be crimped
using suitable pinchers at the highest point on
the boot.
Intermediate driveshaft
(Turbo ie models) #
Description
4On these models, an intermediate
driveshaft is fitted between the final drive of
the transmission and the flange of the
right-hand driveshaft.
5A support bearing assembly for the
intermediate shaft is bolted to the engine
crankcase. The bearing carrier also acts as
the alternator bracket.
Removal
6Drain the transmission oil. Disconnect the
right-hand driveshaft from the intermediate
shaft flange, move the driveshaft aside, and
support it.
7Unscrew and remove the bolts which hold
the intermediate shaft retainer plate to the
crankcase support bracket.
8Withdraw the intermediate shaft from the
final drive housing. The shaft assembly,
complete with bearing, will pass through the
crankcase support bracket until the bearing
retainer and flexible boot can be slipped off
the shaft.
Bearing renewal
9The bearing on the intermediate shaft canbe renewed after removing the plate, circlip
and washer, and pressing the shaft out of the
bearing.
10When fitting the new bearing, apply
pressure only to the inner track, and do not
apply any heat.
Refitting
11This is a reversal of removal. Tighten all
bolts to the specified torque and replenish the
transmission oil.
Inboard CV joints (Turbo
ie models) - overhaul #
12A worn joint is best renewed, but it may
be necessary to dismantle it for cleaning, if
replacement of a split boot has been
neglected.
13Disconnect the boot securing clip and pull
the boot up the shaft. Wipe away the old
grease. 14Extract the joint securing circlip and pull
the joint from the shaft.
15Renew the joint complete if it is worn or
damaged.
16Before dismantling the joint, align the
housing and ball cage marks “A” and “B”
(Fig. 13.100).
17Tap the joint from its backplate.
18Turn the ball/cage assembly through 90º,
mark its relative position to the outer track
and withdraw it (photo).
19The balls are a light snap fit in the cage.
Once they are removed, the inner and outer
cage members can be separated; again, mark
the side of the cages in relation to the outer
track (photos).
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•99
Fig. 13.99 Extracting the CV joint circlip -
Turbo ie models (Sec 13)
Fig. 13.98 Components of the intermediate
driveshaft - Turbo ie models (Sec 13)
1 Bearing retaining
plate
2 Ball bearing3 Wave washer
4 Circlip
5 Bearing cap
Fig. 13.97 Crimping the driveshaft boot
securing band (Sec 13)
13.19C Components of CV joint13.19B Separating inner and outer cage
members
13.19A CV joint balls and cage13.18 Removing inboard CV joint ball/cage
assembly from outer track
Fig. 13.100 CV joint housing and ball cage
alignment marks (A and B) - Turbo ie
models (Sec 13)
13
Page 291 of 303

REF•8General Repair Procedures
Whenever servicing, repair or overhaul work
is carried out on the car or its components,
observe the following procedures and
instructions. This will assist in carrying out the
operation efficiently and to a professional
standard of workmanship.
Joint mating faces and gaskets
When separating components at their
mating faces, never insert screwdrivers or
similar implements into the joint between the
faces in order to prise them apart. This can
cause severe damage which results in oil
leaks, coolant leaks, etc upon reassembly.
Separation is usually achieved by tapping
along the joint with a soft-faced hammer in
order to break the seal. However, note that
this method may not be suitable where
dowels are used for component location.
Where a gasket is used between the mating
faces of two components, a new one must be
fitted on reassembly; fit it dry unless otherwise
stated in the repair procedure. Make sure that
the mating faces are clean and dry, with all
traces of old gasket removed. When cleaning a
joint face, use a tool which is unlikely to score
or damage the face, and remove any burrs or
nicks with an oilstone or fine file.
Make sure that tapped holes are cleaned
with a pipe cleaner, and keep them free of
jointing compound, if this is being used,
unless specifically instructed otherwise.
Ensure that all orifices, channels or pipes
are clear, and blow through them, preferably
using compressed air.
Oil seals
Oil seals can be removed by levering them
out with a wide flat-bladed screwdriver or
similar implement. Alternatively, a number of
self-tapping screws may be screwed into the
seal, and these used as a purchase for pliers or
some similar device in order to pull the seal free.
Whenever an oil seal is removed from its
working location, either individually or as part
of an assembly, it should be renewed.
The very fine sealing lip of the seal is easily
damaged, and will not seal if the surface it
contacts is not completely clean and free from
scratches, nicks or grooves. If the original
sealing surface of the component cannot be
restored, and the manufacturer has not made
provision for slight relocation of the seal
relative to the sealing surface, the component
should be renewed.
Protect the lips of the seal from any surface
which may damage them in the course of
fitting. Use tape or a conical sleeve where
possible. Lubricate the seal lips with oil before
fitting and, on dual-lipped seals, fill the space
between the lips with grease.
Unless otherwise stated, oil seals must be
fitted with their sealing lips toward the
lubricant to be sealed.
Use a tubular drift or block of wood of the
appropriate size to install the seal and, if the
seal housing is shouldered, drive the seal
down to the shoulder. If the seal housing isunshouldered, the seal should be fitted with
its face flush with the housing top face (unless
otherwise instructed).
Screw threads and fastenings
Seized nuts, bolts and screws are quite a
common occurrence where corrosion has set
in, and the use of penetrating oil or releasing
fluid will often overcome this problem if the
offending item is soaked for a while before
attempting to release it. The use of an impact
driver may also provide a means of releasing
such stubborn fastening devices, when used
in conjunction with the appropriate
screwdriver bit or socket. If none of these
methods works, it may be necessary to resort
to the careful application of heat, or the use of
a hacksaw or nut splitter device.
Studs are usually removed by locking two
nuts together on the threaded part, and then
using a spanner on the lower nut to unscrew
the stud. Studs or bolts which have broken off
below the surface of the component in which
they are mounted can sometimes be removed
using a stud extractor. Always ensure that a
blind tapped hole is completely free from oil,
grease, water or other fluid before installing
the bolt or stud. Failure to do this could cause
the housing to crack due to the hydraulic
action of the bolt or stud as it is screwed in.
When tightening a castellated nut to accept
a split pin, tighten the nut to the specified
torque, where applicable, and then tighten
further to the next split pin hole. Never slacken
the nut to align the split pin hole, unless stated
in the repair procedure.
When checking or retightening a nut or bolt
to a specified torque setting, slacken the nut
or bolt by a quarter of a turn, and then
retighten to the specified setting. However,
this should not be attempted where angular
tightening has been used.
For some screw fastenings, notably
cylinder head bolts or nuts, torque wrench
settings are no longer specified for the latter
stages of tightening, “angle-tightening” being
called up instead. Typically, a fairly low torque
wrench setting will be applied to the
bolts/nuts in the correct sequence, followed
by one or more stages of tightening through
specified angles.
Locknuts, locktabs and washers
Any fastening which will rotate against a
component or housing during tightening
should always have a washer between it and
the relevant component or housing.
Spring or split washers should always be
renewed when they are used to lock a critical
component such as a big-end bearing
retaining bolt or nut. Locktabs which are
folded over to retain a nut or bolt should
always be renewed.
Self-locking nuts can be re-used in non-
critical areas, providing resistance can be felt
when the locking portion passes over the bolt
or stud thread. However, it should be noted
that self-locking stiffnuts tend to lose theireffectiveness after long periods of use, and
should then be renewed as a matter of course.
Split pins must always be replaced with
new ones of the correct size for the hole.
When thread-locking compound is found
on the threads of a fastener which is to be re-
used, it should be cleaned off with a wire
brush and solvent, and fresh compound
applied on reassembly.
Special tools
Some repair procedures in this manual
entail the use of special tools such as a press,
two or three-legged pullers, spring com-
pressors, etc. Wherever possible, suitable
readily-available alternatives to the manu-
facturer’s special tools are described, and are
shown in use. In some instances, where no
alternative is possible, it has been necessary
to resort to the use of a manufacturer’s tool,
and this has been done for reasons of safety
as well as the efficient completion of the repair
operation. Unless you are highly-skilled and
have a thorough understanding of the
procedures described, never attempt to
bypass the use of any special tool when the
procedure described specifies its use. Not
only is there a very great risk of personal
injury, but expensive damage could be
caused to the components involved.
Environmental considerations
When disposing of used engine oil, brake
fluid, antifreeze, etc, give due consideration to
any detrimental environmental effects. Do not,
for instance, pour any of the above liquids
down drains into the general sewage system,
or onto the ground to soak away. Many local
council refuse tips provide a facility for waste
oil disposal, as do some garages. If none of
these facilities are available, consult your local
Environmental Health Department, or the
National Rivers Authority, for further advice.
With the universal tightening-up of legis-
lation regarding the emission of environmen-
tally-harmful substances from motor vehicles,
most vehicles have tamperproof devices fitted
to the main adjustment points of the fuel
system. These devices are primarily designed
to prevent unqualified persons from adjusting
the fuel/air mixture, with the chance of a
consequent increase in toxic emissions. If
such devices are found during servicing or
overhaul, they should, wherever possible, be
renewed or refitted in accordance with the
manufacturer’s requirements or current
legislation.
Note: It is
antisocial and
illegal to dump
oil down the
drain. To find
the location of
your local oil
recycling
bank, call this
number free.