1983 FIAT UNO oil change
[x] Cancel search: oil changePage 88 of 303

20By connecting a pressurised container to
the master cylinder fluid reservoir, bleeding is
then carried out by simply opening each bleed
screw in turn and allowing the fluid to run out,
rather like turning on a tap, until no air is
visible in the expelled fluid.
21By using this method, the large reserve of
hydraulic fluid provides a safeguard against
air being drawn into the master cylinder
during bleeding which often occurs if the fluid
level in the reservoir is not maintained.
22Pressure bleeding is particularly effective
when bleeding “difficult” systems or when
bleeding the complete system at time of
routine fluid renewal.
All methods
23When bleeding is completed, check and
top up the fluid level in the master cylinder
reservoir.
24Check the feel of the brake pedal. If it
feels at all spongy, air must still be present in
the system and further bleeding is indicated.
Failure to bleed satisfactorily after a
reasonable period of the bleeding operation,
may be due to worn master cylinder seals.
25Discard brake fluid which has been
expelled. lt is almost certain to be
contaminated with moisture, air and dirt
making it unsuitable for further use. Clean
fluid should always be stored in an airtight
container as it absorbs moisture readily
(hygroscopic) which lowers its boiling point
and could affect braking performance under
severe conditions.
13 Vacuum servo unit-
description
A vacuum servo unit is fitted into the brake
hydraulic circuit on 55 and 70 models in series
with the master cylinder, to provide assistance
to the driver when the brake pedal is
depressed. This reduces the effort required by
the driver to operate the brakes under all
braking conditions.
The unit operates by vacuum obtained from
the induction manifold and comprises basically
a booster diaphragm and non-return valve. The
servo unit and hydraulic master cylinder are
connected together so that the servo unit
piston rod acts as the master cylinder pushrod.
The driver’s braking effort is transmitted
through another pushrod to the servo unit
piston and its built-in control system. The servo
unit piston does not fit tightly into the cylinder,
but has a strong diaphragm to keep its edges
in constant contact with the cylinder wall, so
assuring an air tight seal between the two
parts. The forward chamber is held under
vacuum conditions created in the inlet manifold
of the engine and, during periods when the
brake pedal is not in use, the controls open a
passage to the rear chamber so placing it
under vacuum conditions as well. When the
brake pedal is depressed, the vacuum passageto the rear chamber is cut off and the chamber
opened to atmospheric pressure. The
consequent rush of air pushes the servo piston
forward in the vacuum chamber and operates
the main pushrod to the master cylinder.
The controls are designed so that
assistance is given under all conditions and,
when the brakes are not required, vacuum in
the rear chamber is established when the
brake pedal is released. All air from the
atmosphere entering the rear chamber is
passed through a small air filter.
Under normal operating conditions, the
vacuum servo unit is very reliable and does
not require overhaul except at very high
mileages. In this case, it is far better to obtain
a service exchange unit, rather than repair the
original unit.
It is emphasised that the servo unit assists
in reducing the braking effort required at the
foot pedal and in the event of its failure, the
hydraulic braking system is in no way affected
except that the need for higher pressures will
be noticed.
14 Vacuum servo unit-
servicing and testing
1Regularly, check that the vacuum hose
which runs between the servo unit and the
inlet manifold is in good condition and is a
tight fit at both ends.
2If broken or badly clogged, renew the air
filter which is located around the brake pedal
push rod. Access to this is obtained by
disconnecting the pushrod from the
cross-shaft or pedal arm, withdrawing the
pushrod, dust excluding boot and end cap.
3If the new filter is cut diagonally from its
centre hole, future renewal can be carried out
without the need for disconnection of the
pushrod.
4If the efficiency of the servo unit is suspect,
it can be checked out in the following way.
5Run the engine, then switch off the ignition.
Depress the footbrake pedal; the distinctive
in-rush of air into the servo should be clearly
heard. It should be possible to repeat this
operation several times before the vacuum in
the system is exhausted.
6Start the engine and have an assistant
apply the footbrake pedal and hold it down.
Disconnect the vacuuum hose from the servo.
There should not be any in-rush of air into the
servo through the connecting stub. lf there is,
the servo diaphragm is probably faulty. During
this test, expect the engine to idle roughly,
unless the open end of the hose to the inlet
manifold is plugged. Reconnect the hose.
7With the engine off, depress the brake
pedal fully. Start the engine with the brake
pedal still depressed; the pedal should be felt
to go down fractionally.
8If the results of these tests are not
satisfactory, remove the unit and fit a new one
as described in the next Section.
15 Vacuum servo unit-
removal and refitting
3
1Syphon as much fluid as possible out of the
master cylinder reservolr.
2Disconnect electrical leads from the
terminals in the reservoir cap then uncouple
the rigid pipelines from the master cylinder
body. Be prepared to catch leaking fluid and
plug the open ends of the pipelines.
3The master cylinder can be unbolted now
from the servo unit, or detached later when
the complete assembly is withdrawn.
4Working inside the car, disconnect the
servo pushrod from the pedal then remove the
servo mounting nuts.
5Withdraw the servo assembly into the
engine compartment, then remove it to the
bench. lf the master cylinder is still attached,
cover the wings with protective sheeting, in
case brake fluid is spilled during removal.
6Refitting is a reversal of the removal
process, but adjust the pushrod clearance as
described in Section 9. On completion of
refitting, bleed the complete hydraulic system
as described in Section 12. Note: Where the
help of an assistant is available, the servo
pushrod need not be disconnected from the
pedal. The rod is a sliding fit in the servo and
the servo can be simply pulled off the rod.
Refitting without having disconnected the rod
from the pedal can be difficult unless the help
of an assistant is available.
16 Handbrake- adjustment
1
Adjustment is normally automatic, by the
movement of the rear brake shoes on their
automatic adjusters.
However, owing to cable stretch,
supplementary adjustment is occasionally
required at the control lever adjuster nut. The
need for this adjustment is usually indicated
by excessive movement of the control lever
when fully applied.
1The rear brakes should be fully applied
when the handbrake control lever has been
pulled over four or five notches.
2If adjustment is required, release the
8•8 Braking system
16.2 Handbrake adjuster nuts
Page 101 of 303

3The centralised door locking system can
operate independently of the key.
4To gain access to the lock solenoid and
linkage, remove the front door trim panel as
described in Chapter 12.
5Disconnect the battery negative lead.
6Disconnect the electrical wiring plugs from
the solenoid within the door cavity.
7Disconnect the solenoid from the lock lever
by removing the clip.
8Unscrew the two bolts which secure the
solenoid to the door and remove it.
9Renew the solenoid or switch as necessary.
10Refitting is a reversal of removal.
11Refer to Section 10 for details of system
fuses and relays.
33 Economy gauge
(Econometer)
2
1This device is fitted to ES (energy saving)
models and indicates to the driver the fuel
consumption (in litres per 100 km) coupled
with a needle which moves over coloured
sections of a dial to make the driver aware
that his method of driving is either conducive
to high or low fuel consumption. Refer to
Chapter 3, Section 16.
2The device is essentially a vacuum gauge
which also incorporates a warning lamp to
indicate to the driver when a change of gear is
required.
3A fuel cut-out valve (see Chapter 3, Sec-
tion 11) is used in conjunction with the
economy gauge so that when the accelerator
pedal is released during a pre-determined
engine speed range, fuel supply to the engine
is stopped, but resumes when the engine
speed falls below the specified range.
LED (light emitter diode)
4The gearchange indicator will only light up
at engine speeds in excess of 2000 rev/min
for vacuum pressures up to 600 mm Hg in 1st,
2nd and 3rd speed gears and for vacuum
pressures up to 676 mm Hg in 4th speedgear. The light will not come on if 5th speed
gear is engaged or if the coolant temperature
is below 55ºC.
5There is a two second delay in the light
coming on to prevent it operating during rapid
acceleration in a low gear.
6If the LED light comes on during
deceleration it should be ignored.
Fault finding
7A faulty economy gauge should be checked
in the following way.
8Refer to Section 21 and remove the
instrument panel.
9Disconnect the economy gauge L
connector and then connect a test lamp
between the BN cable contact and earth. If
the lamp comes on then the gauge supply
circuit is not open. If the lamp does not come
on, check all connections in the supply cable
which comes from the interconnecting unit of
the electrical system, also Fuse No 12.
10Now connect a voltmeter between the
white cable and earth. Check the voltage with
the engine not running, but the ignition
switched on. It should be between 0.7 and
0.9 volt. If the reading varies considerably
from that specified, check the connections
between the economy gauge and the fuel
cut-out device control unit. If the fault cannot
be rectified, renew the ignition control unit
(Digiplex system, see Chapter 4).
11Now check the closed throttle valve plate
switch by connecting a voltmeter between the
brown and BN cables of the L connector. With
the valve plate open, there should be no
reading, but with it open, voltage should be
indicated.
12Failure to conform as described will be
due to a faulty earth in the switch or a faulty
fuel cut-out device control unit.
13A further test of the throttle valve plate
switch may be carried out by disconnecting
the multi-plug from the fuel cut-out device
control unit.
14Connect a test lamp to contact 4 (positive
battery terminal). The lamp should come on,
when the engine is idling or the accelerator
released. If it does not, renew the throttle
valve plate switch.15Connect a tachometer to the brown/white
cable contact in the L connector and record
the engine speed with the engine running. If
no reading is obtained, renew the Digiplex
ignition control unit which must be faulty.
34 Check control (warning
module) system
2
1This is fitted into the instrument panel of
certain models to provide a means of
checking the operation of many electrical
circuits and other systems in the interest of
safety. Sensors are used where appropriate.
2The following components are not
monitored by the system, but have separate
warning lamps:
Handbrake “on”
Choke in use
Low engine oil pressure
Battery charge indicator
3The multi-functional electronic device
automatically checks the following functions
whether the engine is running or not:
Coolant level
Disc pad wear
Door closure
Engine oil level
Front parking lamps
Rear foglamps
Stop lamps
4The check information is stored by the
system monitor until the engine is started
when the display panel then indicates the
situation by means of the LEDs (light emitter
diodes) and the general lamp.
5If all functions are in order, the green panel
lamp will come on when the ignition key is
turned and will go out after two to three
seconds.
6If some functions are not in order, then the
red panel lamp will come on also the
appropriate LED.
Sensors - checking
7If a fault signal occurs which is
subsequently found to be incorrect, first
check the wiring connections between the
9•12 Electrical system
Fig. 9.15 Check system control panel (Sec 34)
A Parking lamps
B Coolant levelC Engine oil level
D Door closureE Brake fluid level
F Disc pad wearFig. 9.14 Location of control units (Sec 33)
A Digiplex ignition system control unit
B Fuel cut-out valve control unit
Page 111 of 303

balljoint from the hub carrier using a suitable
“splitter” tool. If such a tool is not available,
support the base of the brake disc and drive
the balljoint taper pin downwards, but screw
on the nut to protect the threads.
4Remove the hub carrier.
5Refitting is a reversal of removal, use a new
driveshaft nut and tighten all nuts and bolts to
the specified torque. Stake the driveshaft nut
after tightening.
6 Track control arm-
removal and refitting
3
1Raise the front of the car and support it
securely.
2Unless a special tool is available to press
the track control arm balljoint from the hub
carrier, the driveshaft will have to be
disconnected as described in Chapter 7,
Section 2, paragraphs 1 to 8 to provide more
space to enable the balljoint taper pin to be
driven from the hub carrier. This should now
be done as described in the preceding
Section (photo).
3Unbolt the inboard end of the track control
arm. This is retained by a pivot bolt and a
clamp (photo).
4As previously explained, a worn balljoint or
flexible pivot bushes will necessitate renewal
of the track control arm complete. Note that itmay, however, be possible to obtain a
replacement balljoint through a motor factor.
5Refitting is a reversal of removal. Tighten all
nuts and bolts to the specified torque. Use a
new driveshaft nut and stake it into the
driveshaft groove after tightening.
7 Front crossmember-
removal and refitting
3
1Raise the front of the car, support securely
with axle stands placed under the
side-members or sill jacking points.
2Remove the front roadwheels.
3Unscrew the nuts from the tie-rod end
balljoint taper pins and then using a balljoint
“splitter” tool disconnect the balljoints from
the steering arms on the hub carrier.
4Unscrew the bolts which hold the inboard
track control arms to the body members, and
also withdraw the pivot bolt from the body
bracket.
5Support the weight of the engine/
transmission using a hoist or support bar
across the top of the engine compartment as
described in Chapter 6.
6Disconnect the lower (central) engine/
transmission flexible mounting from the floor
pan.
7Unscrew the steering rack mounting boltsand remove them. Leave the steering rack
hanging loose.
8Remove the front crossmember mounting
bolts and manoeuvre it from the car.
9Refitting is a reversal of removal. Tighten all
nuts and bolts to the specified torque wrench
settings and on completion, check the front
wheel alignment as described in Chapter 10.
8 Rear shock absorber-
removal and refitting
3
1Open the tailgate and remove the cover
from the shock absorber top mounting which
is located within the luggage area (photo).
2Hold the flats on the spindle with an
open-ended spanner and then unscrew the
self-locking nut.
3Working under the car, disconnect the
shock absorber lower mounting.
4Withdraw the unit from under the wing.
5The shock absorber can be tested as
described in Section 2.
6Refitting is a reversal of removal. Tighten
mounting nuts and bolts to the specified
torque.
9 Rear coil spring-
removal and refitting
3
1Raise the rear of the car and support it
securely on axle stands placed under the
side-members or sill jacking points.
2Remove the roadwheel.
3Place a jack under the brake drum and
support the suspension trailing arm.
4Disconnect the shock absorber lower
mounting and then lower the trailing arm jack
until the coil spring can be withdrawn.
5Refitting is a reversal of removal. If the
spring is being changed, make sure that it is
of the same colour code as the original and
that its lower coil is correctly located up
against its stop in the spring pan.
6Tighten the shock absorber lower mounting
bolt to the specified torque.
11•4 Suspension
8.1 Rear shock absorber upper mounting
coverFig. 11.7 Front crossmember bolts (Sec 7)Fig. 11.6 Steering rack mounting bolts
(Sec 7)
6.3 Track control arm inboard fixing6.2 Separating track control arm balljoint
from hub carrier
Page 127 of 303

Cooling system................................................................................. 8
Part A: 999 cc engine
Description
Maintenance
Thermostat - removal and refitting
Coolant pump - removal and refitting
Part B: 1301 cc Turbo ie engine
Description
Part C: 1372 cc ie and 1372 cc Turbo ie engines
Description
Maintenance
Cooling system - draining, flushing and refilling
Radiator (and cooling fan) - removal and refitting
Thermostat - removal and refitting
Coolant pump - removal and refitting
Coolant pump/alternator drivebelt - checking, renewal and
tensioning
Part D: Heater unit later models
Heater unit - removal and refitting
Heater unit - dismantling and reassembly
Fuel and exhaust systems............................................................... 9
Part A: General
Unleaded fuel
Air cleaner modified types
Fuel pump (999 cc engine) - description, removal and
refitting
Fuel tank (999 cc engine)
Part B: Carburettor models
Carburettor (Weber 32 TLF) - description
Carburettor (Weber 32 TLF) - idle speed and mixture
Carburettor (Weber 32 TLF) - removal and refitting
Carburettor (Weber 32 TLF) - overhaul
Carburettor (Weber 30/32 DMTE) - general
Carburettor (Weber 30/32 DMTE) - overhaul
Carburettor (Weber 32 ICEV 61/250 and DMTE 30/32,
DMTE 30/150) - general
Carburettor (Solex C 30/32-CIC 8) - description
Part C: Bosch LE-2 Jetronic fuel injection system
Description
Maintenance
Fuel filter - renewal
Air cleaner element - renewal
Idle speed and mixture - adjustment
Fuel injection system - electrical tests
Fuel injection system - mechanical tests
Fuel injection system components - removal and
refitting
Throttle control linkage - general
Fuel tank - general
Part D: Bosch Mono-Jetronic fuel injection system
Description
Maintenance
Fuel filter - renewal
Air cleaner element - renewal
Idle speed and mixture adjustment
Accelerator control system - check and adjustment
Fuel system - depressurisation
Fuel pump and supply - system checks
Fuel pump - removal and refitting
Injector unit - removal and refitting
Intake air temperature sensor - removal and refitting
Fuel injector - removal and refitting
Electronic control unit (ECU) - removal and refitting
Inlet manifold - removal and refitting
Exhaust manifold - removal and refitting
Catalytic converter - general information
Fuel evaporation control system - generalPart E: Bosch L3.1/2 Jetronic fuel injection systems
Description
Fuel system - depressurisation
Maintenance
Fuel filter - renewal
Air cleaner element - renewal
Checks and adjustments
Injection system components - removal and refitting
Part G: Turbocharger system
Description
Precautions
Turbocharger (1301 cc ie engine) - removal and refitting
Turbocharger (1372 cc ie engine) - removal and refitting
Intercooler - removal and refitting
Injector cooling fan - removal and refitting
Fault finding - fuel injection system
Fault finding - turbocharger system
Ignition system................................................................................. 10
General
Ignition timing (all later models)
Breakerless ignition system - description
Distributor (breakerless type) - removal and refitting
Distributor (breakerless type) - overhaul
Breakerless ignition system components - testing
Microplex ignition system - description
Distributor (Microplex) - removal and refitting
Microplex ignition system components - testing
Digiplex 2 ignition system - description
Distributor (Digiplex 2) - removal and refitting
Spark plugs and HT leads - general
Fault finding - Microplex ignition system
Clutch................................................................................................ 11
Clutch pedal adjustment (cable clutch)
Hydraulic clutch - description
Maintenance (hydraulic clutch)
Clutch master cylinder - removal, overhaul and
refitting
Clutch operating cylinder - removal, overhaul and
refitting
Clutch hydraulic system - bleeding
Transmission.................................................................................... 12
Part A: 1301 cc Turbo ie engine
Description
Gearchange linkage - removal and refitting
Gearchange linkage (Antiskid models) - general
Final drive output shafts - description and oil seal
renewal
Part B: 1372 cc ie and 1372 cc Turbo ie engines
Description
Maintenance
Oil level - checking
Oil - renewal
Gearlever and linkages - general
Transmission - removal and refitting
Part C: 999 and 1108 cc with C514 type transmission
Description
Maintenance
Driveshafts........................................................................................ 13
Inboard joint boots (non-Turbo models, September 1987 on) -
modification
Intermediate driveshaft (Turbo ie models)
Inboard CV joints (Turbo ie models - overhaul
Right-hand driveshaft damper weight (1108 and 1372 cc
models) - removal and refitting
13•2 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Page 131 of 303
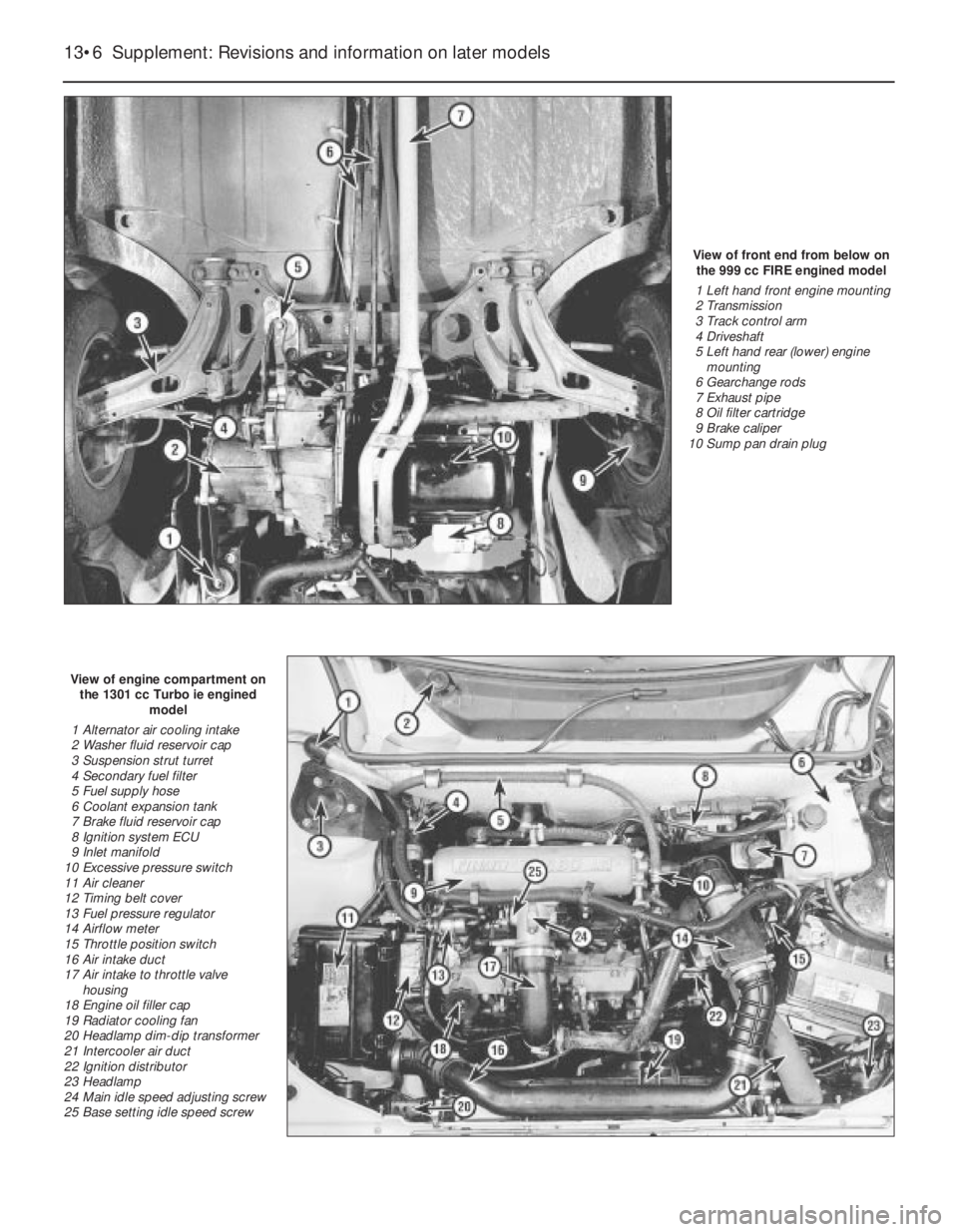
View of front end from below on
the 999 cc FIRE engined model
1 Left hand front engine mounting
2 Transmission
3 Track control arm
4 Driveshaft
5 Left hand rear (lower) engine
mounting
6 Gearchange rods
7 Exhaust pipe
8 Oil filter cartridge
9 Brake caliper
10 Sump pan drain plug
View of engine compartment on
the 1301 cc Turbo ie engined
model
1 Alternator air cooling intake
2 Washer fluid reservoir cap
3 Suspension strut turret
4 Secondary fuel filter
5 Fuel supply hose
6 Coolant expansion tank
7 Brake fluid reservoir cap
8 Ignition system ECU
9 Inlet manifold
10 Excessive pressure switch
11 Air cleaner
12 Timing belt cover
13 Fuel pressure regulator
14 Airflow meter
15 Throttle position switch
16 Air intake duct
17 Air intake to throttle valve
housing
18 Engine oil filler cap
19 Radiator cooling fan
20 Headlamp dim-dip transformer
21 Intercooler air duct
22 Ignition distributor
23 Headlamp
24 Main idle speed adjusting screw
25 Base setting idle speed screw
13•6 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Page 132 of 303

Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•7
View of engine compartment (air
cleaner removed) on the
1372 cc ie engined model
1 Engine oil level dipstick
2 Timing belt cover
3 Engine mounting (right-hand)
4 Clutch master cylinder fluid
reservoir
5 Fuel supply and return hoses
6 Injection unit
7 Inlet manifold
8 Washer reservoir
9 Brake master cylinder and fluid
reservoir
10 Injection system fuse/relay block
11 Suspension strut turret
12 Ignition coil
13 Ignition system ECU
14 Battery
15 Coolant filter expansion tank
16 Ignition distributor
17 Radiator cooling fan
18 Engine oil filler cap
19 Starter motor
20 Oil filter
View of front end from below on
the 1031 cc Turbo ie engined
model
1 Anti-roll bar
2 Exhaust pipe
3 Track control arm
4 Engine centre mounting
5 Gearchange rods
6 Brake caliper
7 Left-hand driveshaft
8 Intermediate driveshaft
9 Right-hand driveshaft
10 Transmission
11 Engine oil drain plug
12 Auxiliary lamp
13 Horn
14 Intercooler
15 Starter motor
16 Oil filter cartridge
17 Oil pressure sender unit
18 Engine oil cooler
19 Right-hand underwing shield
20 Left-hand underwing shield
13
Page 133 of 303

Lubrication system
Oil pump type:
999/1108 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Gear driven from front of crankshaft.
1372 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pump operated from front of crankshaft. Oil pressure relief valve in
front cover.
Tooth tip-to-body clearance (999/1108 cc) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.080 to 0.186 mm
Gear endfloat:
999/1108 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.025 to 0.056 mm
1372 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.040 to 0.106 mm
Oil pressure (at normal operating temperature) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.4 to 4.9 bars
Oil filter:
999/1108 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion F107
1372 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion C106
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Auxiliary shaft sprocket bolt (1372 cc) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83 62
Big-end cap bolts:
999/1108 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 30
1372 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51 38
Camshaft bearing cap bolts:
M8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 14
M6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Camshaft cover screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 6
Camshaft housing to lower cylinder head securing bolt (1372 cc) . . . . . 20 15
Camshaft housing to inlet manifold bracket bolt (1372 cc) . . . . . . . . . . 25 18
Camshaft sprocket bolt
999/1108 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68 50
1372 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83 62
Centre mounting to final drive casing bracket (1201/1301 cc) . . . . . . . . 23 17
Coolant temperature switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 18
Crankshaft pulley bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 18
Crankshaft pulley nut (1372 cc) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197 145
Crankshaft rear oil seal retainer bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Crankshaft sprocket bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79 58
13•8 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
View of front end from below on
the 1372 cc ie engine model
1 Oil filter
2 Engine oil drain plug
3 Starter motor
4 Horns
5 Transmission front mounting
6 Front fog lamp and adjuster
7 Driveshaft
8 Transmission rear mounting
9 Gearchange linkage
10 Exhaust downpipe and system
joint
11 Anti-roll bar
12 Track control arm
13 Tie-rod balljoint
14 Brake unit
15 Driveshaft damper
16 Underwing shield
Page 142 of 303

General dimensions, weights and capacities
Dimensions
Overall length . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3689 mm
Overall width:
Base and Super models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1558 mm
SX and Turbo models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1562 mm
Height (unladen):
1372 cc (except Turbo) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1425 mm
1299/1301 cc (except Turbo) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1420 mm
Turbo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1405 mm
All other models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1415 mm
Weights (kerb)
Note: 3-door model weights are given. Add 15 kg to the following for 5-door models. Weight will also vary according to the model version.
903 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 740 kg
999 cc (45, 45 S and 45 SX) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 740 to 775 kg
1108 cc (60 S and 60 SX) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 760 to 795 kg
1299/1301 cc (70 SX) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 770 kg
1301 cc Turbo ie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 845 kg
1372 cc (1.4 ie S catalyst) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 830 kg
1372 cc ie (70 SX) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 795 to 845 kg
1732 cc Turbo ie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 925 kg
Capacities
Fuel tank:
1372 cc Turbo ie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50 litres
All other models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42 litres
Engine oil (with filter change):
903, 999 and 1108 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.8 litres
1116, 1299/1301 and 1372 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.1 litres
Transmission:
1301 cc Turbo ie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.9 litres
1372 cc Turbo ie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 litres
All other engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.4 litres
Cooling system:
903, 999 and 1108 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.6 litres
1116 and 1299/1301 cc, non-catalyst 1372 cc ie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.2 litres
1372 cc ie with catalyst . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.5 litres
1301 cc Turbo ie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.9 litres
1372 cc Turbo ie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.7 litres
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•17
13