1969 FORD MUSTANG oil type
[x] Cancel search: oil typePage 238 of 413
04-04-07
Rear Axle — Ford Light-Duty (WER)
04-04-07
RUNOUT CHECK
E 1573-A
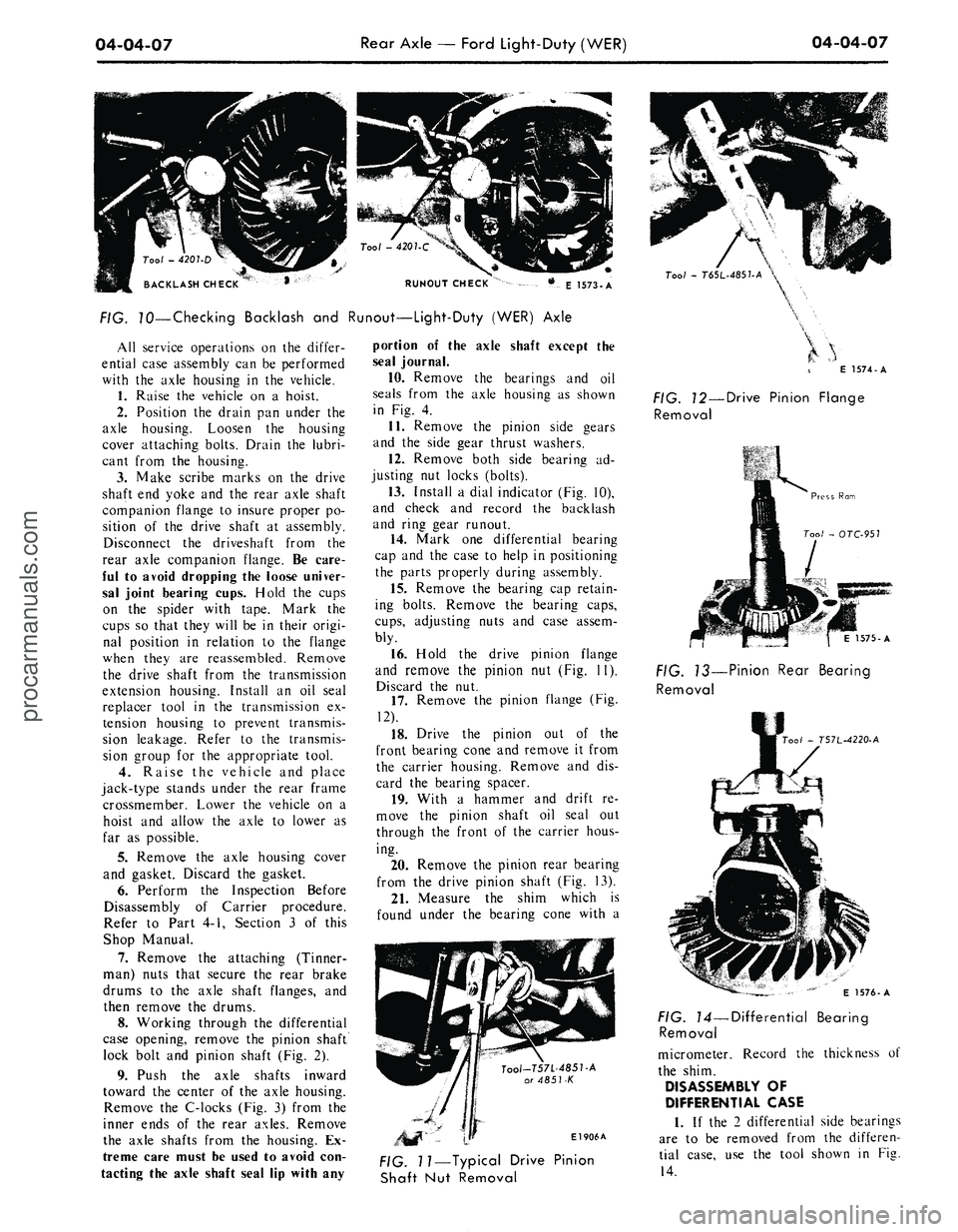
FIG. 70—Checking Backlash and Runout—Light-Duty (WER) Axle
All service operations on the differ-
ential case assembly can be performed
with the axle housing in the vehicle.
1.
Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
2.
Position the drain pan under the
axle housing. Loosen the housing
cover attaching bolts. Drain the lubri-
cant from the housing.
3.
Make scribe marks on the drive
shaft end yoke and the rear axle shaft
companion flange to insure proper po-
sition of the drive shaft at assembly.
Disconnect the driveshaft from the
rear axle companion flange. Be care-
ful to avoid dropping the loose univer-
sal joint bearing cups. Hold the cups
on the spider with tape. Mark the
cups so that they will be in their origi-
nal position in relation to the flange
when they are reassembled. Remove
the drive shaft from the transmission
extension housing. Install an oil seal
replacer tool in the transmission ex-
tension housing to prevent transmis-
sion leakage. Refer to the transmis-
sion group for the appropriate tool.
4.
Raise the vehicle and place
jack-type stands under the rear frame
crossmember. Lower the vehicle on a
hoist and allow the axle to lower as
far as possible.
5.
Remove the axle housing cover
and gasket. Discard the gasket.
6. Perform the Inspection Before
Disassembly of Carrier procedure.
Refer to Part 4-1, Section 3 of this
Shop Manual.
7.
Remove the attaching (Tinner-
man) nuts that secure the rear brake
drums to the axle shaft flanges, and
then remove the drums.
8. Working through the differential
case opening, remove the pinion shaft
lock bolt and pinion shaft (Fig. 2).
9. Push the axle shafts inward
toward the center of the axle housing.
Remove the C-locks (Fig. 3) from the
inner ends of the rear axles. Remove
the axle shafts from the housing. Ex-
treme care must be used to avoid con-
tacting the axle shaft seal lip with any
portion of the axle shaft except the
seal journal.
10.
Remove the bearings and oil
seals from the axle housing as shown
in Fig. 4.
11.
Remove the pinion side gears
and the side gear thrust washers.
12.
Remove both side bearing ad-
justing nut locks (bolts).
13.
Install a dial indicator (Fig. 10),
and check and record the backlash
and ring gear runout.
14.
Mark one differential bearing
cap and the case to help in positioning
the parts properly during assembly.
15.
Remove the bearing cap retain-
ing bolts. Remove the bearing caps,
cups,
adjusting nuts and case assem-
bly.
16.
Hold the drive pinion flange
and remove the pinion nut (Fig. 11).
Discard the nut.
17.
Remove the pinion flange (Fig.
12).
18.
Drive the pinion out of the
front bearing cone and remove it from
the carrier housing. Remove and dis-
card the bearing spacer.
19.
With a hammer and drift re-
move the pinion shaft oil seal out
through the front of the carrier hous-
ing.
20.
Remove the pinion rear bearing
from the drive pinion shaft (Fig. 13).
21.
Measure the shim which is
found under the bearing cone with a
Tool-T57L-485T-A
or 4851-K
El 906A
Tool
-
T6SL-485UA
\
E 1574-A
FIG. 12—Drive Pinion Flange
Removal
1575-A
FIG. 13—Pinion Rear Bearing
Removal
00/
- T57L-4220-A
FIG. 11—Typical Drive Pinion
Shaft Nut Removal
E 1576-A
FIG. 14—Differential Bearing
Removal
micrometer. Record the thickness of
the shim.
DISASSEMBLY OF
DIFFERENTIAL CASE
1.
If the 2 differential side bearings
are to be removed from the differen-
tial case, use the tool shown in Fig.
14.procarmanuals.com
Page 240 of 413

04-04-09
Rear Axle — Ford Light-Duty (WER)
04-04-09
case several revolutions in each direc-
tion while the bearings are loaded to
seat the bearings in their cups. This
step is important.
5. Again loosen the right nut to re-
lease the preload. Check to see that
the left nut contacts the bearing cup.
Using the dial indicator set-up shown
in Fig. 13, Part 4-1, adjust the preload
to 0.008 to 0.012 case spread for new
bearings or 0.005 to 0.008 for the
original bearings, if re-used.
6. Check the runout of the differen-
tial case flange with a dial indicator.
If the runout does not now exceed
specifications, install a new ring gear,
if the runout still exceeds specifica-
tions,
the ring gear is true and the
trouble is due to either a defective
casting or worn bearings.
7.
Remove the differential case
from the carrier and remove the side
bearings from the case.
8. Install new bearings on the case
hubs,
and again install the differential
assembly in the carrier without the
ring gear.
9. Check the case runout again with
the new bearings. If the runout is now
within limits, the old bearings were
excessively worn. Use the new bear-
ings for assembly. If the runout is still
excessive, the case is defective and
should be replaced.
ASSEMBLY OF AXLE
Refer to Part 4-1 of this Shop
Manual for Cleaning and Inspection
procedures before starting assembly
operations.
ASSEMBLY OF
DIFFERENTIAL CASE
1.
Place the ring gear on the differ-
ential case. Install the retaining bolts
and torque them to specification.
2.
If the differential bearings were
removed, press them on as shown in
Fig. 17.
3.
Insert the pinion gear shaft lock
bolt into the case (loosely).
INSTALLATION OF DRIVE
PINION AND
DIFFERENTIAL CASE
1.
Place the shim(s) and pinion rear
bearing cone on the pinion shaft.
Press the bearing and shim(s) firmly
against the pinion shaft shoulder (Fig.
18).
2.
Place a new pinion bearing pre-
load (collapsible) spacer on the pinion
shaft.
REAR BEARING
CONE AND
ROLLER
Press Ram
FIG. 18—Drive Pinion Bearing
Installation
3.
Lubricate the pinion rear bearing
with axle lubricant.
4.
Lubricate the pinion front bear-
ing with axle lubricant. Lubricate the
pinion front bearing cone and place it
in the carrier housing.
5.
Install a new oil seal in the car-
rier casting (Fig. 19).
6. Insert the drive pinion shaft (U-
joint) flange into the pinion seal and
hold it firmly against the pinion front
bearing cone. From the rear of the
carrier casting, insert the pinion shaft
into the flange.
7.
Apply a small amount of lubri-
cant to the washer side of the flange
nut and start the nut. Use a new nut.
Hold the flange with the tool shown in
Fig. 12 and tighten the pinion shaft
nut. As the pinion shaft nut is tight-
ened, the pinion shaft is pulled into
the front bearing cone and into the
flange.
As the pinion shaft is pulled into
the front bearing cone, pinion shaft
end play is reduced. While there is
still end play in the pinion shaft, the
flange and cone will be felt to bottom.
This indicates that the bearing cone
and flange have bottomed on the col-
lapsible spacer.
From this point, a much greater
torque must be applied to turn the
pinion shaft nut, since the spacer must
be collapsed. From this point, also,
the nut should be tightened very slow-
ly and the pinion bearing preload play
checked often, so that the pinion bear-
ing preload does not exceed the speci-
fied limits.
If the pinion shaft nut is tightened
to the point that pinion bearing pre-
load exceeds the limits, the pinion
shaft must be removed and a new col-
lapsible spacer installed. Do not de-
crease the preload by loosening the
/
Tool
-
T58L-4676-A
/ E
1581-A
FIG. 19—Installing Pinion Seal
E 1582-A
FIG. 20—Checking Pinion Bearing
Preload
pinion shaft nut. This will remove the
compression between the pinion front
and rear bearing cones and the col-
lapsible spacer and may permit the
front bearing cone to turn on the pin-
ion shaft.
8. As soon as there is preload on
the bearings, turn the pinion shaft in
both directions several times to seat
the bearing rollers.
9. Adjust the bearing preload to
specification. Measure the preload
with the tool shown in Fig. 20.
10.
Apply a thin coating of lubri-
cant on the bearing bores so that the
differential bearing cups will move
easily.
11.
Place the cups on the bearings
and set the differential case assembly
in the carrier casting.
If the gear set is of the non-hunting
or partial non-hunting type, assemble
the differential case and ring gear as-
sembly in the carrier so that the
marked tooth on the pinion indexes
between the marked teeth on the ring
gear as shown in Fig. 49, Part 4-2.
In almost every case of improper
assembly (gears assembled out of
time),
the noise level and probability
of failure will be higher than they
would be with properly assembled
gears.
When installing the hunting type
gear set (no timing marks), assembleprocarmanuals.com
Page 294 of 413

07-01-03
General Transmission Service
07-01-03
COMPONENT INDEX
FMX Transmission
REAR SUPPORT (FMX)
Inspection
SHIFT POINT CHECKS
STATOR ONE-WAY CLUTCH CHECK
STATOR TO IMPELLOR INTERFERENCE
CHECK
STATOR TO TURBINE INTERFERENCE
CHECK
TRANSMISSION CLEANING
TURBINE AND STATOR END PLAY
CHECK
VACUUM DIAPHRAGM ADJUSTMENT
Altitude Compensating Type
Non-Altitude Compensating Type
VACUUM UNIT CHECK
Altitude Compensating Type
Non-Altitude Compensating Type
MODEL APPLICATION
All
Models
01-06
01-12
01-12
01-12
01-11
01-12
Ford
01-17
01-16
N/A
01-08
N/A
01-05
Mercury
N/A
N/A
N/A
01-08
N/A
01-05
Meteor
01-17
01-16
N/A
01-08
N/A
01-05
Cougar
01-17
01-16
N/A
01-08
N/A
01-05
Fairlane
01-17
01-16
N/A
01-08
N/A
01-05
Falcon
N/A
N/A
N/A
01-08
N/A
01-05
Montego
01-17
01-16
N/A
01-08
N/A
01-05
Mustang
01-17
01-16
N/A
01-08
N/A
01-05
Lincoln-
Continental
N/A
N/A
01-09
N/A
01-06
N/A
Thunderbird
N/A
N/A
01-09
N/A
01-06
N/A
Continental-
Mark
III
N/A
N/A
01-09
N/A
01-06
N/A
A page number indicates that the item is for the vehicle listed at the head of the column.
N/A indicates that the item is not applicable to the vehicle listed.
Three different three-speed trans-
missions are used. The C4 Automatic,
C6 Automatic and the FMX Auto-
matic. Part 7-1 covers testing, com-
mon adjustments and repairs, and
cleaning and inspection for the three
types of transmissions. Where there
are differences in procedures or speci-
fications, the type of transmission af-
fected will be designated.
l
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION TESTS
When diagnosing transmission
problems, refer to the Ford Car and
Truck Diagnosis Manual for the de-
tailed information on the items that
could be causing the problem.
The following preliminary checks
should be made before proceeding
with other diagnosis checks.
TRANSMISSION FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
1.
Make sure that the vehicle is
standing level. Then firmly apply the
parking brake.
2.
Run the engine at normal idle
speed. If the transmission fluid is cold
run the engine at fast idle speed
(about 1200 rpm) until the fluid reach-
es its normal operating temperature.
When the fluid is warm, slow the en-
gine down to normal idle speed.
3.
On a vehicle equipped with a
vacuum brake release, disconnect the
release line and plug the end of the
line;
otherwise the parking brake will
not hold the transmission in any drive
position.
4.
Shift the selector lever through
all positions, and place the lever at P.
Do not turn off the engine during the
fluid level checks.
5.
Clean all dirt from the transmis-
sion fluid dipstick cap before remov-
ing the dipstick from the filler tube.
6. Pull the dipstick out of the tube,
wipe it clean, and push it all the way
back into the tube. Be sure it is prop-
erly seated.
7.
Pull the dipstick out of the tube
again, and check the fluid level. The
fluid level should be above the ADD
mark. If necessary, add enough fluid
to the transmission through the filler
tube to bring the level between the
ADD and FULL marks on the dip-
stick. Do not overfill the transmission.
Install the dipstick, making sure it is
fully seated in the tube.
8. Connect the vacuum brake re-
lease line if so equipped, and test it
for proper operation.
FLUID AERATION CHECK
A fluid level that is too high will
cause the fluid to become aerated:
Aerated fluid will cause low control
pressure, and the aerated fluid may be
forced out the vent.
Check the transmission fluid level.
Low fluid level can affect the opera-
tion of the transmission, and may in-
dicate fluid leaks that could cause
transmission damage.
TRANSMISSION FLUID
LEAKAGE CHECKS
Check the speedometer cable con-
nection at the transmission. Replace
the rubber seal if necessary.
Leakage at the oil pan gasket often
can be stopped by tightening the at-
procarmanuals.com
Page 297 of 413

07-01-06
General Transmission Service
07-01-06
MAKE MARK HERE
BELLOWS INTACT
BELLOWS FAILED
FIG. 9—Checking Vacuum Unit Bellows
tester equipped with a vacuum pump
(Fig. 8). Set the regulator knob so
that the vacuum gauge reads 18 inches
with the end of the vacuum hose
blocked off.
Then connect the vacuum hose to
the transmission vacuum unit. If the
gauge still reads 18 inches, the vacuT
urn unit diaphragm is not leaking. As
the hose is removed from the trans-
mission vacuum unit, hold a finger
over the end of the control rod. When
the hose is removed, the internal
spring of the vacuum unit should push
the control rod outward.
ALTITUDE
COMPENSATING-TYPE
The vacuum diaphragm should be
checked for ruptured or damaged bel-
lows.
Check the diaphragm assembly
as follows:
1.
Remove the diaphragm and
throttle valve rod from the transmis-
sion.
2.
Insert a rod into the diaphragm,
making sure that the rod is buttonec
in the hole. Make a reference mark on
the rod where it enters the diaphragm
hole.
3.
Hold the assembly in such a way
that the end of the rod is resting on
the weighing surface of a scale (Fig.
9).
4.
Gradually press down on the dia-
phragm assembly until the rod is
pressed into the diaphragm body. If
the reference mark on the rod is still
visible with 12 pounds of force regis-
tered on the scale, the bellows are in-
tact. If the mark disappears before 4
pounds of force is exerted, the bellows
have failed and the diaphragm must
be replaced. If the bellows are intact,
then perform various pressure checks.
SHIFT POINT CHECKS
Check the minimum throttle up-
shifts in D. The transmission should
start in first gear, shift to second, and
then shift to third, within the shift
points specified in the specification
section.
While the transmission is in third
gear, depress the accelerator pedal
through the detent (to the floor). The
transmission should shift from third to
second or third to first, depending on
the vehicle speed.
Check the closed throttle downshift
from third to first by coasting down
from about 30 mph in third gear. The
shift should occur within the limits
specified in the specification section.
When the selector lever is at 2, the
transmission can operate only in sec-
ond gear.
With the transmission in third gear
and road speed over 30 mph, the
transmission should shift to second
gear when the selector lever is moved
from D to 2 to 1. The transmission
will downshift from second or third to
first gear when this same manual shift
is made below approximately 25 mph
with a C4 transmission, 30 mph with
D 1791.A
a C6 transmission or 35 mph with an
FMX transmission. This check will
determine if the governor pressure and
shift control valves are functioning
properly.
During the shift point check opera-
tion, if the transmission does not shift
within specifications or certain gear
ratios cannot be obtained, refer to the
Ford Car and Truck Diagnosis Manu-
al to resolve the problem.
AIR PRESSURE CHECKS
A NO DRIVE condition can exist,
even with correct transmission fluid
pressure, because of inoperative
clutches or bands. Erratic shifts could
be caused by a stuck governor valve.
The inoperative units can be located
through a series of checks by subst-
ituting air pressure for the fluid pres-
sure to determine the location of the
malfunction.
To make the air pressure checks,
drain the transmission fluid and re-
move the oil pan and the control valve
body assembly. The inoperative units
can be located by introducing air pres-
sure into the transmission case passa-
ges leading to the clutches, servos, and
governor (Figs. 10, 11 or 12).
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM BENCH
TESTS (FMX TRANSMISSION)
After the transmission has been as-
sembled and is ready for installationprocarmanuals.com
Page 299 of 413

07-01-08
General Transmission Service
07-01-08
3.
Install the bench testing tool on
the transmission.
4.
Remove the
1/8-inch
pipe plug
at the transmission case. Turn the
front pump in a clockwise direction at
75-100 rpm until a regular flow of
transmission fluid leaves the hole in
the transmission case. This operation
bleeds the air from the pump.
5.
Install the pressure gauge (77820
or T57L-77820-A) as shown in Fig.
13.
PRESSURE TESTS
Turn the front pump at 75-100 rpm
and note the gauge readings. The
pressure readings on the bench test
must be within the limits as outlined
in Figure 13, for the engine idle check.
If pressure gauge readings are with-
in limits in all selector lever positions,
install the vacuum diaphragm control
rod unit.
COMMON ADJUSTMENTS AND REPAIRS
TRANSMISSION FLUID DRAIN
AND REFILL
Normal maintenance and lubrica-
tion requirements do not necessitate
periodic automatic transmission fluid
changes.
If a major repair, such as a clutch
band, bearing, etc., is required in the
transmission, it will have to be re-
moved for service. At this time the
converter, transmission cooler and
cooler lines must be thoroughly
flushed to remove any dirt.
When filling a dry transmission and
converter, install five quarts of fluid.
Start the engine, shift the selector
lever as outlined below, and check and
add fluid as necessary.
Following are the procedures for
partial drain and refill due to in-
vehicle repair operation.
C4 TRANSMISSION
1.
On PEA models, disconnect the
fluid filler tube from the transmission
oil pan to drain the fluid.
On PEB and PEE models, loosen
the pan attaching bolts to drain the
fluid from the transmission.
2.
When the fluid has stopped
draining from the transmission, re-
move and thoroughly clean the pan
and the screen. Discard the pan gas-
ket.
3.
Place a new gasket on the pan,
and install the pan on the transmis-
sion.
4.
On PEA models, connect the
filler tube to the pan and tighten the
fitting securely.
5.
Add three quarts of fluid to the
transmission through the filler tube.
6. Run the engine at idle speed for
about two minutes, and then run it at
fast idle speed (about 1200 rpm) until
it reaches it's normal operating temp-
erature. Do not race the engine.
7.
Shift the selector lever through
all the positions, place it at P, and
check the fluid level. The fluid level
should be above the ADD mark. If
necessary, add enough fluid io the
transmission to bring the level be-
tween the ADD and FULL marks on
che dipstick. Do not overfill the trans-
mission.
FMX OK C6
TRANSMISSION
1.
Raise the vehicle on a hoist or
jack stands.
2.
Place a drain pan under the
transmission.
3.
Loosen the pan attaching bolts
to drain the fluid from the transmis-
sion.
4.
After the fluid has drained to the
level of the pan flange, remove the
rest of the pan bolts working from the
rear and both sides of the pan to
allow it to drop and drain slowly.
5.
When the fluid has stopped
draining from the transmission, re-
move and thoroughly clean the pan
and the screen. Discard the pan gas-
ket.
6. Place a new gasket on the pan,
and install the pan on the transmis-
sion.
7.
Add three quarts of fluid to the
transmission through the filler tube.
8. Run the engine at idle speed for
about two minutes, and then run it at
fast idle speed (about 1200 rpm) until
it reaches normal operating tempera-
ture.
Do not race the engine.
9. Shift the selector lever through
all the positions, place it at P, and
check the fluid level. The fluid level
should be above the ADD mark. If
necessary, add enough fluid to the
transmission to bring the level be-
tween the ADD and FULL marks on
the dipstick. Do not overfill the trans-
mission.
OIL COOLER TUBE
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
When fluid leakage is found at the
oil cooler, the cooler must be re-
placed. Cooler replacement is de-
scribed in the Cooling System Section
of Group 11.
When one or more of the fluid
cooler steel tubes must be replaced,
each replacement tube must be fabri-
cated from the same size steel tubing
as the original line.
Using the old tube as a guide, bend
the new tube as required. Add the
necessary fittings, and install the tube.
After the fittings have been tight-
ened, add fluid as needed, and check
for fluid leaks.
VACUUM DIAPHRAGM
ADJUSTMENT NON-ALTITUDE
COMPENSATING TYPE
The C4 and C6 transmissions are
equipped with an adjustable vacuum
diaphragm assembly. A similar ad-
justable diaphragm has been released
for service with the FMX transmis-
sion. However, the FMX service dia-
phragm is not interchangeable with
that used on C4 and C6 models.
The vacuum diaphragm assembly
has an adjusting screw in the vacuum
hose connecting tube (Fig. 14).
SPRING
SEAT
THIS CLEARANCE CHANGED
BY ADJUSTING SCREW
D1830-A
FIG. 14—Adjustable Vacuum Unit
The inner end of the screw bears
against a plate which in turn bears
against the vacuum diaphragm spring.
All readings slightly high or all
readings slightly low may indicate the
vacuum unit needs adjustment to cor-
rect a particular shift condition.procarmanuals.com
Page 302 of 413

07-01-11
General Transmission Service
07-01-11
STOP
PIN
GROMMET
Tool - T67P-734LA
GROMMET
LEVER
CONTROL ROD REMOVAL
GROMMET INSTALLATION
Tool - T67P-734LA
r
CONTROL ROD INSTALLATION
3/16"-1/4'
CONTROL ROD
STOP
PIN
FIG. 18—Removing
or
Installing Shift Linkage Grommet
D 1742-A
MANUAL SHIFT LINKAGE
GROMMET REPLACEMENT-
COLUMN SHIFT
The manual lever assembly
on ve-
hicles equipped with
a
column shift
in-
corporates
an oil
impregnated plastic
grommet
in the end of the
lever
arm.
A special tool T67P-7341-A
is re-
quired
to
install
the
grommet
in the
manual lever,
and to
install
the
manu-
al linkage
rod
into
the
grommet.
Re-
move
and
install
the
grommet
as fol-
lows:
1.
Place
the
lower
jaw of the
tool
between
the
manual lever
and the con-
trol
rod.
Position
the
stop
pin
against
the
end of the
control
rod (Fig. 18)
and force
the rod out of the
grommet.
Remove
the
grommet from
the
manu-
al lever
by
cutting
off the
large shoul-
der with
a
sharp knife.
The
grommet
must
be
removed from
the
manual
lever
and a new one
installed each
time
the rod is
disconnected.
2.
Before installing
a
new grommet,
adjust
the
stop
pin to 1/2
inch
and
coat
the
outside
of the
grommet with
lubricant. Then, place
the
grommet
on
the stop
pin and
force
it
into
the
man-
ual lever hole. Turn
the
grommet
sev-
eral times
to be
sure
it is
properly
seated.
3.
Readjust
the
stop
pin to the
height shown
in Fig. 18. The pin
height
is
determined
by the
length
of
the
rod end
which
is to be
installed
into
the
grommet.
If the pin
height
is
not adjusted,
the
control
rod may be
pushed
too far
through
the
grommet
causing damage
to the
grommet
re-
taining
lip.
4.
With
the pin
height properly
ad-
justed, position
the
control
rod on the
tool
and
force
the rod
into
the
grom-
met until
the
groove
in the rod
seats
on
the
inner retaining
lip of the
grom-
met.
Be
sure
the rod
protrudes
through
the
grommet approximately
1/4 inch after installation.
CLEANING
AND
INSPECTION
CLEANING
TRANSMISSION
Clean
the
parts with suitable solvent
and
use
moisture-free
air to dry off all
the parts
and
clean
out oil
passages.
The composition clutch plates,
bands
and
synthetic seals should
not
be cleaned
in a
vapor degreaser
or
with
any
type
of
detergent solution.
To clean these parts, wipe them
off
with
a
lint-free cloth.
New
clutch
plates
or
bands should
be
soaked
in
transmission fluid
for
fifteen minutes
before
the
plates
or
bands
are as-
sembled.
CONVERTER
The converter cannot
be
disas-
sembled
for
cleaning.
If
there
is rea-
son
to
believe that
the
converter
con-
tains
an
excessive amount
of
foreign
material,
it
should
be
thoroughly
cleaned.
See the
instructions provided
with
the
Rotunda Automatic Trans-
mission Torque Converter
and
Cooler
Cleaner LRE-60081.
OIL COOLER
When
a
clutch
or
band failure
or
other internal trouble
has
occurred
inprocarmanuals.com
Page 307 of 413
07-01-16
General Transmission bervice
07-01-16
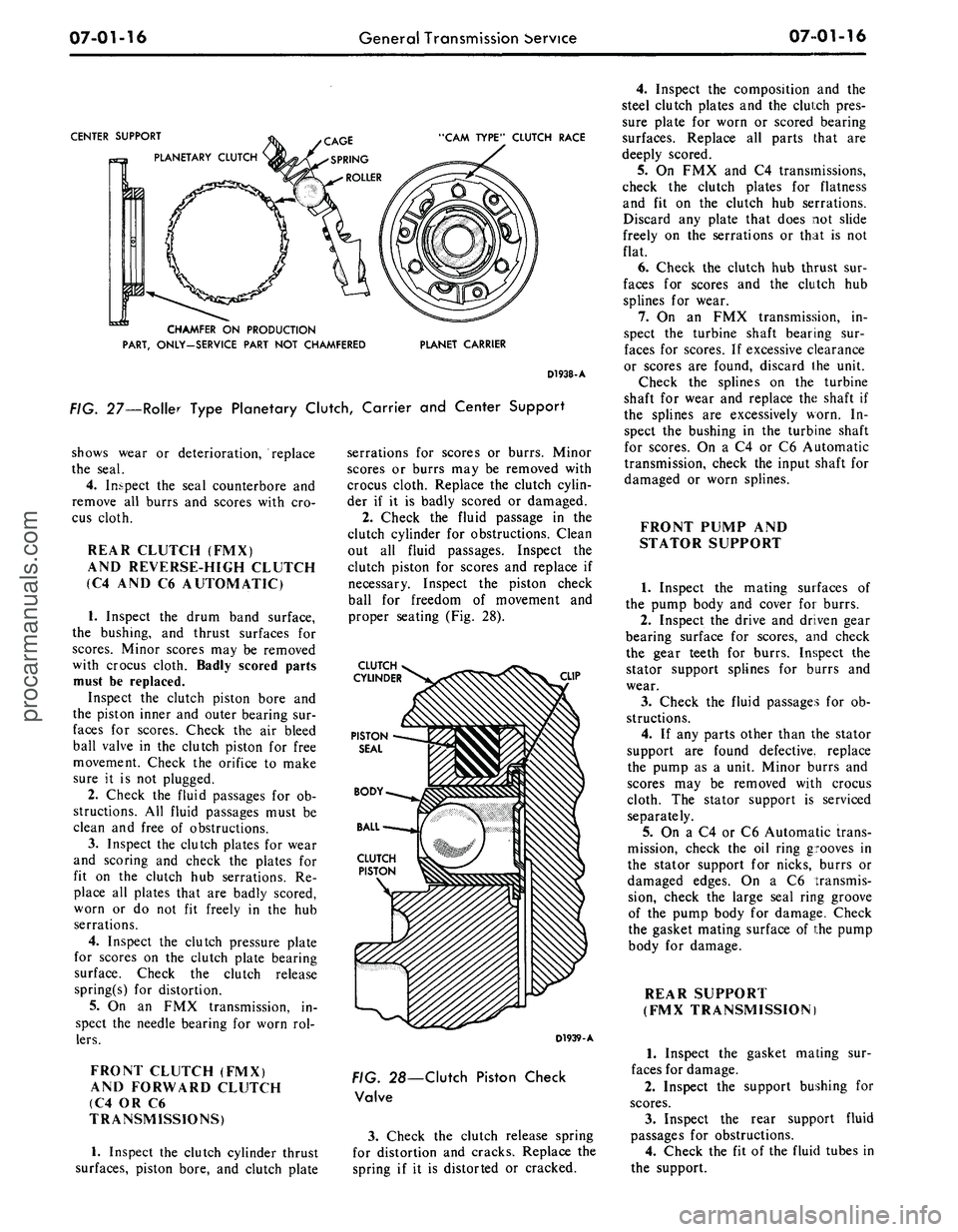
CENTER SUPPORT
PLANETARY CLUTCH
"CAM TYPE" CLUTCH RACE
CHAMFER ON PRODUCTION
PART, ONLY-SERVICE PART NOT CHAMFERED
PLANET CARRIER
D1938-A
FIG. 27—Roller Type Planetary Clutch, Carrier and Center Support
shows wear or deterioration, replace
the seal.
4.
Inspect the seal counterbore and
remove all burrs and scores with cro-
cus cloth.
REAR CLUTCH (FMX)
AND REVERSE-HIGH CLUTCH
(C4 AND C6 AUTOMATIC)
1.
Inspect the drum band surface,
the bushing, and thrust surfaces for
scores. Minor scores may be removed
with crocus cloth. Badly scored parts
must be replaced.
Inspect the clutch piston bore and
the piston inner and outer bearing sur-
faces for scores. Check the air bleed
ball valve in the clutch piston for free
movement. Check the orifice to make
sure it is not plugged.
2.
Check the fluid passages for ob-
structions. All fluid passages must be
clean and free of obstructions.
3.
Inspect the clutch plates for wear
and scoring and check the plates for
fit on the clutch hub serrations. Re-
place all plates that are badly scored,
worn or do not fit freely in the hub
serrations.
4.
Inspect the clutch pressure plate
for scores on the clutch plate bearing
surface. Check the clutch release
spring(s) for distortion.
5.
On an FMX transmission, in-
spect the needle bearing for worn rol-
lers.
FRONT CLUTCH (FMX)
AND FORWARD CLUTCH
(C4 OR C6
TRANSMISSIONS)
1.
Inspect the clutch cylinder thrust
surfaces, piston bore, and clutch plate
serrations for scores or burrs. Minor
scores or burrs may be removed with
crocus cloth. Replace the clutch cylin-
der if it is badly scored or damaged.
2.
Check the fluid passage in the
clutch cylinder for obstructions. Clean
out all fluid passages. Inspect the
clutch piston for scores and replace if
necessary. Inspect the piston check
ball for freedom of movement and
proper seating (Fig. 28).
CLUTCH
CYLINDER
PISTON
SEAL
CLIP
D1939-A
. 28—Clutch Piston Check
Valve
3.
Check the clutch release spring
for distortion and cracks. Replace the
spring if it is distorted or cracked.
4.
Inspect the composition and the
steel clutch plates and the clutch pres-
sure plate for worn or scored bearing
surfaces. Replace all parts that are
deeply scored.
5.
On FMX and C4 transmissions,
check the clutch plates for flatness
and fit on the clutch hub serrations.
Discard any plate that does not slide
freely on the serrations or that is not
flat.
6. Check the clutch hub thrust sur-
faces for scores and the clutch hub
splines for wear.
7.
On an FMX transmission, in-
spect the turbine shaft bearing sur-
faces for scores. If excessive clearance
or scores are found, discard the unit.
Check the splines on the turbine
shaft for wear and replace the shaft if
the splines are excessively worn. In-
spect the bushing in the turbine shaft
for scores. On a C4 or C6 Automatic
transmission, check the input shaft for
damaged or worn splines.
FRONT PUMP AND
STATOR SUPPORT
1.
Inspect the mating surfaces of
the pump body and cover for burrs.
2.
Inspect the drive and driven gear
bearing surface for scores, and check
the gear teeth for burrs. Inspect the
stator support splines for burrs and
wear.
3.
Check the fluid passages for ob-
structions.
4.
If any parts other than the stator
support are found defective, replace
the pump as a unit. Minor burrs and
scores may be removed with crocus
cloth. The stator support is serviced
separately.
5.
On a C4 or C6 Automatic trans-
mission, check the oil ring grooves in
the stator support for nicks, burrs or
damaged edges. On a C6 transmis-
sion, check the large seal ring groove
of the pump body for damage. Check
the gasket mating surface of the pump
body for damage.
REAR SUPPORT
(FMX TRANSMISSION)
1.
Inspect the gasket mating sur-
faces for damage.
2.
Inspect the support bushing for
scores.
3.
Inspect the rear support fluid
passages for obstructions.
4.
Check the fit of the fluid tubes in
the support.procarmanuals.com
Page 361 of 413

07-03-21
FMX Transmission
07-03-21
Tool—1175-AB
Tool— T50T-100-A
D1962-A
FIG. 41—Removing Front Pump
Seal
8. Install
the oil
seal remover
shown
in Fig. 41.
Then pull
the
front
seal from
the
pump body.
9. Clean
the
pump body counter-
bore.
Then inspect
the
bore
for
rough
spots.
Smooth
up the
counterbore
with crocus cloth.
10.
Remove
the
pump body from
the transmission case.
11.
Coat
the
outer diameter
of a
new seal with FoMoCo Sealing
Com-
pound,
or its
equivalent. Then position
the seal
in the
pump body. Drive
the
seal into
the
pump body with
the
tool
shown
in Fig. 42
until
the
seal
is
firm-
ly seated
in the
body. Tool 77837
may
be reworked
(Fig. 43) to
install
the
latest type seal.
FRONT PUMP
BODY
D1963-A
FIG. 42—Installing Front Pump
Seal
CHAMFER
TO
REMOVE BURRS
FRONT PUMP
OIL
SEAL
INSTALLATION
MACHINE
OFF
D1964-A
FIG.
43—
Front Pump Seal
Installing Tool Modification
12.
Place
the
pump driven gear
in
the pump body with
the
mark
on the
gear facing down. Install
the
drive
gear
in the
pump body with
the
cham-
fered side
of the
flats facing down.
13.
Install
the
stator support
and
attaching screws. Check
the
pump
gears
for
free rotation.
REAR SUPPORT BUSHING
REPLACEMENT
1.
Remove
the
three pressure tubes
from
the
support housing.
2.
Remove
the
rear support bushing
if
it is
worn
or
damaged.
Use a
cape
chisel
and cut
along
the
bushing seam
until
the
chisel breaks through
the
bushing wall.
Pry the
loose ends
of
the bushing
up
with
an awl and re-
move
the
bushing.
3.
Press
a new
bushing into
the
support housing with
the
tool shown
in
Fig. 44.
Too/
-
T64L-7003-A2
Handle
D 2050-A
FIG. 44—Installing Rear Support
Housing Bushing
4.
Install
the
pressure tubes.
PRESSURE REGULATOR
1.
Remove
the
valves from
the re-
gulator body.
2.
Remove
the
regulator body cover
attaching screws,
and
remove
the
cover
(Fig. 45).
3.
Remove
the
separator plate.
4.
Wash
all
parts thoroughly
in
clean solvent
and
blow
dry
with
moisture-free compressed
air.
5.
Inspect
the
regulator body
and
cover mating surfaces
for
burrs.
6. Check
all
fluid passages
for ob-
structions.
7.
Inspect
the
control pressure
and
converter pressure valves
and
bores
for
burrs
and
scores. Remove
all
burrs
carefully with crocus cloth.
8. Check
the
free movement
of the
valve
in
their bores. Each valve should
fall freely into
its
bore when both
the
valve
and
bore
are dry.
9. Inspect
the
valve springs
for dis-
tortion.
10.
Position
the
separator plate
on
the regulator cover.
11.
Position
the
regulator cover
and
separator plate
on the
regulator body,
and install
the
attaching screws.
Tor-
que
the
screws
to
specification.
12.
Insert
the
valves
in the
pressure
regulator body
(Fig. 45).
CONTROL VALVE BODY
During
the
disassembly
of the con-
trol valve assembly, avoid damage
to
valve parts
and
keep
the
valve parts
clean. Place
the
valve assembly
on a
clean shop towel while performing
the
disassembly operation.
Do not
sepa-
REGULATOR
BODY
CONTROL PRESSURE
VALVE
SEPARATOR
CONVERTER RETAINER
PRESSURE CONVERTER PRESSURE
VALVE SPRINGS
COVER
RETAINER
1111
1111
D1965-A
FIG. 45— Pressure Regulator Disassembledprocarmanuals.com