1967 CHEVROLET CAMARO rear axle
[x] Cancel search: rear axlePage 419 of 659
FUEL TANK
AND
EXHAUST SYSTEMS
8-13
CHEVY II
FUEL TANKS
INDEX
Page
Page
General Description.
8-13
Component Part Replacement
8-13
Fuel Tanks
8-13
Fuel Lines
8-14
Metering Units (Gauge Sending Unit)
8-13
Fuel Tank Filler- Neck Caps.
. . 8-14
Fuel Tank Vent Lines .......
8-14
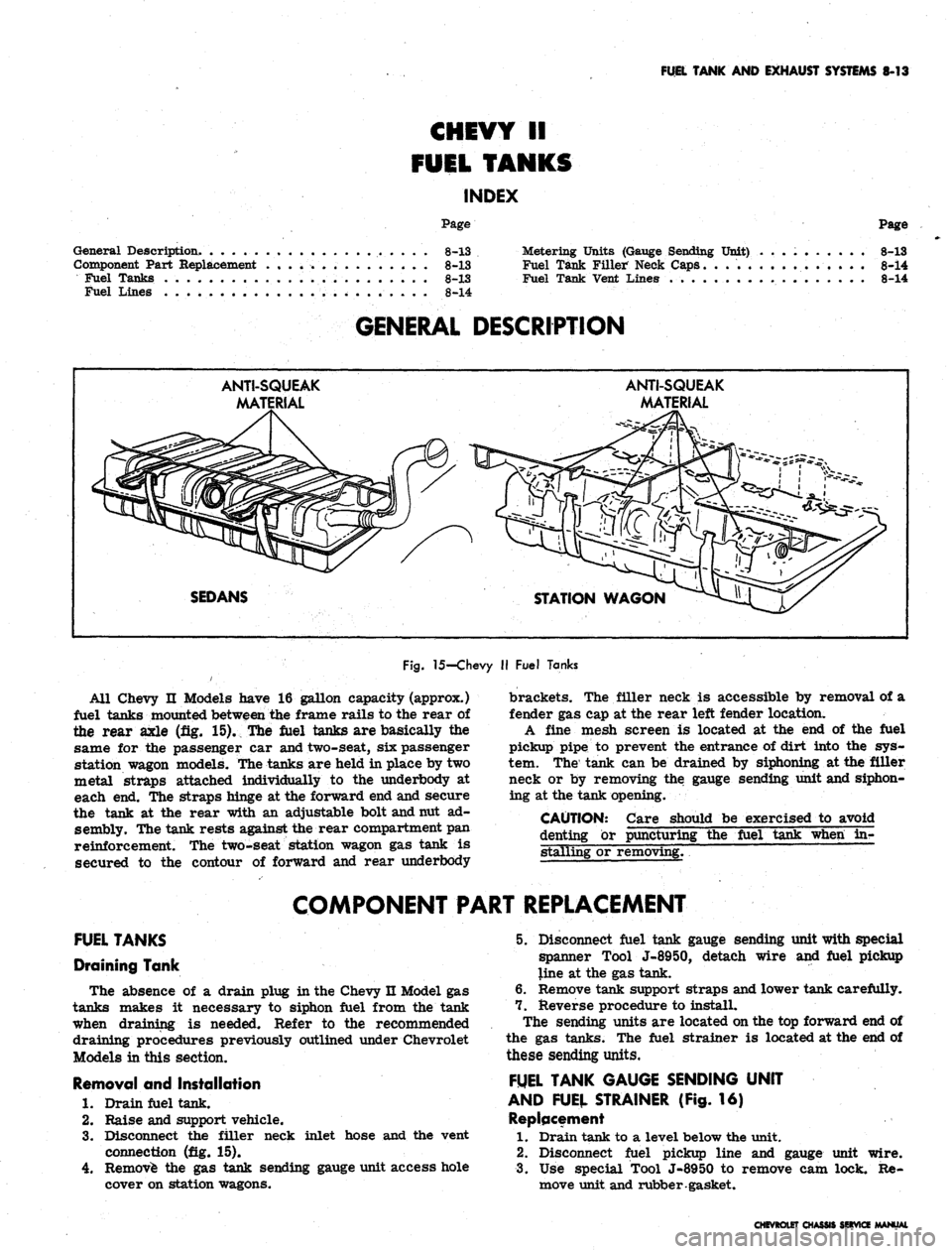
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
ANTI-SQUEAK
MA'
ANTI-SQUEAK
MATERIAL
SEDANS
STATION WAGON
Fig.
15-Chevy
II
Fuel Tanks
All Chevy
II
Models have
16
gallon capacity (approx.)
fuel tanks mounted between
the
frame rails
to the
rear
of
the rear axle
(fig. 15). The
fuel tanks
are
basically
the
same
for the
passenger
car
and two-seat,
six
passenger
station wagon models. The tanks
are
held
in
place
by two
metal straps attached individually
to the
underbody
at
each
end. The
straps hinge
at the
forward
end
and secure
the tank
at the
rear with
an
adjustable bolt and nut
ad-
sembly. The tank rests against the rear compartment
pan
reinforcement.
The
two-seat station wagon
gas
tank
is
secured
to the
contour
of
forward
and
rear underbody
brackets.
The
filler neck
is
accessible
by
removal
of a
fender
gas cap at the
rear left fender location.
A fine mesh screen
is
located
at the end of the
fuel
pickup pipe
to
prevent
the
entrance
of
dirt into
the sys-
tem.
The
tank
can be
drained
by
siphoning
at the
filler
neck
or by
removing
the
gauge sending unit and siphon-
ing
at the
tank opening.
CAUTION: Care should
be
exercised
to
avoid
denting
or
puncturing
the
fuel tank when
in-
stalling
or
removing.
~
COMPONENT PART REPLACEMENT
FUEL TANKS
Draining Tank
The absence
of a
drain plug
in
the Chevy
n
Model
gas
tanks makes
it
necessary
to
siphon fuel from
the
tank
when draining
is
needed. Refer
to the
recommended
draining procedures previously outlined under Chevrolet
Models
in
this section.
Removal
and
Installation
1.
Drain fuel tank.
2.
Raise
and
support vehicle.
3.
Disconnect
the
filler neck inlet hose
and the
vent
connection
(fig. 15).
4.
Remove
the gas
tank sending gauge unit access hole
cover
on
station wagons.
5. Disconnect fuel tank gauge sending unit with special
spanner Tool J-8950, detach wire
and
fuel pickup
line
at the gas
tank.
6. Remove tank support straps and lower tank carefully.
7. Reverse procedure
to
install.
The sending units
are
located on
the top
forward
end of
the
gas
tanks.
The
fuel strainer
is
located
at the end of
these sending units.
FUEL TANK GAUGE SENDING UNIT
AND FUEL STRAINER
(Fig. 16)
Replacement
1.
Drain tank
to a
level below
the
unit.
2.
Disconnect fuel pickup line
and
gauge unit wire.
3.
Use
special Tool J-8950
to
remove
cam
lock.
Re-
move unit and rubber gasket.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 433 of 659

FUEL TANK AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS 8-27
CAMARO
INDEX
Page
General Description 8-27
Service Operations
Fuel Tank 8-28
Fuel Lines 8-28
Metering Units (Gauge Sending Unit) 8-28
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
All models use an 18.5 gallon capacity (approx.) fuel
tank mounted between the frame rails behind the rear
axle (fig. 32). All fuel tanks are vented through an anti-
surge type filler cap assembly consisting of cap and
handle. The carrying straps hook through a double slot
in the front of the rear compartment reinforcements and
attach to strap bolts positioned in slots provided at the
rear panel reinforcements. A conventional fuel meter
VIEW B
Fig.
32—Fuel Tank Assembly
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 437 of 659

FUEL TANK
AND
EXHAUST SYSTEMS
8-31
EXHAUST SYSTEMS
INDEX
Page
General Description
8-31
Component Part Replacement
8-31
Muffler Assembly
8-31
Exhaust Pipe
. 8-31
Tailpipe and/or Resonator
8-32
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The single exhaust system
cm
six* cylinder engine
models
(fig. 36)
consists
of an
exhaust pipe, extension,
muffler
and
tailpipe with necessary attaching brackets
and clamps.
On V-8
engine models with single exhaust
assemblies
(fig. 36) an
exhaust crossover pipe
is
added
to connect
the
right exhaust manifold
to the
system.
The
dual exhaust system available
on V-8
engine models
(fig.
37) includes
two
front exhaust pipes -with
or
without
resonators,
two
rear exhaust pipes, dual inlet-outlet
muffler, tailpipes and attaching hardware.
The assemblies
are
secured
to the
engine
at the ex-
haust manifolds,
to the
rear compartment pan reinforce-
ment ahead
of
axle
and
adjacent
to the gas
tank
at the
end
of the
tailpipe.
The
assemblies
are
suspended
on
brackets with insulators
for
rattle free operation.
The muffler
is an
all-welded construction with
a
•
capacity
for
muffling
the
noise
and at the
same time,
minimizing back pressure
for
maximum engine effici-
ency.
The
internal parts
are
electric welded
to
eliminate
premature failure
or
rattle.
The exhaust system center mounting
at the
muffler
location consists
of an
underbody bracket,
an
insulator
and
a
clamp.
The
clamp holds
the
muffler and tailpipe
with
a
"U" bolt and
at
the same time secures
the
muffler
and pipe
to the
body.
The exhaust system mounting
at the
end
of
the tailpipe
secures
the
pipe
to a
bracket assembly
and
insulator
attached
to an
existing underbody bracket.
COMPONENT PART REPLACEMENT
EXHAUST PIPE
Replacement
1.
Loosen
"U"
bolt clamp
at
rear exhaust pipe
connection.
2.
Remove exhaust pipe
to
manifold attaching nuts,
ex-
tension
and.
packing then separate pipe from manifold
studs.
NOTE:
Right exhaust crossover pipe
on V-8
engine single exhaust models
is an
integral part
of
the
exhaust pipe assembly and
is not
serviced
separately.
3.
Separate front exhaust pipe from rear exhaust pipe
extension.
4.
To
install exhaust pipe, connect pipe
to
rear exhaust
pipe extension
or
resonator
and
secure
to
exhaust
manifold. Note clearances
for
the standard and auto-
matic control linkages, underbody
and
crossmember.
5. Tighten exhaust pipe
to
manifold attaching nuts
and
rear "U" bolt clamp nuts.
EXHAUST PIPE EXTENSION
Replacement
1.
Remove "U" bolt clamps
at
muffler inlet and exhaust
pipe
or
resonator connections.
2.
Disconnect exhaust pipe extension
at
muffler
and
exhaust pipe
or
resonator connection.
3.
To
install extension, connect extension
to
exhaust
pipe
or
resonator and
to
muffler.
4.
Install
"V"
bolt clamps
and
tighten clamp nuts.
MUFFLER ASSEMBLY
Replacement
1.
Remove "U" bolt clamp
at
muffler inlet.
2.
Remove tailpipe support clamp.
3.
Separate muffler from rear exhaust pipe
and
remove
muffler from vehicle.
4.
If
usable,
cut
tail pipe from muffler.
5. Connect muffler inlet
to
exhaust pipe and install
"U"
bolt clamp
at
muffler inlet.
6. Connect tailpipe
to
muffler outlet
and
install rear
support clamp.
7. Install
"U"
bolt clamp
at
tailpipe
to
muffler outlet
connection and tighten nuts.
TAILPIPE
Replacement
1.
Remove
"U"
bolt clamp
at
muffler outlet.
If
replac-
ing right tail pipe, eut pipe
at
muffler outlet.
2.
Remove tail pipe rear hanger clamp and detach pipe
from muffler.
&IS SBtVKE MANUAL
Page 481 of 659

SECTION 10
WHEELS AND TIRES
INDEX
Page
General Description
10-1
Maintenance
and
Adjustments
.............. 10—1
Tires
10-1
Pressures . 10-1
Inspection 10-1
Wear 10-1
Rotation 10-4
Noise 10-4
Cleaning 10-4
Change (W/Wheels) 10-4
Wheels 10-5
Static Balancing (w/Tire) 10-5
Page
Dynamic Balancing (w/Tire) . 10-5
Run Out (w/o Tire) 10-5
Cleaning 10-5
Service Operations 10-5
Tires 10-5
Removal 10-5
Installation 10-5
Repair 10^6
Wheels . 10-6
Valve Assembly 10-6
Repair (Rim) 10-7
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
WHEELS
Chevrolet, Chevelle, Camaro, Chevy n, and Corvette
are base equipped with welded steel wheels. Five studs
with nuts fasten each wheel to the front hub or rear axle
flange. Disc brake equipped vehicles (except Chevrolet
and Corvette) require special 14 inch diameter wheels
with a revised design for clearance, Chevrolet disc brake
equipped vehicles have 15 in. diameter wheels as do all
Corvettes.
Chevrolet station wagons, Chevelle Super Sport 396,
Corvette and Camaro Super Sport 350 are base equipped
with 6 in. width wheels. All other vehicles have 5 in.
width wheels, except Chevy n 100, 300 and 500 Series
Sedans, which have 4 in. width wheels.
Do not install 6 inch width wheels or snow chains on
Chevrolets equipped with rear fender skirts.
TIRES
The factory installed tires on Chevrolet passenger
cars are selected to provide the best all around tire
performance for all normal operation. They are de-
signed to operate satisfactorily with loads up to and in-
cluding the specified full rated load capacity of the
automobile when inflated as recommended in the Vehicle
Capacity Rating and Recommended Tire Inflation Pres-
sures Table (see Specifications).
Optional Oversize and 8-Ply Rating Tires
{Chevrolet and Chevelle Only)
Oversize or 8-ply rating tires are not necessary on
passenger cars for normal requirements. However, an
extra margin of tire service is available when these
options are used at loads up to and including full rated
load.
Optional oversize 4-ply rating and/or 8-ply rating
tires are available on models as indicated in the Tire
Usage Chart (see Specifications). On some models (ex-
ample—Station Wagon), space limitations do not permit
the use of a larger size tire; hence, the 8-ply rating
tire is an available option.
In either case, these tires are applicable to extended
operation at or near full rated load or for trailer towing
when an extra margin of tire service is desired. How-
ever, use of a larger tire or an 8-ply rating tire should
not be construed as permitting an increase in the full
rated vehicle load (see Specifications).
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
TIRES
Inflation Pressures
To ensure the proper tire inflation pressure for the
owners particular requirements follow the recommenda-
tions in the Vehicle Capacity Rating and Recommended
Tire Inflation Pressures Table (seeSpecifications). Keep
tires properly inflated, and check inflation pressures
periodically. This will ensure the best tire life and riding
comfort, over the full range of driving conditions.
Inspection
Every few thousand miles and at each lubrication, tires
should be checked for sharp objects or stones in the
tread. H tire is punctured, it should be repaired using
one of several repair kits available through tire manu-
facturers1 outlets.
Wear
Misalignment
This is wear due to excessive toe-in or toe-out. In
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 484 of 659

WHEELS AND TIRES 10-4
the road and it slips, grinding off the tread on the inside
half of the tire at an excessive rate. This type of tire
shows much the same appearance of tread wear as tire
wear caused by negative camber.
Second, the transfer of weight may also over-load the
outside tires so much that they are laterally distorted
resulting in excessive wear on the outside half of the
tire producing a type of wear like that caused by ex-
cessive positive camber.
Cornering wear can be most easily distinguished from
abnormal camber wear by the rounding of the outside
shoulder or edge of the tire and by the roughening of the
tread surface which denotes abrasion.
Cornering wear often produces a fin or raised portion
along the inside edge of each row in the tread pattern.
In some cases this fin is almost as pronounced as a
toe-in fin, and in others, it tapers into a row of tread
blocks to such an extent that the tire has a definite step
wear appearance.
The only remedy for cornering wear is proper in-
struction of owners.
Fig.
5 - Tire Rotatidh
Rotation
To minimize the possibility of tire noise and to equal-
ize tire wear, it is recommended that tires be inter-
changed every 6000 miles as shown in Figure 5 or more
frequently in the case of extremely heavy wear.
NOTE:
Rotate Corvette tires at 4000 miles or
sooner.
Interchanging tires will effectively prevent undue wear
on any particular tire. II tire interchanging is followed
as recommended above, all tires will have the same
number of miles in each wheel position at the end of the
fourth change. When interchanging tires, inspect for
signs of abnormal wear, bulging, etc., stones, glass, and
nails should be removed before reinstallation.
Noise
Noise caused by the normal action of tire treads on
various road surfaces is often confused with rear axle
gears or other noises in the car.
The determination of whether tires are causing the
noise complained of is relatively simple. The car should
be driven at various speeds and note taken of part
throttle, and sudden acceleration and deceleration. Axle
and exhaust noises show definite variations under these
conditions, while tire noise will remain constant. Tire
noise is, however, most pronounced at speeds of approx-
imately twenty or thirty miles per hour.
The tires may be further checked by driving the ear
over smooth pavement with the tires at normal pressure
and again over the same stretch of pavement when the
tires have been inflated to fifty pounds pressure. Reduce
the tires to normal pressure one at a time to determine
the faulty tire or tires. This high inflation pressure
should immediately be reduced to normal after test. If
the noise for which the test is being made is caused by
tires,.
it will noticeably decrease when the tire pressure
is increased, whereas axle noise should show no change
in volume.
If, on inspection, the tires on the front wheels are
found to be creating most of the noise the alignment of
the front wheels should be checked. Excessive tire noise
usually results from lower than recommended tire pres-
sure, incorrect alignment, uneven tire wear, or defective
(thumper) tire.
Cleaning
A great deal of ordinary road dirt which collects on
white sidewall tires may be sponged off with clear water
or a mild soap solution.
A good brand of whitewall tire cleaner, however, is
a quicker and more effective cleaner for removing dirt
and stains from whitewall tires and in many cases it
will remove stains and discoloration that the simpler
method of soap and water will not remove.
Under no circumstances should gasoline, kerosene or
any cleaning fluid containing a solvent derived from oil
be used to clean whitewall tires. Oil in any form is
detrimental to tire rubber and a cleaner with an oil base
will discolor or injure whitewall tires.
Change (W/Wheels)
To change the road wheels using the jack that comes
with the car, observe the following procedure:
1.
Set hand brake and block front wheels if rear wheel
is being changed.
2.
Remove hub cap or wheel disc and break wheel
mounting nuts loose.
3.
Place the jack as directed tinder, General Informa-
tion,
Section 0 and raise car until wheel clears
ground.
4.
Remove wheel mounting nuts and remove wheel from
hub or drum.
5. To replace road wheel, reverse the above instrue-
. tions. Proper torque on nuts is 55-75 ft. lbs.
torque (70-85 ft. lbs. for Corvette aluminum wheel
nuts).
CAUTION: On models equipped with discs, in-
dex the pilot hole in the disc on the valve stem.
(To insure that the anti-rotation notches in wheel
disc register on lugs in wheel rim.)
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 630 of 659

SPECIFICATIONS 3
REAR SUSPENSION
REAR AXLE
SECTION 4
CHEVROLET, CAMARO, CHEVELLE AND CHEVY II
Gear Backlash . . (.005"-.008" preferred) .003"-.010"
Pinion Bearing Preload (in. lbs.)
New 20-30
Used . 5-15
Lubricant Capacity
Large Carrier 4-1/2 pints
Small Carrier 3-1/2 pints
Bolt Torques (Ft Lbs.)
Carrier Cover 20
Ring Gear 50
Differential Bearing Caps 55
Filler Plug . . 20
Differential Pinion Lock . 20
CORVETTE
Gear Backlash . (.
005"-,
008"
preferred). . .003"-.010"
Pinion Bearing Preload (in. lbs.)
New 20-25
Used 5-15
Lubricant Capacity 3-3/4 pints
Bolt Torques (Ft Lbs.)
Carrier Cover 50
Ring Gear . 50
Differential Bearing Caps . 55
Filler Plug 20
Differential Pinion Lock 20
Type
Heavy Duty Axle
Light Duty Axle
Bolt Torque (ft lbs.)
Spring Retainer
Control Arm Upper
Front Bracket
Upper Bushings
Lower Bushings
Shock Absorber
Upper Nut
Upper Bracket
Lower Nut
Spring Shackle
Front
Rear
Tie Rod
Attaching Nuts
Stud to Axle Bracket
Universal Joint
Companion Flange
Transmission Yoke
Wheel Stud Nuts
Axle Drive Shaft
to Spindle
to Yoke
Chevrolet
4-Link
System
3-Link
System
25
55
70
110
15
65
65
110
15
65
Chevelle
4-Link
System
80
80
12
65
15
65
Chevy H
Semi-Elliptic
Tapered
Single Leaf
40
10
10
50
55
50
15
65
Camaro*
Semi-Elliptic
Tapered
Single Leaf
50
8
10
45
100
50
15
65
Corvette
Independent
Three-Link
System
65
50
35
15
15
75
75
15
@ Station Wagon all
4-Link
System
CHEVROLET a
SfRVK