1953 JEEP DJ radiator cap
[x] Cancel search: radiator capPage 54 of 376

D
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
against the hub of the crankshaft pulley.
Timing
gears are accessible for inspection or replacement
with
the
engine
installed in the vehicle after re moving the radiator, belt drive pulley, and timing
cover.
Should
it be necessary to replace the timing gears, attention must be given to the end float of both
the camshaft and crankshaft and to the running
clearance
of both gears. It is also advisable to
check
both the oil jet and oil passage to the
crank
shaft front bearing to be sure that they are clear.
D-55.
Inspection and
Repair
Check
the general condition of both gears and
inspect for evidence of excessive wear. Replace
excessively worn or damaged gears. Inspect the
cover and replace if bent or damaged. It is recom mended that the crankshaft oil seal in the cover
be replaced when the cover is removed to ensure a
good
seal around the crankshaft. To replace this
seal
with the
engine
in the vehicle
requires
removing
the radiator and water pump.
D-56.
Valves, Springs, and Guides
The
exhaust valves seat on the top of the cylinder
block
with the
stems
extending down through
replaceable valve guides. The exhaust valves are actuated by the camshaft through exhaust valve
tappets. The exhaust valve springs are assembled
and
locked on the lower end of the exhaust valve
stems. The retaining locks are the split type, which
fit in a recess on the valve
stems
and into the taper
in
the valve spring retainers.
Adjustment
of exhaust valves is by means of the
adjusting
screw threaded into the upper end of the
exhaust valve tappets. An exhaust valve rotator used as a valve spring retainer is installed on the
lower end of the exhaust valve.
This
valve rotator,
known
as "Roto Cap", is a spring-loaded
ball
bearing
device. On each lift, or opening stroke of
a
valve, the rotator
gives
the valve a slight positive
clockwise rotation.
The
intake valves operate in valve
guides
in the
cylinder
head and are actuated by rocker arms.
The
rocker arms are actuated by valve push rods
and
the intake valve tappets. The intake valve
springs,
the intake valve spring retainers, and the
intake
valve spring retainer locks make up the
remainder
of the valve operating parts. An intake
valve spring retainer oil seal which encircles the
upper
end of the intake valve
between
the valve
locks and the upper end of the valve spring re
tainer,
controls the passage of oil along the valve
stem and guide.
Note:
When
engine
trouble indicates defective
valves as a possible source of trouble, also check
all
vacuum line connections for possible leaks.
D-57.
Inspection of Valves, Springs,
and
Guides
Clean
the valves on a wire wheel, making sure that
all
carbon is removed from the top and the under
side of the heads and that all gum and varnish
deposits
are removed from the stems.
Polish
the valve
stems
with steel wool or crocus
cloth.
Visually
inspect all valves for warpage,
cracks,
or excessive burning and discard if one of
these
conditions exists. Replace any worn, pitted,
or
corroded valves that cannot be cleaned with a
wire
brush.
Replace any valves when
seats
are pitted, burned, or corroded so badly that they
cannot be cleaned up with a light refacing on a valve refacing machine.
Replace
valves with marks of scoring or abrasion visible on the stem. Replace any valves with bent
stems
which
will
be apparent when the valve is
mounted in the valve refacing machine.
Note:
Use only hard-face exhaust valves for
replacement.
Examine
the
stems
of valves which employ the
ball
bearing rotators.
Wear
marks around the
cir
cumference of the
stems
indicates that the valve is
rotating satisfactorily.
Vertical
heavy pressure
areas
indicate that the valve is not rotating and the valve spring retainer (Roto
Cap)
should be replaced
if
at fault.
Check
the diameter of the valve stem at two or three places along the length of the stem
with
a micrometer. The intake valve stem diameter is .3733" to .3738" [9,482 a
9,495
mm.]. The
exhaust valve stem diameter is .371" to .372"
[9,423
a
9,449
mm.].
Note:
Exhaust
and intake valve springs are
similar
in appearance. They must not be inter
changed as they have different spring
charac
teristics.
Wash
the valve springs thoroughly in solvent.
Visually
examine the springs and replace any that
are
deformed or obviously damaged. Examine for
corrosion
from moisture or acid etching which might
FIG.
D-19—TESTING
VALVE
SPRING
1—
Torque
Wrench
2—
Spring
Testing
Fixture
3—
Valve
Spring
54
Page 68 of 376

D
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
D-101.
Install
Manifold
If
manifold studs were removed for replacement,
apply sealer on the stud threads
before
installing
a
new stud.
See Section Fl for exhaust emission controlled
engines.
Make
certain that no foreign objects are inside the manifold and that all
passages
are clear. Place a
new set of manifold
gaskets
in position on the side
of the cylinder block.
Then,
carefully slide the manifold
onto
the studs and against the cylinder block being careful not to damage the gaskets.
Torque
all manifold attaching nuts evenly 29 to
35 lb-ft. [4,0 a 4,8 kg-m.].
D-102.
Install
Oil
Filler
Tube
When
installing the oil filler tube, be sure that the
beveled lower end is away from the crankshaft.
Place a
piece
of
hard
wood
over the top of the
tube
to prevent damage to the cap gasket seat.
D-103.
Install
Water Pump
Make
certain that the mating surfaces of the water pump and the cylinder block are clean and smooth.
Install
the gasket on the
flange
of the pump and
install
the pump in position on the cylinder block.
Torque
the water pump attaching
bolts
alternately
and
evenly 12 to 17 lb-ft. [1,7 a 2,3 kg-m.].
D-104.
Install
Water Outlet Fitting
Install
the thermostat and the water
outlet
fitting.
Torque
the water
outlet
fitting attaching
bolts
20
to 25 lb-ft. [2,8 a 3,4 kg-m.].
FIG.
D-42—INSTALLING HURRICANE F4 ENGINE
IN
VEHICLE
1—
Lifting
Sling
2— Hoist
Cable
3—
Hurricane
F4 Engine
4— Dowel Bolt
5—
Flywheel
Housing
D-105.
ENGINE INSTALLATION
a.
Install
lifting sling to
engine
and using suitable hoist raise the
engine
from its blocking or stand
and
then slowly lower it
into
the
engine
compartment of the vehicle.
Note:
When installing the
Hurricane
F4 Engine,
two % x 4 inch
guide
bolts
or
dowels
should be
used to properly
guide
and align the
engine
to the
flywheel housing (See Fig. D-42).
b. Slightly tilt the
engine
downward and at the
same time slide the
engine
rearward
while lining up the transmission main gear shaft with the clutch
throw-out bearing and disc spline.
Note
:The
engine
crankshaft may have to be turned
slightly to align the transmission main gear shaft
with the clutch disc spline.
c. Remove the
guide
bolts
or
dowels
and secure
the
engine
to the housing.
d.
Secure the front
engine
mounts to the frame brackets and
bolt
ground cable to
engine.
e. Remove lifting sling from
engine.
f. Connect exhaust pipe to
engine
manifold flange.
g. Connect throttle and choke cables to carburetor.
h.
Install
fan to water pump pulley.
i.
Connect fuel pump line to main fuel line,
j.
Replace starting motor assembly. k. Connect
engine
wiring harness connectors at
front of cowl.
I.
Connect wires to starting motor assembly, water
temperature and oil pressure sending units and alternator.
NOTE:
ON
ENGINES EQUIPPED WITH EX
HAUST
EMISSION CONTROL,
REPLACE
THE
AIR
PUMP,
AIR
DISTRIBUTOR
MANI
FOLD,
AND
ANTI-BACKFIRE (DIVERTER)
VALVE.
SEE
SECTION
Fl.
m. Replace radiator and radiator grille support
rods and connect coolant
hoses
to
engine.
Note:
Replace heater
hoses
if vehicle is equipped
with hot water heater.
n. Fill
radiator with coolant and
engine
with oil
(see
Lubrication
Chart).
o.
Install
air cleaner and connect carburetor air
hose.
p. Connect battery cables and start
engine,
q.
Install
hood
and road
test
vehicle.
D-103.
FINAL
IN-VEHICLE
ADJUSTMENTS
a.
Clean
battery terminals and check battery. b.
Check
ignition terminals and check battery.
c. Service carburetor air cleaner.
d.
Service positive crankcase ventilation valve.
e.
Check
fuel lines. f. Gap and install new
spark
plugs.
g.
Check
distributor
points
and capacitor; replace
if
necessary. 68
Page 79 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
12710
FIG.
D1
-3—HYDRAULIC VALVE
LIFTER
ASSEMBLY, CROSS-SECTIONAL VIEW
1—
Snap
Ring
6—Ball Retainer
2— Rod
Seat
7—Plunger Spring
3—
Oil
Inlets
8—Lifter
Body
4—
Plunger
9—Bronzed
Cap
5— Feed
Hole
sages
in the block and cylinder head.
The
water cooled system is pressurized to provide efficient
engine
cooling. It consists of a centrifugal-
type water pump, mounted on the timing chain cover, and is driven by the
engine
fan pulley. The
pump provides coolant flow equally to both
cylin
der banks under control of a thermostat. Coolant
flow is around the cylinders and through the
cylinder
head to dispel the heat of combustion in
the engine.
Dl-3.
Engine Mounts
The
engine-transmission unit is mounted to the chassis at three points by rubber pads. The two
front mounts are bolted to the
engine
cylinder
block and the frame members. These mounts sup port most of the
engine
weight, and absorb
vibra
tion which would otherwise be caused by changes
in
engine
output torque. The single
rear
mount is
placed
between
the transmission and the trans mission support. It supports part of the engine'
and
transmission weight, and locates the
rear
of
the
engine
with respect to the centerline of the
vehicle.
Dl-4. ENGINE REMOVAL
To
remove the
engine
from the vehicle follow the
procedurers listed below:
a.
Remove hood. b. Disconnect battery cables from battery and
engine. c. Remove air cleaner.
d.
Drain
coolant from radiator and engine.
e.
Drain
engine
oil.
f. Disconnect alternator wiring harness from con nector at regulator.
cj.
Disconnect the fuel evaporative purge line con nected to the
P.C.V.
valve.
h.
Disconnect upper and lower radiator
hoses
from
the engine.
i.
Remove right and left radiator support
bars,
j.
Remove radiator from the vehicle.
k.
Disconnect
engine
wiring harnesses from con
nectors located on
engine
firewall.
I.
On
engines
equipped with exhaust emission con
trol,
remove the air pump, air distribution manifold,
and
anti-backfire (gulp) valve. See Section F2 for
procedure.
m.
Disconnect battery cable and wiring from en
gine
starter assembly.
n.
Remove
engine
starter assembly from engine,
o.
Disconnect
engine
fuel
hoses
from fuel lines at
right
frame
rail,
p. Plug fuel lines.
q.
Disconnect choke cable from carburetor and cable support bracket mounted on engine,
r.
Disconnect exhaust pipes from right and left
engine
manifolds.
s. Place
jack
under transmission and support trans
mission weight.
f. Remove
bolts
securing
engine
to front motor mounts.
u.
Attach suitable sling to
engine
lifting
eyes
and,
using hoist, support
engine
weight.
v. Remove
bolts
securing
engine
to flywheel housing.
w. Raise
engine
slightly and slide
engine
forward
to remove transmission main shaft from clutch plate spline.
Note:
Engine and transmission must be raised
slightly to release the main shaft from the clutch
plate while sliding the
engine
forward.
x. When
engine
is free of transmission shaft raise
engine
and remove from vehicle,
y. Place
engine
on suitable blocking or
engine
stand and remove sling from engine.
Dl-5.
ENGINE DISASSEMBLY
Engine
disassembly is presented in the sequence to be followed when the
engine
is to be completely
overhauled after removal from the vehicle. Some of the operations of the procedure are also applicable separately with the
engine
in the vehicle,
provided that wherever necessary the part of the
engine
to be worked on is first made accessible by removal of
engine
accessories or other parts.
When
the disassembly operations are performed
with
the
engine
out of the vehicle, it is assumed,
in
this procedure, that all of the accessories have
been removed
prior
to starting the disassembly and
the oil has been drained.
Page 96 of 376

Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
Note:
During
engine
reassembly, use Perfect Seal
Aerosol
Spray Sealer
Part
No.
994757
on all en
gine
gaskets to ensure against vacuum, oil, gasoline
and
water leaks. Apply to head gaskets, valve covers, water pumps, oil pan gaskets, radiator and
heater
hose
connections, felt gaskets, gasoline and
oil
line connections, stud bolts, spark plug threads,
and
grease retainer washers. Refer to manufac
turer's
instructions on container for proper appli
cation procedure.
Dl-72.
Cylinder
Block
and Crankshaft
Rear
Oil Seals
Braided
fabric seals are pressed into
grooves
of
cylinder
block and
rear
main bearing cap, to
rear
of the oil collecting groove, to seal against oil leak age at the crankshaft. Refer to Fig. Dl-32.
FIG.
Dl-32—INSTALLING
CRANKSHAFT REAR
OIL
SEAL
1—Neoprene
Seal
2—Fabric
Seal
A
neoprene composition (stick) seal is installed in
grooves
in the sides of the
rear
main bearing cap
to seal against leakage in the joints
between
the
cap and cylinder block. The neoprene composition
expands in the presence of oil and heat.
This
seal
is undersize when newly installed. Refer to Fig.
Dl-32.
a.
The braided fabric seal can be installed in the
cylinder
block only when the crankshaft is re moved; however, the seal in the cap can be replaced
whenever the cap is removed. Remove oil seal and place new seal in groove, with both ends projecting
above parting surface of cap. Force seal into
groove
by rubbing down with hammer handle or smooth
stick
until seal projects above the
groove
not more
than
[1,59 mm.]. Cut ends off flush with
sur
face of cap, using sharp knife or razor blade.
Lubricate
the seal with heavy
engine
oil just before
installation.
Caution:
The
engine
must be operated at slow
speed when first started after new braided seal
has been installed.
b. The neoprene composition seal is slightly longer
than
the
grooves
in the bearing cap. The seal must
not be cut to length. The seals are installed after the bearing cap is installed in the block and torqued
firmly
in place. Dip the neoprene seals in kerosene
approximately IV2 minutes, then install seals into
bearing cap grooves. The protruding ends of the seals are, again, squirted with kerosene, wiped off,
and
peaned over with a hammer to be sure of a
seal
at the upper parting line
between
the cap and
cylinder
block.
Dl-73.
Main
Bearing and Crankshaft
Installation
Refer
to Fig. Dl-6.
This
procedure assumes that crankshaft main bear
ings have been inspected and proven satisfactory,
or
that new crankshaft main bearings of appropriate size have been selected. If necessary, check or select
main
bearings as described in Par. Dl-41 and
Pars.
Dl-42 and Dl-43.
a.
Install
four upper main bearing halves in
seats
of cylinder block so that prong of each bearing half
fits into corresponding notch of seat. Flanged thrust
bearing must be installed in the second seat from
front of engine.
Install
a new upper crankshaft
rear
oil seal in the cylinder block as described in
Par.
Dl-72.
Caution:
Upper main bearing halves have an oil groove, while lower halves are plain. They must
not be interchanged.
b. Apply
engine
oil to upper bearing surfaces.
Install
the crankshaft so that its four journals rest
in
the upper bearing halves.
c. Seat all four lower main bearing halves in cor
responding bearing caps.
Install
a new lower
crank
shaft
rear
oil seal and cylinder block
rear
oil seal
described in
Par.
Dl-72, a and b.
Lubricate
all lower
main
bearing surfaces with
engine
oil. Position bear ing caps to cylinder block and crankcase journals.
Install
two cap bolts,
loosely,
at each cap.
d.
It is necessary to align thrust surfaces of the
second main bearing whenever it has been removed
from
the engine. To do this, pry the crankshaft
back
and forth several times, throughout its entire end travel, with cap
bolts
of second main bearing
only finger tight.
e. Tighten alternate cap
bolts
of each main bearing
cap,
a little at a time, until they have been tight ened to 80 to 110 lb-ft. [11,1 a 15,2 kg-m.] torque.
D1-74. Crankshaft End Play Check
To
measure crankshaft end play, mount a dial
indicator
on the cylinder block and index its plung
er
to either a front or
rear
face of one crankshaft
counterweight. Pry the crankshaft to one limit
of its end travel and adjust the dial indicator to
zero. Pry the crankshaft to its
opposite
end travel
limit
and
note
end play as indicated by the dial
indicator.
Crankshaft end play tolerances are .004"
to .008" [0,102 a
0,204
mm.]. If end play is too great, it can be corrected only by replacement of
the second main (thrust) bearing.
Dl-75.
Piston and Connecting Rod
Installation
This
procedure assumes that connecting rod bear ings have been inspected and proven satisfactory,
or
that new connecting rod bearings of appropriate 96
Page 104 of 376

Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
e.
Connect electrical wiring harness to coolant
temperature sending unit. Connect two distributor leads to ignition coil. Connect fuel line
between
fuel pump and carburetor, vacuum
hose
between
distributor and carburetor, and crankcase vent
hose
to intake manifold
below
rear
of carburetor.
FIG.
D1-46—-INTAKE
MANIFOLD
INSTALLATION
1—Long Bolt 2—Open Bolt Hole
Dl-102.
ENGINE INSTALLATION
Install
the
engine
in the vehicle in the following
procedure listed
below:
a.
Attach suitable sling to
engine
lifting
eyes
and,
using a hoist, lift the
engine
from blocks or
engine
stand.
b. When
engine
is free of the stand lower it slowly
into
the
engine
compartment of the vehicle.
Note:
The
engine
and transmission must be lined
up to
engage
the main shaft and clutch plate spline
while sliding the
engine
rearward
into
the mounting
position.
c.
Install
and tighten up
bolts
securing
engine
to
flywheel housing.
d.
Install
and tighten front
engine
mounting bolts.
e.
Remove sling from the
engine.
I.
Connect exhaust pipes to right and
left
engine
manifolds.
g. Connect choke cable support bracket to
car
buretor.
h.
Connect
engine
fuel
hoses
and fuel lines at right
frame
rail.
I.
Connect fuel lines.
j.
Mount
engine
starter motor assembly to
engine.
k.
Connect battery cable and wiring to
engine
starter
motor.
I.
Connect
engine
wiring harnesses to connectors
located on
engine
firewall.
Note:
On
engines
equipped with exhaust emission
control, replace the air pump, air distributor mani
fold, and anti-backfire (gulp) valve. See Section F2.
m. Replace radiator, and secure with bolts,
n.
Replace and tighten right and
left
radiator sup
port rods.
0. Connect upper and lower radiator
hoses
to the
engine.
p. Connect alternator wiring harness from connec
tor at regulator,
q.
Replace air cleaner.
r.
Connect battery ground cable from the battery
to the
engine
and the
engine
ground strap,
s.
Replace the hood.
After
the
engine
is installed in the vehicle,
fill
radiator
with coolant and
engine
with oil (Refer to
Lubrication
Section B), then perform an
engine
Tune-up
and road
test
(Refer to Tune-up Sec
tion C).
Dl-103.
FINAL IN-VEHICLE ADJUSTMENTS
a.
Clean
battery terminals and check battery.
b.
Check
ignition wires and connections.
c. Service carburetor air cleaner.
d.
Service positive crankcase ventilation valve.
e.
Check
fuel lines.
f. Gap and install new
spark
plugs.
g.
Check
distributor
points
and capacitor; replace
if
necessary.
h.
Check
ignition (distributor) timing; reset if
necessary. 1.
Check
carburetor adjustments; reset if necessary,
j.
With
engine
fully warmed up, tighten cylinder
head and manifold
bolts
and nuts to specified
torque.
Check
cylinder head
gaskets
and
bolts
for
air
or coolant leaks.
Note:
Tightness of cylinder head
bolts
should be
checked and corrected after 500 miles [800 km.]
of normal operation and again at 1000 miles [1600
km.].
k.
Check
fan belt tension; adjust if necessary.
I.
Check
for and correct any oil leak, fuel leak or
coolant leak. 104
Page 159 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
F2
F2-35.
EXHAUST EMISSION CONTOL SYSTEM
DISTRIBUTOR SPECIFICATIONS
Distributor:
Make
Delco-Remy Prestolite Prestolite
Model...
1110376
IAT-4501 or IAT-4502 IAT-4502A
Breaker
Point Gap .016"
[0,406
mm.] .016"
[0,406
mm.] .016"
[0,406
mm.]
Breaker
Arm Tension 19 to 23 oz. [538 a 652 gr.] 17 to 22 oz. [482 a 623 gr.] 17 to 22 oz. [482 a 623 gr.]
Cam
Angle. 29° to 31° 29° + 3° 29° ± 3°
Max.
Auto Advance
(Crankshaft
Degrees). 13° to 15° at 1,950 rpm. 16° (& 1800 rpm. 21° @ 1800 rpm.
26°
@
4200
rpm. (Max.) 32° @
4200
rpm. (Max.)
Max.
Vac. Advance
(Distributor
Degrees) 8° 8° 8°
Condenser Capacity. .18 to .23 mfd. .25 to .28 mfd. .25 to .28 mfd.
Timing:
Crankshaft
5°
(BTC)
@ Idle 5°
(BTC)
© Idle 0°
(TDC)
© Idle
Mark
Location Crankshaft Pulley Crankshaft Pulley Crankshaft Pulley
Firing
Order
1-6-5-4-3-2 1-6-5-4-3-2 1-6-5-4-3-2
F2-36.
SPARK PLUG
GAP
Spark
Plug Gap. .035"
[0,889
mm.]
IMPORTANT
NOTICE
The
Exhaust Emission Systems covered in this publication
meet
State and Federal
requirements for hydrocarbon and carbon
monoxide
emissions.
To
assure continued proper operation,
these
systems
must be inspected regularly,
parts must be replaced at factory-recommended intervals and
engine
tune-up services
performed at intervals specified in the Exhaust Emission Control System Maintenance
charts.
For
the
above
reasons,
these
systems
must not, under any circumstances, be altered
to anything other than required specifications provided in this publication.
Further,
the Exhaust Emission Control System, or any of its components, must not be physi
cally
altered or modified in any respect.
DATA
TAG
For
the serviceman's guidance, each vehicle equipped with exhaust emission control
will
have data tag permanently affixed to the radiator shroud — in example:
VEHICLE EMISSION CONTROL INFORMATION MODEL V6-225 C.I.D.
•
ENGINE
AT
NORMAL OPERATING TEMPERATURE
•
LIGHTS
AND ALL
ACCESSORIES
OFF
•
IDLE MIXTURE
.. .
LEAN BEST IDLE
•
IGNITION TIMING
0*
(TDC)
*
SPARK PLUG
GAP 035
•
DWELL
. . . 30* (.016
POINT
GAP) •
IDLE SPEED
. . .
650- 700
RPM
TRANSMISSION
IN
NEUTRAL DURING TUNE
UP
SEE
SERVICE MANUAL FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
THIS VEHICLE CONFORMS
TO U.S. DEPT. OF H.E.W.
REGULATIONS APPLICABLE
TO
1971
MODEL YEAR
NEW
MOTOR VEHICLES
Jeep
CORPORATION
14400
NOTE:
The
above
tag applies to vehicles equipped with Distributor Model
IAT-4502A.
On
vehicles equipped with Distributor Models
1110376,
IAT-4501 and IAT-4502 the tag is the same
except
that Ignition Timing is 5°
T.D.C.
Always
refer to the data tag when checking or re-adjusting ignition timing, idle speed, and idle mixture.
159
Page 161 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
COOLING
SYSTEM
Contents
SUBJECT
PAR.
GENERAL
.G-l Antifreeze Solutions. .G-l6
Cylinder
Block.
..................
.G-8
Draining
Cooling System............... G-3
Engine
Overheating..
.................
.G-19
Fan
Belt.
......... .........
.G-18
Filling
Cooling System.................
G-2
Inhibited
Coolant Solution .G-l7
Temperature
Sending Unit.
...........
.G-l0
Thermostat
.........................
G-9
RADIATOR
.G-5
Radiator
and Heater Hoses.............
G-7
SUBJECT
PAR.
Radiator
Pressure
Cap.................
G-4
Radiator
Removal and Replacement..... G-6
WATER
PUMP.
. . .G-ll
Water
Pump Disassembly. .............G-13
Water
Pump Inspection.
..............
.G-12
Water
Pump Reassembly.
.............
.G-14
Water
Pump Removal and Replacement. .G-l5
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS.
.G-20
SPECIFICATIONS
. .G-21
ANTIFREEZE
CHART.
..... ... .G-22
G-l. GENERAL
a.
The satisfactory performance of the Hurricane
F4
engine
is controlled to a great
extent
by the proper operation of the cooling system. The
engine
block is full length water jacketed which prevents
distortion of the cylinder walls. Directed cooling
and
large water holes, properly placed in the cylin
der head gasket cause more water to flow past the
valve
seats
(which are the
hottest
parts of the
block)
and
carry
the heat away from the valves, giving positive cooling of valves and seats.
Minimum
temperature of the coolant is controlled by a thermostat mounted in the
outlet
passage of
the engine. When the coolant temperature is below
thermostat-rated temperature, the thermostat re mains closed and the coolant is directed through
the radiator-bypass
hose
to the water pump. When the thermostat opens, coolant flow is directed to
the top of the radiator. The radiator dissipates the
excess
engine
heat before the coolant is recirculated
through the engine.
The
cooling system is pressurized. Operating pres
sure
is regulated by the rating of the radiator cap
which
contains a relief valve, b. The Dauntless V-6
engine
efficiency and performance is controlled to a great
extent
by proper
operation of the cooling system. The cooling system
does
more than cool the engine. It also directs
the flow of coolant to provide the
best
operating
temperature range for each part of the engine.
In
the Dauntless V-6
engine
coolant is forced by
the water pump into two main passages that run the length of the block on each side (Fig. G-l).
FIG.
G-1—COOLANT
FLOW
THROUGH
THE
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
161
Page 162 of 376
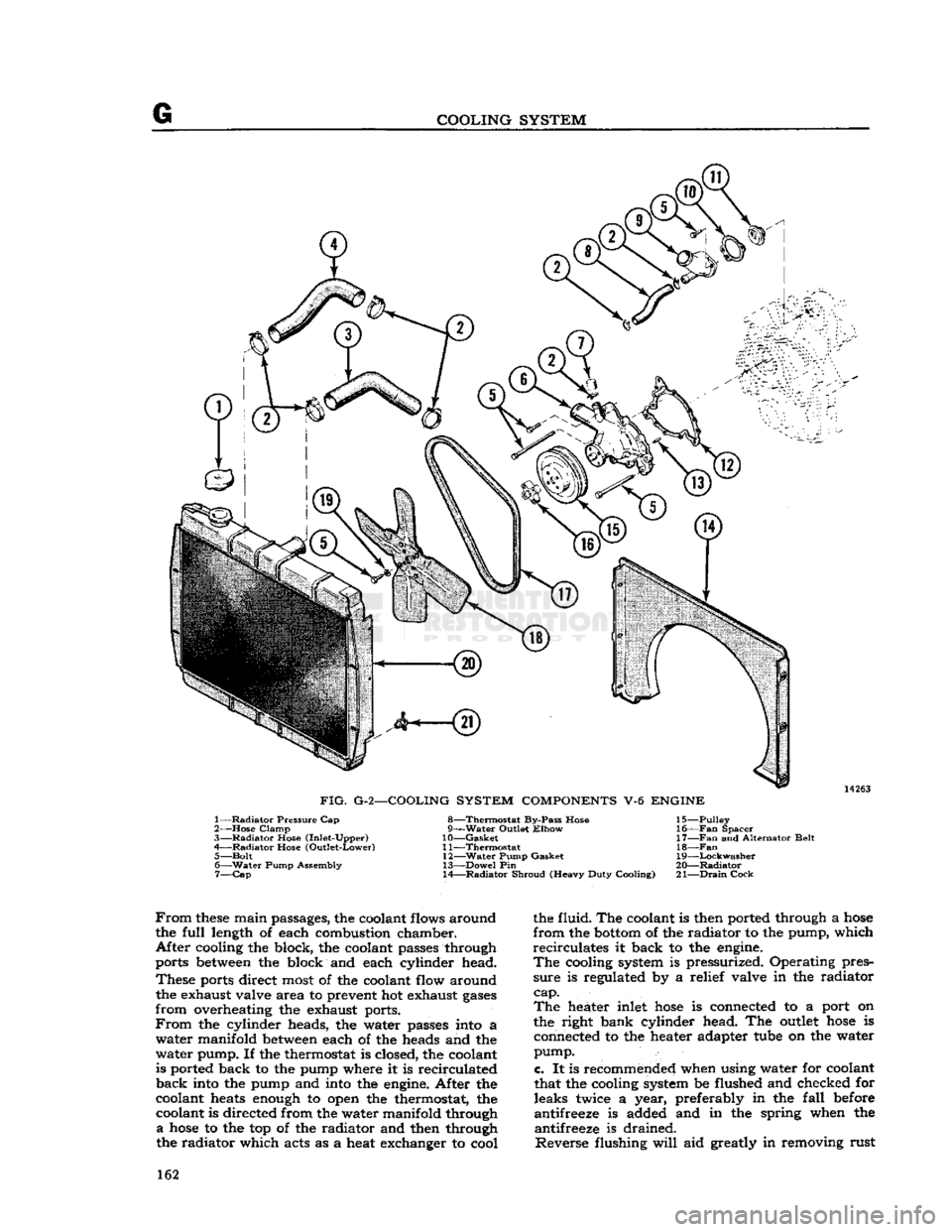
COOLING
SYSTEM
14263
FIG.
G-2—COOLING SYSTEM
COMPONENTS
V-6
ENGINE
1—
Radiator
Pressure Cap
2—
Hose
Clamp
3—
Radiator
Hose (Inlet-Upper)
4—
Radiator
Hose (Outlet-Lower) 5—
Bolt
6—
Water
Pump Assembly 7—
Cap
8—Thermostat
By-Pass Hose
g—Water Outlet
Elbow
10—
Gasket
11—
Thermostat
12—
Water
Pump Gasket
13—
Dowel
Pin
14—
Radiator
Shroud (Heavy Duty Cooling) 15—
Pulley
16—
Fan
Spacer
17—
Fan
and Alternator Belt
18—Fan
19—
Lockwasher
20—
Radiator
21—
Drain
Cock
From
these
main passages, the coolant flows around
the
full
length of each combustion chamber.
After
cooling the block, the coolant passes through
ports between the block and each cylinder head.
These
ports direct most of the coolant flow around the exhaust valve area to prevent hot exhaust
gases
from
overheating the exhaust ports.
From
the cylinder heads, the water passes into a
water
manifold between each of the heads and the
water
pump. If the thermostat is closed, the coolant
is ported back to the pump where it is recirculated
back
into the pump and into the engine. After the
coolant heats enough to open the thermostat, the coolant is directed from the water manifold through
a
hose
to the top of the radiator and then through
the radiator which acts as a heat exchanger to cool the fluid. The coolant is then ported through a
hose
from
the bottom of the radiator to the pump, which
recirculates
it back to the engine.
The
cooling system is pressurized. Operating pres
sure
is regulated by a relief valve in the radiator
cap. The
heater inlet
hose
is connected to a port on
the right bank cylinder head. The outlet
hose
is connected to the heater adapter tube on the water
pump.
c.
It is recommended when using water for coolant
that the cooling system be flushed and checked for leaks twice a year, preferably in the
fall
before
antifreeze is added and in the spring when the antifreeze is drained.
Reverse
flushing
will
aid greatly in removing rust 162