1953 JEEP DJ radiator
[x] Cancel search: radiatorPage 7 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
B
LUBRICATION
AND
PERIODIC SERVICES
Contents
PAR. SUBJECT
PAR.
SUBJECT
GENERAL
.B-l
Chassis
Lubrication
B-7
Engine
Lubrication System B-4, B-6
Special
Lubricants B-2
Fresh
Lubricant.
.B-3
LUBRICATION CHARTS
. Pages 8, 9
SERVICE
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE.
.B-8
Air
Cleaner
B-2
5,
B-2
6
Air
Filter
—
F.E.E.C.
System Canister
B-2
4
Axle
U-Bolts B-49 Body
Lube
Points: B-65 Hood Hinge Pivot Points B-66
Glove
Compartment Door
Latch
B-6
7
Tailgate Hinges .B-68
Brakes,
Adjust .B-41
Brake
Linings .B-42
Brake
Master Cylinder B-40
Charging
Circuit
B-l9
Clutch
. B-43, B-44
Cooling System—Radiator. B-28, B-29 Differentials
........
.B-50, B-51, B-52, B-53
Distributor
B-14, B-l5
Engine
Oil B-9
Engine
Oil
Filter
B-10, B-ll
Engine
Tune-Up B-20
Exhaust
Emission Control System
B-2
2
Exhaust
Manifold Heat Control Valve. . . .B-l2
Exhaust
System
B-2 3
Fan
Belt . .B-21
Front
Axle U-Joint B-54, B-55
Generator
.B-16
Headlights B-61
Heater Controls B-62
Lights
and Controls B-59 Positive Crankcase Ventilation Valve. . . .B-l3
Shock Absorbers B-48
Spark
Plugs. B-17
Speedometer Cable. .B-60
Spring
Bushings.. . .B-46
Spring
Shackles .B-47
Steering
Gear
B-2 7
B-l. GENERAL
All
'Jeep' Universal vehicles require periodic
lubri
cation and other maintenance services for normal
vehicle
usage
and application to promote satis factory operation and prevent
excessive
wear. Un
der severe operating or atmospheric conditions
these
services should be performed more
often
than
under normal conditions. It should also be remem
bered that common short trips and
stop-and-go
driving
are more severe on lubrication
points
than
Starting
Circuit
B-l8
Tie
Rod and Drag
Link
Sockets
.
B-45
Tires
B-64
Transmission
and Transfer Case—
Lubricant
Level
Check B-30
General
B-31
Transfer
Case B-32
Transmission
.B-33
Transmission
and Transfer
Case
—
Lubricant
Change .B-34
General
.B-35
Transfer
Case B-36
Transmission
B-3
7, B-38
Transfer
Case Linkage B-39
Universal
Joints and Slip Joints.
.......
.B-58
Wheel
Bearings..
.........
. . .B-56, B-57
Windshield
Wiper and Washer B-63
LUBRICATION
OF
OPTIONAL EQUIPMENT
B-69
Centrifugal
Governor. .B-71
Pintle Hook .B-70
Powr-Lok
or
Trac-Lok
Differential B-72
PARTS REQUIRING
NO LUBRICATION.
. . .B-73
Alternator
Bearings. B-76
Clutch
Release Bearings.
.............
.B-74
Shock Absorbers B-78
Springs
B-7
7
Starter
Motor Bearings B-75
Water
Pump Bearings B-74
LUBRICATION REQUIREMENTS FOR OFF-HIGHWAY OPERATIONS
B-79
Air
Cleaner B-82
Chassis
Lubrication
B-83
Engine
Oil B-80
Engine
Oil
Filter
B-81
Differentials .B-86
Front
Axle U-Joints. B-84
Transfer
Case and Transmission .B-85
constant
speed
driving on highways, and even more
intensified in extreme cold or hot weather; there fore, vehicles driven under
these
conditions must
be lubricated and serviced more
often
than nor mally operated vehicles. The specifications of
types
and
amounts of lubricant given in the Lubrication
Chart
and
text
of this section should be closely
followed. The off-highway operation lubrication
notes,
given in the last part of the section, should
be followed when applicable. 7
Page 12 of 376
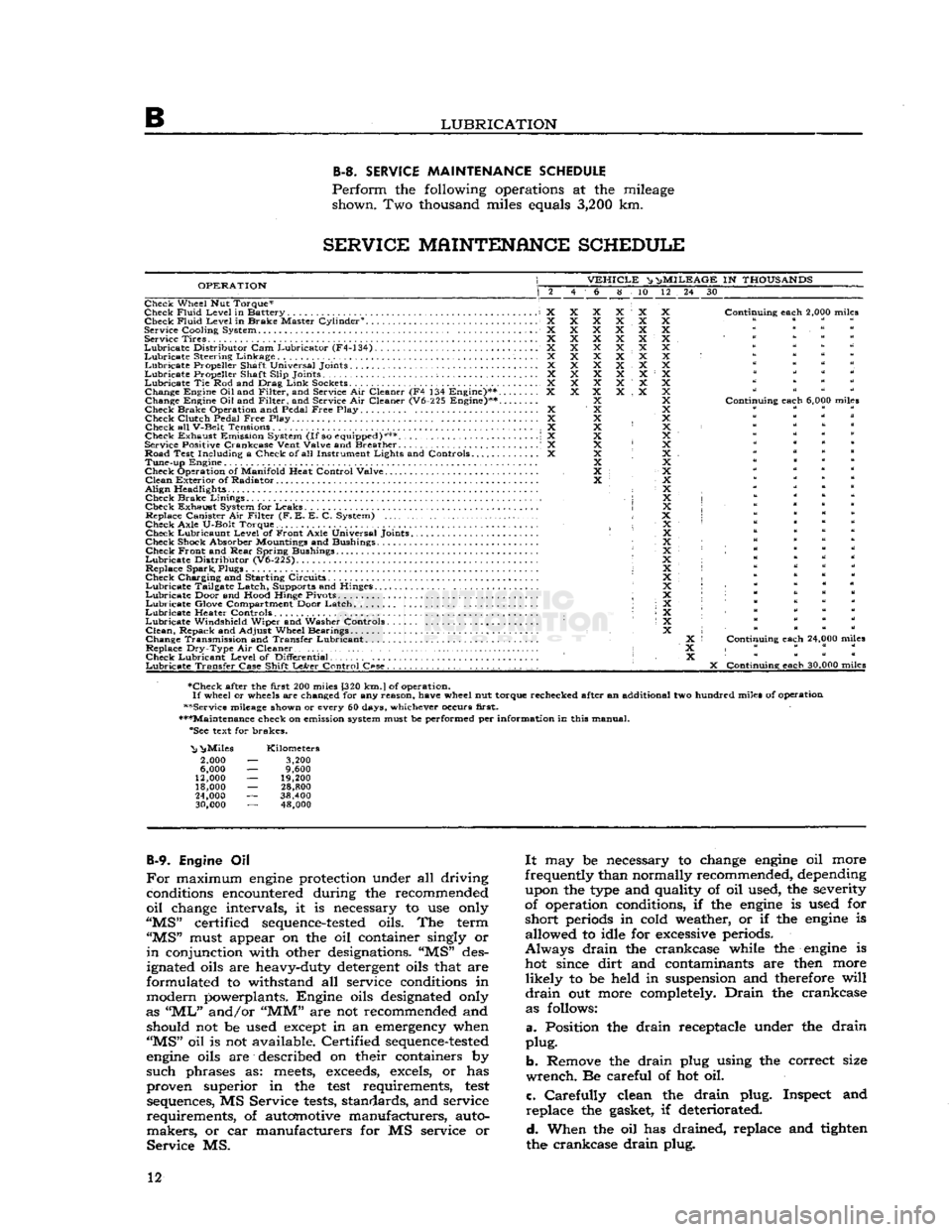
B
LUBRICATION B-3.
SERVICE
MAINTENANCE
SCHEDULE
Perform
the following operations at the mileage shown. Two thousand miles equals
3,200
km.
SERVICE
MAINTENANCE
SCHEDULE
OPERATION
VEHICLE
^ n>
MILEAGE
IN
THOUSANDS
6 8 10 12 24 30
Check Wheel Nut Torque*
Check
Fluid
Level
in Battery X Check
Fluid
Level
in Brake Master Cylinder0. X
Service
Cooling
System X Service Tires X
Lubricate
Distributor
Cam Lubricator (F4-134) X
Lubricate
Steering Linkage X
Lubricate
Propeller Shaft Universal Joints X
Lubricate
Propeller Shaft
Slip
Joints ; X
Lubricate
Tie Rod and Drag
Link
Sockets................................... X Change Engine
Oil
and
Filter,
and Service Air Cleaner (F4 134 Engine)** X
Change Engine Oil and
Filter,
and Service Air Cleaner (V6-225 Engine)**....
Check Brake Operation and Pedal
Free
Play X Check
Clutch
Pedal
Free
Play. .... X
Check all
V-Belt
Tensions X
Check Exhaust Emission System
(If
so equipped)*** \ X
Service Positive
Crankcase
Vent
Valve
and Breather . .' X
Road Test
Including
a Check of all Instrument
Lights
and Controls X Tune-up Engine
Check Operation of
Manifold
Heat
Control
Valve
Clean
Exterior of Radiator
Align
Headlights • Check Brake
Linings
,
Check Exhaust System for Leaks Replace Canister Air
Filter
(F. E. E. C. System)
Check
Axle
U-Bolt
Torque. Check Lubricaunt
Level
of Front
Axle
Universal Joints
Check Shock Absorber Mountings and Bushings Check Front and
Rear
Spring Bushings
Lubricate
Distributor
(V6-225).
Replace Spark, Plugs
Check Charging and Starting Circuits
Lubricate
Tailgate Latch, Supports and Hinges.
Lubricate
Door and
Hood
Hinge Pivots ;
Lubricate
Glove Compartment Door Latch
Lubricate
Heater Controls •
Lubricate
Windshield
Wiper and Washer Controls
Clean,
Repack and
Adjust
Wheel Bearings
Change Transmission and Transfer Lubricant. .
Replace
Dry-Type
Air Cleaner • Check Lubricant
Level
of
Differential
Lubricate
Transfer
Case
Shift
LeArer
Control
C«se.
. , . . . . . . . .
Continuing
each
2,000 miles
Continuing
each
6,000 miles
Continuing
each
24,000 miles
X
Continuing
each
30,000 miles
•Check after the
first
200 miles [320
km.
J
of operation.
If
wheel or wheels are changed for any
reason,
have
wheel nut torque rechecked after an additional two hundred miles of operation
••Service mileage shown or every 60 days, whichever occurs
first.
•••Maintenance check on emission system must be performed per
information
in this manual. "See text for brakes.
"Nj
^Miles
2,000
6,000
12,000
18,000
24,000
30,000
Kilometers
3,200
9,600
19,200
28,800
38,400 48,000
B-9.
Engine Oil
For
maximum
engine
protection under all driving conditions encountered during the recommended
oil
change intervals, it is necessary to use only
"MS"
certified
sequence-tested
oils. The term
"MS"
must appear on the oil container singly or
in
conjunction with other designations. "MS" des
ignated oils are heavy-duty detergent oils that are
formulated to withstand all service conditions in
modern powerplants. Engine oils designated only
as
"ML"
and/or
"MM"
are not recommended and should not be used except in an emergency when
"MS"
oil is not available. Certified
sequence-tested
engine
oils are described on their containers by
such
phrases as:
meets,
exceeds,
excels, or has
proven superior in the
test
requirements,
test
sequences, MS Service
tests,
standards, and service
requirements,
of automotive manufacturers, auto
makers,
or car manufacturers for MS service or
Service
MS.
It
may be necessary to change
engine
oil more
frequently than normally recommended, depending upon the type and quality of oil used, the severity
of operation conditions, if the
engine
is used for
short
periods in cold weather, or if the
engine
is allowed to idle for excessive periods.
Always
drain
the crankcase while the
engine
is hot since
dirt
and contaminants are then more
likely
to be held in suspension and therefore
will
drain
out more completely.
Drain
the crankcase as follows:
a.
Position the
drain
receptacle under the
drain
plug.
b.
Remove the
drain
plug using the correct size
wrench.
Be careful of hot oil.
c.
Carefully
clean the
drain
plug. Inspect and
replace
the gasket, if deteriorated.
d.
When the oil has drained, replace and tighten
the crankcase
drain
plug. 12
Page 15 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
B
solvent.
Wrap
the polyurethane element in a clean
dry
cloth and
squeeze
to remove all possible sol
vent. Do not wring the element or it may
become
torn.
After cleaning, oil the polyurethane element
liberally
with
engine
oil
(SAE
10W30) and
squeeze
to evenly distribute the oil through the element and to remove
excess
oil. The element should be damp
with
oil, not dripping.
Install
the polyurethane element on the paper element, taking care to have
edges
of the polyurethane element over the plastic end plates of the paper element.
Replace
the complete air cleaner element assembly every
24,000
miles
[38.400
km.]. Replace more
frequently if there is any apparent damage or evidence of plugging.
The
crankcase ventilation filter should be replaced, not cleaned, every
6,000
miles
[9.600
km.]. The
filter
is located inside the air cleaner housing.
12992
FIG.
B-7—DRY-TYPE
AIR
CLEANER DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
1—
Crankcase
Ventilation
Filter
2—
Polyurethane
Element
3—
Paper
Element
B-27.
Steering
Gear
Check
that the steering gear lubricant is at the
level of the fill-hole. If not, add lubricant to the
level of the fill-hole with the lubricant recom mended in the
Lubrication
Specifications. If abnor
mally
low, check the steering gear for possibility
of leaks.
B-28.
Cooling System
Check
the coolant level in the
radiator.
It should be
half
an inch below the neck. If not,
fill
the radiator
to
half
inch below the neck with the proper coolant.
Refer
to Section G.
If
the level of the coolant is abnormally low, check
the radiator,
hoses
and water pump for possible
leaks.
If a leak is suspected, refer to Section G.
B-29.
Clean
Exterior
of Radiator
For
proper cooling efficiency the radiator should be cleaned of foreign objects. Refer to Section G.
B-30.
Transmission
and
Transfer Case
Lubricant
Level
Cheek
•
Refer to Par. B-31 through B-33 as applicable.
B-31.
General
All
transfer cases and transmissions should be
serviced
separately even though drilled passages
are
provided for oil circulation
between
some
trans
mission and the transfer case housings. Procedure
from
the appropriate Par. below should be fol lowed to check the lubricant level of the various
types
of transfer cases and transmissions.
If
the transfer case or transmission fluid levels
are
found to be abnormally low, check both units
for any possible leaks.
B-32.
Transfer
Case
:
The
transfer case fill-hole is located on the right side of the transfer case housing. To check the
lubricant
level, remove the
fill
plug.
Lubricant
should be level with this fill-hole. If not, bring up to level by adding make-up lubricant as specified
in
the
Lubrication
Specifications.
B-33.
Transmission
The
transmission fill-hole is located on the right side of the transmission housing. To check the
lubricant
level, remove the
fill
plug.
Lubricant
should be level with this fill-hole. If not, bring
up to level by adding make-up
lubricant
as specified
in
the
Lubrication
Specifications.
B-34.
Transmission and Transfer
Case
Lubricant
Change
•
Refer to Par. B-35 through B-37 as applicable.
B-35.
General
Transfer
case and transmission lubricants should
be changed at the same time.
B-36.
Transfer
Case
To
drain
the transfer case, first remove the transfer
case fill-hole plug and then the transfer case
drain-
hole
plug. Let all fluid
drain
from case.
Then
install
the transfer case drainhole plug, and
refill
the
transfer
case through the fill-hole using the correct
lubricant
as specified in the
Lubrication
Specifica
tions.
At
30,000
mile
[48,000
km.] intervals lube the
transfer
case shift levers with
Lubriplate
No.
130AA.
Late
models have a lube fitting. To lube
older models, (without lube fitting) remove the
bottom
cover of the case, clean thoroughly and
pack
case
full
of lubricant.
B-37.
Transmission (3-Speed)
To
change the lubricant on all vehicles equipped
with
a three speed synchromesh transmission,
drain
the old fluid by first removing the fill-hole plug
and
then removing the drainhole plug. Since on
some
transmissions there are drilled passages be tween the transmission and transfer case that allow
oil
to circulate
between
the two units, the transfer
case should be drained before refilling the trans
mission.
When
all the fluid is completely drained, replace
the drainhole plugs only. For the correct specifi
cations and quantity, refer to the
Lubrication
Specifications. 15
Page 41 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
D
insulator
mountings attached to the frame side
rail
brackets. The
rear
of the engine-transmission
assembly is supported by a rubber insulator
mounting under the
rear
of the transmission on
the frame center cross member.
This
cross member
is bolted to the frame side
rails
so that it can be
dropped when removing the transmission or engine-
transmission
assembly. The rubber insulators allow
free side and vertical oscillation to effectively
neutralize
engine
vibration at the source.
The
rubber
insulator mountings should be inspected
for separation and deterioration by jacking the
power plant away from the frame, near the sup
ports. Vibration cannot be effectively absorbed by
separated or worn insulators. They should be re placed if faulty.
D-4.
Engine
Ground
Strap
To
be sure of an
effective
ground for the electrical
circuits,
a ground strap bridges the right front
engine
support to the chassis. The connections of this strap must be kept clean and tight for proper
operation of the electrical system.
D-5. ENGINE REMOVAL
Should
the
engine
require overhauling, it is neces
sary
to remove it from the vehicle. The following procedure covers removal of the
engine
only.
The
engine, transmission and transfer case may be
removed as a unit by removing (in addition to the following procedure) the radiator guard and the
access plates in the floor pan.
a.
Drain
the cooling system by opening the
drain
cocks at the
bottom
of the radiator and lower right
side of the cylinder block.
b.
Disconnect the battery at the positive terminal
to avoid the possibility of short
circuit.
c. Remove the air cleaner horn from the carburetor
and
disconnect the breather
hose
at the oil filler
pipe.
d.
Disconnect the carburetor choke and throttle controls by loosening the clamp
bolts
and set
screws.
e. Disconnect the fuel-tank-to-fuel-pump line at the fuel pump by unscrewing the connecting nut.
f- Plug the fuel line to prevent fuel leakage.
g. Remove the radiator and radiator grille support
rods.
h. Remove the upper and lower radiator
hoses
by
loosening the
hose
clamps and slipping the clamps
back
on the
hose.
If so equipped, remove the heater
hoses
(one to the water pump, one to the
rear
of
the cylinder head) in the same manner.
i.
Remove the four
bolts
from the fan hub and re
move
the fan hub and fan blades.
j.
Remove the four radiator attaching screws. Re
move
the radiator and shroud as one unit, k. Remove the starting motor cables. Remove the
starting
motor.
I.
Disconnect the wires from the alternator or
generator. Disconnect the ignition
primary
wire
at the ignition coil.
NOTE:
ON
ENGINES EQUIPPED WITH EX
HAUST
EMISSION CONTROL, REMOVE THE
AIR
PUMP,
AIR
DISTRIBUTION
MANI
FOLD,
AND
ANTI-BACKFIRE (DIVERTER)
VALVE.
SEE SECTION
Fl
FOR PROCEDURE.
m.
Disconnect the oil pressure and temperature
sending unit wires at the units.
n.
Disconnect the exhaust pipe at the exhaust
manifold by removing the stud nuts.
o.
Disconnect the
spark
plug cables at the plugs
and
remove the cable bracket from the rocker arm cover stud.
p.
Remove the rocker arm cover by removing the
attaching stud nuts.
q.
Attach a lifting bracket to the
engine
using
existing head bolt locations. Be sure the
bolts
selected
will
hold the
engine
with the weight
balanced.
Attach lifting bracket to a boom hoist,
or
other lifting device, and take up all slack,
r.
Remove the two nuts and
bolts
from each front
engine
support. Disconnect the
engine
ground strap.
Remove the
engine
supports.
Lower
the
engine
slightly to permit access to the two top
bolts
on
the flywheel housing.
s. Remove the
bolts
which attach the flywheel
housing to the engine.
t.
Pull
the
engine
forward, or
roll
the vehicle back
wards,
until the clutch clears the flywheel housing.
Lift
the
engine
from the vehicle.
D-6. ENGINE DISASSEMBLY
Engine
disassembly is presented in the sequence to be followed when the
engine
is to be completely
overhauled after removal from the vehicle. Some
of the operations of the procedure are also ap
plicable
separately with the
engine
in the vehicle,
provided
that wherever necessary the part of the
engine
to be worked on is first made accessible by
removal
of
engine
accessories or other parts.
When
the disassembly operations are performed
with
the
engine
out of the vehicle, it is assumed,
in
this procedure, that all of the accessories have been removed
prior
to starting the disassembly
and
the oil has been drained.
In
addition to the instructions covering operations
for disassembling the
engine
out of the vehicle,
special
instructions are given to cover different
operations required when disassembly is
done
with the
engine
installed.
During
disassembly operations, the
engine
should
be mounted in a suitable
engine
repair
stand. Where
practicable,
modify or adapt an existing repair
stand
as necessary to accommodate the engine. If
an
engine
repair stand is not used, take care to
perform
disassembly operations in a manner that
will
protect personnel against an accident and the
engine
and its parts against damage.
NOTE:
If the
engine
is being disassembled because
of possible valve failure, check the valve tappet
clearance
before disassembly. Improper valve
clearance
could be the possible cause of valve
failure,
indicating a need for more frequent valve
checks and adjustments. 41
Page 54 of 376

D
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
against the hub of the crankshaft pulley.
Timing
gears are accessible for inspection or replacement
with
the
engine
installed in the vehicle after re moving the radiator, belt drive pulley, and timing
cover.
Should
it be necessary to replace the timing gears, attention must be given to the end float of both
the camshaft and crankshaft and to the running
clearance
of both gears. It is also advisable to
check
both the oil jet and oil passage to the
crank
shaft front bearing to be sure that they are clear.
D-55.
Inspection and
Repair
Check
the general condition of both gears and
inspect for evidence of excessive wear. Replace
excessively worn or damaged gears. Inspect the
cover and replace if bent or damaged. It is recom mended that the crankshaft oil seal in the cover
be replaced when the cover is removed to ensure a
good
seal around the crankshaft. To replace this
seal
with the
engine
in the vehicle
requires
removing
the radiator and water pump.
D-56.
Valves, Springs, and Guides
The
exhaust valves seat on the top of the cylinder
block
with the
stems
extending down through
replaceable valve guides. The exhaust valves are actuated by the camshaft through exhaust valve
tappets. The exhaust valve springs are assembled
and
locked on the lower end of the exhaust valve
stems. The retaining locks are the split type, which
fit in a recess on the valve
stems
and into the taper
in
the valve spring retainers.
Adjustment
of exhaust valves is by means of the
adjusting
screw threaded into the upper end of the
exhaust valve tappets. An exhaust valve rotator used as a valve spring retainer is installed on the
lower end of the exhaust valve.
This
valve rotator,
known
as "Roto Cap", is a spring-loaded
ball
bearing
device. On each lift, or opening stroke of
a
valve, the rotator
gives
the valve a slight positive
clockwise rotation.
The
intake valves operate in valve
guides
in the
cylinder
head and are actuated by rocker arms.
The
rocker arms are actuated by valve push rods
and
the intake valve tappets. The intake valve
springs,
the intake valve spring retainers, and the
intake
valve spring retainer locks make up the
remainder
of the valve operating parts. An intake
valve spring retainer oil seal which encircles the
upper
end of the intake valve
between
the valve
locks and the upper end of the valve spring re
tainer,
controls the passage of oil along the valve
stem and guide.
Note:
When
engine
trouble indicates defective
valves as a possible source of trouble, also check
all
vacuum line connections for possible leaks.
D-57.
Inspection of Valves, Springs,
and
Guides
Clean
the valves on a wire wheel, making sure that
all
carbon is removed from the top and the under
side of the heads and that all gum and varnish
deposits
are removed from the stems.
Polish
the valve
stems
with steel wool or crocus
cloth.
Visually
inspect all valves for warpage,
cracks,
or excessive burning and discard if one of
these
conditions exists. Replace any worn, pitted,
or
corroded valves that cannot be cleaned with a
wire
brush.
Replace any valves when
seats
are pitted, burned, or corroded so badly that they
cannot be cleaned up with a light refacing on a valve refacing machine.
Replace
valves with marks of scoring or abrasion visible on the stem. Replace any valves with bent
stems
which
will
be apparent when the valve is
mounted in the valve refacing machine.
Note:
Use only hard-face exhaust valves for
replacement.
Examine
the
stems
of valves which employ the
ball
bearing rotators.
Wear
marks around the
cir
cumference of the
stems
indicates that the valve is
rotating satisfactorily.
Vertical
heavy pressure
areas
indicate that the valve is not rotating and the valve spring retainer (Roto
Cap)
should be replaced
if
at fault.
Check
the diameter of the valve stem at two or three places along the length of the stem
with
a micrometer. The intake valve stem diameter is .3733" to .3738" [9,482 a
9,495
mm.]. The
exhaust valve stem diameter is .371" to .372"
[9,423
a
9,449
mm.].
Note:
Exhaust
and intake valve springs are
similar
in appearance. They must not be inter
changed as they have different spring
charac
teristics.
Wash
the valve springs thoroughly in solvent.
Visually
examine the springs and replace any that
are
deformed or obviously damaged. Examine for
corrosion
from moisture or acid etching which might
FIG.
D-19—TESTING
VALVE
SPRING
1—
Torque
Wrench
2—
Spring
Testing
Fixture
3—
Valve
Spring
54
Page 62 of 376

D
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE d.
Remove the intake valve adjusting screw lock-
nuts from each of the rocker arm valve lash ad
justing
screws. Remove the screws from the rocker
arms.
D-76.
Inspection and
Repair
Run
a round wire brush through the bore of the
rocker
arm shaft and clean out the drilled oil holes.
Clean
out the oil
holes
in the rocker arm shaft
brackets,
and the oil
holes
and
grooves
in the bores
of the rocker arm.
Inspect
the diameter of the shaft at the rocker arm
bearing
areas. Replace the shaft if there are scores
or
abrasion marks along the length of the shaft.
Check
the shaft for alignment by rolling it across
a
smooth level surface. If the shaft
will
not
roll
freely, or if it rolls with a bumping motion, the
shaft is out of alignment and must be replaced.
Inspect
the threads of the adjusting screw
hole
in
the rocker arms and if necessary clean with a
proper
size tap. Replace the adjusting screw lock-
nut or the adjusting screw if either part is damaged
or
deformed.
Inspect
the threads in the tapped
hole
in the top
of the rocker arm shaft brackets and if necessary
clean
with a proper size tap. Replace the bracket
if
either side is worn or scored.
D-77.
Reassembly
a.
Install
two rocker arm shaft plugs, one in each
end of the shaft. Slide two
rocker
arm
shaft brackets
onto
the center of the shaft. Align the tapped
holes
in
the brackets with the drilled
holes
in the top of
the shaft and install the rocker arm shaft lock
screws,
making sure the points of the screws enter
the drilled
holes
in the shaft.
b.
Screw the intake valve adjusting screws into
the rocker arms and install the locknuts.
c.
The rocker arms are paired; that is, two of the
arms
are angled to the right and two are angled to
the left. One of each type is used on each end of
the rocker arm shaft. Slide a rocker arm with the
adjusting
screw end of the rocker arm angling
away
from the bracket
onto
the shaft so that the
adjusting
screw is on the same side of the shaft
as the mounting
hole
in the bracket.
d.
Temporarily
secure the end bracket in place by
installing
a rocker arm cover stud in the tapped
opening in the top of the support.
e. Assemble the parts on the
opposite
end of the
rocker
arm shaft repeating
steps
c and d above.
D-78. ENGINE REASSEMBLY
The
engine
reassembly procedure in the following
paragraphs
is given in the sequence to be followed
when the
engine
is being completely overhauled.
Individual
inspection,
repair,
and fitting operations
previously covered in detail are made throughout
the reassembly procedure. The reassembly pro
cedure
does
not cover accessories. If a new cylinder
block
fitted with pistons is used, many of the
operations
will
not be required.
Mount
the cylinder block in an
engine
repair stand.
If
an
engine
stand is not available, perform the fol
lowing reassembly operation in a manner designed to protect personnel against an accident and the
engine
and its parts against damage.
Note:
During
engine
reassembly, use Perfect Seal
Aerosol
Spray
Sealer
Part
No.
994757
on all
engine
gaskets to ensure against vacuum, oil, gasoline and
water
leaks. Apply to head gaskets, valve covers,
water
pumps, oil pan gaskets, radiator and heater
hose
connections, felt gaskets, gasoline and oil line
connections, stud bolts,
spark
plug threads, and
grease retainer washers. Refer to manufacturer's in
structions on container for proper application pro
cedure.
D-79.
Install
Oil
Gallery
Plug
Coat
plug threads with a suitable sealing compound
and
install the plugs in the front and
rear
ends of
the oil gallery in the cylinder block and the
rear
end of the cylinder head. Torque the plugs 20 to 25 lb-ft. [2,8 a 3,4 kg-m.].
There
is also a pipe plug
(}/g,f
[3,2 mm.] slotted, headless) in the opening in the main oil gallery inside the cylinder block at No. 2 cylinder and another pipe plug
(}/g
"
square-head) in the opening
in
the oil passage directly below the oil pump intake
passage. If
these
two pipe plugs were removed,
make
certain they are reinstalled in the locations
described above or the counterweight of the
crankshaft
might strike the projecting head of the
square-head
plug.
D-80.
Install
Tappets
Turn
the block upside down. Beginning at the
rear
end of the cylinder block, install the intake
and
exhaust valve tappets in the tappet bores in the cylinder block in the following order: one
exhaust, two intake, two exhaust, two intake, and
finally
one exhaust valve tappet.
Check
the tappet to bore fit of each tappet as it
is installed in the block. If the stem-to-block
clearance
tolerance of .0005" to .002" [0,0127 a
0,051 mm.] is
exceeded
install a new tappet fitting
within
this tolerance or ream the bore to accomo date the next oversize tappet which is available
in
.004" oversize.
D-81.
Install
Camshaft and
Thrust
Plate
Lubricate
all camshaft bearings and cam surfaces generously with clean, light
engine
oil.
Carefully,
so not to damage or score the camshaft front bear
ing,
install the camshaft, locating it properly in the bearings. Do not allow the
rear
end of the camshaft to strike sharply against the expansion plug
installed
in the
rear
end of the bore.
Install
the camshaft thrust plate. Slide the thrust
plate spacer
onto
the end of the camshaft with the
beveled inner
edge
of the spacer facing the cam
shaft. If the same camshaft is being reinstalled,
install
any shims previously removed. These shims
are
placed
between
the camshaft shoulder and the
spacer.
Torque the thrust plate attaching
bolts
20
to 26 lb-ft. [2,8 a 3,6 kg-m.].
End
play of the camshaft is determined by running
clearance
between
the
rear
face of the camshaft
gear and the thrust plate. The standard clearance 62
Page 68 of 376

D
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
D-101.
Install
Manifold
If
manifold studs were removed for replacement,
apply sealer on the stud threads
before
installing
a
new stud.
See Section Fl for exhaust emission controlled
engines.
Make
certain that no foreign objects are inside the manifold and that all
passages
are clear. Place a
new set of manifold
gaskets
in position on the side
of the cylinder block.
Then,
carefully slide the manifold
onto
the studs and against the cylinder block being careful not to damage the gaskets.
Torque
all manifold attaching nuts evenly 29 to
35 lb-ft. [4,0 a 4,8 kg-m.].
D-102.
Install
Oil
Filler
Tube
When
installing the oil filler tube, be sure that the
beveled lower end is away from the crankshaft.
Place a
piece
of
hard
wood
over the top of the
tube
to prevent damage to the cap gasket seat.
D-103.
Install
Water Pump
Make
certain that the mating surfaces of the water pump and the cylinder block are clean and smooth.
Install
the gasket on the
flange
of the pump and
install
the pump in position on the cylinder block.
Torque
the water pump attaching
bolts
alternately
and
evenly 12 to 17 lb-ft. [1,7 a 2,3 kg-m.].
D-104.
Install
Water Outlet Fitting
Install
the thermostat and the water
outlet
fitting.
Torque
the water
outlet
fitting attaching
bolts
20
to 25 lb-ft. [2,8 a 3,4 kg-m.].
FIG.
D-42—INSTALLING HURRICANE F4 ENGINE
IN
VEHICLE
1—
Lifting
Sling
2— Hoist
Cable
3—
Hurricane
F4 Engine
4— Dowel Bolt
5—
Flywheel
Housing
D-105.
ENGINE INSTALLATION
a.
Install
lifting sling to
engine
and using suitable hoist raise the
engine
from its blocking or stand
and
then slowly lower it
into
the
engine
compartment of the vehicle.
Note:
When installing the
Hurricane
F4 Engine,
two % x 4 inch
guide
bolts
or
dowels
should be
used to properly
guide
and align the
engine
to the
flywheel housing (See Fig. D-42).
b. Slightly tilt the
engine
downward and at the
same time slide the
engine
rearward
while lining up the transmission main gear shaft with the clutch
throw-out bearing and disc spline.
Note
:The
engine
crankshaft may have to be turned
slightly to align the transmission main gear shaft
with the clutch disc spline.
c. Remove the
guide
bolts
or
dowels
and secure
the
engine
to the housing.
d.
Secure the front
engine
mounts to the frame brackets and
bolt
ground cable to
engine.
e. Remove lifting sling from
engine.
f. Connect exhaust pipe to
engine
manifold flange.
g. Connect throttle and choke cables to carburetor.
h.
Install
fan to water pump pulley.
i.
Connect fuel pump line to main fuel line,
j.
Replace starting motor assembly. k. Connect
engine
wiring harness connectors at
front of cowl.
I.
Connect wires to starting motor assembly, water
temperature and oil pressure sending units and alternator.
NOTE:
ON
ENGINES EQUIPPED WITH EX
HAUST
EMISSION CONTROL,
REPLACE
THE
AIR
PUMP,
AIR
DISTRIBUTOR
MANI
FOLD,
AND
ANTI-BACKFIRE (DIVERTER)
VALVE.
SEE
SECTION
Fl.
m. Replace radiator and radiator grille support
rods and connect coolant
hoses
to
engine.
Note:
Replace heater
hoses
if vehicle is equipped
with hot water heater.
n. Fill
radiator with coolant and
engine
with oil
(see
Lubrication
Chart).
o.
Install
air cleaner and connect carburetor air
hose.
p. Connect battery cables and start
engine,
q.
Install
hood
and road
test
vehicle.
D-103.
FINAL
IN-VEHICLE
ADJUSTMENTS
a.
Clean
battery terminals and check battery. b.
Check
ignition terminals and check battery.
c. Service carburetor air cleaner.
d.
Service positive crankcase ventilation valve.
e.
Check
fuel lines. f. Gap and install new
spark
plugs.
g.
Check
distributor
points
and capacitor; replace
if
necessary. 68
Page 79 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
12710
FIG.
D1
-3—HYDRAULIC VALVE
LIFTER
ASSEMBLY, CROSS-SECTIONAL VIEW
1—
Snap
Ring
6—Ball Retainer
2— Rod
Seat
7—Plunger Spring
3—
Oil
Inlets
8—Lifter
Body
4—
Plunger
9—Bronzed
Cap
5— Feed
Hole
sages
in the block and cylinder head.
The
water cooled system is pressurized to provide efficient
engine
cooling. It consists of a centrifugal-
type water pump, mounted on the timing chain cover, and is driven by the
engine
fan pulley. The
pump provides coolant flow equally to both
cylin
der banks under control of a thermostat. Coolant
flow is around the cylinders and through the
cylinder
head to dispel the heat of combustion in
the engine.
Dl-3.
Engine Mounts
The
engine-transmission unit is mounted to the chassis at three points by rubber pads. The two
front mounts are bolted to the
engine
cylinder
block and the frame members. These mounts sup port most of the
engine
weight, and absorb
vibra
tion which would otherwise be caused by changes
in
engine
output torque. The single
rear
mount is
placed
between
the transmission and the trans mission support. It supports part of the engine'
and
transmission weight, and locates the
rear
of
the
engine
with respect to the centerline of the
vehicle.
Dl-4. ENGINE REMOVAL
To
remove the
engine
from the vehicle follow the
procedurers listed below:
a.
Remove hood. b. Disconnect battery cables from battery and
engine. c. Remove air cleaner.
d.
Drain
coolant from radiator and engine.
e.
Drain
engine
oil.
f. Disconnect alternator wiring harness from con nector at regulator.
cj.
Disconnect the fuel evaporative purge line con nected to the
P.C.V.
valve.
h.
Disconnect upper and lower radiator
hoses
from
the engine.
i.
Remove right and left radiator support
bars,
j.
Remove radiator from the vehicle.
k.
Disconnect
engine
wiring harnesses from con
nectors located on
engine
firewall.
I.
On
engines
equipped with exhaust emission con
trol,
remove the air pump, air distribution manifold,
and
anti-backfire (gulp) valve. See Section F2 for
procedure.
m.
Disconnect battery cable and wiring from en
gine
starter assembly.
n.
Remove
engine
starter assembly from engine,
o.
Disconnect
engine
fuel
hoses
from fuel lines at
right
frame
rail,
p. Plug fuel lines.
q.
Disconnect choke cable from carburetor and cable support bracket mounted on engine,
r.
Disconnect exhaust pipes from right and left
engine
manifolds.
s. Place
jack
under transmission and support trans
mission weight.
f. Remove
bolts
securing
engine
to front motor mounts.
u.
Attach suitable sling to
engine
lifting
eyes
and,
using hoist, support
engine
weight.
v. Remove
bolts
securing
engine
to flywheel housing.
w. Raise
engine
slightly and slide
engine
forward
to remove transmission main shaft from clutch plate spline.
Note:
Engine and transmission must be raised
slightly to release the main shaft from the clutch
plate while sliding the
engine
forward.
x. When
engine
is free of transmission shaft raise
engine
and remove from vehicle,
y. Place
engine
on suitable blocking or
engine
stand and remove sling from engine.
Dl-5.
ENGINE DISASSEMBLY
Engine
disassembly is presented in the sequence to be followed when the
engine
is to be completely
overhauled after removal from the vehicle. Some of the operations of the procedure are also applicable separately with the
engine
in the vehicle,
provided that wherever necessary the part of the
engine
to be worked on is first made accessible by removal of
engine
accessories or other parts.
When
the disassembly operations are performed
with
the
engine
out of the vehicle, it is assumed,
in
this procedure, that all of the accessories have
been removed
prior
to starting the disassembly and
the oil has been drained.