1953 JEEP DJ fold seats
[x] Cancel search: fold seatsPage 31 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
C
FIG.
C-22—-CHECKING
FUEL
PUMP
PRESSURE
—
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE a
couple of strokes to be sure the pump is primed.
Using
a half-pint
bottle
or similar measure, pump
Vi
pint [0,24 It] of fuel by cranking the
engine
with
the starter motor. Count the strokes neces
sary
to
fill
the measure. If more than 20 strokes
are
required, the fuel pump is inefficient, the tank
line is leaking air, or the fuel supply is restricted.
Check
fuel filter in the fuel tank if line is restricted.
C-24.
Check Manifold Vacuum
To
check the intake manifold vacuum on the
Hurri
cane F4 engine, remove the ventilation valve and
L
fitting from the manifold and install special adapter. On the Dauntless V-6
engine
remove the
pipe plug located in the right
rear
of the intake
FIG.
C-23—CHECKING MANIFOLD VACUUM
—
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
manifold and install special adapter. Connect the
vacuum
gauge
tube to the special adapter as shown
in
Fig. C-23 for the
Hurricane
F4 engine.
Start
the engine. Connect a Tachometer
Tool,
C-3896,
from the distributor
primary
terminal to ground and set the
engine
speed at the specified
rpm.
given in Par. C-30. Observe the vacuum
read
ing and interpret as follows:
a.
A steady reading from 18" to 20" [457 a 508
mm.] of mercury is a normal reading, indicating
that valve and
spark
timing, valve seating, and
piston ring sealing are all satisfactory.
b. A steady but below normal reading indicates
a
condition common to all cylinders such as a
leak
at the carburetor gasket, late ignition or valve
timing, or uniform piston ring and bore wear.
c.
A slowly fluctuating or drifting reading in dicates that the carburetor idle mixture is incorrect
Look
for the cause in the fuel system.
d.
A rhythmic pulsating reading is caused by a
condition affecting one or more cylinders, but not
all,
and indicates leaky valve, gasket blowby, re
stricted intake port, or an electrical miss.
e. An intermittent pulsating reading is caused by
an
occasional malfunction, such as a sticking valve
(all
valves may be
erratic
in operation if the valve
springs are weak), electrical miss caused by insuffi
cient distributor point tension or low coil
voltage
coupled with inconsistent
spark
plug
gaps
or fouled
plugs, or
dirt
in the fuel system finding its way into
passages of
critical
size or valve
seats
in the
car
buretor.
f.
A normal reading that quickly falls off (with
engine
running at
2000
rpm.) indicates exhaust
back
pressure caused by a restriction in the exhaust
system.
g.
Make indicated corrections to bring vacuum to 18" to 20" [457 a 508 mm.] of mercury normal
reading.
C-25.
Carburetor Adjustments
•
Refer to Fig. C-24, C-25 and C-26.
Carburetor
adjustments should not be attempted
until
it is known that
engine
ignition and com
pression are in
good
order. Any attempt to adjust
or
alter the carburetor to compensate for faulty conditions elsewhere
will
result in reduced econ
omy and overall performance.
Caution:
If an
engine
is idling too slow or rough,
this may be caused by a
clogged
ventilator valve
or
hose;
therefore, never adjust the carburetor idle
without first checking the crankcase ventilator
check valve and
hose.
The
air cleaner must be left in place while making
idle speed and mixture adjustments. All lights and accessories, must be turned off. The positive
crank
case ventilator system should also be in
good
oper
ating condition when making carburetor adjust ments.
Either
of
these
items noticeably affects the
air
fuel ratio at idle.
•
Hurricane
F4 Engine.
Note:
The idle mixture adjustment procedure for
the late model
YF-4941S
and
YF-6115S
Carter
31
Page 34 of 376

TUNE-UP
C-29.
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS
POOR
FUEL ECONOMY Ignition Timing Slow or Spark Advance Stuck
Carburetor
Float High
Accelerator Pump Not Properly Adjusted High Fuel Pump Pressure
Fuel
Leakage
Leaky
Fuel Pump Diaphragm Loose Engine Mounting Causing High Fuel Level in Carburetor
Low
Compression
Valves Sticking
Spark
Plugs Bad
Spark
Plug Cables Bad
Weak
Coil
or Condenser Improper Valve Tappet Clearance
Carburetor
Air Cleaner Dirty
High Oil Level in Air Cleaner Dragging Brakes
Front
Wheels Out of Alignment
Tires
Improperly Inflated Inaccurate Odometer
Faulty
Fuel Tank Cap
Clogged
Muffler or Bent Exhaust Pipe Sticking Exhaust Manifold Valve
LACK
OF POWER
Low
Compression Ignition System (Timing Late)
Improper Functioning Carburetor
or Fuel Pump
Fuel
Lines
Clogged
Air
Cleaner Restricted Engine Temperature High Improper Tappet Clearance
Sticking Valves
Valve Timing Late
Leaky
Gaskets
Muffler
Clogged
Bent Exhaust Pipe Sticking Exhaust Manifold Valve —
Dauntless V-6 Engine
LOW
COMPRESSION
Leaky
Valves Poor Piston Ring Seal Sticking Valves
Valve Spring Weak or Broken
Cylinder
Scored or Worn
Tappet Clearance Incorrect Piston Clearance too Large
Leaky
Cylinder Head Gasket
BURNED
VALVES AND SEATS Sticking Valves or too Loose in Guides
Improper Timing
Excessive Carbon Around Valve Head and Seat Overheating
Valve Spring Weak or Broken
Valve Tappet Sticking
Valve Tappet Clearance Incorrect
Clogged
Exhaust System
Defective
Valve
Lifter
— Hydraulic
VALVES
STICKING
Warped Valve Improper Tappet Clearance Carbonized or Scored Valve
Stems
Insufficient Clearance Valve Stem to Guide
Weak or Broken Valve Spring Valve Spring Cocked Contaminated Oil
OVERHEATING
Inoperative Cooling System
Theromstat Inoperative Improper Ignition Timing
Improper Valve Timing
Excessive Carbon Accumulation
Fan
Belt too Loose
Clogged
Muffler or Bent Exhaust Pipe
Oil
System Failure Scored or Leaky Piston Rings
Sticking Exhaust Manifold Valve — Dauntless V-6 Engine
POPPING-SPITTING-DETONATION
Improper Ignition Improper Carburetion
Excessive Carbon
Deposit
in
Combustion Chambers
Poor Valve Seating Sticking Valves
Broken Valve Spring Tappets Adjusted too Close
Spark
Plug Electrodes Burned
Water or Dirt in Fuel
Clogged
Lines Improper Valve Timing
Clogged
Fuel Filter Sticking Exhaust Manifold Valve —
Dauntless V-6 Engine
EXCESSIVE
OIL CONSUMPTION Piston Rings Stuck in Grooves, Worn or Broken Piston Rings Improperly Fitted or Weak Piston Ring Oil Return
Holes
Clogged
Excessive Clearance, Main and
Connecting Rod Bearings
Oil
Leaks at Gaskets or Oil Seals
Excessive Clearance, Valve Stem
to Valve Guide (Intake)
Cylinder
Bores Scored, Out-of-
Round or Tapered
Too Much Clearance, Piston to Cylinder Bore
Misaligned Connecting Rods
High Road
Speeds
or Temperature
Crankcase
Ventilator Not Operating
BEARING
FAILURE
Crankshaft
Bearing Journal Out-of-Round
Crankshaft
Bearing Journal Rough
Lack
of Oil
Oil
Leakage
Dirty
Oil
Low
Oil Pressure or Oil Pump Failure
Drilled
Passages
in Crankcase or Crankshaft
Clogged
Oil
Screen Dirty
Connecting Rod Bent 34
Page 77 of 376
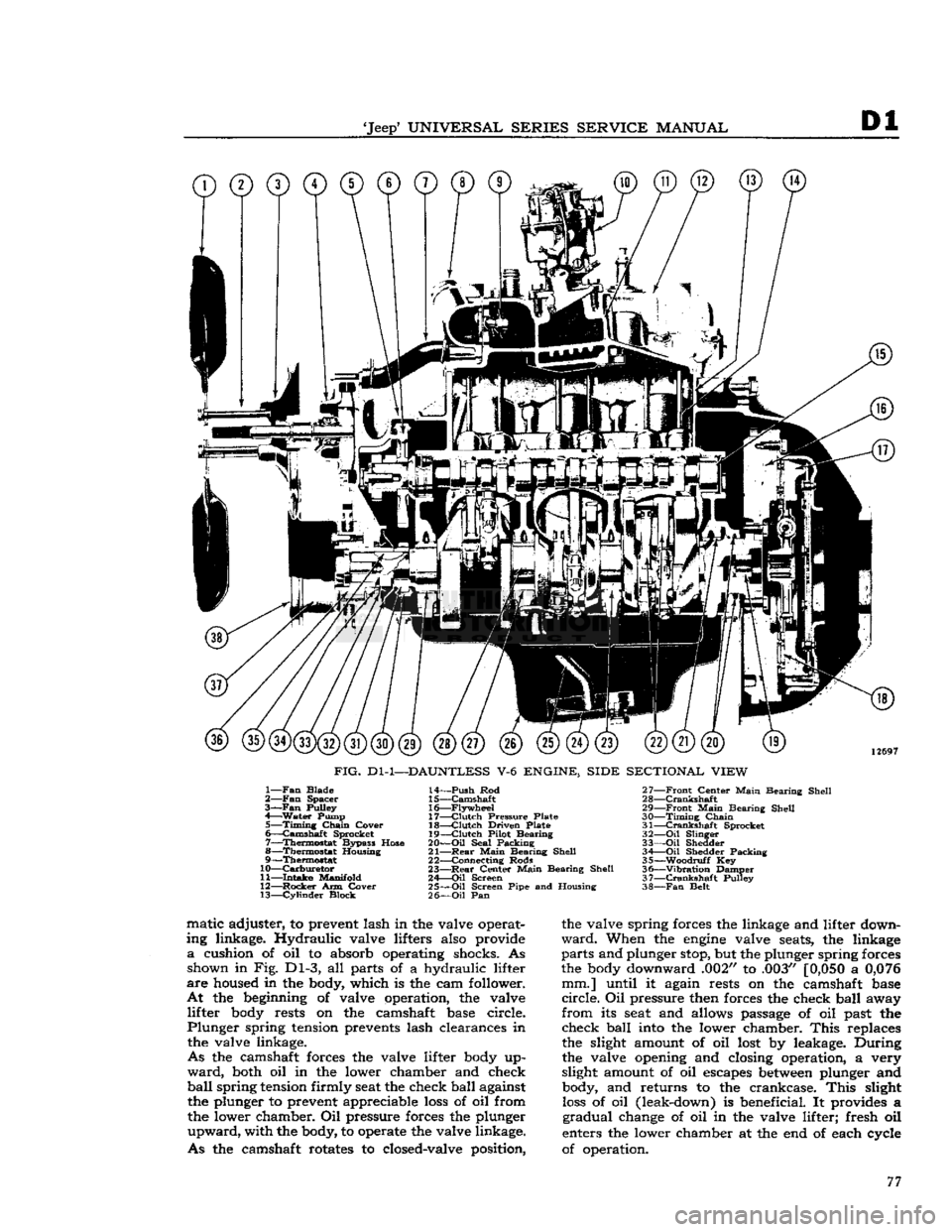
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
©©©©©©©©©
12697
FIG.
Dl-1—DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE, SIDE SECTIONAL VIEW
1—
Fan
Blade
2—
Fan
Spacer
3—Fan
Pulley
4—
Water
Pump 5—
Timing
Chain
Cover
6—
Camshaft
Sprocket
7—
Thermostat
Bypass Hose
8—
Thermostat
Housing
9—
Thermostat
10—
Carburetor
11—
Intake
Manifold
12—
Rocker
Arm Cover 13—
Cylinder
Block 14—
Push
Rod
15—
Camshaft
16—
Flywheel
17—
Clutch
Pressure Plate
18—
Clutch
Driven Plate
19—
Clutch
Pilot Bearing
20—
Oil
Seal Packing
21—
Rear
Main
Bearing Shell
22— Connecting Rods
23—
Rear
Center
Main
Bearing Shell
24—
Oil
Screen
25—
Oil
Screen Pipe and Housing
26—
Oil
Pan 27—
Front
Center
Main
Bearing Shell
28—
Crankshaft
29—
Front
Main
Bearing Shell
30—
Timing
Chain
31—
Crankshaft
Sprocket
32—
Oil
Slinger
33—
Oil
Shedder 34 Oil Shedder Packing
35—
-Woodruff
Key
36—
"Vibration
Damper
37—
Crankshaft
Pulley
38—
Fan
Belt matic adjuster, to prevent lash in the valve operat
ing linkage. Hydraulic valve lifters also provide
a
cushion of oil to absorb operating shocks. As shown in Fig. Dl-3, all parts of a hydraulic lifter
are
housed in the body, which is the cam follower.
At
the beginning of valve operation, the valve lifter body rests on the camshaft base circle.
Plunger
spring tension prevents lash clearances in the valve linkage.
As
the camshaft forces the valve lifter body up
ward,
both oil in the lower chamber and check
ball
spring
tension firmly seat the check ball against the plunger to prevent appreciable
loss
of oil from
the lower chamber. Oil pressure forces the plunger
upward,
with the body, to operate the valve linkage.
As
the camshaft rotates to closed-valve position, the valve spring forces the linkage and lifter down
ward.
When the
engine
valve seats, the linkage
parts
and plunger stop, but the plunger spring forces
the body downward .002" to .003"
[0,050
a
0,076
mm.] until it again rests on the camshaft base
circle.
Oil pressure then forces the check ball away
from
its seat and allows passage of oil past the check ball into the lower chamber.
This
replaces
the slight amount of oil lost by leakage. During
the valve opening and closing operation, a very
slight amount of oil escapes
between
plunger and body, and returns to the crankcase.
This
slight
loss
of oil (leak-down) is beneficial. It provides a
gradual
change of oil in the valve lifter; fresh oil
enters the lower chamber at the end of each cycle
of operation. 77
Page 105 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
Dl-104.
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS
Poor Fuel Economy
Ignition Timing Late or Spark Advance Inoperative
Carburetor
Float Setting Too High
Accelerator Pump Improperly Adjusted
Fuel
Pump Pressure High
Fuel
Line
Leakage
Fuel
Pump Diaphragm Leakage
Cylinder
Compression Low
Valves Do Not Seat Properly
Spark
Plugs
Defective
Spark
Plug Cables
Defective
Ignition
Coil
or Capacitor
Defective
Carburetor
Air Cleaner Dirty
Brakes
Drag
Wheel Alignment Incorrect
Tire
Pressure Incorrect Odometer Inaccurate
Fuel
Tank
Cap Clogged or
Defective
Muffler or Exhaust Pipe Clogged or Bent
Lack
of
Power
Cylinder
Compression Low
Ingitdon Timing Late
Carburetor
or
Fuel
Pump Clogged or
Defective
Fuel
Lines Clogged
Air
Cleaner Restricted
Engine Temperature High Valves Do Not Seat Property
Valve
Timing Late Intake Manifold or Cylinder Head
Gasket Leaks
Muffler or Exhaust Pipe Clogged or Bent
Spark
Plugs Dirty or
Defective
Breaker
Point Gap Incorrect
Breaker
Points
Defective
Ignition
Coil
or Capacitor
Defective
Electrical
Connection Loose
Broken
Valve Spring
Broken
Piston Ring or Piston
Cylinder
Head Gasket
Defective
Distributor Cap Cracked
Low
Compression
Valves Not Seating Properly Piston Rings Seal Poorly
Valve
Spring Weak or Broken
Cylinder
Scored or Worn
Piston Clearance Too Great
Cylinder
Head Gasket Leaks
Burned
Valves and
Seats
Valves Stick or Are Too Loose in Guides
Valve
Timing Incorrect
Valve
Head and Seat Have Excessive Carbon
Engine Overheats
Valve
Spring Weak or Broken
Valve
Lifter Seized or Collapsed
Exhaust
System Clogged
Valves Sticking
Valve
Stem Warped
Valve
Stem Carbonized or Scored
Valve
Stem Clearance Insufficient in Guide
Valve
Spring Weak or Broken
Valve
Spring Distorted
Oil
Contaminated
Overheating
Cooling System Inoperative
Thermostat Inoperative Ignition Timing Incorrect
Valve
Timing Incorrect
Carbon
Accumulation Excessive
Fan
Belt Loose
Muffler or Exhaust Pipe Clogged or Bent
Oil
System Failure
Piston Rings Worn or Scored
Popping,
Spitting,
Detonation
Ignition Timing Incorrect
Carburetion
Improper
Carbon
Deposit
in Combustion
Chambers Excessive
Valves Not Seating Properly
Valve
Spring Broken
Spark
Plug Electrodes Burned
Water or Dirt in
Fuel
Fuel
Line
Clogged
Valve
Timing Incorrect
Excessive
Oil
Consumption
Piston Rings Stuck in Grooves, Weak,
Worn,
Broken, or Incorrectly Fitted
Crankshaft
Main Bearings or
Connecting Rod Bearings Have
Excessive Clearance
Gaskets or Oil Seals
Leak
Cylinder
Bores Worn, Scored,
Out-of-Round or Tapered
Pistons Have Too Great Clearance to Cylinder Bores
Connecting Rods Misaligned High Road Speed
High Temperature
Crankcase
Ventilation System Inoperative
Bearing Failure
Crankshaft
Bearing Journal Rough or Out-of-Round
Oil
Level Low
Oil
Leakage
Oil
Dirty
Oil
Pressure Low or Lacking
(Oil
Pump Failure)
Drilled
Passages
in Crankshaft or
Crankcase
Clogged
Oil
Screen Dirty
Connecting Rod Bent 105
Page 121 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
FIG.
E-19—
MAIN
METERING SYSTEM
1—
Main
Nozzle
2—
Mixture
Passage
3—
Boost
Venturi
4—
Main
Venturi
5—
Throttle
Valve 6—
Main
Metering Jet
7—
Main
Well
Insert
8—
Main
Well
Tube
9—
Main
Well
Air Bleed fuel through calibrated
holes
in the main well tube.
Fuel-air
mixture then
moves
upward into a channel
where another calibrated amount of air is injected through the main air bleed. It then flows down
ward
through the channel to the venturi, where it is discharged into the air stream, and then to the
intake manifold.
E-29.
Power System
A
vacuum-operated power piston in the air horn
and
a power valve in the
bottom
of the float bowl
enrich
fuel-air mixture when more power is desired.
This
system also operates during extreme high
speed driving. Through a vacuum passage from the
carburetor
base to the power cylinder, the power
piston is
exposed
to manifold vacuum. See Fig.
E-20.
During
idle and part throttle operation, relatively
high vacuum holds the power piston in upward
FIG.
E-20—POWER
SYSTEM
position against spring tension so that the power
valve remains closed.
Increase
in
engine
load decreases manifold vacuum.
When
vacuum decreases sufficiently, the spring
overcomes vacuum and the power piston
moves
downward.
This
opens
the power valve to allow
additional fuel to flow through calibrated restric
tions into the main well.
As
the
engine
load decreases, resulting higher
vacuum
overcomes spring tension on the power
piston and draws the power piston upward.
This
closes
the power valve.
This
carburetor has a
two-stage
power valve. In
the first
stage,
fuel is metered by the valve itself.
This
stage
occurs under light load. During heavy
load,
the valve is fully opened to the second
stage;
in
this position, the power valve supplies fuel to
be metered by power restrictions in the fuel chan
nel
to the fuel bowl.
The
power piston cavity is connected to the main
air
flow passage by a vacuum relief passage.
This
passage prevents transfer of vacuum to fuel in the
float bowl. Any leakage of air past the piston
will
be compensated for by this relief passage; hence it
will
not affect carburetor metering.
E-30.
Accelerator Pump System
When
the throttle valve
opens
rapidly, air flow
and
manifold vacuum change almost instantaneous
ly.
However, heavier fuel-air mixture
does
not flow immediately.
Thus,
momentarily, the
engine
does
not have sufficient fuel. The accelerator pump pro vides additional fuel necessary for
engine
operation
during
acceleration.
A
double-spring loaded pump plunger supplies fuel for acceleration. Top and
bottom
springs
move
the
plunger to furnish a smooth, sustained charge of
fuel for acceleration. See Fig. E-21.
Fuel
is drawn into the pump well past the inlet
check ball during the plunger intake (upward)
stroke.
Downward
motion of the pump plunger
seats
the
inlet check ball and forces fuel through the dis charge
passage.
This
unseats
the pump discharge
check
ball.
Fuel
then sprays through the discharge
12837
FIG.
E-21—ACCELERATOR
PUMP
SYSTEM
1— Piston Vacuum Chamber
2—
Vacuus*
Relief Passage
3—
Main
Well
4— ^Power Restrictions 5— Power Valve
6— Power Piston Spring 7— Power Piston 1— Pump
Jets
2—
Discharge
Check
Ball
3—
Discharge
Passage
4—
Inlet
Check
Ball
5—
Inlet
Screen
6—
Vapor
Vent
Check
Ball
7—
Pump
Plunger
121
Page 372 of 376

ALPHABETICAL
INDEX
SUBJECT
PAR.
SUBJECT
PAR.
Ignition Cable Test C-l9 Ignition
Coil
C-20, H-19, H-31
Ignition Switch H-89 Ignition System H-3
Ignition
Timing
C-14, H-18, H-30 Ignition Wires C-18
Intake Manifold '." Dl-7, Dl-101
Instrument, Electrical H-122
L
License Plate Light H-l36
Lighting
System H-l25
Light
Switch, Main . H-l 26
Lubrication
B-l
Lubrication,
Body B-65
Lubrication
Maintenance Schedule B-8
Lubrication
of Optional Equipment B-69
Lubrication,
Off Highway B-79
Lubrication,
Special. B-2
M
Main
Bearings D-43, D-82, Dl-32, Dl-42, Dl-73
Main
Light Switch. H-l26
Maintenance, Clutch 1-2 Maintenance, Exhaust System.,
-
F-4
Manifold, Exhaust -F-6 Manifold, Intake D-7, Dl-101
Manifold Vacuum Check. .C-24 Master Cylinder, Brake B-40, P-2, P-20
Miscellaneous Data U-16 Mountings, Engine • • •
-
D-3, Dl-3
Muffler. F-9
O
Oil
Filter B-10, B-ll,
D-lll,
Dl-13, Dl-93
Oil
Pan D-19, D-66, D-97, Dl-29, Dl-51, Dl-77
Oil
Pump. D-14, D-65, D-93, Dl-19, Dl-50, Dl-87
P
Paint and
Trim
Plate • • A-7
Parking
Brake Adjustment P-ll
Parking
Lights H-133
Pilot Bushing, Crankshaft D-70, 1-8
Pintle Hook U-7
Pistons D-20, D-95, Dl-31, Dl-48, Dl-75 Piston Rings. • • •
•
D-37, Dl-47 Positive Crankcase Vent. B-13, C-6, D-110
Powr-Lok
Differential B-72, N-20
Primary
Circuit,
Electrical H-4 Propeller Shaft U-Joints .B-58, L-2, L-3 Propeller Shaft Specifications <:' L-7
R
Radiator
B-28, B-29, G-5
Radiator
Hoses. G-7
Radiator
Pressure Cap G-4
Rear
Axle. B-50, B-51, B-52, N-9
Rear
Axle Reassembly • N-l
7
Rear
Axle Disassembly N-l
2
Rear
Axle Pinion Adjustment N-l6
Rear
Axle Shaft N-2, N-3
Rear
Bearing Seal, Crankshaft D-63, D-85, Dl-62
Rear
Wheel Bearings B-56, B-57, N-4, Q-3
Regulator Test, Voltage H-47, H-71
Rocker
Arm Cover.. . Dl-65
Rocker
Arms D-16, D-74, D-99, Dl-60 Rotor, Alternator H-76, H-79
S
Seats
• T-8 Secondary
Circuit,
Electrical H-5
Shock Absorbers B-48, S-7
Solenoid Switch. H-l21 Special Lubricants B-2
Spark
Plugs C-4, H-33
Special Tools • U-ll
Speedometer
Cable B-60 Springs B-77, S-4, S-5
Spring
Bushings S-2
Spring
Pivot Bolts S-3
Spring
Shackles S^2
Spring
Specifications S-8 372 Starting Motor B-18, H-92, H-108
Starting Motor Bearings B-75
Starting Motor Bendix Drive H-105, H-106
Starting System H-7, H-88
Starting System Maintenance H-93 Stator, Alternator H-84
Steering • • •
•
O-l
Steering Arm P-10
Steering Column Adjustments 0-4
Steering Column and Wheel Service O-20 Steering Gear. . B-27, 0-22
Steering Gear Adjustment 0-5
Steering Gear Function 0-2
Steering Knuckle. B-27, M-8 Steering Linkage 0-14
Stop
Light Switch H-128
Switch, Heater U-10 Switch, Ignition H-89
Switch, Wiper Motor H-142
T
Tail
Light . H-134
Tail
Pipe F-10 Temperature Sending Unit G-10
Thermostat G-9
Timing
Chain Dl-22, Dl-66, Dl-84
Timing
Chain Cover Dl-20, Dl-67, Dl-86
Timing
Gears D-22, D-54, Dl-22, Dl-66, Dl-84
Timing,
Ignition. C-14, H-18, H-30
Tire
Service . •
•
Q-l
1
Toe-in Adjust 0-7, 0-8 Tools, Special. . .
........
U-ll Torque Specifications, Chassis U-14
Torque Specifications, Engine .U-13
Top,
Canvas. T-5
Trac-Lok
Differential N-24
Transfer
Case B-36, K-1
Transfer
Case Reassembly K-6
Transfer
Case Disassembly K-3
Transfer
Case Linkage - K-8
Transfer
Case Removal K-2 Transmission and Transfer Case. B-30, J-7 Transmission —
3-Speed
B-37, B-38, J-l
Transmission —
4-Speed
... J-20
Transmission Brake P-4 Transmission Brake Adjustment P-l
2
Transmission,
Cane Shift .J-8 thru J-19
Transmission,
Remote Shift J-4
Transmission Remote Shift Adjustment J-3
Transmission Specifications
-
J-27
Tune-Up
Sequence
C-2
Tune-Up
Specifications C-30
U
U-Joint, Front Axle . . B-54, B-55, M-7
U-Joint, Propeller Shaft B-58, L-l
Vacuum
C-24 Valves D-21, D-56, D-90, Dl-56, Dl-63
Valve
Adjustment D-107
Valve
Lifter Dl-57, Dl-81
Valve
Seats
D-59
Valve
Springs .D-56, D-90, Dl-63
Valve
Tappets C-8, D-29, D-62, D-80
Valve
Timing D-109
Vehicle Description A-2
Vehicle Identification A-3
Vehicle Serial Number. A-5
Vibration
Damper D-l2, D-96, Dl-17, Dl-70 Voltage Regulator. H-41, H-71
W
Water Pump G-ll thru G-15
Water Pump Bearings B-74
Wheels Q-l
Wheel Balancing Q-2 Wheel Bearing Adjustment Q-5, Q-6, Q-7
Wheel Brake Service P-6 Wheel Bearing Service Q-3
Wheel Cylinder, Brake P-21 Windshield T-3 Windshield Wiper Motor . .H-142
SM-1046
PRINTED
IN U.S.A.
110-CH6M