1953 JEEP DJ length
[x] Cancel search: lengthPage 6 of 376
GENERAL
DATA
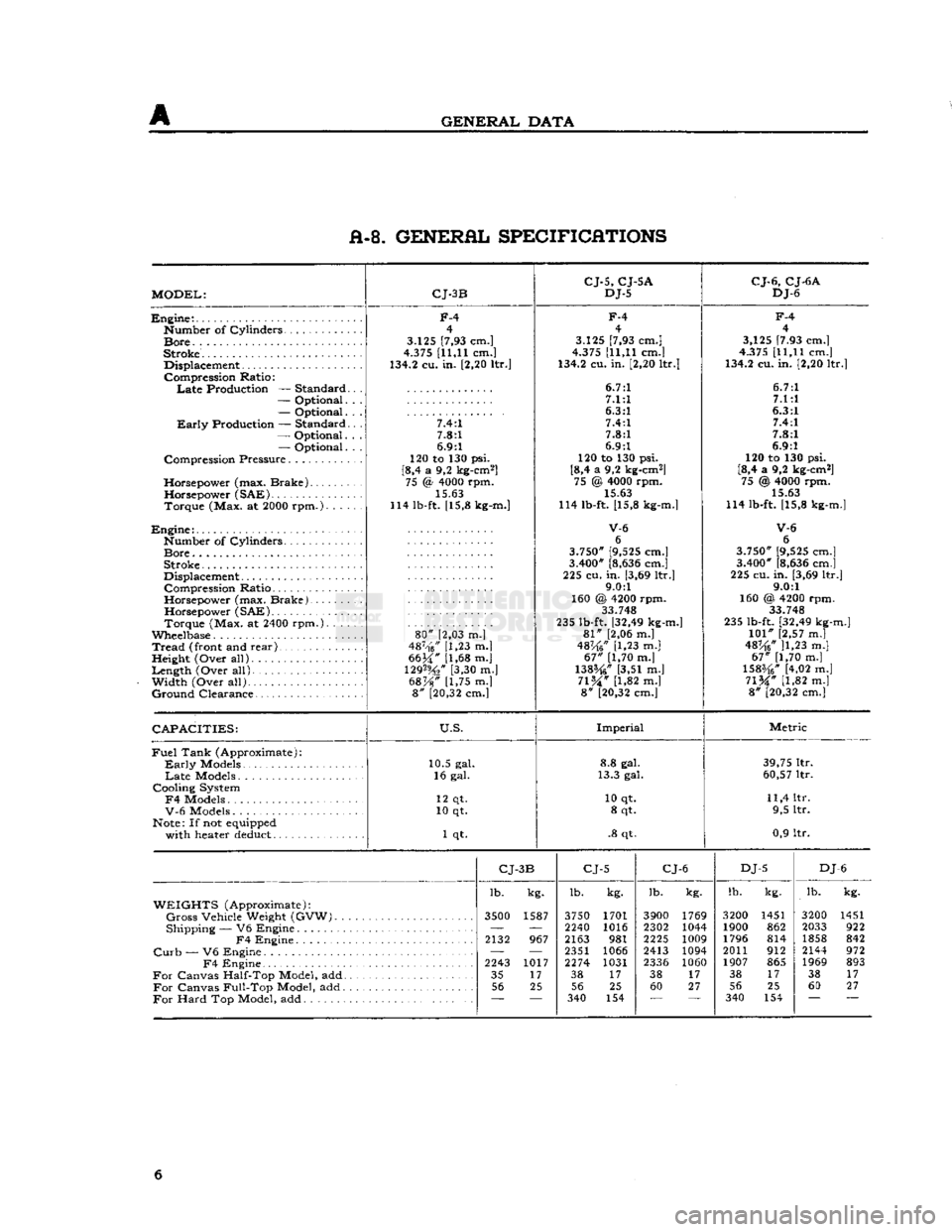
A-8. GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
MODEL:
CJ-3B
CJ-5,
CJ-5A
DJ-5
CJ-6,
CJ-6A
DJ-6
Engine:.
Number
of
Cylinders
Bore.
.
Stroke.
Displacement
Compression
Ratio:
Late
Production —
Standard
—
Optional.
—
Optional.
Early
Production —
Standard
—
Optional.
—
Optional.
Compression
Pressure
Horsepower
(max.
Brake)
Horsepower
(SAE)
Torque
(Max. at 2000
rpm.).
. . .
Engine:
Number
of
Cylinders
Bore
Stroke
Displacement
Compression
Ratio
Horsepower
(max.
Brake).
Horsepower
(SAE)
Torque
(Max. at 2400
rpm.).
. . .
Wheelbase
Tread
(front and
rear)
,
Height
(Over
all)
Length
(Over
all).
Width
(Over
all)
Ground
Clearance
F-4
4
3.125 [7,93 cm.]
4.375 [11,11 cm.]
134.2 cu. in. [2,20 ltr.]
7.4:1 7.8:1
6.9:1
120 to 130 psi.
[8,4 a 9,2 kg-cm2] 75 <§ 4000 rpm.
15.63
114 lb-ft. [15,8 kg-m.]
80"
[2,03 m.]
487-'f6/' [1,23 m.|
6634" [1,68 m.j
129%"
[3,30 m.]
68%"
[1,75 m.] 8" [20,32 cm.]
F-4
4
3.125 [7,93 cm.]
4.375 [11,11 cm.]
134.2 cu. in. [2,20 ltr.]
6.7:1 7.1:1
6.3:1 7.4:1
7.8:1
6.9:1
120 to 130 psi.
[8,4 a 9,2 kg-cm2] 75 @ 4000 rpm. 15.63
114 lb-ft. [15,8 kg-m.]
V-6
6
3.750" [9,525 cm.]
3.400" [8,636 cm.]
225 cu.
in.
[3,69 ltr.] 9.0:1
160 @ 4200 rpm. 33.748
235 lb-ft. [32,49 kg-m.]
81"
[2,06 m.]
48K6"
[1,23 m.]
67"
[1,70 m.]
138%"
[3,51 m.]
71%"
[1,82 m.] 8" [20,32 cm.]
F-4
4
3,125 [7.93 cm.]
4.375 [11,11 cm.]
134.2 cu. in. [2,20 ltr.]
6.7:1 7.1:1
6.3:1 7.4:1
7.8:1
6.9:1
120 to 130 psi.
[8,4 a 9,2 kg-cm2] 75 @ 4000 rpm.
15.63
114 lb-ft. [15,8 kg-m.]
V-6
6
3.750" [9,525 cm.]
3.400" [8,636 cm.]
225 cu. in. [3,69 ltr.] 9.0:1
160 @, 4200 rpm. 33 748
235 lb-ft. [32,49 kg-m.]
101"
[2,57 m.]
48^6* ]1,23 m.]
67"
[1,70 m.]
1583/4" [4,02 m.]
71%"
[1,82 m.] 8" [20,32 cm.]
CAPACITIES:
U.S.
Imperial
Metric
Fuel
Tank
(Approximate):
Early
Models
Late
Models
Cooling
System
F4
Models
V-6
Models
Note: If not equipped
with
heater deduct 10.5 gal.
16 gal.
12 qt.
10 qt.
1 qt. 8.8 gal.
13.3 gal.
10 qt. 8 qt.
.8 qt. 39,75 ltr.
60,57 ltr.
11,4 ltr. 9,5 ltr.
0,9 ltr.
CJ-
3B
CJ-5
CJ-6
DJ-5
DJ
-6
lb. kg. lb.
kg. lb.
kg. lb.
kg. lb.
kg.
WEIGHTS
(Approximate):
Gross
Vehicle
Weight
(GVW).
3500
1587 3750 1701 3900 1769 3200 1451 3200 1451
Shipping
— V6
Engine
—
'—
2240 1016 2302 1044 1900 862 2033 922
F4
Engine
2132
967 2163
981 2225
1009 1796 814 1858 842
Curb
— V6
Engine
— —
2351 1066 2413 1094 2011 912 2144 972
F4
Engine
2243
1017 2274 1031
2336 1060 1907 865 1969 893
For
Canvas
Half-Top
Model, add 35
17 38
17 38
17 38
17 38 17
For
Canvas
Full-Top
Model, add 56
25 56 25 60 27 56 25 60 27
For
Hard
Top Model, add
~~
340
154 340 154 6
Page 11 of 376
'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
13330
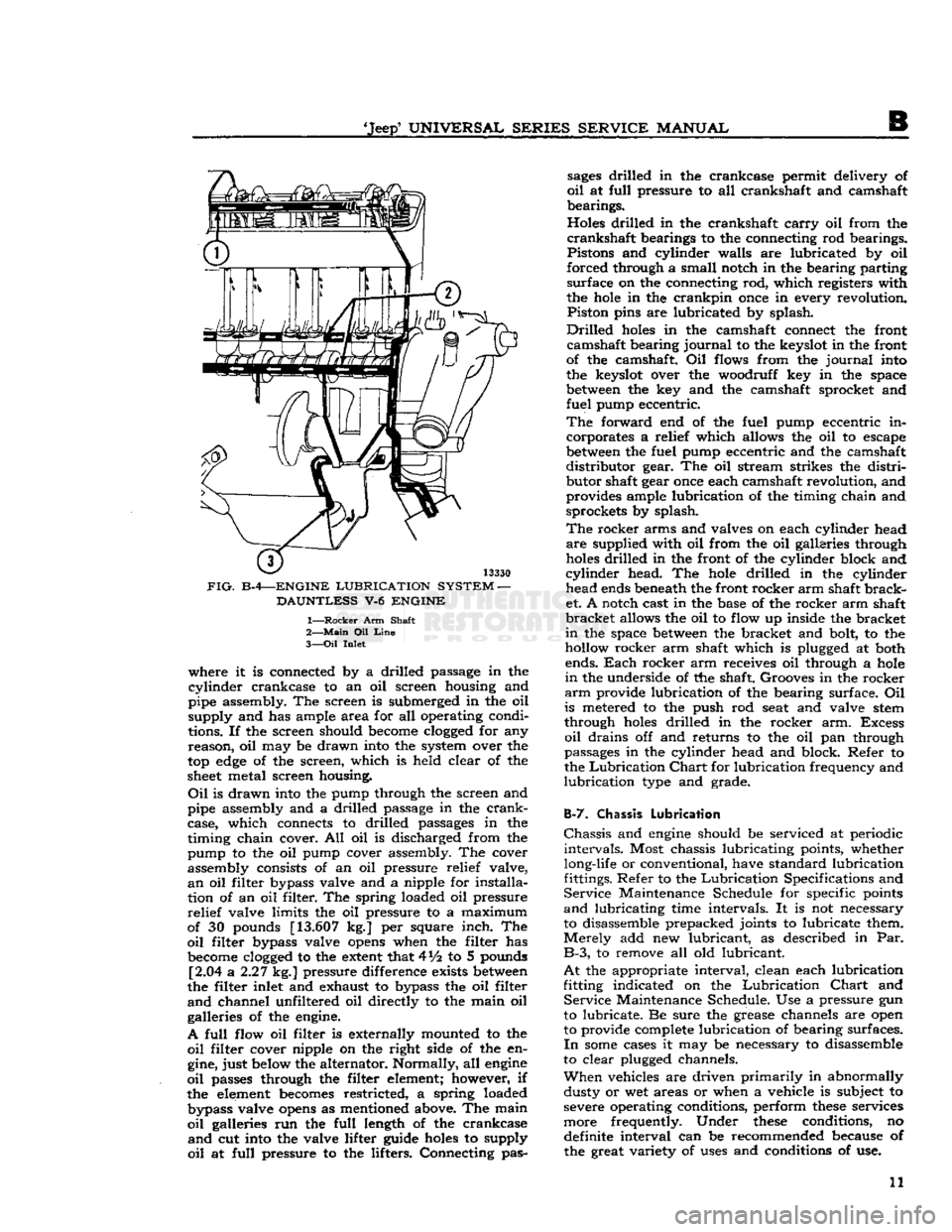
FIG.
B-4—ENGINE
LUBRICATION
SYSTEM
—
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
1—
Rocker
Arm Shaft
2—
Main
Oil
Line
3—
Oil
Inlet where it is connected by a drilled passage in the
cylinder
crankcase to an oil screen housing and
pipe assembly. The screen is submerged in the oil supply and has ample area for all operating condi
tions. If the screen should
become
clogged
for any reason, oil may be drawn into the system over the
top
edge
of the screen, which is held clear of the
sheet
metal screen housing.
Oil
is drawn into the pump through the screen and
pipe assembly and a drilled passage in the
crank
case, which connects to drilled passages in the
timing chain cover. All oil is discharged from the
pump to the oil pump cover assembly. The cover
assembly consists of an oil pressure relief valve,
an
oil filter bypass valve and a nipple for installa
tion of an oil filter. The spring loaded oil pressure
relief
valve limits the oil pressure to a maximum
of 30 pounds [13.607 kg.] per square inch. The
oil
filter bypass valve
opens
when the filter has
become
clogged
to the
extent
that
4V2
to 5 pounds [2.04 a 2.27 kg.] pressure difference exists
between
the filter inlet and exhaust to bypass the oil filter
and
channel unfiltered oil directly to the main oil galleries of the engine.
A
full flow oil filter is externally mounted to the
oil
filter cover nipple on the right side of the en gine, just below the alternator. Normally, all
engine
oil
passes through the filter element; however, if
the element
becomes
restricted, a spring loaded bypass valve
opens
as mentioned above. The main
oil
galleries run the full length of the crankcase
and
cut into the valve lifter guide
holes
to supply
oil
at full pressure to the lifters. Connecting pas
sages
drilled in the crankcase permit delivery of
oil
at full pressure to all crankshaft and camshaft
bearings.
Holes drilled in the crankshaft
carry
oil from the
crankshaft
bearings to the connecting rod bearings.
Pistons and cylinder walls are lubricated by oil
forced through a small notch in the bearing parting
surface on the connecting rod, which registers with
the
hole
in the crankpin
once
in every revolution. Piston pins are lubricated by splash.
Drilled
holes
in the camshaft connect the front camshaft bearing
journal
to the key slot in the front
of the camshaft. Oil flows from the
journal
into
the keyslot over the woodruff key in the space
between
the key and the camshaft sprocket and fuel pump eccentric.
The
forward end of the fuel pump eccentric in corporates a relief which allows the oil to escape
between
the fuel pump eccentric and the camshaft
distributor
gear. The oil stream strikes the distri
butor shaft gear
once
each camshaft revolution, and provides ample lubrication of the timing chain and
sprockets by splash.
The
rocker arms and valves on each cylinder head
are
supplied with oil from the oil galleries through
holes
drilled in the front of the cylinder block and
cylinder
head. The
hole
drilled in the cylinder
head ends beneath the front rocker
arm
shaft brack et. A notch cast in the base of the rocker arm shaft
bracket
allows the oil to flow up inside the bracket
in
the space
between
the bracket and bolt, to the
hollow rocker arm shaft which is plugged at both
ends.
Each
rocker arm receives oil through a
hole
in
the underside of the shaft. Grooves in the rocker
arm
provide lubrication of the bearing surface. Oil
is metered to the push rod seat and valve stem
through
holes
drilled in the rocker arm. Excess
oil
drains off and returns to the oil pan through
passages in the cylinder head and block. Refer to
the
Lubrication
Chart
for lubrication frequency and
lubrication
type and grade.
B-7.
Chassis
Lubrication
Chassis
and
engine
should be serviced at periodic
intervals.
Most chassis lubricating points, whether
long-life or conventional, have standard lubrication
fittings. Refer to the
Lubrication
Specifications and
Service
Maintenance Schedule for specific points
and
lubricating time intervals. It is not necessary
to disassemble prepacked joints to lubricate them.
Merely
add new lubricant, as described in Par.
B-3,
to remove all old lubricant.
At
the appropriate interval, clean each lubrication
fitting indicated on the Lubrication
Chart
and
Service
Maintenance Schedule. Use a pressure gun
to lubricate. Be sure the grease channels are open
to provide complete lubrication of bearing surfaces.
In
some
cases it may be necessary to disassemble
to clear plugged channels.
When
vehicles are driven primarily in abnormally dusty or wet areas or when a vehicle is subject to
severe operating conditions, perform
these
services
more frequently. Under
these
conditions, no definite interval can be recommended because of the great variety of
uses
and conditions of use. 11
Page 20 of 376

c
TUNE-UP
C-2.
TUNE-UP SEQUENCE
The
following
Pars.
C-3 through
C-2
7
give the
sequence and describe the services to be performed
when tuning the engine.
C-3.
Clean
and
Check
Battery
Inspect
battery and cables. If the battery is not
satisfactory, install a fully-charged battery to allow
completion of the tune-up.
Note: If the battery fails any of the following tests,
remember that the cause may be other electrical
trouble, and not necessarily only a defective battery.
Refer
to Section H for electrical troubleshooting
and
tests.
a.
Check
the specific gravity of the eletrolyte in
each cell of the battery. A hydrometer reading of 1.260 indicates that the battery is fully charged.
If
the reading is 1.225 or below, the battery
needs
recharging.
If one or more cells is 25 "points" (.025)
or
more lower than the other cells, this indicates
that the cell is shorted, the cell is about to
fail,
or
there is a
crack
in the battery partition in the case.
Unless the battery is repaired or replaced, battery trouble
will
soon be experienced.
b.
Check
the electrolyte level in each cell, add
distilled
water to maintain the solution %" [9.5
mm.] above the plates. Avoid overfilling. Replace
the filler caps and tighten securely. It is important
to keep the electrolyte level above the plates at
all
times because plates that are exposed for any
length of time
will
be seriously damaged.
c.
Check
the wing nuts on the hold-down frame
for tightness. Tighten them only with finger pres
sure,
never with pliers or a wrench. Excessive pres
sure
could damage the battery case.
d.
Clean
the battery terminals and cable connec-
FIG.
C-l—FRAME
GROUND
STRAP
—
HURRICANE
F4
1—
Right
Front
Engine Mount
2—
Frame
Ground
Strap
DAUNTLESS
V-6
tors.
Prepare a strong solution of baking soda and
water
and brush it around the terminals to remove
any
corrosion that is present. The cell caps must
be tight and their vents sealed to prevent cleaning
solution entering the cells. After cleaning install
cable connectors on terminals and coat the ter
minals
and connectors with heavy grease.
e. Inspect the battery cables and replace if badly
corroded
or frayed.
Check
tightness of terminal
screws to ensure
good
electrical connections.
Check
the tightness of the negative ground cable connec tion at the engine to ensure a
good
ground con nection.
f.
Load
test
the battery. Connect a voltmeter across the battery. Run the starting motor for 15 seconds.
If
the voltage
does
not drop below 10 volts on a 12 volt battery the battery is satisfactory. If the
voltage falls below
these
values, yet the specific
gravity
is above
1.225,
the condition of the battery
is questionable.
g.
Make sure the engine to frame ground strap or
cable connections are tight. If
these
connections
are
loose,
corroded or dirty,
hard
starting or failure
of the vehicle electrical system may result. Refer
to
Fig.
C-l
for location of the
Hurricane
F4 engine
to frame ground strap and its connections. Refer to Fig. C-2 for location of the Dauntless V-6 en gine to frame ground cable.
C-4.
Clean and
Adjust
Spark Plugs
Clean,
inspect, and gap
spark
plugs. Do not install
spark
plugs until completion of compression tests.
a.
Use a
Spark
Cable
and Installing
Plier
Tool,
W-2
74,
to remove the leads from the
spark
plugs.
Caution:
Pulling on the cables to remove them
from
the
spark
plugs can cause internal breaks in
the leads that
will
cause ignition failure.
b.
Using a
spark
plug wrench, loosen each
spark
plug one or two turns to break
loose
any carbon
deposits on the plug base. 20
Page 45 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
D
Remove the screws and lockwashers that attach
the main bearing caps to the cylinder block. Use
a
lifting bar beneath the ends of each bearing cap.
Be
careful not to exert too much pressure to cause
damage to the cap or
dowels
and pry the caps free.
CAUTION:
If main bearing caps are not removed
carefully
by raising both sides of each cap evenly
until
free of the dowels, the
dowels
may be bent.
A
bent main bearing cap dowel can cause misalign ment of the cap and resultant
rapid
bearing wear
necessitating replacement. Therefore, remove each
main
bearing cap carefully. If there is reason to
believe any of the
dowels
have been bent during
the bearing cap removal, remove them and install
new
dowels
as detailed in Par. D-34c.
Remove the upper
half
of the
rear
main bearing
oil
seal from the cylinder block and the lower
half
from
the oil seal
groove
in the
rear
main bearing
cap.
Install
the main bearing caps and bearings on
the cylinder block in their original positions.
Note;
Removal of the crankshaft may be ac
complished only with the
engine
out of the vehicle.
D-27.
Remove
Exhaust
Valves and Springs
Access to the valve chamber is obtained by re moving the attaching parts and the valve spring
cover and gasket from the cylinder block. Use cloths
to block off the three
holes
in the exhaust valve
chamber to prevent the valve retaining locks falling
into the crankcase, should they be accidentally dropped.
With
a valve
/
spring compressor, compress the valve springs on
those
valves which are in the
closed position (valve seated against cylinder
block).
Remove the exhaust valve spring retainer
locks,
the exhaust valve spring retainer, and the exhaust valve spring. Close the other valves by
rotating the camshaft and repeat the above opera
tion for the other valves in the same manner.
Lift
out all the exhaust valves and tag or place them in
a
rack
to indicate the location where each was removed from the cylinder block. If a valve sticks in
the guide and cannot be easily lifted out,
pull
the valve upward as far as possible and remove the
spring.
Lower
the valve and remove any carbon
deposits
from the valve stem.
This
will
permit re moval of the valve.
For
intake valve and spring removal, see
Par.
D-l7.
D-28.
Remove Camshaft
a.
Push the intake and exhaust valve tappets into the cylinder block as far as possible so the ends of
the tappets are not in contact with the camshaft. b. Secure each tappet in the raised position by in
stalling a common clip-type clothes pin on the
shank
of each tappet or tie them up in the valve
chamber.
c. Remove the camshaft thrust plate attaching
screws.
Remove the camshaft thrust plate and
spacer.
d.
Pull
the camshaft forward out of the cylinder
block using care to prevent damage to the cam
shaft bearing surfaces.
D-29.
Remove Valve Tappets
Remove the intake and exhaust valve tappets from
the
bottom
or crankshaft side of the cylinder block
after the camshaft has been removed. Tag each
tappet or place them in a marked
rack
so they may be reassembled in their original positions.
D-30.
Remove Oil
Gallery
Plugs
Remove the plug at each end of the oil gallery in the cylinder block.
This
operation is only applicable
when the
engine
is out of the vehicle and
will
allow access to the oil gallery so it may be cleaned.
D-31. ENGINE INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
The
inspection and repair procedures detailed here
in
are recommended to be followed when a com
plete
engine
overhaul is to be made with the
engine
out of the vehicle. These instructions can generally be applied individually with the
engine
in the
vehicle. Wherever the procedure differs due to
the
engine
being in the vehicle, the necessary
special
instructions are provided. Inspection and
repair
instructions are included to cover the
cylinder
block, cylinder head, crankshaft and bearings, connecting rods and bearings, oil pump, valves and tappets, pistons and rings, flywheel,
timing gears, and the camshaft and bearings. In addition, fitting operations for
these
engine
com
ponents
are included.
Important:
Before the inspection and repair pro
cedures listed below are begun, the
engine
serial
number must be checked for the presence of
code
letters denoting undersize bearings or oversize
pistons. Refer to Par. D-2.
D-32.
Cylinder
Block
The
cylinder block must be thoroughly cleaned, inspected and repaired as detailed in the following
paragraphs.
D-33.
Cleaning
The
cylinder block may be steam cleaned or cleaned
with
a suitable solvent. A scraper is recommended
to remove
hard
deposits, except on highly finished surfaces. Special attention must be directed to the
cleaning of the oil passages, valve chamber,
crank
case, and cylinder walls to remove all sludge,
dirt
and
carbon deposits. After cleaning, use air pressure to dry the block thoroughly.
D-34. Inspection
Examine
the cylinder block for minute cracks and
fractures.
Rusted valve springs or evidence of rust
in
the valve chamber or the cylinder walls is a
good
indication of a possible
crack
in the block,
a.
Examine all machined surfaces of the cylinder block for
burrs
and scores.
Check
for cylinder block
distortion by placing a straight
edge
along the
length of the cylinder head surface of the block.
With
a feeler
gauge,
check for clearance
between
the straight
edge
and the block, particularly be
tween adjacent cylinders. Maximum permissible
out of line for service is .010"
[0,254
mm.] over the
full
length of the block. 45
Page 47 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
D
straight
in the hole, then tap the dowel lightly
with
a hammer until it
bottoms.
d.
When installing bearing eaps, be sure to tighten
the
bolts
evenly in each cap to
pull
it into place
without bending the
dowels
or distorting the
bearing
cap.
e. Other parts of the block which require inspec tion
and
possible
repair,
but which are directly
related
to other
engine
components (such as tappets, pistons, camshaft, valves, crankshaft, and
oil
pump) are covered later in this section.
D-35.
Cylinder
Bores
The
cylinder bores may be reconditioned by honing
or
reboring. Use oil-soaked rags to protect
crank
shaft
journals
and other
engine
parts from abrasive
dust during all reconditioning operations.
Both
honing and reboring of the cylinders must be
done
carefully to fit the pistons and to obtain
specified clearances. If reboring of the cylinder bores is not required but the walls are glazed, use
a
finishing
hone
to remove the glaze. Reboring the cylinders must not be attempted unless ade
quate facilities and experienced service technicians
are
available. The amount of material to be removed is determined from the original diameter
of the cylinder bores (3.125" to 3.127") [79,375 a
79,426
mm.] plus the amount of oversize in diameter
of the oversize pistons to be fitted. Pistons are
available
in the following oversizes.
.010"
[0,254
mm.] .030" [0,762 mm.] .020" [0,508 mm.] .040" [1,016 mm.}
The
largest cylinder bore
will
determine the over
size to which all cylinders must be rebored, since the size and weight of all pistons must be uniform
to maintain proper
engine
balance. The maximum rebore should not exceed .040" [1,016 mm.] from
standard.
Measure
the cylinder diameters by making mea
surements both parallel to and at right angles to
crankshaft
over entire piston travel and at
bottom
of cylinder. Proceed as follows:
a.
If bores are scored; if out-of-round
exceeds
.005
"
[0,127 mm.]; if diameters differ more than .005";
or
if taper
exceeds
.005
"
on diameter, it is generally
recommended that cylinders be reconditioned by
reboring
and honing to the next oversize using new
pistons of the proper size.
Note:
If reboring is performed, allow .0015"
[0,0381
mm.] for final honing.
All
cylinder bore diameters must be within .002
"
[0,0508
mm.] after reconditioning.
b.
If bore measurements are within the above
limits,
but indicate hollows or waviness, cylinders should be honed with 250 grit
stone
hone. Pump
hone
up and down in cylinder while it is rotating
to produce a satin-finish, diamond cross-hatched
pattern
approximately 30° with horizontal. Hone
only enough to correct waviness.
c. If cylinder bore correction is unnecessary, break the glaze on cylinder walls with a 250 grit
stone
hone
or with a suitable deglazing tool. Operate the
hone
or deglazer to obtain diamond cross-hatched
pattern
previously mentioned.
d.
Regardless of type of correction on cylinder
walls,
wash out bores thoroughly afterwards and
apply
a light coat of
engine
oil. If cylinders have
been rebored or honed heavily, measure cylinder
diameters again to assure proper selection of piston
size.
D-36.
Pistons, Rings, and Connecting Rods
Pistons are each fitted with three rings, two com pression rings and one oil control
ring.
The pistons have an extra
groove
above the top ring which acts as a heat dam or insulating
groove
to protect
against sealing of the top ring in the ring
groove
with
hard
carbon. The piston pin is secured by the lock screw.
The
pistons and connecting rods were removed from
the
engine
as assemblies. If cylinders were rebored,
new oversized pistons and rings
will
have to be in
stalled.
Disassemble the pistons and rods. Remove the
two compression rings, the oil control
ring,
and the oil control ring expander from each piston. Do not remove the
bolts
from the lower end of the
connecting rods unless the
bolts
are damaged.
Clamp
each connecting rod and piston assembly
in
a padded bench vise and remove the piston pin
lock
screw and lockwasher. Press the piston pin
out of the piston and connecting rod.
Clean
all
carbon,
gum, and lacquer
deposits
from both the
inner
and outer surfaces of each piston, connecting
rod,
and piston pin. Use a ring
groove
cleaner or a
broken
ring filed to a sharp square
edge
to clean
the carbon from the piston ring
grooves
and the
insulator
groove. Use care not to scrape metal from
the sides of the
grooves
or make
burrs
on ring
groove
surfaces. Run a length of wire through the
oil
spray
hole
near the lower end of the connecting
rod
to clear the
hole
of hardened oil
deposits
or
foreign matter.
Carefully
inspect the pistons and
replace
any that are broken or cracked. Replace
pistons if any of the ring lands are chipped, broken,
or
rounded on the
edges;
or if the piston is scored,
scratched,
or burned so seriously that the imperfec
tions cannot be removed with a hand honing
stone
or
crocus cloth.
Replace
the pistons as follows:
a.
After cylinder bores have been carefully checked for out-of-round and taper (Par. D-35), check fit
of each piston to cylinder bore with block and
pistons clean and dry and at approximately 70
°F.
[21°C]
by using Piston Fitting Gauge And Scale
Tool
No. C-690 as shown in Fig. D-7. Use a .003"
[0,0762
mm.] thickness
gauge
%" [19 mm.] wide.
The
piston is fitted upside down in the block to
facilitate the operation. The
gauge
must extend the
full
length of the piston on the thrust side
(opposite
side from slot in piston
skirt).
Scale should register
5
to 10 pounds [2,3 a 4,5 kg.]
pull
to remove the
thickness
gauge
from
between
cylinder
wall
and piston. Excessive
pull
indicates need for a slightly
smaller
piston or additional honing of cylinder. In sufficient
pull
indicates need for fitting a larger piston. 47
Page 51 of 376
![JEEP DJ 1953 Service Manual
-Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
E>
[5,928 a
5,926
cm.] for all main bearings. Allowable
taper or out-of-round of the journals is .001"
[0,0254
mm.].
D-42.
Checking Connecting Ro JEEP DJ 1953 Service Manual
-Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
E>
[5,928 a
5,926
cm.] for all main bearings. Allowable
taper or out-of-round of the journals is .001"
[0,0254
mm.].
D-42.
Checking Connecting Ro](/manual-img/16/57041/w960_57041-50.png)
-Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
E>
[5,928 a
5,926
cm.] for all main bearings. Allowable
taper or out-of-round of the journals is .001"
[0,0254
mm.].
D-42.
Checking Connecting Rod
Crankpins
Check
the crankpin diameters with a micrometer
to ensure that they are not out-of-round or tapered more than .001"
[0,0254
mm.] The standard
crank-
pin
diameter is
1.9383*
to
1.9375"
[4,9233
a
4,9213
cm.].
D-43.
Crankshaft
Main
Bearings
The
crankshaft rotates on three main bearings
with
a running clearance of .0003" to .0029"
[0,0076
a
0,0736
mm.].
These
bearings are positioned and prevented from
rotating in their supports in the cylinder block by
dowel pins. Dowel pins are used in both the center
and
the
rear
bearing caps. No dowel pins are used
in
the front bearing cap because the bearing has
a
flange. The front main bearing takes the end
thrust
of the crankshaft. The main bearings are of premium type which provides long bearing life.
They
are replaceable and when correctly installed, provide proper clearance without filing, boring,
scraping,
or shimming. Crankshaft bearings can
be removed from this
engine
only with the
engine
out of the vehicle. Crankshaft bearings must be replaced as a complete set of three bearings, each
bearing consisting of two halves.
Main
bearings
are
available in the standard size and the following
undersizes:
.001" [0,025mm.] .012" [0,305 mm.] .002" [0,051mm.] .020" [0,508 mm.] .010" [0,254mm.] .030" [0,762 mm.]
The
.001" and .002" undersize main bearings are
for use with standard size crankshafts having
slightly worn
journals.
The .010", .020", and .030" undersize bearings are for use with undersize
crankshafts
in
those
sizes. The .012" undersize
bearings are for use with .010" undersize
crank
shafts having slightly worn journals. Bearing sizes
are
rubber stamped on the reverse side of each
bearing half.
D-44. Crankshaft
Main
Bearing Inspection
The
crankshaft
journals
must be carefully inspected
as detailed previously in Par. D-41. Worn journals
will
require undersize bearings. Scored, flaked, or
worn
bearings must be replaced. Measure the main
bearing bores in the cylinder block using a
telescope
gauge
and micrometer. Measure the bores at right
angles to the split line and at 45° to the split line.
The
bores should not be over .001"
[0,0254
mm.]
out-of-round or .001" in taper from end to end.
Also,
the bores should not be more then .001"
oversize, considering the average diameter of the
bore.
D-45.
Fitting Crankshaft
Main
Bearings
Using
Plastigage
After
wiping and carefully inspecting the bearing bore, install the proper bearing. See that the oil
hole
in the bearing upper half registers properly
with
the oil
hole
in the block, and that the bearing
lock fits properly in the notch in the block.
Install
the crankshaft if replacing bearings with the
engine
out of the vehicle. The desired running fit (dif
ference
between
the diameter of the crankshaft
journal
and the inside diameter of the fitted bear ing) for a main bearing is .0003" to .0029"
[0,0076
a
0,0736
mm.]. With a dimension in
excess
of this
standard
running fit, a satisfactory bearing replacement cannot be made and it
will
be necessary to
regrind
the crankshaft.
Install
the bearing lower
half
and the bearing cap and draw the nuts down
equally and only slightly tight. Rotate the
crank
shaft by hand to be sure it turns freely without
drag.
Pull
the nuts tighter, first one then the other,
a
little at a time, intermittently rotating the
crank
shaft by hand until the recommended torque of
35 to 45 lb-ft. [4,8 a 6,2 kg-m.] is reached. If the
bearings are of the correct size, and lubricated with
light oil before installation, the crankshaft should
turn
freely in the bearings. If the crankshaft cannot
be turned, a larger bearing is
required.
If there is no binding or tightness, it is still necessary to check
clearance to guard against too
loose
a fit. Never file
either the bearing cap or the bearing to compensate
for too much clearance. Do not use shims under a
bearing cap or behind a bearing shell. Do not run a
new bearing half with a worn bearing half. The use
of "Plastigage" of the proper size to measure .001" [0,025 mm.] clearance is recommended for check
ing crankshaft main bearing clearance. The method
of checking clearance is as follows:
a.
Remove the bearing cap and carefully wipe
all
oil from the bearing and the
journal.
b.
Lay a piece of "Plastigage" y%" [3 mm.]
shorter than the width of the bearing across the
journal
(lengthwise of the crankshaft).
c.
Install
the bearing and cap and tighten first
one nut, then the other, a little at a time to the specified torque. As the bearing
tightens
down
around
the
journal,
the "Plastigage" flattens to a
width that indicates the bearing clearance.
d.
Remove the cap and measure the width of
the flattened "Plastigage," using the scale printed
on the
edge
of the envelope. The proper size "Plasti
gage"
will
accurately measure clearance down to .001".
e. If the flattened "Plastigage" tapers toward the middle, or toward the end, or both ends, there
is a difference in clearance, indicating a taper, a
low
spot,
or other irregularity of the bearing or
journal.
D-46.
Fitting Crankshaft
Main
Bearings
Using
Shim Stock
Thin
feeler or shim stock may be used instead of "Plastigage" to check bearing clearances. The
method is simple, but care must be taken to protect
the bearing metal surface from
injury
by too much pressure against the feeler stock,
a.
Cut a piece of .001" [0,025 mm.] thick, by Yl [12,7 mm.] wide, feeler stock }4" [3 mm.]
shorter than the width of the bearing. Coat this 51
Page 54 of 376

D
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
against the hub of the crankshaft pulley.
Timing
gears are accessible for inspection or replacement
with
the
engine
installed in the vehicle after re moving the radiator, belt drive pulley, and timing
cover.
Should
it be necessary to replace the timing gears, attention must be given to the end float of both
the camshaft and crankshaft and to the running
clearance
of both gears. It is also advisable to
check
both the oil jet and oil passage to the
crank
shaft front bearing to be sure that they are clear.
D-55.
Inspection and
Repair
Check
the general condition of both gears and
inspect for evidence of excessive wear. Replace
excessively worn or damaged gears. Inspect the
cover and replace if bent or damaged. It is recom mended that the crankshaft oil seal in the cover
be replaced when the cover is removed to ensure a
good
seal around the crankshaft. To replace this
seal
with the
engine
in the vehicle
requires
removing
the radiator and water pump.
D-56.
Valves, Springs, and Guides
The
exhaust valves seat on the top of the cylinder
block
with the
stems
extending down through
replaceable valve guides. The exhaust valves are actuated by the camshaft through exhaust valve
tappets. The exhaust valve springs are assembled
and
locked on the lower end of the exhaust valve
stems. The retaining locks are the split type, which
fit in a recess on the valve
stems
and into the taper
in
the valve spring retainers.
Adjustment
of exhaust valves is by means of the
adjusting
screw threaded into the upper end of the
exhaust valve tappets. An exhaust valve rotator used as a valve spring retainer is installed on the
lower end of the exhaust valve.
This
valve rotator,
known
as "Roto Cap", is a spring-loaded
ball
bearing
device. On each lift, or opening stroke of
a
valve, the rotator
gives
the valve a slight positive
clockwise rotation.
The
intake valves operate in valve
guides
in the
cylinder
head and are actuated by rocker arms.
The
rocker arms are actuated by valve push rods
and
the intake valve tappets. The intake valve
springs,
the intake valve spring retainers, and the
intake
valve spring retainer locks make up the
remainder
of the valve operating parts. An intake
valve spring retainer oil seal which encircles the
upper
end of the intake valve
between
the valve
locks and the upper end of the valve spring re
tainer,
controls the passage of oil along the valve
stem and guide.
Note:
When
engine
trouble indicates defective
valves as a possible source of trouble, also check
all
vacuum line connections for possible leaks.
D-57.
Inspection of Valves, Springs,
and
Guides
Clean
the valves on a wire wheel, making sure that
all
carbon is removed from the top and the under
side of the heads and that all gum and varnish
deposits
are removed from the stems.
Polish
the valve
stems
with steel wool or crocus
cloth.
Visually
inspect all valves for warpage,
cracks,
or excessive burning and discard if one of
these
conditions exists. Replace any worn, pitted,
or
corroded valves that cannot be cleaned with a
wire
brush.
Replace any valves when
seats
are pitted, burned, or corroded so badly that they
cannot be cleaned up with a light refacing on a valve refacing machine.
Replace
valves with marks of scoring or abrasion visible on the stem. Replace any valves with bent
stems
which
will
be apparent when the valve is
mounted in the valve refacing machine.
Note:
Use only hard-face exhaust valves for
replacement.
Examine
the
stems
of valves which employ the
ball
bearing rotators.
Wear
marks around the
cir
cumference of the
stems
indicates that the valve is
rotating satisfactorily.
Vertical
heavy pressure
areas
indicate that the valve is not rotating and the valve spring retainer (Roto
Cap)
should be replaced
if
at fault.
Check
the diameter of the valve stem at two or three places along the length of the stem
with
a micrometer. The intake valve stem diameter is .3733" to .3738" [9,482 a
9,495
mm.]. The
exhaust valve stem diameter is .371" to .372"
[9,423
a
9,449
mm.].
Note:
Exhaust
and intake valve springs are
similar
in appearance. They must not be inter
changed as they have different spring
charac
teristics.
Wash
the valve springs thoroughly in solvent.
Visually
examine the springs and replace any that
are
deformed or obviously damaged. Examine for
corrosion
from moisture or acid etching which might
FIG.
D-19—TESTING
VALVE
SPRING
1—
Torque
Wrench
2—
Spring
Testing
Fixture
3—
Valve
Spring
54
Page 55 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
develop
into surface cracks and cause failure.
Measure
the over all free length of the springs and
replace any that do not measure to standard: 1%" [35,7 mm.] for intake valve springs and 2j^"
[63,5 mm.] for exhaust valve springs. If possible,
check each valve spring in a valve spring testing
fixture C-647 or equivalent as shown in Fig. D-l9.
Test
each spring when compressed to the two
different spring lengths given (representing valve closed and valve open spring length). If any spring
fails to register spring tension equal to or greater
than
the minimum load limit in pounds specified for that spring length, replace the spring.
Length
Minimun
Load
Intake
valve spring. . .
1.660"
[4,216 cm.] 66 lb. [29,9 kg.]
1.400"
[3,556 cm.] 140 lb. [63,5 kg.]
Exhaust
valve spring. 2.109" [5,356 cm.] 47 lb. [21,3 kg.]
1.750"
[4,445 cm.] 110 lb. [49,9 kg.]
Note:
When using a spring checking fixture C-647
or
equivalent as shown in Fig. D-l9, it is necessary
to convert the torque wrench reading which is in pounds-feet to the static pound pressure specified above according to the instructions furnished with
the wrench. For example, should the torque wrench reading be 50 lb-ft. and the wrench is two
feet
long
the static pressure of the spring
will
be 50 x 2 or 100 lbs.
Clean
the valve
guides
with a standard valve guide
cleaner or a wire
brush.
Check
the valve
guides
in the cylinder block. Replace valve
guides
which are
broken
or worn enough to cause excessive valve
stem-to-guide
clearance. See Par. D-61.
Standard
intake valve clearance is .0007" to .0022"
[0,0178
a
0,0559
mm.] and the exhaust valve
clearance is .0025" to .0045" [0,0635 a
0,1143
mm.].
Excessive
clearance
between
the valve
stems
and
guides
will
cause improper seating and burned
valves. When there is a tendency to draw oil vapor
through the guide causing excessive oil consump tion, fouled
spark
plugs, and poor low-speed per
formance. To check the clearance of the valve stem
to the valve guide, take a new valve and place in
each valve guide.
Check
the clearance with a
suitably mounted
dial
indicator or feel the clearance by moving the valve stem back and forth. If this
check shows excessive clearance it
will
be necessary to replace the valve guide.
D-58.
Refacing Valves
Re
face the valves with a valve refacer. The valve
refacer
manufacturer's instructions should be fol
lowed carefully to ensure a valve face concentric
with
the valve stem. Reface both intake and ex
haust valves to an angle of 46°.
Take
off only the
minimum
of metal required to clean up the valve faces.
If
the thickness of the
edge
of the valve head is
reduced to
less
than
J^>"
[0>8 mm.] replace the valve.
Note:
Cocked or deformed valve springs or im
properly
installed or missing locks can be responsible
for valve problems.
D-59.
Valve Seat Inspection
and
Refacing
Inspect the valve
seats
for
cracks,
burns, pitting,
ridges, or improper angle.
During
any general
engine
overhaul it is advisable to reface the valve
seats
in both the cylinder block and head regardless
of their condition. If the valve
guides
are to be re placed, this must be
done
before refacing the valve
seats.
Note
that later
engines
have hardened
exhaust valve seat inserts.
Valve
seat inserts must be concentric with finish
ream
of valve stem
guides
(exhaust) within .002"
[0,051
mm.] total indicator reading.
When
necessary to reface the valve seats, use a
valve seat grinder in accordance with the grinder
manufacturer's
instructions. Any grinding of valve
seats
should be preceded by touching up the
grinding
stone
so that their angles are accurate and
the
stone
is not
clogged.
Grind
each valve seat to
a
true 45° angle. Never grind any more than is necessary to clean up pits, grooves, or to correct
the valve seat runout.
Check
the valve
seats
with
10465
FIG.
D-20—VALVE
WITH
ROTO
CAP
FIG.
D-21—GAUGING
VALVE
SEATS
55