2023 ALFA ROMEO STELVIO steering
[x] Cancel search: steeringPage 129 of 268

127
Left Lane Departure — Both Lanes Detected
When the system is active, both lane lines on the
display illuminate in white to indicate the
successful detection of both limits.
When lane markings are detected, the system is
ready to provide indications in case the driver
unintentionally leaves the lane (turn signal not
activated).
As the Lane Keeping Assist system detects the
lane markings while the vehicle is in motion, it will
adjust the display accordingly (from white to
yellow and yellow to white, and increase their
thickness).
If a lane line is crossed, the driver is alerted by an
audible signal as well as the visual indication in
the instrument cluster. The signal is emitted
through the speakers on the side of the lane
marking which is being crossed (e.g. if the vehicle
is exceeding the left line of the lane, the audible
signal will come from the speakers on the left of
the vehicle).
Hands Presence On The Steering Wheel
Detection
The system is able to detect the presence of the
driver’s hands on the steering wheel.
When the system does not detect the presence of
hands on the steering wheel for a few seconds
(up to 6 seconds), a yellow indicator light will be
displayed on the instrument cluster display. No
acoustic warning will be emitted in this case.Hand Presence On The Steering Wheel Not
Detected Display (Up To 6 Seconds)
When the system does not detect the presence of
hands on the steering wheel for a few seconds
(from 6 to 15 seconds), a red indicator light will
be displayed on the instrument cluster display. A
short acoustic signal will sound if hands are not
detected on the steering wheel for 6 to 12
seconds. A continuous signal will sound if hands
are not detected on the steering wheel for 12 to
15 seconds.
Hand Presence On The Steering Wheel Not Detected Display (6 To 15 Seconds) After 15 seconds with the hands removed from
the steering wheel, the LKA system will be
deactivated and a dedicated message will be
shown on the instrument cluster display.
A short acoustic signal will sound in this case.
In any of the situations above where the hands
are removed from the steering wheel for more
than 6 seconds, it is necessary to reposition the
hands on the steering wheel.
Changing The System Sensitivity
The system's sensitivity can be set through the
radio system in the Driver Assistance menu.
Select “Lane Keep Assist - Settings” and then
“Keeping sensitivity”. Sensitivity “Early” or
“Late” can be selected.
Changing The System Strength
The system’s strength can be set through the
radio system in the Driver Assistance menu.
Select “Lane Keep Assist - Settings” and then
“Strength”. Strength “Low” or “High” can be
selected.
Limited Operation Warning
If a message appears on the display, a condition
limiting the LKA system operation may have
occurred. This could be an obstruction of the
camera view, or a fault in the system.
If an obstruction is detected, clean the area of the
windshield by the interior rearview mirror.
Although the vehicle can still be driven in normal
conditions, the system may not function properly.
When the conditions limiting the system are
corrected, it will go back to normal operation.
Should a fault persist, contact an authorized
dealer.
23_GU_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 127
Page 131 of 268

129
When enabled in the radio settings, active
guidelines are overlaid on the image to illustrate
the width of the vehicle and its projected back up
path based on the steering wheel position. A
dashed center line overlay indicates the center of
the vehicle to assist in rear parking maneuvers or
trailer hitch alignment. Different colored zones
indicate the distance to the rear of the vehicle.
The following table shows the approximate
distances for each zone:
Messages On The Display
If the liftgate is opened, the camera will not detect
any obstacle behind the vehicle. The display will
show a dedicated warning message.
Make sure the liftgate is closed by pushing next to
the lock until it clicks.Important Notes
Ice, snow or mud on the surface of the camera
may reduce its sensitivity. It is important to
keep the camera surface clean, and free from
debris.
When parking, be aware of obstacles that may
be above or below the camera range.
REFUELING THE VEHICLE
Before refueling, make sure that the fuel type is
correct
Ú
page 249.
Also, stop the engine before refueling.
NOTE:
An inefficient catalytic converter leads to
harmful exhaust emissions, thus contributing to
air pollution.
REFUELING CAPACITY
To ensure that you fill the tank completely, top off
twice after the first click of the fuel nozzle.
Further top-off could cause faults in the fuel
feeding system.
AreaDistance From The
Rear Of The Vehicle
Red 0–11.8 inches
(0–30 cm)
Yellow 11.8 inches to 3.3 feet
(30 cm–1 m)
Green 3.3 feet or more
(1 m or more)
WARNING!
Drivers must be careful when backing up even
when using the Rear Back Up Camera. Always
check carefully behind your vehicle, and be
sure to check for pedestrians, animals, other
vehicles, obstructions, or blind spots before
backing up. You are responsible for the safety
of your surroundings and must continue to pay
attention while backing up. Failure to do so
can result in serious injury or death.
CAUTION!
To avoid vehicle damage, Rear Back Up
Camera should only be used as a parking aid.
The Rear Back Up Camera is unable to view
every obstacle or object in your drive path.
To avoid vehicle damage, the vehicle must
be driven slowly when using the Rear Back
Up Camera to be able to stop in time when an
obstacle is seen. It is recommended that the
driver look frequently over his/her shoulder
when using the Rear Back Up Camera.
CAUTION!
Never introduce leaded fuel to the tank,
even in small amounts in an emergency, as
this would damage the catalytic converter
beyond repair.
23_GU_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 129
Page 135 of 268

133
TRAILER TOWING
In this section you will find safety tips and
information on limits to the type of towing you can
reasonably do with your vehicle. Before towing a
trailer, carefully review this information to tow
your load as efficiently and safely as possible.
To maintain the New Vehicle Limited Warranty
coverage, follow the requirements and
recommendations in this manual concerning
vehicles used for trailer towing.
COMMON TOWING DEFINITIONS
The following trailer towing related definitions will
assist you in understanding the following
information:
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR)
The GVWR is the total allowable weight of your
vehicle. This includes driver, passengers, cargo
and tongue weight. The total load must be limited
so that you do not exceed the GVWR
Ú
page 132.
Gross Trailer Weight (GTW)
The GTW is the weight of the trailer plus the
weight of all cargo, consumables, and equipment
(permanent or temporary) loaded in or on the
trailer in its "loaded and ready for operation"
condition.
The recommended way to measure GTW is to put
your fully loaded trailer on a vehicle scale. The
entire weight of the trailer must be supported by
the scale.
Gross Combination Weight Rating
(GCWR)
The GCWR is the total allowable weight of your
vehicle and trailer when weighed in combination.
Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR)
The GAWR is the maximum capacity of the front
and rear axles. Distribute the load over the front
and rear axles evenly. Make sure that you do not
exceed either front or rear GAWR
Ú
page 132.
Tongue Weight (TW)
The tongue weight is the downward force exerted
on the hitch ball by the trailer. You must consider
this as part of the load on your vehicle.
Trailer Frontal Area
The frontal area is the maximum height multiplied
by the maximum width of the front of a trailer.
Weight-Carrying Hitch
A weight-carrying hitch supports the trailer tongue
weight, just as if it were luggage located at a hitch
ball or some other connecting point of the vehicle.
These kinds of hitches are the most popular on
the market today and they are commonly used to
tow small and medium sized trailers.
Weight-Distributing Hitch
A weight-distributing hitch system works by
applying leverage through spring (load) bars. They
are typically used for heavier loads to distribute
trailer tongue weight to the tow vehicle's front
axle and the trailer axle(s). When used in
accordance with the manufacturer's directions, it
provides for a more level ride, offering more
consistent steering and brake control thereby
enhancing towing safety. The addition of a
friction/hydraulic sway control also dampens
sway caused by traffic and crosswinds and
contributes positively to tow vehicle and trailer
stability. Trailer Sway Control and a
weight-distributing (load equalizing) hitch are
recommended for heavier Tongue Weights (TW)
and may be required depending on vehicle and
trailer configuration/loading to comply with Gross
Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) requirements.
WARNING!
It is important that you do not exceed the
maximum front or rear GAWR. A dangerous
driving condition can result if either rating is
exceeded. You could lose control of the vehicle
and have a collision.
WARNING!
An improperly adjusted weight-distributing
hitch system may reduce handling, stability,
braking performance, and could result in a
collision.
Weight-distributing hitch systems may not be
compatible with surge brake couplers.
Consult with the hitch and trailer
manufacturer or a reputable Recreational
Vehicle dealer for additional information.
23_GU_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 133
Page 137 of 268
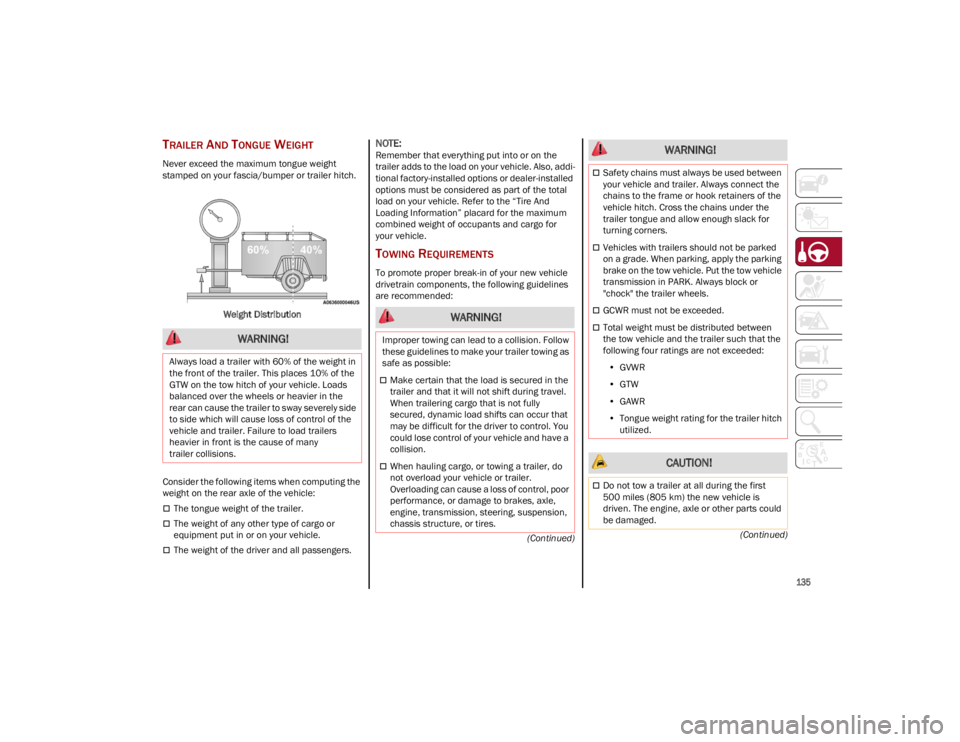
135
(Continued)
(Continued)
TRAILER AND TONGUE WEIGHT
Never exceed the maximum tongue weight
stamped on your fascia/bumper or trailer hitch.
Weight Distribution
Consider the following items when computing the
weight on the rear axle of the vehicle:
The tongue weight of the trailer.
The weight of any other type of cargo or
equipment put in or on your vehicle.
The weight of the driver and all passengers.
NOTE:
Remember that everything put into or on the
trailer adds to the load on your vehicle. Also, addi -
tional factory-installed options or dealer-installed
options must be considered as part of the total
load on your vehicle. Refer to the “Tire And
Loading Information” placard for the maximum
combined weight of occupants and cargo for
your vehicle.
TOWING REQUIREMENTS
To promote proper break-in of your new vehicle
drivetrain components, the following guidelines
are recommended:
WARNING!
Always load a trailer with 60% of the weight in
the front of the trailer. This places 10% of the
GTW on the tow hitch of your vehicle. Loads
balanced over the wheels or heavier in the
rear can cause the trailer to sway severely side
to side which will cause loss of control of the
vehicle and trailer. Failure to load trailers
heavier in front is the cause of many
trailer collisions.
WARNING!
Improper towing can lead to a collision. Follow
these guidelines to make your trailer towing as
safe as possible:
Make certain that the load is secured in the
trailer and that it will not shift during travel.
When trailering cargo that is not fully
secured, dynamic load shifts can occur that
may be difficult for the driver to control. You
could lose control of your vehicle and have a
collision.
When hauling cargo, or towing a trailer, do
not overload your vehicle or trailer.
Overloading can cause a loss of control, poor
performance, or damage to brakes, axle,
engine, transmission, steering, suspension,
chassis structure, or tires.
Safety chains must always be used between
your vehicle and trailer. Always connect the
chains to the frame or hook retainers of the
vehicle hitch. Cross the chains under the
trailer tongue and allow enough slack for
turning corners.
Vehicles with trailers should not be parked
on a grade. When parking, apply the parking
brake on the tow vehicle. Put the tow vehicle
transmission in PARK. Always block or
"chock" the trailer wheels.
GCWR must not be exceeded.
Total weight must be distributed between
the tow vehicle and the trailer such that the
following four ratings are not exceeded:
• GVWR
• GTW
• GAWR
• Tongue weight rating for the trailer hitch
utilized.
CAUTION!
Do not tow a trailer at all during the first
500 miles (805 km) the new vehicle is
driven. The engine, axle or other parts could
be damaged.
WARNING!
23_GU_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 135
Page 142 of 268
140
(Continued)
SAFETY
This very important section describes the safety
systems that your vehicle may be equipped with,
and provides instructions on how to use them
correctly.
ACTIVE SAFETY SYSTEMS
The vehicle may be equipped with the following
active safety devices:
Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS)
Active Torque Vectoring (ATV) System
Dynamic Steering Torque (DST) System
Drive Train Control (DTC) System
Electronic Stability Control (ESC) System
Hill Descent Control (HDC) System
Hill Start Assist (HSA) System
Panic Brake Assist (PBA) System
Traction Control System (TCS)
For system operation, see the following pages.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS)
An integral part of the braking system, the ABS
prevents one or more wheels from locking and
slipping in all road surface conditions, regardless
of the intensity of the braking action. The system
ensures that the vehicle can be controlled even
during emergency braking, allowing the driver to
optimize stopping distances.
The system intervenes during braking when the
wheels are about to lock, typically in emergency
braking or low-grip conditions where locking may
be more frequent. The system also improves control and stability of
the vehicle when braking on a surface where the
grip of the left and right wheels varies, such as in
a corner.
The Electronic Braking Force Distribution (EBD)
system works with the ABS, allowing the brake
force to be distributed between the front and rear
wheels.
System Intervention
The ABS equipped on this vehicle is provided with
the "Brake-By-Wire", Integrated Brake System
(IBS), function. With this system, the command
given by pressing the brake pedal is not
transmitted hydraulically, but electrically.
Therefore, the light pulsation that is felt on the
pedal with the traditional system is no longer
noticeable.
ACTIVE TORQUE VECTORING (ATV)
S
YSTEM — IF EQUIPPED
The dynamic drive control is used to optimize and
balance the drive torque between the wheels of
the same axles. The ATV system improves the grip
in turns, sending more drive torque to the
external wheel.
Given that, in a turn, the external wheels of the
car travel more than the internal ones and
therefore turn faster, sending a higher thrust to
the external rear wheel allows for the car to be
more stable and to not suffer an "understeer"
condition. Understeer occurs when the vehicle is
turning less than appropriate for the steering
wheel position.
WARNING!
The ABS contains sophisticated electronic
equipment that may be susceptible to
interference caused by improperly installed
or high output radio transmitting equipment.
This interference can cause possible loss of
anti-lock braking capability. Installation of
such equipment should be performed by
qualified professionals.
Pumping of the Anti-Lock Brakes will
diminish their effectiveness and may lead to
a collision. Pumping makes the stopping
distance longer. Just press firmly on your
brake pedal when you need to slow down or
stop.
The ABS cannot prevent the natural laws of
physics from acting on the vehicle, nor can it
increase braking or steering efficiency
beyond that afforded by the condition of the
vehicle brakes and tires or the traction
afforded.
The ABS cannot prevent collisions, including
those resulting from excessive speed in
turns, following another vehicle too closely,
or hydroplaning.
The capabilities of an ABS equipped vehicle
must never be exploited in a reckless or
dangerous manner that could jeopardize the
user’s safety or the safety of others.
WARNING!
23_GU_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 140
Page 143 of 268

141
(Continued)
DYNAMIC STEERING TORQUE (DST)
S
YSTEM
DST uses the integration of the Electronic
Stability Control (ESC) system with the electric
power steering to increase the safety level of the
whole vehicle.
In critical situations (e.g. braking on surfaces with
different grip conditions), the ESC system
influences the steering through the DST function
to implement an additional torque contribution
on the steering wheel in order to suggest the
most correct maneuver to the driver.
The coordinated action of the brakes and steering
increases the safety and control of the vehicle.
NOTE:
The DST feature is only meant to help the driver
realize the correct course of action through small
torques on the steering wheel, which means the
effectiveness of the DST feature is highly depen -
dent on the driver’s sensitivity and overall reac -
tion to the applied torque. It is very important to
realize that this feature will not steer the vehicle,
meaning the driver is still responsible for steering
the vehicle.
DRIVE TRAIN CONTROL (DTC) SYSTEM
Some models of this vehicle are equipped with an
All-Wheel Drive (AWD) system, which offers an
optimal drive for countless driving conditions and
road surfaces. The system reduces tire slipping to
a minimum, automatically redistributing the
torque to the front and rear wheels as needed. To maximize fuel savings, the vehicle with AWD
automatically passes to Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD)
when the road and environmental conditions are
such that they wouldn't cause the tires to slip.
When the road and environmental conditions
require better traction, the vehicle automatically
switches to AWD mode.
NOTE:
There may be a brief delay in shifting to
AWD mode after a tire slipping event occurs.
If the system failure symbol switches on, after
starting the engine or while driving, it means
that the AWD system is not working properly. If
the warning message activates frequently, it is
recommended to carry out the maintenance
operations.
ELECTRONIC STABILITY CONTROL (ESC)
S
YSTEM
The ESC system improves the directional control
and stability of the vehicle in various driving
conditions.
The ESC system corrects the vehicle’s understeer
and oversteer, distributing the brake force on the
appropriate wheels. The torque supplied by the
engine can also be reduced in order to maintain
control of the vehicle.
The ESC system uses sensors installed on the
vehicle to determine the path that the driver
intends to follow and compares it with the
vehicle’s effective path. When the real path
deviates from the desired path, the ESC system
intervenes to counter the vehicle’s oversteer or
understeer.
Oversteer occurs when the vehicle is turning
more than it should according to the angle of
the steering wheel.
Understeer occurs when the vehicle is turning
less than it should according to the angle of the
steering wheel.
System Intervention
The intervention of the system is indicated by the
flashing of the ESC Warning Light on the
instrument panel, to inform the driver that the
vehicle stability and grip are critical.
WARNING!
Electronic Stability Control (ESC) cannot
prevent the natural laws of physics from
acting on the vehicle, nor can it increase the
traction afforded by prevailing road
conditions. ESC cannot prevent accidents,
including those resulting from excessive
speed in turns, driving on very slippery
surfaces, or hydroplaning. ESC also cannot
prevent accidents resulting from loss of
vehicle control due to inappropriate driver
input for the conditions. Only a safe,
attentive, and skillful driver can prevent
accidents. The capabilities of an ESC
equipped vehicle must never be exploited in
a reckless or dangerous manner which could
jeopardize the user’s safety or the safety of
others.
23_GU_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 141
Page 144 of 268

SAFETY
142
HILL DESCENT CONTROL (HDC)
S
YSTEM — IF EQUIPPED
The HDC function is an integral part of the
Electronic Stability Control (ESC) system, keeping
the vehicle at a constant speed while descending
a hill by actively controlling the brakes.
HDC aims to create vehicle stability and safer
driving in various situations, including poor grip
conditions and steep descents.
The system has three different modes:
Off: the system is deactivated
Enabled: the system is enabled and ready
to intervene when the activation conditions
are met
Active: the system actively controls the
vehicle speed Enabling The System
To enable the system, push the HDC switch
located on the steering wheel.
HDC Switch
The system is enabled if the car speed is below
20 mph (30 km/h). The system stays enabled
until the car speed reaches 37 mph (60 km/h),
the system is disabled at speeds above 37 mph
(60 km/h).
Activation of the HDC system is indicated by the
white icon appearing in the instrument
cluster display.
HDC Symbol Activation Of The System
Once enabled, the HDC system will activate
automatically if the vehicle is driven on a downhill
slope with sufficient gradient, greater than 8%.
The speed set for the HDC system can be
adjusted using the SET switch located on the
steering wheel.
HDC Speed SET Switch
Once the desired speed has been reached,
release the SET switch and the HDC system will
maintain the set speed. After set speed is
established, the HDC system will automatically
brake to keep the vehicle at the set speed if the
accelerator pedal is released and the vehicle gets
close to the set speed.
It is possible to reduce the set speed with the
brake pedal. When the pedal is released, the
system will adjust the set speed to the new
current speed.
Vehicle modifications, or failure to properly
maintain your vehicle, may change the
handling characteristics of your vehicle, and
may negatively affect the performance of the
ESC system. Changes to the steering system,
suspension, braking system, tire type and
size or wheel size may adversely affect ESC
performance. Improperly inflated and
unevenly worn tires may also degrade ESC
performance. Any vehicle modification or
poor vehicle maintenance that reduces the
effectiveness of the ESC system can
increase the risk of loss of vehicle control,
vehicle rollover, personal injury and death.
WARNING!
23_GU_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 142
Page 148 of 268

SAFETY
146
Rear Cross Path Detection (RCP) System
The Rear Cross Path Detection (RCP) system
assists the driver during reverse maneuvers in
the case of reduced visibility.
The RCP system monitors the rear detection
areas on both sides of the vehicle to detect
objects moving toward the sides of the vehicle,
with a minimum speed between approximately
1 mph (1 km/h) and 2 mph (3 km/h) and objects
moving at a maximum speed of 21 mph
(35 km/h), in areas such as parking lots.
The system activation is signaled to the driver by
an audible warning.
NOTE:
If the sensors are covered by objects or
vehicles, the system may not work as
intended.
For the system to operate correctly, the rear
fascia/bumper area where the radar sensors
are located must stay free from snow, ice and
dirt gathered from the road surface.
Do not cover the rear fascia/bumper area
where the radar sensors are located with any
object (e.g. adhesives, bike rack, etc.).Operating Mode
The system may be activated/deactivated via the
radio system. To access the function, select the
following items on the main menu in sequence:
1. “Driving Assistance”
2. “Blind Spot Alert”
“Blind Spot Alert”, “Visual” Mode
When the system is enabled, the warning light
within the door mirror on the side of the detected
object illuminates.
The visual warning on the mirror will blink if the
driver activates the turn signals, indicating a lane
change.
The warning light will be constant if the driver
stays in the same lane. “Blind Spot Alert” Function Deactivation
When the system is deactivated (“Blind Spot
Alert” mode off), the BSM or RCP systems will
not emit an audible or a visual warning.
The BSM system will store the operating mode
that was active when the engine was stopped.
Each time the engine is started, the operating
mode stored previously will be recalled and used
Ú
page 259.
ACTIVE BLIND SPOT ASSIST (ABSA)
S
YSTEM — IF EQUIPPED
The ABSA system is to help avoid/limit lateral
collisions with cars coming from adjacent lanes
changing the vehicle’s trajectory in order to try to
keep it in the detected lane.
The system warns the driver about the presence
of other vehicles in the detection area by illumi -
nating the warning light located within the door
mirror on the side in which the other vehicle was
detected and by means of an acoustic signal
and/or vibration on the steering wheel and/or
counter-steering torque on the steering wheel
(if the respective item on the “Driver Assistance”
menu is set up and then “Safety” is selected on
the radio system).
When the engine is started, the warning light
illuminates briefly to signal the driver that the
system is active (the warning light comes on even
if the system is activated through the radio
system menu).
WARNING!
Rear Cross Path Detection (RCP) is not a back
up aid system. It is intended to be used to help
a driver detect an oncoming vehicle in a
parking lot situation. Drivers must be careful
when backing up, even when using RCP.
Always check carefully behind your vehicle,
look behind you, and be sure to check for
pedestrians, animals, other vehicles,
obstructions, and blind spots before backing
up. Failure to do so can result in serious injury
or death.
23_GU_OM_EN_USC_t.book Page 146