2015 FORD SUPER DUTY engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 4 of 84

Introduction
About This Supplement.................................3
Instrument Cluster
Gauges..................................................................8
Warning Lamps and Indicators...................8
Starting and Stopping the Engine
Starting a Diesel Engine...............................10
Switching Off the Engine..............................13
Engine Idle Shutdown
...................................13
Engine Block Heater.......................................14
Fuel and Refueling
Fuel Quality
.......................................................15
Selective Catalytic Reduction System............................................................21
Refueling...........................................................29
Emission Control System
...........................30
Fuel Tank Selector Switch..........................36
Brakes
General Information......................................37
Towing
Towing a Trailer...............................................38
Roadside Emergencies
Fuel Shutoff.....................................................39
Jump Starting the Vehicle...........................39
Maintenance
Under Hood Overview..................................42
Engine Oil Check............................................43
Engine Coolant Check
..................................45
Changing the Engine Air Filter...................50 Vehicle Care
Cleaning the Engine......................................54
Cleaning the Exhaust...................................54
Capacities and Specific-
ations
Engine Specifications
...................................55
Motorcraft Parts
.............................................55
Technical Specifications
..............................57
Scheduled Maintenance
General Maintenance Information
..........59
Normal Scheduled Maintenance.............62
Special Operating Conditions Scheduled Maintenance................................................65
Scheduled Maintenance Record
...............71
1
Super Duty (TFA) , enUSA Table of Contents
Page 6 of 84

ABOUT THIS SUPPLEMENT
This supplement will acquaint you with the
Power Stroke diesel engine. It provides
recommendations on engine care and
operating procedures. For complete vehicle
information, also refer to your Owner
’s
Manual included with the vehicle. It also
describes equipment and gives
specifications for equipment that was in
effect when this guide was approved for
printing, and should be considered a
permanent part of the vehicle.
Note: Your vehicle ’s powertrain control
systems can detect and store information
about vehicle modifications that increase
horsepower and torque output such as
whether or not performance-enhancing
powertrain components commonly referred
to as performance chips have been used.
This information will stay in the system ’s
memory cannot be erased even if the
modification is removed. Ford Motor
Company, Ford of Canada, Ford of Mexico
and service or repair facilities can retrieve
this information when servicing your vehicle.
Ford Motor Company may use this
information to determine if your warranty
covers any needed repairs.
Note: Some aftermarket products may
cause severe engine/transmission and/or
exhaust system damage; refer to your
warranty information for more information.
Your new diesel engine will feel, drive and
function somewhat differently than a
gasoline engine. Therefore it is very
important that you read and thoroughly
familiarize yourself and others operating
the vehicle with this guide. A special
procedure for turning off the diesel engine
is in the Starting and Stopping the Engine
chapter, See Starting a Diesel Engine
(page 10). It is important to read and
understand this material in order to
maintain the best service life for your
engine. Ford may discontinue models or change
specifications without any notice and
without incurring obligations.
Warnings WARNING
Throughout this guide, you will find
warnings identified by the warning
symbol. Warnings remind you to be
especially careful to reduce the risk of
personal injury. Breaking-In Your Vehicle
Your vehicle does not need an extensive
break-in. Try not to drive continuously at
the same speed for the first 1000 miles
(1600 kilometers) of new vehicle
operation. Vary your speed to allow parts
to adjust themselves to other parts.
Drive your new vehicle at least 500 miles
(800 kilometers) before towing a trailer.
Make sure you use the specified engine oil.
See Technical Specifications (page 57).
Do not add friction modifier compounds
or special break-in oils during the first few
thousand miles (kilometers) of operation,
since these additives may prevent piston
ring seating. See Engine Oil Check (page
43
).
Diesel Engine Information
The diesel engine fuel system is a
pressurized two-stage filtration system
and consists of:
• A frame-mounted Fuel and Water
Separator primary filter with an electric
fuel pump and water drain
• An engine-mounted secondary fuel
filter
• A fuel injector for each cylinder (8
total)
• A high-pressure fuel pump
3
Super Duty (TFA) , enUSA Introduction
Page 7 of 84

•
A high-pressure fuel rail for each
cylinder bank (2 total)
• Numerous high-pressure pipes from
the high-pressure pump to the rails,
and rails to the injectors
The fuel and water separator removes
both water and impurities from the fuel.
The engine mounted filter filters finer
impurities from the diesel fuel. The
engine-mounted fuel filter and the fuel and
water separator filter should be changed
at the recommended service interval or
when indicated by the information display
LOW FUEL PRESSURE message. Refer to
the scheduled maintenance information
in this supplement for more information.
The fuel and water separator should be
drained at regular intervals (recommended
at every oil change) or when indicated by
the information display and water in fuel
indicator light. See Fuel Quality (page
15).
Proper fuel filter maintenance and prompt
water draining when the water in fuel light
illuminates is essential to prevent injection
equipment damage. Ignoring the water in
fuel light can cause your vehicle to go into
a reduced power mode.
A frame-mounted electric fuel pump
located inside the fuel and water separator
draws fuel from the fuel tank to provide
pressurized fuel to the engine. The fuel
pump contains a pressure relief valve for
overpressure protection in the event of
restricted flow.
The fuel injection system is controlled
through the powertrain control module. Engine protection mode
Ford diesel engines are equipped with
engine protection and emission control
systems. These systems monitor critical
temperatures and pressures, and modify
engine operation accordingly. These
modified engine performance
characteristics are normal.
If these modified engine performance
characteristics persist for an extended
period and either the service engine soon
or powertrain malfunction,reduced power,
electronic throttle control light is
illuminated, have the system checked by
an authorized dealer.
Service engine soon
Powertrain malfunction, reduced
power, electronic throttle control
Lubrication system
It is important to change the engine oil at
the recommended service intervals to
maintain oil viscosity. Extending the oil and
filter change interval beyond the
recommended interval can negatively
affect engine performance, fuel economy
and engine life. See
Engine Oil Check
(page 43).
Fast start glow plug system
The diesel engine glow system consists of:
• Eight glow plugs (one per cylinder)
• Glow Plug Control Module
• Engine Coolant Temperature sensor
• Barometric pressure sensor
• Environmental temperature sensor
4
Super Duty (TFA) , enUSA Introduction
Page 8 of 84

The powertrain and glow plug control
modules electronically control the glow
plug system. After you switch the ignition
on the glow plug control module
immediately energizes the glow plugs. The
glow plug control module using the engine
coolant temperature, barometric pressure
sensor and environmental temperature
sensor will determine how long the glow
plugs stay energized. The required time for
the glow plugs to be energized decreases
as the coolant temperature, barometric
pressure and environmental temperature
increase.
Glow Plug
Engine and secondary cooling system
The cooling system contains a primary
cooling loop to cool the engine and a
secondary cooling loop to cool the
transmission, charge air, and fuel. The
coolant serves three primary purposes: to
provide heat transfer, freeze point
protection, and corrosion protection using
additives.
Vehicles with diesel engines typically are
used to carry heavy loads and accumulate
mileage rapidly. These two factors may
cause the additives in the coolant to wear
out in a shorter time. For more information
about coolant additives and coolant
change intervals See Engine Coolant
Check (page 45). . Operating the engine
with insufficient coolant or coolant additive
can cause severe engine damage
Diesel Particulate Filter system
Your vehicle is equipped with a diesel
particulate filter in the exhaust system. The
diesel particulate filter reduces carbon
emissions by trapping exhaust particulates
(soot) before they reach the tailpipe. You
must properly maintain your diesel
particulate filter in order for it to function properly. Regeneration of the diesel
particulate filter occurs automatically
during operation above 30 mph (48 km/h)
and requires no actions from the driver. If
you do a lot of idling or stop and go driving,
pay attention to maintenance messages
that alert you when you need to drive to
clean the diesel particulate filter, or
perform operator commanded
regeneration. See
Emission Control
System (page 30).
Selective catalytic reduction system
Your vehicle is equipped with a selective
catalytic reduction system designed to
reduce emission levels of nitrogen oxides
from the exhaust of your diesel engine. This
system relies on the use of Diesel Exhaust
Fluid (DEF) that you must replenish at
certain intervals. Failure to maintain proper
DEF levels or if the DEF becomes
contaminated will result in vehicle speed
limitations or result in your vehicle entering
an idle-only mode. See
Selective
Catalytic Reduction System (page 21).
Speed control
If your vehicle speed goes outside a
predetermined range from the set speed,
the RSM (Resume) function will not reset
your vehicle speed. You will need to reset
your vehicle speed with the SET+ or SET-
button after reaching the desired speed
using the accelerator pedal.
Minor Troubleshooting Guide
If the engine won ’t crank WARNING
Battery posts, terminals and related
accessories contain lead and lead
compounds. Wash hands after
handling. 5
Super Duty (TFA) , enUSA Introduction
Page 9 of 84

Turn on the headlights. If the lights are dim,
do not go on at all or when the ignition is
turned to START the lights become dim or
go out, the battery connections may be
loose or corroded, or the battery may be
discharged. If there is a clicking or
stuttering sound coming from the engine
compartment when you turn the key to
START, this may also indicate a loose or
corroded battery connection.
Check the battery connections at the
battery posts, cable connection to the
engine grounding point and at the starter
connection.
If you suspect a discharged battery, have
it checked and corrected.
•
The gearshift lever must be in P (Park)
or N (Neutral) in order for the starter
to operate.
• Try operating the starter switch several
times. This operation may clean
potentially corroded contacts or make
the switch temporarily operable until
you can reach the dealer.
• If all electrical connections are tight
and you need assistance to start, refer
to Jump Starting in the Roadside
Emergencies chapter of your Owner ’s
Manual.
If engine cranks but won ’t start
Prolonged starter cranking (in excess of 10
seconds) could cause damage to the
starter motor or the high-pressure fuel
pump. •
Check the fuel gauge. You may be out
of fuel. If the gauge shows that there
is fuel in the tank, the trouble may be
in the electrical system or the fuel
system. If equipped with an auxiliary
tank, be sure that the tank control
switch is set for the tank with fuel and
not on an empty tank.
• Leaving your ignition key turned to on
for over two minutes without starting
may make starting difficult because
the glow plugs will cease activation.
Reset the system by turning the ignition
key to off and then back to on again.
Note: If the system is out of fuel and the
engine will not start, do not continue
cranking the engine. Continued cranking can
damage the high-pressure fuel pump.
If the engine runs hot
The following could cause the engine to
overheat:
• Lack of coolant
• Dirty cooling system.
• Plugged radiator fins, A/C condenser
and/or oil cooler
• Malfunctioning fan drive
• Driving with frozen coolant
• Sticking thermostat
• Overloading or pulling heavy trailers
during hot weather
• Grill or radiator air blockage
• Slipping or missing drive belt
• Plugged or very dirty air filter
6
Super Duty (TFA) , enUSA Introduction
Page 11 of 84
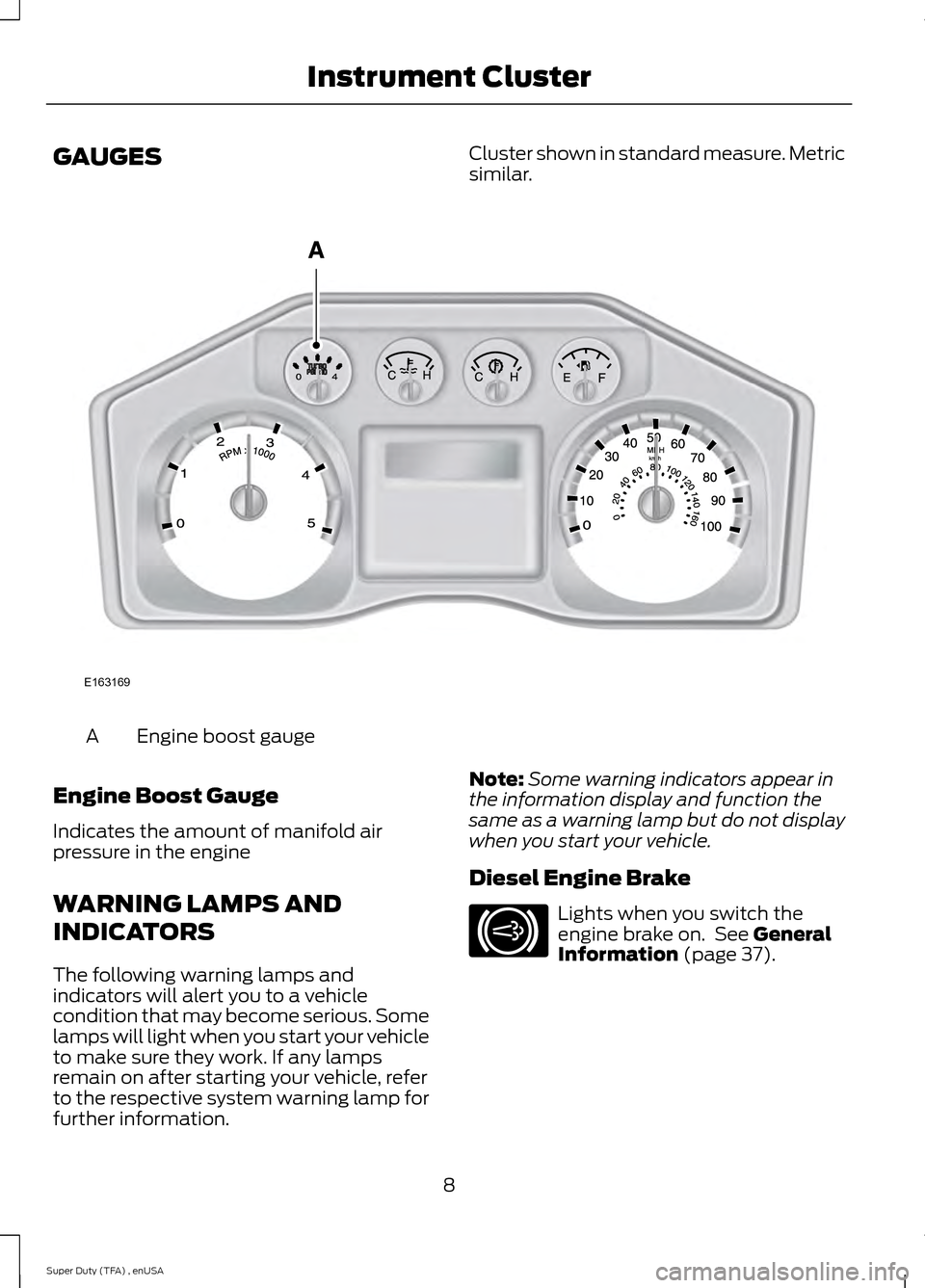
GAUGES
Cluster shown in standard measure. Metric
similar.Engine boost gauge
A
Engine Boost Gauge
Indicates the amount of manifold air
pressure in the engine
WARNING LAMPS AND
INDICATORS
The following warning lamps and
indicators will alert you to a vehicle
condition that may become serious. Some
lamps will light when you start your vehicle
to make sure they work. If any lamps
remain on after starting your vehicle, refer
to the respective system warning lamp for
further information. Note:
Some warning indicators appear in
the information display and function the
same as a warning lamp but do not display
when you start your vehicle.
Diesel Engine Brake Lights when you switch the
engine brake on. See General
Information (page 37).
8
Super Duty (TFA) , enUSA Instrument ClusterE163169 E171217
Page 12 of 84

Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) (If
Equipped) With the key in the on position,
lights when the DEF is
contaminated or low. See
Selective Catalytic Reduction System
(page
21).
Glow Plug Pre-Heat With the key in the on position,
lights when the glow plug heat
is necessary as a starting aid.
Wait until the light goes off before starting.
See
Starting a Diesel Engine (page 10).
After you start the engine, the light should
turn off. When the engine is cold, the light
should always light for a short period.
Water In Fuel During refueling, it is possible for
you to pump
water-contaminated diesel fuel
into your fuel tank. Your vehicle ’s fuel
system is equipped with a fuel filter and
water separator to remove water from the
fuel. The water in fuel indicator lights when
the fuel and water separator has a
significant quantity of water in it and
requires immediate draining.
If the water in fuel lights when the engine
is running, stop your vehicle as soon as
safely possible, shut off the engine, then
drain the fuel and water separator. See
Fuel Quality
(page 15). Allowing water
to stay in the fuel system, after the water
in fuel indicator lights, could result in
extensive damage or failure of the fuel
injection system. WARNING
Do not drain the fuel and water
separator while the engine is running.
Fuel may ignite if the separator is
drained while the engine is running or the
vehicle is moving. Note:
Do not drain the fuel and water
separator while the engine is running. Air will
enter into the fuel system causing the engine
not to operate properly.
9
Super Duty (TFA) , enUSA Instrument ClusterE163176
Page 13 of 84

STARTING A DIESEL ENGINE
Read all starting instructions carefully
before you start your vehicle.
For temperatures below 32°F (0°C), the
use of the correct grade engine oil is
essential for proper operation. Refer to
Engine oil specifications for more
information. See Technical
Specifications (page 57).
Your vehicle may be equipped with a cold
weather starting strategy that prevents
severe engine damage by assisting in
engine lubrication warm-up. In extremely
cold ambient temperatures, this strategy
activates and prevents the accelerator
pedal from being used for 30 seconds after
starting your vehicle. A message will
appear in the information display as your
vehicle warms up. By not allowing the
accelerator pedal to be used, the engine
oil is allowed to properly lubricate the
bearings preventing engine damage due
to lack of proper lubrication. After the 30
second warm-up period, the accelerator
pedal will be operational again and a
message will appear informing you the
vehicle is ok to drive.
When starting the engine in extremely cold
temperatures (-15°F [– 26°C]), it is
recommended to allow the engine to idle
for several minutes before driving the
vehicle.
Before starting the engine check the
following:
• Make sure all occupants have fastened
their safety belts.
• Make sure the headlamps and
electrical accessories are off.
• Make sure the parking brake is on.
• Make sure the gearshift lever is in
P
(Park)
• Turn the ignition key to the on position. Note:
Do not press the accelerator during
starting.
Cold Weather Starting WARNINGS
Do not use starting fluid, such as
ether, in the air intake system (see
air filter decal). Such fluid could
cause immediate explosive damage to the
engine and possible personal injury Do not add gasoline, gasohol, alcohol
or Kerosene to diesel fuel. This
practice creates a serious fire hazard
and causes engine performance problems. It is recommended that the engine block
heater be used for starting when the
temperature is -10°F (-23°C) or colder.
Refer to Engine block heater later in this
chapter for more information.
When operating in cold weather,
Motorcraft® cetane improvers or
non-alcohol-based cetane improvers from
a reputable manufacturer may be used as
needed.
Do not crank the engine for more than 10
seconds as starter damage may occur. If
the engine fails to start, turn the key to
position 3 (off) and wait 30 seconds
before trying again.
1. Turn the key to on without turning the
key to start. Do not start the engine
until the glow-plug indicator turns off.
10
Super Duty (TFA) , enUSA Starting and Stopping the Engine