Page 314 of 796

13-71793-00
2) Input/Output Devices
3) Control Logic
The EGR system controls the EGR amount based on the map values shown below:
Main map value: Intake air volume
Auxiliary map value: ※
※
Compensation by the coolant temperature
Compensation by the atmospheric pressure: Altitude compensation
Compensation by the boost pressure deviation (the difference between the requested value and
the measured value of boost pressure)
Compensation by the engine load: During sudden acceleration
Compensation by the intake air temperature -
-
-
-
-
The engine ECU calculates the EGR amount by adding main map value (intake air volume) and
auxiliary map value and directly drives the solenoid valve in the E-EGR to regulate the opening extent
of the EGR valve and sends the feedback to the potentiometer.
(1) Operating conditions
Intake air temperature: between -10 and 50℃
Atmospheric pressure: 0.92 bar or more
Engine coolant temperature: between 0 and 100°C
When there is no fault code related to EGR -
-
-
-
(2) Shut off conditions
Abrupt acceleration: with engine speed of 2600 rpm or more
When the engine is idling for more than 1 minute
Vehicle speed: 100 km/h or more
Engine torque: 380 Nm or more -
-
-
-
Page 316 of 796

14-4
2) Designated Engine Oil for CDPF (Low Ash Oil)
Need to use the designated engine oil for CDPF
1.
The smoke from the vehicle may generate the particle material in the ambient air. CDPF is the
device to reduce the smoke by collecting and recycling it. To ensure the performance of
CDPF, the designated engine oil should be used.
The smoke including combusted sulfur in fuel cannot be recycled in CDPF. This smoke
generates the ash, resulting in clogging the filter. -
-
Advantages when using the designated engine oil for CDPF
2.
Reduces the amount of ash
Improves the fuel economy and reduces the CO2
Increases the life span of engine oil
Available for all engines (diesel and gasoline) -
-
-
-
Problems when using non-designated engine oil for CDPF
3.
Decreases the life span of engine oil due to accumulated ash in DPF (around 30%)
Decreases the fuel economy due to friction resistance, exhaust gas resistance and frequent
recycling process of DPF -
-
The fuel containing high sulfur may cause the same problems.
Page 318 of 796

14-6
Overload of CDPF
(warning lamp blinking)Excessive overload of CDPF
(warning lamp illuminated)
5) Warning Lamp Related to CDPF
CDPF regeneration process (warning lamp NOT illuminated) ▶
The CDPF system enters the regeneration mode
when the driving distance becomes approx. 600 to
1,200 km (may differ by the driving condition and
driving style). Then, the engine ECU performs the
CDPF regeneration operation. However, the driver
is not informed with this operation by any engine
warning lamp or vehicle signal, so he/she may not
detect this operation. The control logic at the post-
injection dur-ing the regeneration process is to
increase the fuel injection volume and control the
intake air volume (by the throttle body) in order to
increase the temperature of the exhaust gas. The
driver may not feel any particular difference from
the vehicle.
If the CDPF cannot reach the regeneration
temperature due to low speed driving or other
reason during the regeneration process, the soot is
continuously accumulated in the CDPF. W hen this
condition continues and the CDPF is overloaded
with soot, the engine warning lamp blinks to inform
this situation to the driver.
In order to solve this problem, drive the vehicle at a
speed of approx. 80 km/h for 15 to 20 minutes to
perform the CDPF regeneration process.
If the engine warning lamp on the instrument
cluster blinks, the CDPF is overloaded. In this
case, perform the step 2. 1.
2.
3.If the vehicle is driven at a speed of 5 to 10 km/h
for an extended period of time, the soot
accumulated in the CDPF cannot be burned as the
CDPF cannot reach the regeneration temperature.
Then, an excessive amount of soot can be
accumulated in the CDPF.
This case is much worse than the simple over-load
of the CDPF. To inform this to the driver, the
engine warning lamp comes on and the engine
power is decreased to protect the system.
To solve this problem, blow soot between the
engine and exhaust system several times and
erase the related DTC. Then, check if the same
DTC is regenerated again. If so, check the DTC
related to the differential pressure sensor. 1.
2.
3.
OFF
Blinking Illuminating
Blinking Illuminating
Page 319 of 796

14-72412-02
1. OVERVIEW
The low emission vehicle is being sold increasingly in the market as a countermeasure for complying
with the environment regulations such as a special act on Seoul metropolitan air quality improvement
and for reducing the PM (Particulate Material) from the diesel-powered vehicle. For the CDPF system,
the DOC (two-way catalytic converter or catalytic combustion system) fitted to the conventional diesel
engine has the high purification rate for HC or CO but not have a high reduction rate for the PM. For
this reason, a necessity has been raised in order to consider a countermeasure to reduce the PM
since the existing DOC can't meet the regulation, which is getting tighter.
This results in a development of the CDPF (Catalyst & Diesel Particulate Filter) that is combination of
the existing DOC (Diesel Oxydation Catalyst) and DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter). While the DOC
converts the CO and HC into the CO2 and H2O - unharmful to human body - using a oxidation
reaction, the DPF collects the PF (Particulate Material) for regeneration of it. However, each of these
devices can only reduce a part of the exhaust gas. This evoked the necessity of the CDPF with both
features. The DOC capacity is more on the manual transmission than the automatic transmission.
DOC(Diesel Oxidation Catalyst) ▶
It is called as a oxidation catalyst, which purifies CO and HC in exhaust gas. The three-way catalyst is
used for the gasoline vehicle. But, the diesel engine oxidates CO and HC excepting NOx into H2O and
CO2 in order to purify the exhaust gas since the exhaust gas has a rich oxygen at all times.
DPF(Diesel Particulate Filter) ▶
It consists of mainly the aluminum and titanium and there is a porous thin film, which emits the exhaust
gas but does not emit the PM in it. It emits the exhaust gas generated during combustion and filters the
PM which is a byproduct of combustion to burn it when a certain amount of it is collected in the filter.
When a certain amount of the PM builds up, exposure to high exhaust gas causes carbon, the
fundamental ingredient in PM, to burn and release into the atmosphere in form of CO2.
Page 321 of 796
14-92412-02
Differential Pressure Sensor
Calculates the amount of PM
collected by reading the pressure
difference between pre-CDPF and
post-CDPF.Engine ECU (D20DTR)
Post injection
Electric Throttle Body
Regulates the air intake
rate.CDPF
(DOC+DPF)Front EGT Sensor
Measures the combustion
temperature.
Rear EGT Sensor
Measures the CDPF
temperature.
2. COMPONENTS
For details, refer to section "Engine Control". *
Page 323 of 796

14-112412-02
4. POST-INJECTION AND AIR MASS CONTROL
A DPS (Differential Pressure Sensor) measures the pressure difference between before and after the
CDPF and detects whether the soot is collected in the CDPF or not. If PM is collected in the CDPF (In
this case the pressure difference between before and after the CDPF exceeds the specified value.
Normally, the system sends the signal when the driving distance becomes approx. 600 to 1,200 km), the
temperature of exhaust gas is increased and the post-injection is started for regeneration. The amount
of fuel post-injection is controlled by the exhaust gas temperature measured by the rear temperature
sensor. If the temperature is less than 600℃, the amount of post-injection is increased to
increase the regeneration temperature. Otherwise, the fuel injection amount is decreased or the fuel is
not injected.
When the engine is running with low load, the intake air amount is also controlled as well as fuel injection
amount. This function is used to increaser the combustion temperature by increasing the amount of fuel
post-injection with the lowest air amount within the specified control logic.
Page 324 of 796
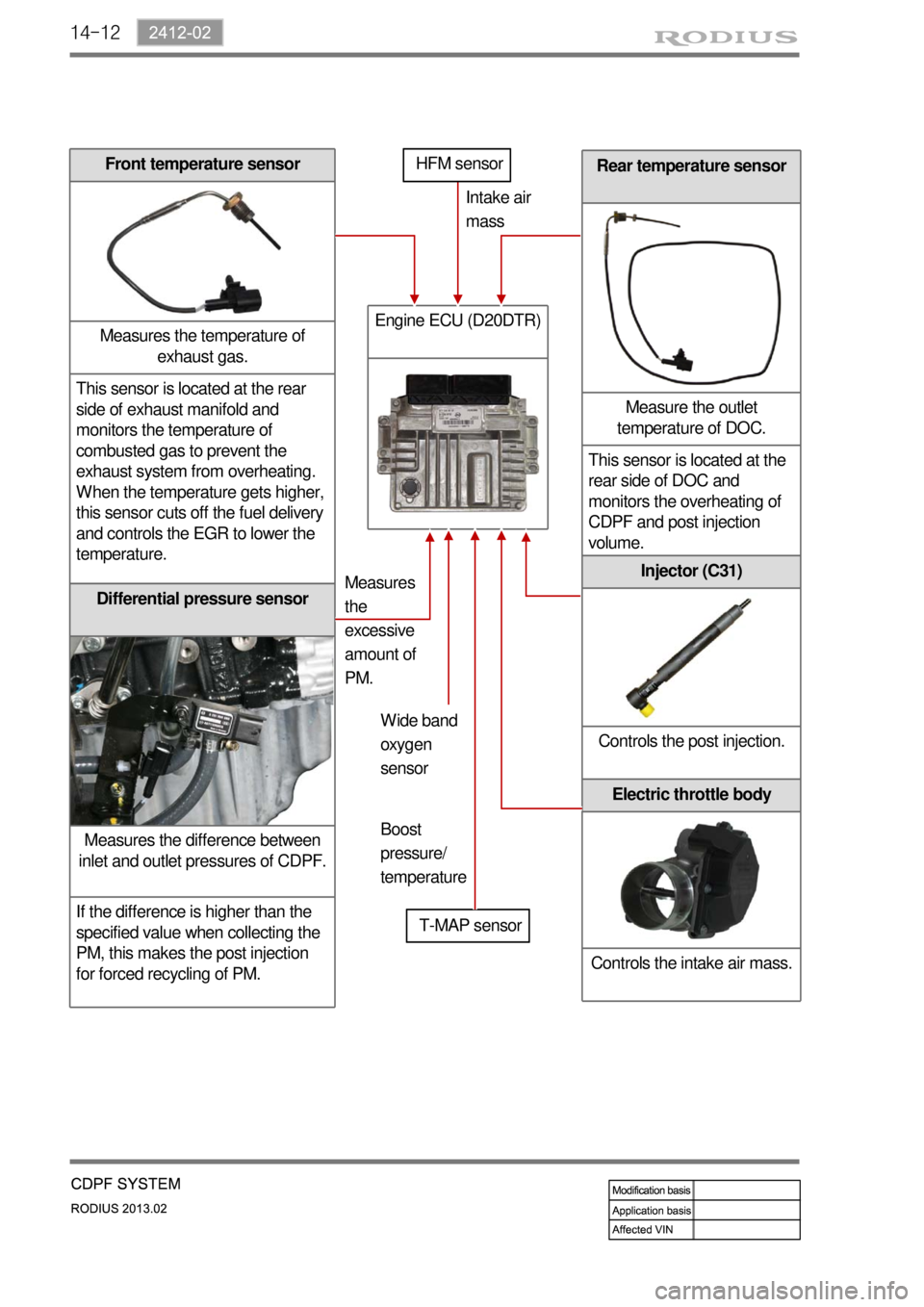
14-12
Rear temperature sensor
Measure the outlet
temperature of DOC.
This sensor is located at the
rear side of DOC and
monitors the overheating of
CDPF and post injection
volume.
Differential pressure sensor
Measures the difference between
inlet and outlet pressures of CDPF.
If the difference is higher than the
specified value when collecting the
PM, this makes the post injection
for forced recycling of PM.
Front temperature sensor
Measures the temperature of
exhaust gas.
This sensor is located at the rear
side of exhaust manifold and
monitors the temperature of
combusted gas to prevent the
exhaust system from overheating.
When the temperature gets higher,
this sensor cuts off the fuel delivery
and controls the EGR to lower the
temperature.
Engine ECU (D20DTR)
T-MAP sensorIntake air
mass
Measures
the
excessive
amount of
PM.
Injector (C31)
Controls the post injection.
Electric throttle body
Controls the intake air mass.
HFM sensor
Wide band
oxygen
sensor
Boost
pressure/
temperature
Page 325 of 796
14-132412-02
Collecting PM
→ Regeneration
The engine ECU detects the
amount of PM collected by the
information from the
temperature sensors and
differential pressure sensor.
When the soot is accumulated,
the engine ECU performs post-
injection to increase the
exhaust gas temperature and
burns the collected PM at
approx. 600°C.Oxidation (DOC)
When the exhaust gas enters
into the CDPF assembly, its
CO, HC and PM are reduced
by the redox reaction of the
DOC. The remaining PM is
filtered and collected in CDPF,
and the temperature of the
exhaust gas is increased to
between 450 and 500°C.
5. OPERATING PROCESS
[Configuration and principle of operation]
The exhaust gas
passed through the
exhaust manifold
enters into the CDPF
assembly (at approx
250℃).