Page 665 of 796
09-194891-01
4) ARP (Active Roll-Over Protection)
The ARP (Active Roll-over Protection) system is a safety assistant device that minimizes, by controlling
brakes and the engine, the physical tendency of the vehicle rollover during sharp lane changes or U-
turns. For the system, software is added to the existing ESP system and no additional device or switch
is needed. One must note that the ARP system, just as general assistant devices including the ABS, is
only a safety assistant device using the ESP system and its function is useless when the situation
overcomes the physical power. Following picture shows how the ARP compensates the vehicle
position by varying each wheel's braking power to overcome the physical tendency of the vehicle
rollover during sharp turns.
The vehicle driving condition is controlled by the internally programmed logic according to the input
signals from wheel speed sensor, steering angle sensor and lateral sensor.
Page 666 of 796
09-20
During the ARP operation, vehicle safety (rollover prevention) takes the first priority and thus,
stronger engine control is in effect. Consequently, the vehicle speed decreases rapidly, so the
driver must take caution for the vehicle may drift away from the lane.
The ARP function is still available even when turning off the ESP system by ESP OFF switch.
However, if the ESP system is shut off due to a system failure, the ARP system is also not
available. -
-
Page 667 of 796

09-214891-01
4. SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
When equipped with ABS, the braking force at each wheel will be controlled with 3-channel 4-sensor
method. And when equipped with ESP, 4 wheels will be controlled independently with 4-channel
method. (When controlling ABS system only, it will be operated with 3-channel method.) When
compared to the vehicle equipped with ABS/EBD only, the internal hydraulic circuit has a normally-open
separation valve and a shuttle valve in primary circuit and in secondary circuit. When the vehicle brakes
are not applied during engine running or when applying the non-ABS operating brakes, the normally-
open separation valve and the inlet valve are open, whereas the normally-closed shuttle valve and the
outlet valve are closed. When the ESP system is operating, the normally-open separation valve will be
closed by the solenoid valve operation and the hydraulic circuit will be established by the shuttle valve.
Then, the inlet and outlet valves will be
closed or open depending on the braking pressure increase, decrease or unchanged conditions.
▶The warning lamp comes on and warning beep sounds when the ESP is operating
Driving feeling when the ESP is operating ▶
▶Noise and vibration that driver senses when the ESP is operating
1) Hydraulic Circuit Diagram
When the ESP operates during vehicle movement, the ESP warning lamp on the instrument panel
flickers and beep comes on every 0.1 second. The ESP operation shows that the vehicle stability is
extremely unstable and it is used to warn the driver. The ESP system is just a supplementary system
for the vehicle motion and it cannot control the vehicle when it exceeds the physical limits. Do not
solely rely on the system but be advised to drive the vehicle safely.
When the ESP system activates, the driving feeling can be different depending on vehicle driving
conditions. For example, you will feel differently when the ESP system is activated during when ABS
is operating with the brakes applied and when brakes are not applied on a curve. Thus, the ESP
system would make the driver feel more abruptly when the brakes are applied during the ESP
system activation.
The ESP system may transfer noise and vibration to the driver due to the pressure changes caused
by the motor and valve operations in a very short period of time. Extreme cornering will trigger the
ESP operation and this will make the driver feel noise and vibration due to sudden brake application.
Also, the ESP system controls the engine output. So, the driver may notice the engine output
decrease even when the accelerator pedal is being applied.
Page 668 of 796
09-22
(1) Hydraulic Circuit Diagram
When compared to the vehicle equipped with ABS/EBD only, the internal hydraulic circuit has a
normally-open separation valve and a shuttle valve in primary circuit and in secondary circuit.
When the vehicle brakes are not applied during engine running or when applying the non-ABS
operating brakes, the normally-open separation valve and the inlet valve are open, whereas the
normally-closed shuttle valve and the outlet valve are closed.
When the ESP system is operating, the normally-open separation valve will be closed by the solenoid
valve operation and the hydraulic circuit will be established by the shuttle valve. Then, the inlet and
outlet valves will be closed or open depending on the braking pressure RISE, HOLD or DUMP
conditions.
Page 690 of 796

11-8
Free Play Check ▶
Start the engine and place the wheels at
straight ahead direction.
Turn the steering wheel until the tires starts
to move and measure the distance on the
circumference of the steering wheel. A.
B.
Free play30 mm
If the free play is out of the specified value,
check the free play in steering column shaft
connection and steering linkage. Replace or
repair if necessary.
Steering Effort Check ▶
Park the vehicle on a paved and flat ground
and place the front wheels at straight ahead
direction.
Start the engine and let it run around 1,000
rpm.
Install the spring scale on the circumference of
the steering wheel and measure the steering
effort in both directions. A.
B.
C.
Steering effort in
standstillbelow 3.0 kg
The difference between both sides should
be within 0.6 kg.
Steering Angle Check ▶
Place the front wheel on a turning radius
measuring tool.
Turn the steering wheel to the both ends and
measure the maximum steering angle. A.
B.
Steering
angleInner36.4°
Outer31.5°
If the steering angle is out of the specified
value, check and adjust the toe-in.
Page 691 of 796
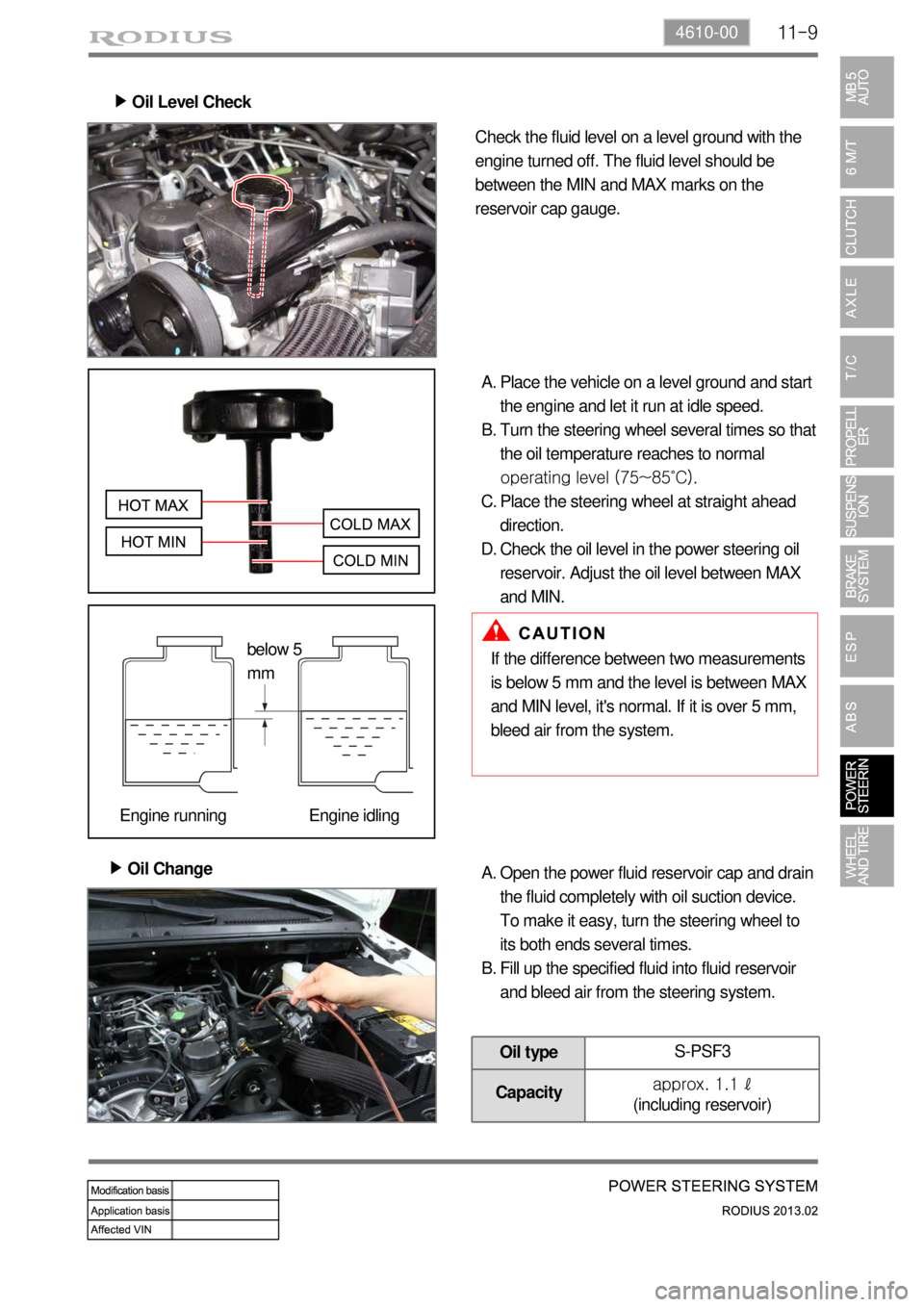
11-94610-00
Oil Level Check ▶
Check the fluid level on a level ground with the
engine turned off. The fluid level should be
between the MIN and MAX marks on the
reservoir cap gauge.
Place the vehicle on a level ground and start
the engine and let it run at idle speed.
Turn the steering wheel several times so that
the oil temperature reaches to normal
operating level (75~85˚C).
Place the steering wheel at straight ahead
direction.
Check the oil level in the power steering oil
reservoir. Adjust the oil level between MAX
and MIN. A.
B.
C.
D.
Oil Change ▶
If the difference between two measurements
is below 5 mm and the level is between MAX
and MIN level, it's normal. If it is over 5 mm,
bleed air from the system.
Open the power fluid reservoir cap and drain
the fluid completely with oil suction device.
To make it easy, turn the steering wheel to
its both ends several times.
Fill up the specified fluid into fluid reservoir
and bleed air from the steering system. A.
B.
Oil typeS-PSF3
Capacityapprox. 1.1 ℓ
(including reservoir)
below 5
mm
Engine running Engine idling
Page 692 of 796
11-10
Air Bleeding ▶
The air bleeding should be done after servicing
the power steering system and when the
difference between two measurements (cooled
and normal temperature) is prominent.
Normal
AbnormalLift up the vehicle very carefully.
Turn the steering wheel to its both ends
several times and add the oil up to MAX line
in the steering oil reservoir.
Periodically crank the starting motor and turn
the steering wheel to its both ends without
any interruption.
Check the oil level again. If the oil level is
fluctuated, repeat the procedures from step
3 to step 5.
Start the engine.
Turn the steering wheel to its both ends until
any bubble can be found in the steering oil
reservoir.
Perform the test drive and check the
steering wheel for normal operation and
noise.
If the oil level abruptly goes up, bleed the air
from the system again. A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
F.
G.
H.
If the air bleeding is not properly performed,
the life span of the power steering pump
may be shortened. -
Page 693 of 796
11-114610-00
Oil Pump Pressure Check ▶
Check the oil pump pressure to locate any
defect in oil pump.
Before checking the pressure, check the oil
level and belt tension. Prepare the empty
container to collect the spilled oil during the
service.
Unscrew the pressure line fitting in power
steering pump.
Install the pressure gauge between the
power steering pump and the power steering
oil pressure line.
Place the shift lever to neutral position. Apply
the parking brake.
Open the valve in pressure gauge. Start the
engine and let it run at idle speed.
Turn the steering wheel several times so that
the oil temperature reaches to normal
operating level. A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Fully close the valve in pressure gauge and
measure the oil pressure. F.
To prevent internal damage, do not close the
gauge valve over 10 seconds.
Keep the oil temperature at proper range. -
-
Relief pressure93.3 ~ 100.4 kgf/cm²