Page 622 of 751

11-20
5) ARP (Active Roll-Over Protection
The ARP (Active Roll-over Protection) system is a safety assistant device that minimizes, by controlling
brakes and the engine, the physical tendency of the vehicle rollover during sharp lane changes or U-
turns. For the system, software is added to the existing ESP system and no additional device or switch is
needed. One must note that the ARP system, just as general assistant devices including the ABS, is only
a safety assistant device using the ESP system and its function is useless when the situation overcomes
the physical power. Following picture shows how the ARP compensates the vehicle position by varying
each wheel's braking power to overcome the physical tendency of the vehicle rollover during sharp turns.
Lateral sensor
(In sensor cluster)
Vehicle speedBrake force
Radius
The vehicle driving condition is controlled by the internally programmed logic according to the input
signals from wheel speed sensor, steering angle sensor and lateral sensor.
During the ARP operation, vehicle safety (rollover prevention) takes the first priority and thus, stronger
engine control is in effect. Consequently, the vehicle speed decreases rapidly, so the driver must take
caution for the vehicle may drift away from the lane.
Page 624 of 751

11-22
Circuit description ▶
When compared to the vehicle equipped with ABS/EBD only, the internal hydraulic circuit has a
normally-open separation valve and a shuttle valve in primary circuit and in secondary circuit.
When the vehicle brakes are not applied during engine running or when applying the non-ABS operating
brakes, the normally-open separation valve and the inlet valve are open, whereas the normally-closed
shuttle valve and the outlet valve are closed.
When the ESP system is operating, the normally-open separation valve will be closed by the solenoid
valve operation and the hydraulic circuit will be established by the shuttle valve. Then, the inlet and outlet
valves will be closed or open depending on the braking pressure RISE, HOLD or DUMP conditions.
Flashing warning lamp and warning sound during ESP operation ▶
When the ESP operates while the vehicle is moving, the ESP warning lamp on the instrument panel
flickers and the buzzer sounds at every 0.1 second. The ESP lamp operation is to inform a driver that the
vehicle is extremely unstable.
The ESP system is just a supplementary system for the vehicle and it cannot control the vehicle over the
physical limit. Do not solely rely on the system but be advised to drive the vehicle safely.
Drive feeling during ESP operation ▶
When the ESP system activates, the driving feeling can be different depending on vehicle driving
conditions. For example, it will feel different when the ESP system is activated while the ABS is operated
by depressing the brake pedal and when the ESP system is in control without the brake pedal
depressed on the same curve.
If the ESP system operates with the brake applied, the brake pressure will be increased on the
corresponding wheel which already has braking pressure for the ESP controls. In other words, the ESP
system would make the driver feel more abruptly braked compared to the situation that the braking
pressure is applied to wheel which had no braking force.
Noise and vibration that driver senses during ESP operation ▶
The ESP system may transfer noise and vibration to a driver due to the pressure changes caused by the
motor and valve operations in a very short period of time.
Extreme cornering will trigger the ESP operation and this will make the driver sense noise and vibration
due to sudden brake application.
Also, the ESP system controls the engine power. Therefore, the driver may notice the engine power
decreases even when the accelerator pedal is depressed.
Page 629 of 751
11-274890-10
5) Hydraulic Circuit of HBA
The above figure shows one front and one rear wheel and the same hydraulic circuit forms as in the
ESP operation. When HECU recognizes that it is an emergency and it is required for hard braking,
depending on the pressure value of the brake pressure sensor and pressure changes caused by the
pressure sensor timing, it operates the pump immediately to apply the brake pressure at the wheels.
Then, the pressure in the pump increases until just before the corresponding wheel gets locked. The
motor still keeps rotating and the outlet valve and the separation valve will stay closed. When the wheel
starts to lock, the HBA function cancels and switches to ABS operation.
Page 637 of 751
12-8
Change of Steering Wheel & Steering Column Shaft ▶
Appearance of steering wheel boss part changed
Steering wheel assembly boss part
Page 646 of 751
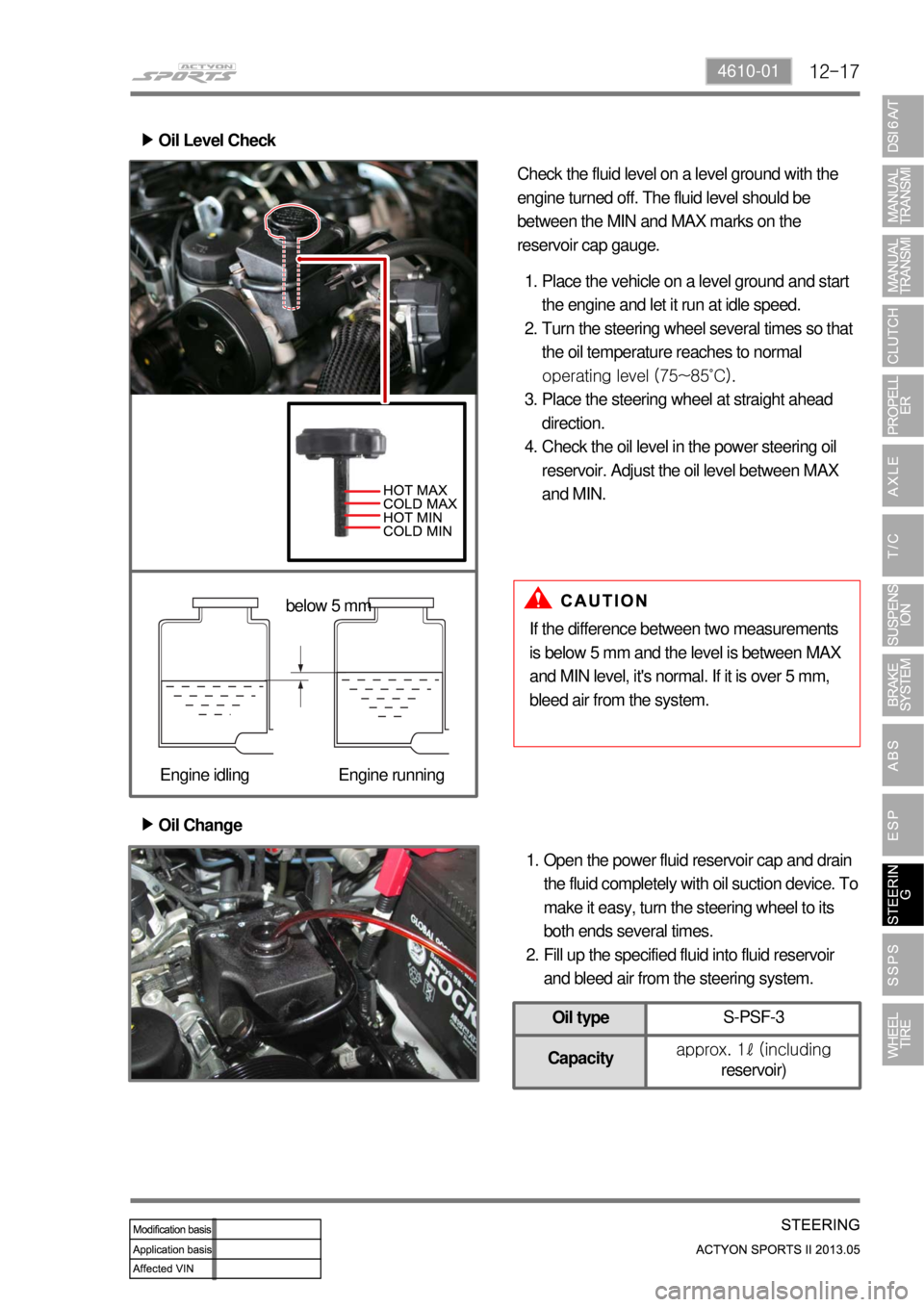
12-174610-01
Oil Change ▶
Open the power fluid reservoir cap and drain
the fluid completely with oil suction device. To
make it easy, turn the steering wheel to its
both ends several times.
Fill up the specified fluid into fluid reservoir
and bleed air from the steering system. 1.
2. Oil Level Check ▶
Place the vehicle on a level ground and start
the engine and let it run at idle speed.
Turn the steering wheel several times so that
the oil temperature reaches to normal
operating level (75~85˚C).
Place the steering wheel at straight ahead
direction.
Check the oil level in the power steering oil
reservoir. Adjust the oil level between MAX
and MIN. 1.
2.
3.
4.
If the difference between two measurements
is below 5 mm and the level is between MAX
and MIN level, it's normal. If it is over 5 mm,
bleed air from the system. Check the fluid level on a level ground with the
engine turned off. The fluid level should be
between the MIN and MAX marks on the
reservoir cap gauge.
below 5 mm
Engine idling Engine running
Oil typeS-PSF-3
Capacityapprox. 1ℓ (including
reservoir)
Page 659 of 751
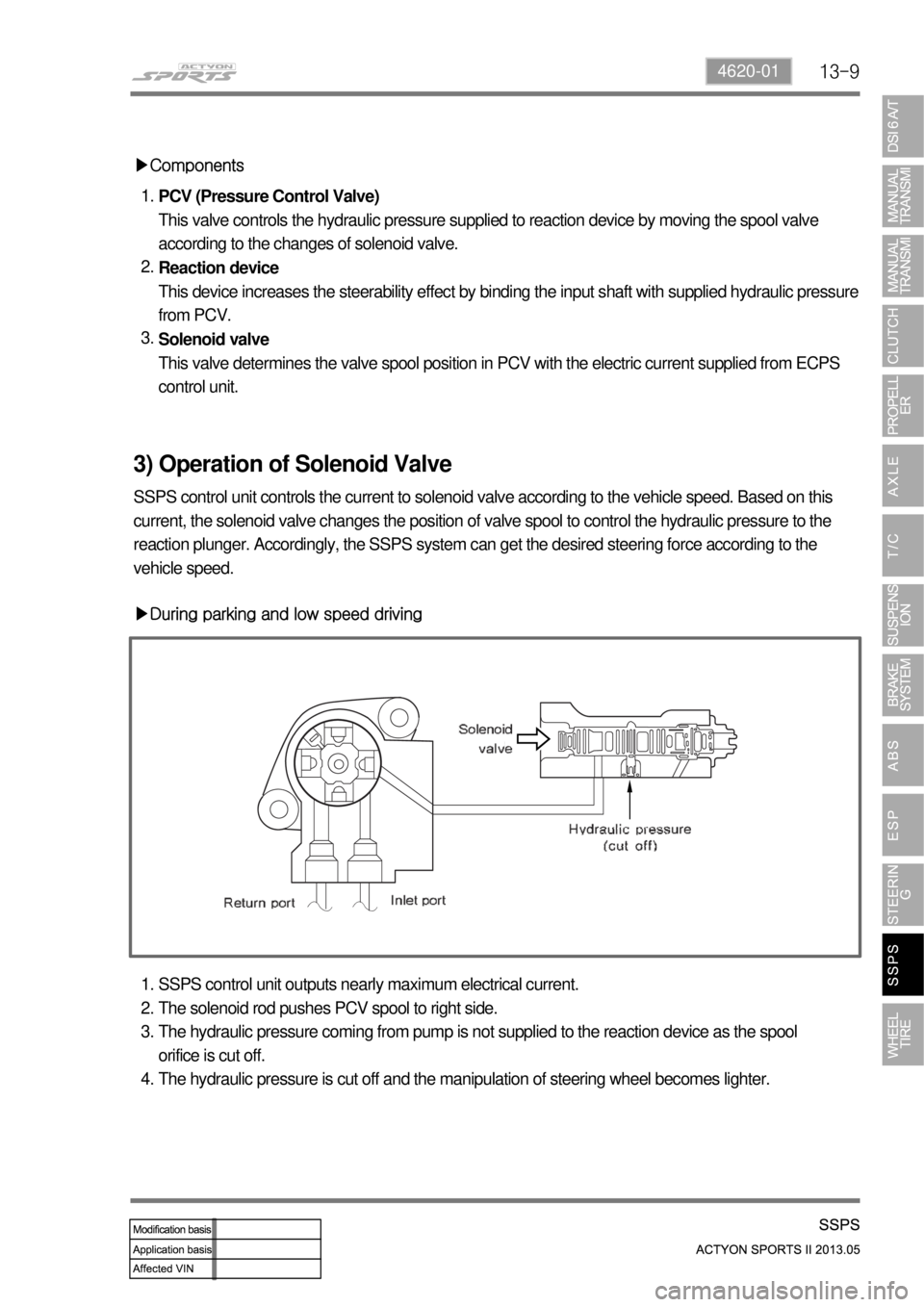
13-94620-01
▶Components
PCV (Pressure Control Valve)
This valve controls the hydraulic pressure supplied to reaction device by moving the spool valve
according to the changes of solenoid valve.
Reaction device
This device increases the steerability effect by binding the input shaft with supplied hydraulic pressure
from PCV.
Solenoid valve
This valve determines the valve spool position in PCV with the electric current supplied from ECPS
control unit. 1.
2.
3.
3) Operation of Solenoid Valve
SSPS control unit controls the current to solenoid valve according to the vehicle speed. Based on this
current, the solenoid valve changes the position of valve spool to control the hydraulic pressure to the
reaction plunger. Accordingly, the SSPS system can get the desired steering force according to the
vehicle speed.
▶During parking and low speed driving
SSPS control unit outputs nearly maximum electrical current.
The solenoid rod pushes PCV spool to right side.
The hydraulic pressure coming from pump is not supplied to the reaction device as the spool
orifice is cut off.
The hydraulic pressure is cut off and the manipulation of steering wheel becomes lighter. 1.
2.
3.
4.
Page 664 of 751
14-34170-09
1. SPECIFICATIONS
2. MAJOR CHANGES
Wheel assembly
16-inches silver 18-inches silver 18-inches hyper silver
PN: 41730-32000 PN: 41730-32200 PN: 41730-32300
- Added 18-inches hyper silver to wheel assembly
- Wheel offset and tire size are identical with existing specifications
Existing specifications New specifications
Description Specification
Tire 16 inch 225/75R 16
18 inch 255/60R 18
Tire inflation pressure Front: 32 psi
Rear: 32 psi (44 psi: when the vehicle is fully laden
with luggage)
Wheel 16 inch 6.5J x 16
18 inch 7.5J x 18
Balance weight 16 inch Inner: Attachment type
Outer: Clip type
18 inch Inner: Attachment type
Outer: Attachment type
Tightening torquse of wheel bolt 127.4 ~ 156.8 Nm
Page 665 of 751
14-4
3. TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
Problem Possible Cause Action
Uneven tire wear Incorrect tire pressure Adjust
Unbalanced wheel Adjust
Improper location change of tire Change tire location in
specified interval
Incorrect toe adjustmen Adjust
Incorrect wheel bearing preload adjustment Adjust
Malfunction of brake syste Adjust
Tire squeal, vibration Too low tire pressure Adjust
Unbalanced wheel or tire Adjust
Heavy vibration of wheel or tire Uneven tire wear
Uneven tire wear Check and adjust
Premature tire wear Too high tire pressure Adjust
Fast driving with low pressure tire Adjust
Overload Adjust