Page 30 of 751
01-130000-00
NameSizeNumbers of
fastener Tightening
torque (Nm) Note (total
tightening torque)
Idler pulley/tensioner pulley 1
45±4.5Nm -
Glow plug M5 4 20±2Nm -
Vacuum pump M6×25 3 10±1Nm -
Timing gear case cover M6×40 7 10±1Nm -
M6×45 1 10±1Nm -
M6×50 3 10±1Nm -
Cylinder head cover M6×35 21 10±1Nm -
Oil dipstick gauge cover M6×16 1 10±1Nm -
Oil filter cap 1 25±2.5Nm -
Fuel rail M8×25 2 25±2.5Nm -
Injector clamp bolt M6×44 2 9±1.0Nm
130˚±10˚ -
High pressure pipe
(between high pressure pump and fuel rail assembly) M17 1
30±3Nm -
High pressure pipe
(between fuel rail assembly and injector) M17 4
30±3Nm -
Crankshaft position sensor M5×14
1 8±0.4Nm -
Main wiring M6×16 5 10±1Nm -
Intake duct M8×25 425±2.5Nm -
Power steering pump M8×100 3 25±2.5Nm -
Cylinder head front cover M6×10
5 10±1Nm -
Ladder frame M8×355 30±3Nm
-
EGR pipe bolt
(to air duct) M6×16
2 10±1Nm -
EGR pipe bolt
(to EGR cooler) M8×25
225±2.5Nm -
Page 37 of 751
02-6
ComponentSizeBolt
Quantity Specified torque
(Nm) Remark
(Total torque)
Glow plug M5 4 20±2Nm -
Vacuum pump M6×253 10±1Nm -
Timing gear case cover M12×55 3 85±8.5Nm -
M6×25 7 10±1Nm -
M6×45 1 10±1Nm -
M6×50 3 10±1Nm -
Cylinder head cover M6×35 21 10±1Nm -
Oil gauge tube M6×16 1 10±1Nm -
Oil filter cap 1 25±2.5Nm -
Fuel rail M8×35SOC 2 25±2.5Nm -
Injector clamp bolt M6×60 2 10±1Nm,
120˚+10˚ -
High pressure pipe
(between HP pump and fuel rail) M17 1
30±3Nm -
High pressure pipe
(between fuel rail and injector) M17 4
30±3Nm -
Crank position sensor M5×14 1 5±1.0Nm -
Main wiring M6×16 5 10±1Nm -
Intake duct M8x25 4 25±2.5Nm -
Power steering pump M8×100 3 25±2.5Nm -
Cylinder head front cover M6×10 5 10±1Nm -
Ladder frame M8×16 5 30±3Nm -
Oil pump M8×35 3 25±2.5Nm -
EGR Cooler
MTG Bolt M8×16
225±2.5Nm -
M8×70 225±2.5Nm -
Idle pulley/Tensioner pulley 1
45±4.5Nm -
Page 60 of 751
02-290000-00
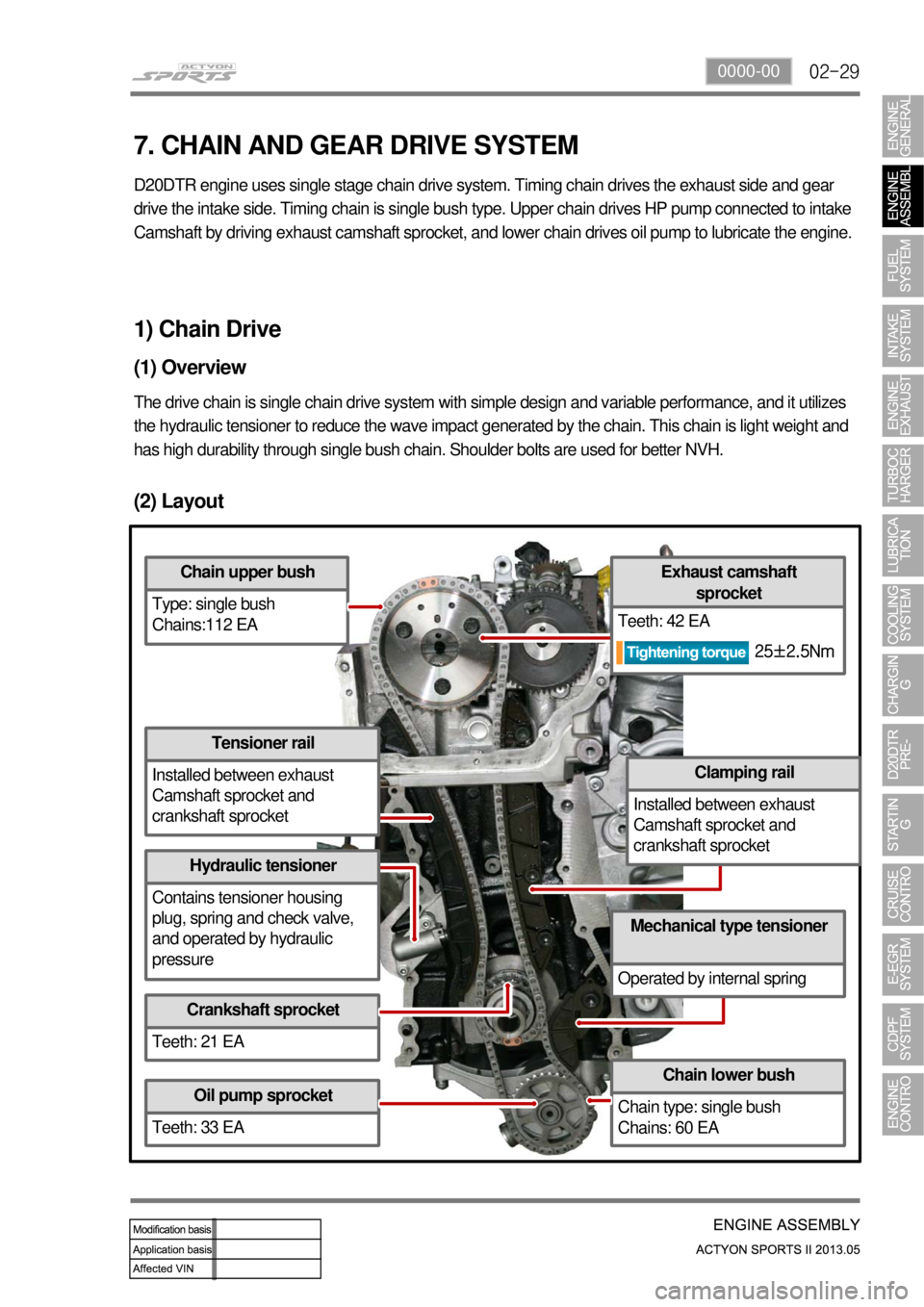
(2) Layout
Chain upper bush
Type: single bush
Chains:112 EA
Tensioner rail
Installed between exhaust
Camshaft sprocket and
crankshaft sprocket
Hydraulic tensioner
Contains tensioner housing
plug, spring and check valve,
and operated by hydraulic
pressure
Crankshaft sprocket
Teeth: 21 EA
Oil pump sprocket
Teeth: 33 EA
Chain lower bush
Chain type: single bush
Chains: 60 EA
Mechanical type tensioner
Operated by internal spring
Clamping rail
Installed between exhaust
Camshaft sprocket and
crankshaft sprocket
Exhaust camshaft sprocket
Teeth: 42 EA
1) Chain Drive
(1) Overview
The drive chain is single chain drive system with simple design and variable performance, and it utilizes
the hydraulic tensioner to reduce the wave impact generated by the chain\
. This chain is light weight and
has high durability through single bush chain. Shoulder bolts are used f\
or better NVH.
7. CHAIN AND GEAR DRIVE SYSTEM
D20DTR engine uses single stage chain drive system. Timing chain drives the exhaust side and gear
drive the intake side. Timing chain is single bush ty pe. Upper chain drives HP pump connected to intake
Camshaft by driving exhaust camshaft sprocket, and lowe r chain drives oil pump to lubricate the engine.
25±2.5Nm
Page 61 of 751
02-30
2) Timing Chain and Gear
(1) Timing chain
Simple layout: optimized timing, enhanced
NVH
Single stage layout: minimized chain load -
-
Chain upper bush
- Single bush type (112 EA)
Chain lower bush
- Single bush type (60 EA)
(2) Tensioner
Tensioner adjusts the chain tension to keep it tight during engine running. This reduces the wear in
guide rail and spoke.
Operating principle
- Use the spring tension in tensioner and hydraulic pressure
Tensioner type
- Compensation and impact absorbing
Static and dynamic force
- Spring + Hydraulic pressure 1.
2.
3.
Plunger
HousingSpring
Check valve
Hydraulic tensioner assembly ▶
Page 63 of 751
02-32
Screw plug
Oil sealTiming gear case cover
(5) Timing gear case cover
Timing gear case cover (TGCC)
Page 64 of 751
02-330000-00
Features
Major function: Protecting the chain drive system, minor function: Shielding the chain noise.
Install crankshaft front seal and screw plug on the timing gear case cover. ▶
-
-
Do not touch the inner lip of crankshaft front seal.
Be careful not to damage the screw thread when removing the lock pin to release the chain
tensioner.
Be careful not to damage the O-ring when installing the screw plug. -
-
-
A671 997 01 46
Crankshaft front seal
Location of chain tensioner screw
plug
Page 95 of 751

03-18
3. CAUTIONS FOR DI ENGINE
1) Cautions for DI Engine
This chapter describes the cautions for DI engine equipped vehicle. This includes the water separation
from engine, warning lights, symptoms when engine malfunctioning, causes and actions.
DI Engine 1.
Comparatively conventional diesel engines, DI engine controls the fuel injection and timing electrically,
delivers high power and reduces less emission..
System Safety Mode 2.
When a severe failure has been occurred in a vehicle, the system safety mode is activated to protect the
system. It reduces the driving force, restricts the engine speed (rpm) and stops engine operation. Refer
to "Diagnosis" section in this manual.
Engine CHECK Warning Lamp 3.
The Engine CHECK warning lamp on the instrument cluster comes on when the fuel or
major electronic systems of the engine are not working properly. As a result, the
<008c0095008e00900095008c02c5009a004700970096009e008c009900470096009c009b0097009c009b00470094008800a00047008b008c008a0099008c0088009a008c0047009600990047009b008f008c0047008c0095008e00900095008c0047009400
8800a00047009a009b0088009300930055>
Water Separator Warning Lamp 4.
When the water level inside water separator in fuel filter exceeds a certain level (approx.
45 cc), this warning light comes on and buzzer sounds.
Also, the driving force of the vehicle decreases (torque reduction). If these conditions
occur, immediately drain the water from fuel filter.
Page 211 of 751

15-110000-00
2) ECU Control
(1) Function
a. ECU Function
ECU receives and analyzes signals from various sensors and then modifies those signals into
permissible voltage levels and analyzes to control respective actuators.
ECU microprocessor calculates injection period and injection timing proper for engine piston speed and
crankshaft angle based on input data and stored specific map to control the engine power and emission
gas.
Output signal of the ECU microprocessor drives pressure control valve to control the rail pressure and
activates injector solenoid valve to control the fuel injection period and injection timing; so controls
various actuators in response to engine changes. Auxiliary function of ECU has adopted to reduce
emission gas, improve fuel economy and enhance safety, comforts and conveniences. For example,
there are EGR, booster pressure control, autocruise (export only) and immobilizer and adopted CAN
communication to exchange data among electrical systems (automatic T/M and brake system) in the
vehicle fluently. And Scanner can be used to diagnose vehicle status and defectives.
<00760097008c00990088009b00900095008e0047009b008c00940097008c00990088009b009c0099008c0047009900880095008e008c00470096008d0047006c006a007c00470090009a0047009500960099009400880093009300a000470054005b005700
47009b009600470052005f005c00b6006a004700880095008b> protected from factors like oil,
water and electromagnetism and there should be no mechanical shocks.
To control the fuel volume precisely under repeated injections, high current should be applied instantly
so there is injector drive circuit in the ECU to generate necessary current during injector drive stages.
Current control circuit divides current applying time (injection time) into full-in-current-phase and hold-
current-phase and then the injectors should work very correctly under every working condition.
b. Control Function
Controls by operating stages
To make optimum combustion under every operating stage, ECU should calculate proper injection
volume in each stage by considering various factors.
Starting injection volume control
During initial starting, injecting fuel volume will be calculated by function of temperature and engine
cranking speed. Starting injection continues from when the ignition switch is turned to ignition
position to till the engine reaches to allowable minimum speed.
Driving mode control
If the vehicle runs normally, fuel injection volume will be calculated by accelerator pedal travel and
engine rpm and the drive map will be used to match the drivers inputs with optimum engine power. -
-
-