Page 385 of 1336

3. Idle Speed Controller
The idle speed controller consists of 2 principal modules:
The first module determines the required idle speed according to:
* The operating conditions of the engine (coolant temperature, gear engaged)
* Any activation of the electrical consumers (power steering, air conditioning, others)
* The battery voltage
* The presence of any faults liable to interface with the rail pressure control or the injection control. In
this case, increase the idle speed to prevent the engine from stalling.
The second module is responsible for providing closed loop control of the engine's idle speed by
adapting the minimum fuel according to the difference between the required idle speed and the
engine speed. -
-
4. Flow Limitation
The flow limitation strategy is based on the following strategies:
The flow limitation depending on the filling of the engine with air is determined according to the
engine speed and the air flow. This limitation allows smoke emissions to be reduced during
stabilized running.
The flow limitation depending on the atmospheric pressure is determined according to the engine
speed and the atmospheric pressure. It allows smoke emissions to be reduced when driving at
altitude.
The full load flow curve is determined according to the gear engaged and the engine speed. It
allows the maximum torque delivered by the engine to be limited.
A performance limitation is introduced if faults liable to upset the rail pressure control or the
injection control are detected by the system. In this case, and depending on the gravity of the fault,
the system activates: -
-
-
-
Reduced fuel logic 1: Guarantees 75 % of the performance without limiting the engine speed.
Reduced fuel logic 2: Guarantees 50 % of the performance with the engine speed limited to 3,000 rpm.
Reduce fuel logic 3: Limits the engine speed to 2,000 rpm.
The system chooses the lowest of all values.
A correction depending on the coolant temperature is added to the flow limitation. This correction makes
it possible to reduce the mechanical stresses while the engine is warming up. The correction is
determined according to the coolant temperature, the engine speed and the time which has passed
since starting.
Superchager Flow Demand
The supercharge flow is calculated according to the engine speed and the coolant temperature. A
correction depending on the air temperature and the atmospheric pressure is made in order to increase
the supercharge flow during cold starts. It is possible to alter the supercharge flow value by adding a flow
offset with the aid of the diagnostic tool.
Page 405 of 1336

Coolant temp.
sensor
Refrigerant pres.
sensor
A/C compressor
ECU
D20DTFDSI 6 A/T
(ATF temp.)
Cooling fan module
HFM sensor
(Intake air
temperature)
Engine room
relay box
(8) Cooling fan control
a. Overview of cooling fan and A/C compressor
The cooling system maintains the engine temperature at an efficient level during all engine operating
conditions. The water pump draws the coolant from the radiator. The coolant then circulates through
water jackets in the engine block, the intake manifold, and the cylinder head. When the coolant reaches
the operating temperature of the thermostat, the thermostat opens. The coolant then goes back to the
radiator where it cools. The heat from automatic transaxle is also cooled down through the radiator by
circulating the oil through the oil pump.
There are two cooling fans (200W+150W) in D20DTF engine. ECU controls the electric cooling fans
with three cooling fan relays to improve the engine torque and air conditioning performance.
For details about A/C compressor and refrigerant pressure sensor, refer to Chapter "Air Conditioning
System" in "Body" section.
b. Components
Page 572 of 1336
6) Cooling Fan Control
(1) Overview of Cooling Fan and A/C Compressor
The cooling system maintains the engine temperature at an efficient level during all engine operating
conditions. The water pump draws the coolant from the radiator. The coolant then circulates through
water jackets in the engine block, the intake manifold, and the cylinder head. When the coolant reaches
the operating temperature of the thermostat, the thermostat opens. The coolant then goes back to the
radiator where it cools. The heat from automatic transaxle is also cooled down through the radiator by
circulating the oil through the oil pump. There are two cooling fans (180W+120W) in G20DF engine. ECU
controls the electric cooling fans with three cooling fan relays to improve the engine torque and air
conditioning performance.
(2) Components
Refrigerant pressure
sensorCoolant temperature
sensorG20DF Engine
ECURelay box in engine
compartment
A/C compressorCooling fan moduleT-MAP sensor
Page 1192 of 1336
1. OVERVIEW
The climate system in the vehicle is an air regulating system which keeps the indoor air pleasant through
the heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems. The air conditioning systems fall in to two
categories; FATC (Full Automatic Temperature Control), which is a temperature control device which
receives signals from various sensors (ambient temperature sensor, water temperature sensor, sun-
load sensor, AMP sensor) and control switches to control the blower motor and all kinds of actuator
(mode door actuator, mix door actuator, air source door actuator) through MICOM in the FATC,
therefore, the interior temperature of the vehicle is kept to the temperature which is set by a driver and
MTC (Manual Temperature Control), which controls all the actuator and blower motor by the driver.
Page 1196 of 1336
2) Interior Layout
Sun load sensor
It is mounted to the upper left-
hand of the instrument panel and
detects the sun-load enters to the
interior through the windshield
with a photo diode. Incar sensor
It is mounted to the rear of the
heater and A/C control panel
(with FATC) and detects the
interior air temperature drawn
through the senor inlet.Air conditioner module
It is mounted to inside of the
instrument panel and has the
evaporator core, heater core,
PTC heater and corresponding
actuator and different sensors.
Heater & A/C control assembly
With FATC With MTC
It falls in to two categories; FATC (Full Automatic Temperature Control) and MTC (Manual Temperature
Control), which controls the air conditioning system's operation.
Page 1210 of 1336
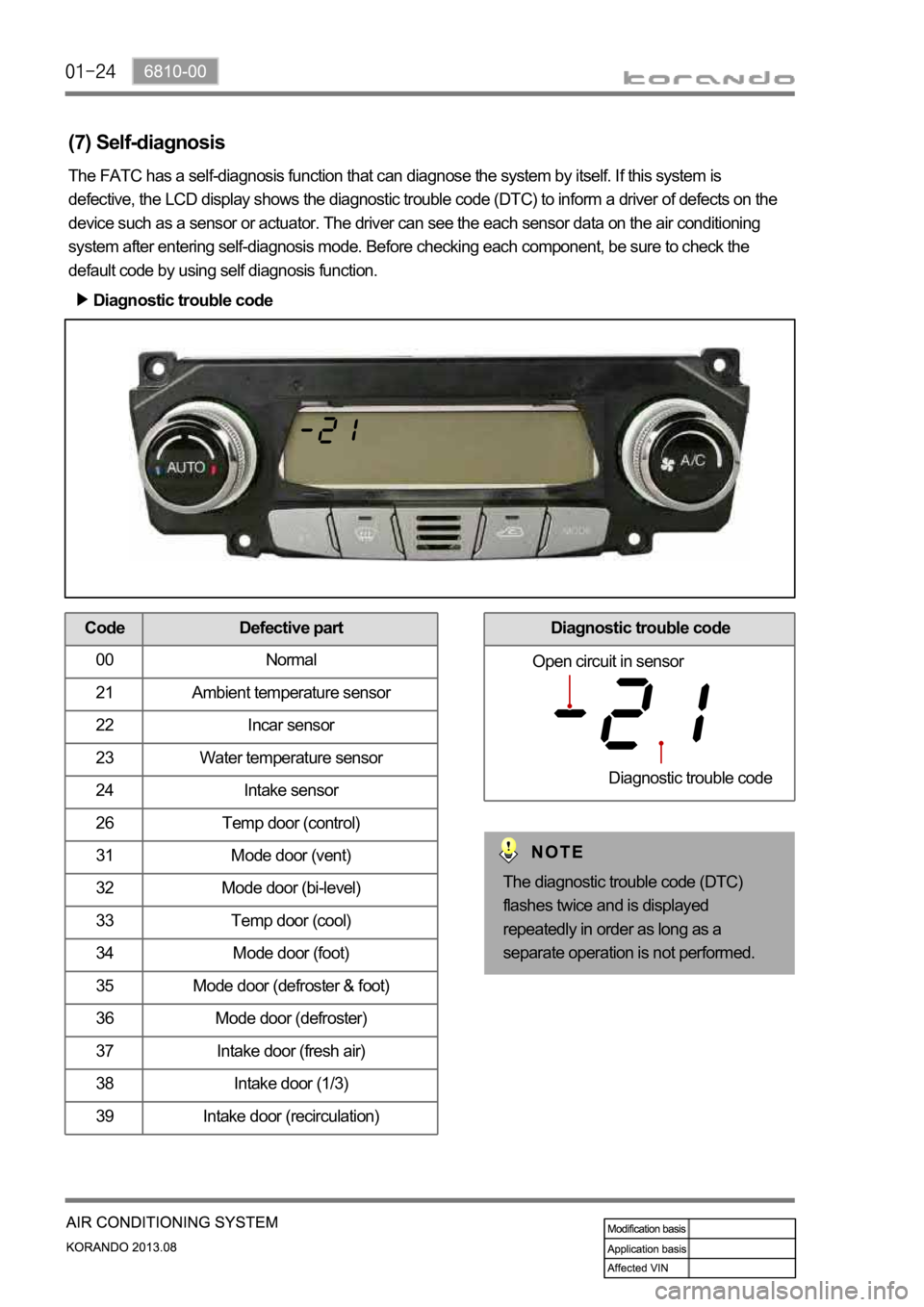
(7) Self-diagnosis
Diagnostic trouble code
The FATC has a self-diagnosis function that can diagnose the system by itself. If this system is
defective, the LCD display shows the diagnostic trouble code (DTC) to inform a driver of defects on the
device such as a sensor or actuator. The driver can see the each sensor data on the air conditioning
system after entering self-diagnosis mode. Before checking each component, be sure to check the
default code by using self diagnosis function.
The diagnostic trouble code (DTC)
flashes twice and is displayed
repeatedly in order as long as a
separate operation is not performed.
Code Defective part
00 Normal
21 Ambient temperature sensor
22 Incar sensor
23 Water temperature sensor
24 Intake sensor
26 Temp door (control)
31 Mode door (vent)
32 Mode door (bi-level)
33 Temp door (cool)
34 Mode door (foot)
35 Mode door (defroster & foot)
36 Mode door (defroster)
37 Intake door (fresh air)
38 Intake door (1/3)
39 Intake door (recirculation)Diagnostic trouble code
Open circuit in sensor
Diagnostic trouble code
Page 1212 of 1336
If the ON/OFF switch of the FATC is pressed for more than 5 seconds within 10 seconds after turning
the ignition key from the "OFF" position to the "ON" position, all the segments in LCD display comes on
for 3 seconds. 1.
The LCD display shows "2" and starts to check the sensor and actuator in the air conditioning system
automatically. 2.
3.
The self diagnosis ends when turning the ignition key from the "OFF" position to the "ON" position or
pressing the AUTO mode switch. 4.
Press for more
than 5 sec.
Segments comes on for 3 sec.
Page 1214 of 1336
4. MTC SYSTEM OPERATION PROCESS
1) Input/Output Factors
The MTC (Manual Temperature Control) system controls all the actuator and blower motor by the driver.
The heater and A/C control assembly with MTC has the dials and switches with the indicators so that the
driver can know the air conditioning system's operation.