Page 1145 of 1336
0000-00
1. SPECIFICATION (HPS)
Component Item Specification
Steering wheel Type 3-spoke
Outside diameter
Number of revolutions 3.09 rotations
Heated wire Simple ON/OFF
Gear box Type Rack and pinion
Gear ratio 46.94
Rack stroke
Steering angle Inner
Outer
Wheel alignment Toe-in
Oil pump Type Vane (removable pump and reservoir)
Maximum pressure
Displacement
Pulley diameter
Steering column Tilting angle Up + 2.0 deg
Down - 3.0 deg
Lower shaft Type Ball slip
Steering oil Oil type S-PSF 3
Oil reservoir capacity
Change interval EU (Diesel): Check and add at every 20,000
km
GEN (Diesel, Gasoline): Check and add at
every 15,000 km
Turning capability Min. turning radius 5.35 m
Page 1146 of 1336
2. TIGHTENING TORQUE
Item Tightening torque Remark
1. Power steering reservoir mounting bolt 8.8 to 13.7 Nm 12 mm x 2 EA
2. Power steering
pumpUpper mounting bolt/nut
13 mm x 1 EA
Lower mounting bolt
12 mm x 2 EA
3. Oil pipe Eye bolt (pump side) 53.9 to 63.7 Nm 22 mm
Steering gear box side nut 31.4 to 37.2 Nm 17 mm
4. Oil pipe bracket mounting nut 6.8 to 10.8 Nm 10 mm
5. Tie rod end lock nut 44.1 to 53.9 Nm 17 mm
6. Tie rod nut 63.7 to 78.4 Nm 22 mm
7. Lower shaft Lower mounting bolt
(gear box side)17.6 to 24.5 Nm 12 mm
Upper mounting bolt (column
side)17.6 to 24.5 Nm 12 mm
8. Column shaft Lower mounting bolt 19.6 to 24.5 Nm 12 mm
Upper mounting nut 19.6 to 24.5 Nm 12 mm
9. Steering wheel nut 39.2 to 49.1 Nm 22 mm
10. Loosened gear box mounting bolt/nut Left: 98.0 to 127.4 Nm 17 mm
Right: 88.3 to 107.9 Nm 17 mm
11. Heat shield mounting bolt 8.8 to 13.7 Nm 12 mm x 2 EA
Page 1147 of 1336
0000-00
3. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN HPS AND EPS
HPS EPS
1 Crankshaft pulley (DDU)
2 Auto tensioner
3 Tensioner pulley
4 Vacuum pump
5 A/C compressor pulley
6 Alternator pulley
7 Water pump pulley
8 No.1 idle pulley
9 No.2 idle pulley
10 Power steering pump -
HPS (Hydraulic Power Steering)EPS (Electric Power Steering)
Page 1148 of 1336

1. SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The power steering has been designed to make the wheel move more easily than in a manual steering
system. The hydraulic power assists the process utilizing hydraulic fluid. The fluid increases pressure in
the power steering pump and aids the movement of the steering mechanism.
The power steering system consists of pump, oil reservoir, rack and gear box.
The power steering pump is a vane type and delivers hydraulic pressure to operate the power steering
system.
The pressure relief valve in the pump controls the discharging pressure.
The rotary valve in the rack and the pinion gear directs the oil from the power steering pump to one side
of the rack piston. The integrated rack piston converts the hydraulic pressure to linear movement. The
operating force of the rack moves the wheels through the tie rod, the tie rod end and the steering knuckle.
Even though the hydraulic pressure cannot be generated, a driver can steer the vehicle without power
assist but it needs very high steering force.
In this case, the operating force of the steering wheel is conveyed to the pinion, and the movement of the
pinion moves the rack through the pinion gear combined to the rack gear.
Page 1149 of 1336
0000-00
Installation of steering
gear box and pipe
Installation of reservoir and hoseInstallation of power steering pump
and pipe
2. SYSTEM LAYOUT
The steering pump is driven by the engine power through a belt. This pump circulates the power steering
oil from the reservoir -> steering pump -> oil supply pipe -> steering gear box -> oil return pipe ->
reservoir to perform steering operations.
Return pipe
Supply pipe
Page 1150 of 1336
4610-00
1. SPECIFICATION
Unit Description Specification
System operationOperating type Motor driven power steering system
Operating temperature
Rated voltage 12 V
Rated current 85 A
Operating voltageNetwork 8 to 16 V
C-EPS ECU 8 to 16 V
Full Performance 10 to 16 V
MotorType 3-Phase BLAC (Brushless AC)
Rated current/voltage 85 A / 12 V (at idle 0.5 A)
Position sensor type Hall sensor type
Torque & angle sensorType Non-contact type
Steering columnOperating type Manual tilting & telescoping
Lower shaftType Sliding (Ball slip) type
Steering gearGear ratio 50.7 mm/rev
Rack stroke 145 mm
Maximum steering angleInner wheel
Outer wheel
Page 1152 of 1336
4610-00
3. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN HPS AND EPS
HPS EPS
1 Crankshaft pulley (DDU)
2 Auto tensioner
3 Tensioner pulley
4 Vacuum pump
5 A/C compressor pulley
6 Alternator pulley
7 Water pump pulley
8 No.1 idle pulley
9 No.2 idle pulley
10 Power steering pump -
HPS (Hydraulic Power Steering)EPS (Electric Power Steering)
Page 1153 of 1336
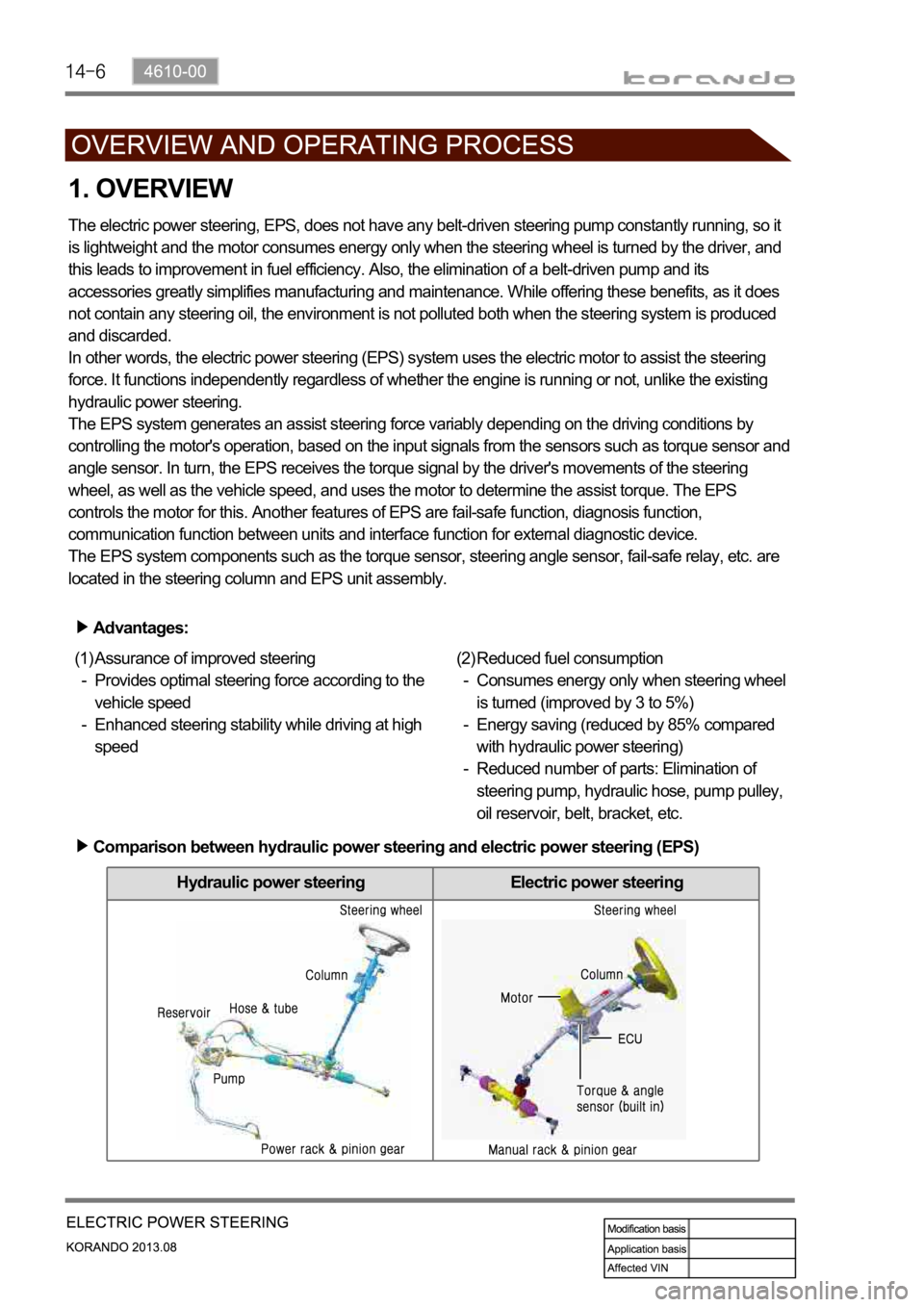
Hydraulic power steering Electric power steering
1. OVERVIEW
The electric power steering, EPS, does not have any belt-driven steering pump constantly running, so it
is lightweight and the motor consumes energy only when the steering wheel is turned by the driver, and
this leads to improvement in fuel efficiency. Also, the elimination of a belt-driven pump and its
accessories greatly simplifies manufacturing and maintenance. While offering these benefits, as it does
not contain any steering oil, the environment is not polluted both when the steering system is produced
and discarded.
In other words, the electric power steering (EPS) system uses the electric motor to assist the steering
force. It functions independently regardless of whether the engine is running or not, unlike the existing
hydraulic power steering.
The EPS system generates an assist steering force variably depending on the driving conditions by
controlling the motor's operation, based on the input signals from the sensors such as torque sensor and
angle sensor. In turn, the EPS receives the torque signal by the driver's movements of the steering
wheel, as well as the vehicle speed, and uses the motor to determine the assist torque. The EPS
controls the motor for this. Another features of EPS are fail-safe function, diagnosis function,
communication function between units and interface function for external diagnostic device.
The EPS system components such as the torque sensor, steering angle sensor, fail-safe relay, etc. are
located in the steering column and EPS unit assembly.
Advantages:
Assurance of improved steering
Provides optimal steering force according to the
vehicle speed
Enhanced steering stability while driving at high
speed (1)
-
-Reduced fuel consumption
Consumes energy only when steering wheel
is turned (improved by 3 to 5%)
Energy saving (reduced by 85% compared
with hydraulic power steering)
Reduced number of parts: Elimination of
steering pump, hydraulic hose, pump pulley,
oil reservoir, belt, bracket, etc. (2)
-
-
-
Comparison between hydraulic power steering and electric power steering (EPS)