Page 984 of 1336
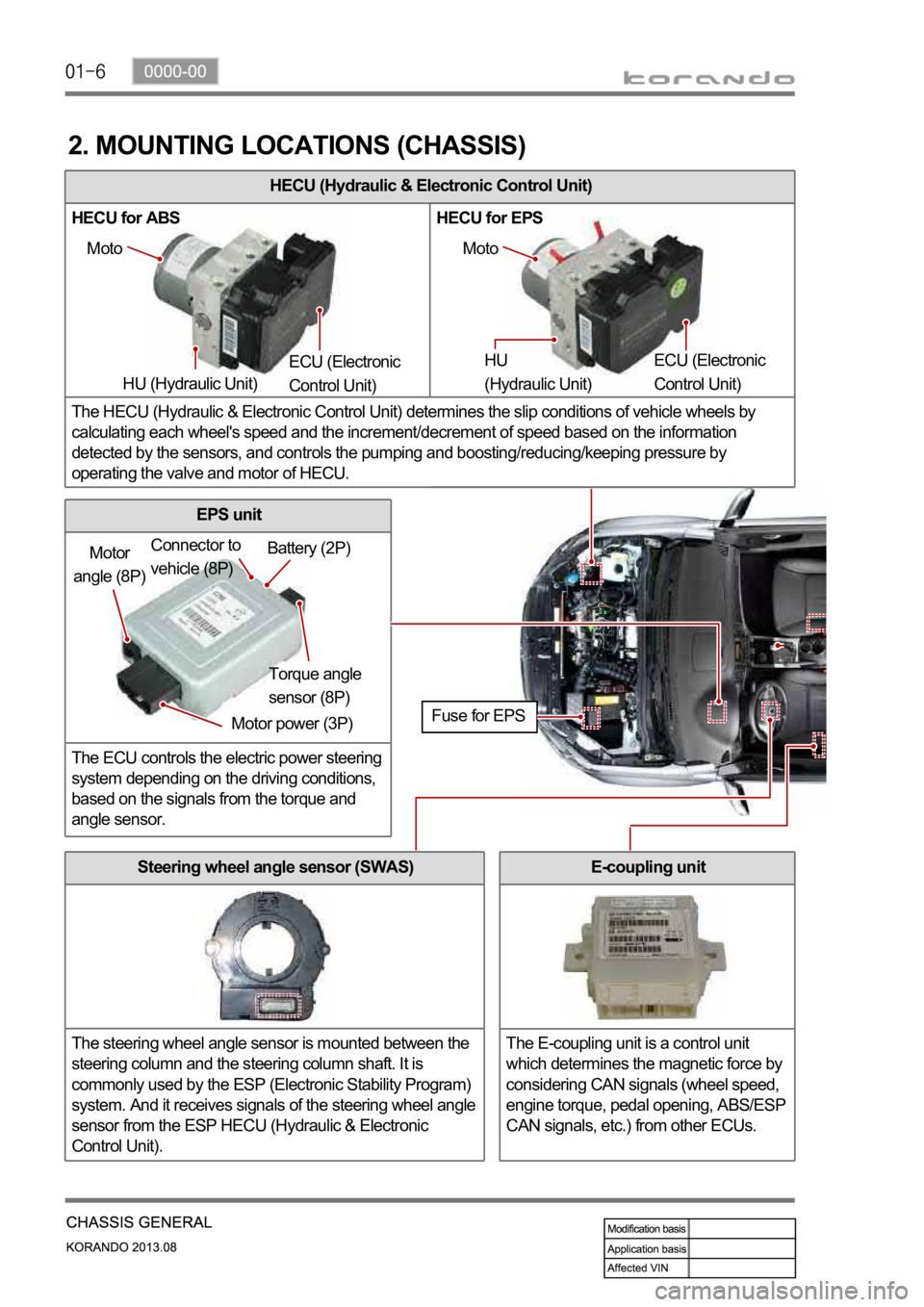
HECU (Hydraulic & Electronic Control Unit)
HECU for ABS HECU for EPS
The HECU (Hydraulic & Electronic Control Unit) determines the slip conditions of vehicle wheels by
calculating each wheel's speed and the increment/decrement of speed based on the information
detected by the sensors, and controls the pumping and boosting/reducing/keeping pressure by
operating the valve and motor of HECU.
2. MOUNTING LOCATIONS (CHASSIS)
Moto
HU (Hydraulic Unit) ECU (Electronic
Control Unit) Moto
HU
(Hydraulic Unit) ECU (Electronic
Control Unit)
Motor
angle (8P)
Motor power (3P)Torque angle
sensor (8P) Battery (2P) Connector to
vehicle (8P)
Fuse for EPS
Steering wheel angle sensor (SWAS)
The steering wheel angle sensor is mounted between the
steering column and the steering column shaft. It is
commonly used by the ESP (Electronic Stability Program)
system. And it receives signals of the steering wheel angle
sensor from the ESP HECU (Hydraulic & Electronic
Control Unit).
EPS unit
The ECU controls the electric power steering
system depending on the driving conditions,
based on the signals from the torque and
angle sensor.
E-coupling unit
The E-coupling unit is a control unit
which determines the magnetic force by
considering CAN signals (wheel speed,
engine torque, pedal opening, ABS/ESP
CAN signals, etc.) from other ECUs.
Page 985 of 1336

0000-00
TPMS ECU
The TPMS ECU is located to the rear bumper rail
under the vehicle. It outputs the tire pressure and
cluster, based on the wheel module information
and CAN data.
G-sensor(4WD, ABS)
For the vehicle with the ABS, a speed difference
between the wheels is not noticeable as all the wheels
are slipping during abrupt braking. Therefore, the
vehicle needs the speed information from other sensors
other than the wheel speed sensor. The longitudinal
acceleration sensor (G-sensor) is used for this case. It
controls the ABS by using the signals from the sensor
during abrupt braking and acceleration.
TCU unit
The transmission control unit (TCU) is installed
under the driver seat, and controls the
transmission. The TCU is operated by the ignition
power supply and receives and processes the
following information from the inner sensors
through CAN buses.
TGS Lever assembly
The TGS communicates with TCU
(Transmission Control Unit), ECU,
ESP HECU and instrument cluster
to let the driver select the desired
transmission gear and to maintain
the desired driving condition. Also,
the tip switch is installed on the
lever knob and the steering wheel
so that the driver select the gear
manually when the shift lever is in
"M".Sensor cluster
The sensor cluster is linked to
the sensors on the unit board
and CAN interface. And they
are housed in one case and
mounted to the body.
Page 995 of 1336
0000-00
H. Parking brake
M/T A/T
The parking brake is the mechanical device to
hold the vehicle. When pulling up the lever, the
parking brake cable between the lever and the
rear drum brake trailing shoe pulls the parking
brake lining to contact to drum.
E. Rear brake assembly
The disc brake for 4WD vehicle has the same
structure with the one for 2WD vehicle, but the
appearance and knuckle shape is different from
each other.
Caliper
G. Brake pedal
Disc
F. Parking brake
4WD and 2WD
Front side2WD Rear side
The wheel speed sensor for 4WD has the same
structure and mounting location with the one for
2WD vehicle. But the rear side wheel speed
sensor for 2WD vehicle has different sensor
appearance and mounting status because the
knuckle shape is different from the 4WD vehicle.
Page 997 of 1336
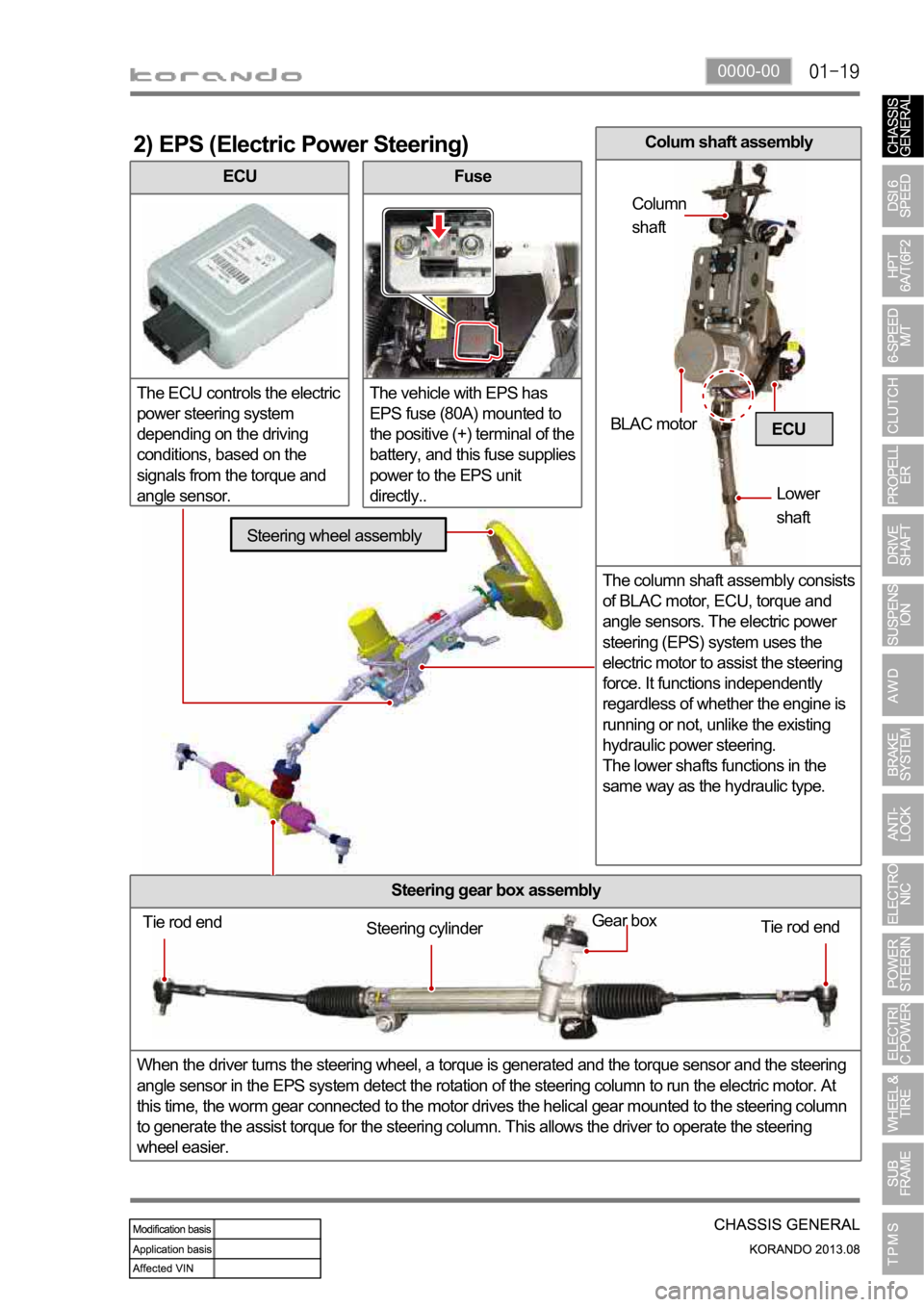
0000-00
ECU
The ECU controls the electric
power steering system
depending on the driving
conditions, based on the
signals from the torque and
angle sensor.
2) EPS (Electric Power Steering)
Fuse
The vehicle with EPS has
EPS fuse (80A) mounted to
the positive (+) terminal of the
battery, and this fuse supplies
power to the EPS unit
directly..
Steering gear box assembly
When the driver turns the steering wheel, a torque is generated and the torque sensor and the steering
angle sensor in the EPS system detect the rotation of the steering column to run the electric motor. At
this time, the worm gear connected to the motor drives the helical gear mounted to the steering column
to generate the assist torque for the steering column. This allows the driver to operate the steering
wheel easier.
ECU
Tie rod end
Tie rod end Gear boxSteering cylinder
Steering wheel assembly
BLAC motor
Lower
shaft Column
shaft
Colum shaft assembly
The column shaft assembly consists
of BLAC motor, ECU, torque and
angle sensors. The electric power
steering (EPS) system uses the
electric motor to assist the steering
force. It functions independently
regardless of whether the engine is
running or not, unlike the existing
hydraulic power steering.
The lower shafts functions in the
same way as the hydraulic type.
Page 1003 of 1336

3680-01
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
Automatic transaxle (M11)
The Model 11 six speed automatic transaxle is
available in two variants: four wheel drive and two
wheel drive.
Six forward speeds
One reverse gear
A toruqe converter with an integral converter
lock-up clutch with slip control capabilities
Electronic shift and pressure controls
A single planetary gear-set
A double planetary gear-set
One hydraulically controlled brake bands
Three multi-plate clutches
One multi plate brake
All hydraulic functions are directed by electronic
solenoids to control: -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Engagement feel
Shift feel
Shift scheduling
Modulated torque converter clutch
applications 1)
2)
3)
4) Inhibitor switch
Oil pan
Torque converter
TCU (located under driver's seat)
TCU is located under the driver's seat and controls
the transaxle operations.
TCU is activated and deactivated by the ignition
voltage, and connected to the transaxle through
pin 26 in connector.
TCU receives and uses the signals from sensors
and switches through CAN bus with analog and
digital types.
E-coupling unit
TCU
Page 1005 of 1336
3680-01
2. SPECIFICATIONS
1) Specifications
Type/Weight M11 6-speed automatic transaxle /
approx. 102 kg (including ATF)
TORQUE 400 Nm
Overall length / Center length 367 mm / 205 mm
Descriptions Specification
Gear ratio 1st gear 4.156
2nd gear 2.375
3rd gear 1.522
4th gear 1.144
5th gear 0.859
6th gear 0.676
Reverse gear 3.178
Oil Type Fuchs TITAN ATF 3292
Capacity approx. 7.5 L
Change interval EU: Inspect every 20,000 km or 12 months (But,
change every 60,000 km under severe condition)
General: Inspect every 15,000 km or 12 months
(But, change every 60,000 km under severe
condition)
Resistance of oil
temperature sensor-20
0
20
100
D
N
P
R
Inhibitor switch
Page 1008 of 1336

1. OVERVIEW
Engine power reaches the transaxle via a torque converter with integral converter lock-up clutch. The six
forward gears and one reverse gear are obtained from a single planetary set, followed by a double
planetary set. This type of gear-set arrangement is commonly known as Lepelletier type gear-set.
The Model M11 6 speed automatic transaxle is electronically controlled. The control system is
comprised of the following components:
External transaxle control unit (TCU)
Internal embedded memory module (EMM)
Input and output speed sensors
Valve body unit comprised of four ON/OFF solenoid valves and six variable bleed solenoids (VBS)
Torque converter -
-
-
-
-
TCU controls the oil pressure for various internal clutches and bands to select the gear. It also controls
the electronic elements, shift pressure and torque converter slip. If the system is defective, TCU provides
FMEC (Failure Mode Effect Control) to maintain the functionality of transaxle. This keeps the basic
function of transaxle (gear selection) even when there are failure in controls and power supply.
There are selector shaft position sensor (inhibitor switch) and oil temperature sensor in transaxle. In
manual mode, TCU receives the information from TGS (Transmission Gear Selector) through PCB
(Printed Circuit Board) when driver selects the manual shift mode. TCU communicates with other
electric control modules through CAN. In order to ensure a safe driving state and to prevent damage to
the automatic transmission, TCU switches to Limp-Home mode in the event of critical faults.
Page 1010 of 1336
2) Transaxle Cooling
The transaxle cooling system ensures rapid warm-up and constant operating temperature resulting in
reduced fuel consumption and refined shift quality.
It also includes a cooler by-pass within the hydraulic system to allow sufficient lubrication to the transaxle
drivetrain in the event of a blockage in the transaxle cooler.
3) Shift Strategy
Gear Change
Transaxle gear change is controlled by the
TCU. The TCU receives inputs from various
engine and vehicle sensors to select shift
schedules and to control the shift feel and
torque converter clutch (TCC) operation at each
gear change.
Coast down
Coast down down shifts occur at 0% pedal
when the vehicle is coasting down to a stop.
Torque Demand
Torque demand down shifts occur
(automatically) when the driver demand for
torque is greater than the engine can provide at
that gear ratio. If applied, the transaxle will
disengage the TCC to provide added
acceleration.