2013 SKODA ROOMSTER wheel
[x] Cancel search: wheelPage 105 of 219
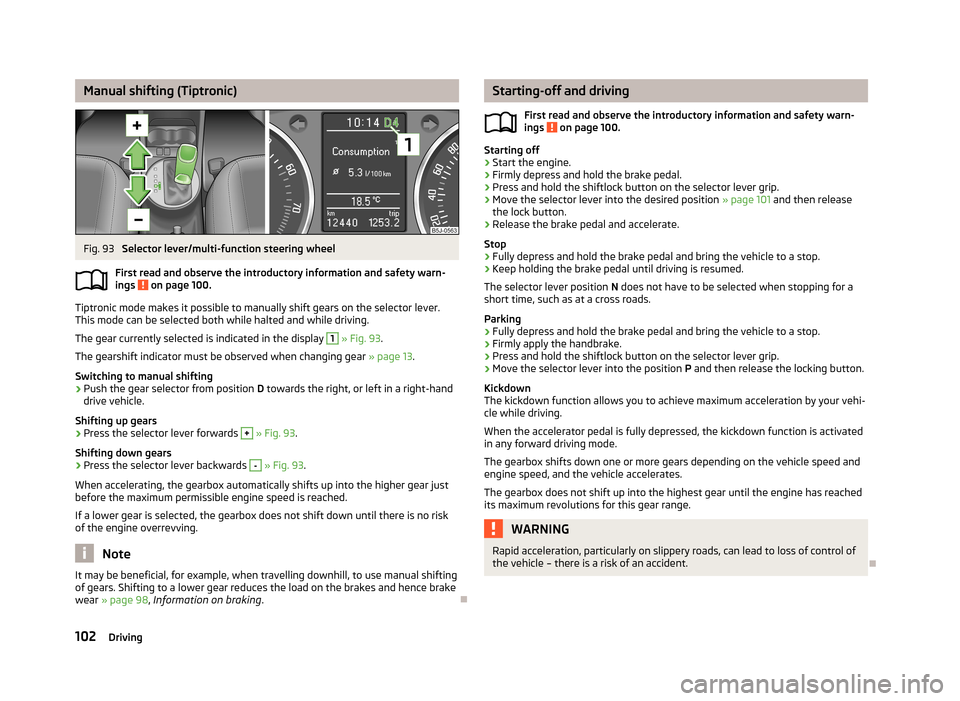
Manual shifting (Tiptronic)Fig. 93
Selector lever/multi-function steering wheel
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 100.
Tiptronic mode makes it possible to manually shift gears on the selector lever.
This mode can be selected both while halted and while driving.
The gear currently selected is indicated in the display
1
» Fig. 93 .
The gearshift indicator must be observed when changing gear » page 13.
Switching to manual shifting
›
Push the gear selector from position D towards the right, or left in a right-hand
drive vehicle.
Shifting up gears
›
Press the selector lever forwards
+
» Fig. 93 .
Shifting down gears
›
Press the selector lever backwards
-
» Fig. 93 .
When accelerating, the gearbox automatically shifts up into the higher gear just
before the maximum permissible engine speed is reached.
If a lower gear is selected, the gearbox does not shift down until there is no riskof the engine overrevving.
Note
It may be beneficial, for example, when travelling downhill, to use manual shifting
of gears. Shifting to a lower gear reduces the load on the brakes and hence brake
wear » page 98 , Information on braking .
Starting-off and driving
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 100.
Starting off
›
Start the engine.
›
Firmly depress and hold the brake pedal.
›
Press and hold the shiftlock button on the selector lever grip.
›
Move the selector lever into the desired position » page 101 and then release
the lock button.
›
Release the brake pedal and accelerate.
Stop
›
Fully depress and hold the brake pedal and bring the vehicle to a stop.
›
Keep holding the brake pedal until driving is resumed.
The selector lever position N does not have to be selected when stopping for a
short time, such as at a cross roads.
Parking
›
Fully depress and hold the brake pedal and bring the vehicle to a stop.
›
Firmly apply the handbrake.
›
Press and hold the shiftlock button on the selector lever grip.
›
Move the selector lever into the position P and then release the locking button.
Kickdown
The kickdown function allows you to achieve maximum acceleration by your vehi-
cle while driving.
When the accelerator pedal is fully depressed, the kickdown function is activated
in any forward driving mode.
The gearbox shifts down one or more gears depending on the vehicle speed and engine speed, and the vehicle accelerates.
The gearbox does not shift up into the highest gear until the engine has reached
its maximum revolutions for this gear range.
WARNINGRapid acceleration, particularly on slippery roads, can lead to loss of control of
the vehicle – there is a risk of an accident.
102Driving
Page 113 of 219
Assist systems
Brake assist systems
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
110
Antilock Braking System (ABS)
111
Traction Control System (ASR)
111
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)
111WARNING■ A lack of fuel can cause irregular engine running or cause the engine to shut
down. The brake assist systems would then fail to function – risk of accident!■
Adjust the speed and driving style to the current visibility, weather, road and
traffic conditions. The increased safety provided by the brake assist systems
must not tempt you to take safety risks – risk of accident!
■
In the event of an ABS fault, visit a specialist garage immediately. Adjust
your style of driving according to the damage to the ABS, as you will not know
the exact extent of the damage or the extent to which this is limiting the
braking efficiency.
CAUTION
■ All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres approved by the manufactur-
er to ensure the brake assist systems operate correctly.■
Changes to the vehicle (e.g. to the engine, brakes, chassis) can influence the
functionality of the brake assist systems » page 146, Services, modifications and
technical alterations .
■
If a fault occurs in the ABS system, the ESC, TCS and EDL will also fail to work.
An ABS fault is indicated with the warning light » page 24 .
Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 110.
The ESC system helps improve control of the vehicle in situations where it is be-
ing operated at its dynamic limits, such as a sudden change to the direction of
travel. Depending on the road surface conditions, the risk of skidding is reduced,
thereby improving the vehicle's driving stability .
The ESC system is automatically activated each time the ignition is switched on.
The direction which the driver wishes to take is determined based on the steering angle and the speed of the vehicle and is constantly compared with the actual
behaviour of the vehicle. In the event of deviations, such as the car beginning to
skid, the ESC system will automatically brake the appropriate wheel.
During an intervention of the system, the warning light
flashes in the instru-
ment cluster.
The following systems are integrated into the electronic stabilisation control
(ESC) :
› Antilock brake system (ABS),
› Traction control (TCS),
› Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)
› Hydraulic Brake Assist (HBA)
› Hill Hold Control (HHC).
The ESC system cannot be deactivated. The
» Fig. 99 on page 111 button can
only be used to deactivate the TCS. The
warning light comes on in the instru-
ment cluster when the TCS is deactivated.
In the event of an ESC fault, the ESC warning light illuminates in the instrumentcluster
» page 23 .
Hydraulic Brake Assist (HBA)
HBA increases the braking effect and helps to shorten the braking distance.
The HBA is activated by very quick operation of the brake pedal. In order to ach-
ieve the shortest possible braking distance, the brake pedal must be applied firm-
ly until the vehicle has come to a standstill.
The HBA function is automatically switched off when the brake pedal is released. The ABS is activated faster and more effectively with the intervention of the HBA.
110Driving
Page 114 of 219
Hill Hold Control (HHC)
When driving on slopes, HHC allows you to move your foot from the brake pedal
to the accelerator pedal without having to use the handbrake.
The system holds the brake pressure produced by the activation of the brakepedal for approx. 2 seconds after the brake pedal is released.
The brake pressure drops gradually the more you operate the accelerator pedal. Ifthe vehicle does not start off within 2 seconds, it starts to roll back.
HHC is active on slopes of >5 % when the driver door is closed. HHC is always only
active on slopes when in forward or reverse start off. When driving downhill, it is inactive.
Antilock Braking System (ABS)
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 110.
ABS prevents the wheels locking when braking. Thus helping the driver to main-
tain control of the vehicle.
The intervention of the ABS is noticeable from the pulsating movements of the
brake pedal which is accompanied by noises.
When the ABS system is active, do not brake periodically or reduce the pressure
on the brake pedal.
Traction Control System (ASR)
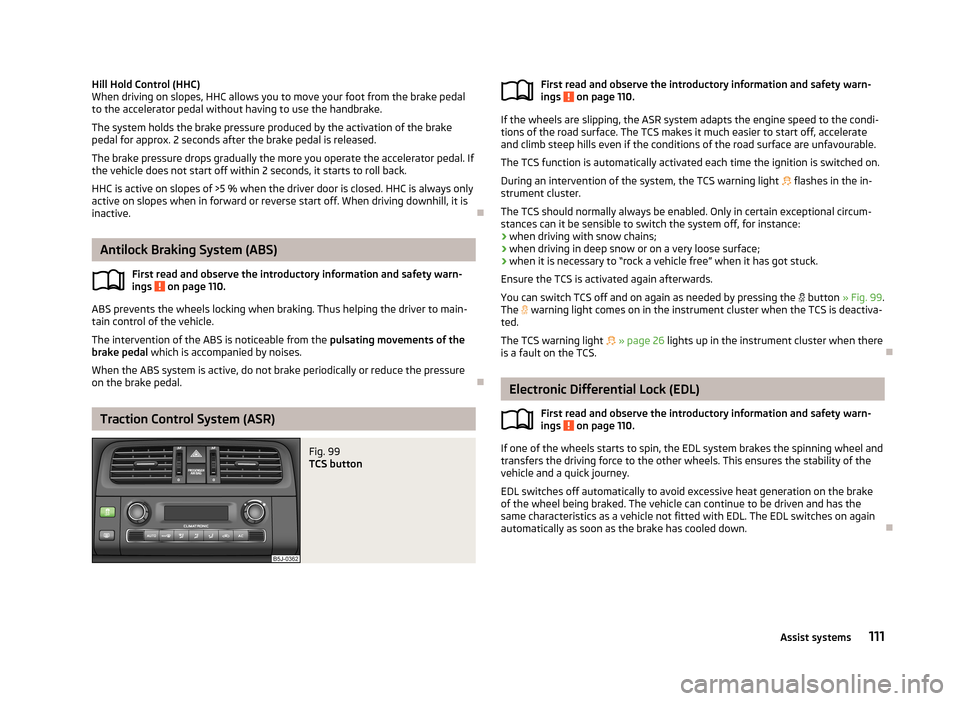
Fig. 99
TCS buttonFirst read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 110.
If the wheels are slipping, the ASR system adapts the engine speed to the condi-
tions of the road surface. The TCS makes it much easier to start off, accelerate
and climb steep hills even if the conditions of the road surface are unfavourable.
The TCS function is automatically activated each time the ignition is switched on.
During an intervention of the system, the TCS warning light flashes in the in-
strument cluster.
The TCS should normally always be enabled. Only in certain exceptional circum-
stances can it be sensible to switch the system off, for instance:
› when driving with snow chains;
› when driving in deep snow or on a very loose surface;
› when it is necessary to “rock a vehicle free” when it has got stuck.
Ensure the TCS is activated again afterwards.
You can switch TCS off and on again as needed by pressing the
button » Fig. 99 .
The
warning light comes on in the instrument cluster when the TCS is deactiva-
ted.
The TCS warning light
» page 26 lights up in the instrument cluster when there
is a fault on the TCS.
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 110.
If one of the wheels starts to spin, the EDL system brakes the spinning wheel and
transfers the driving force to the other wheels. This ensures the stability of the
vehicle and a quick journey.
EDL switches off automatically to avoid excessive heat generation on the brake of the wheel being braked. The vehicle can continue to be driven and has the
same characteristics as a vehicle not fitted with EDL. The EDL switches on again
automatically as soon as the brake has cooled down.
111Assist systems
Page 120 of 219
Towing a trailer
Towing device
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Description
117
Adjusting the ready position
118
Fitting the ball head
118
Check proper fitting
119
Removing the ball head
119
Use and care
120
If your vehicle has already been factory-fitted with towing equipment or is fitted
with towing equipment from ŠKODA Original Accessories, then it meets all of the technical requirements and national legal provisions for towing a trailer.
Your vehicle is fitted with a 13-pin power socket for the electrical connection be-tween the vehicle and trailer. If the trailer that is to be towed has a 7-pin connec-
tor , you can use a suitable adapter from ŠKODA Original Accessories.
The maximum trailer drawbar load is 50 kg/h.
WARNING■
Check that the ball head is seated correctly and is secured in the mounting
recess before starting any journey.■
Do not use the ball head if it is not correctly inserted in the mounting recess.
■
Do not use the towing equipment if it is damaged or incomplete.
■
Do not modify or adapt the towing equipment in any way.
■
Never release the ball head while the trailer is still coupled.
CAUTION
Take care with the ball head to avoid damaging the paintwork on the bumper.
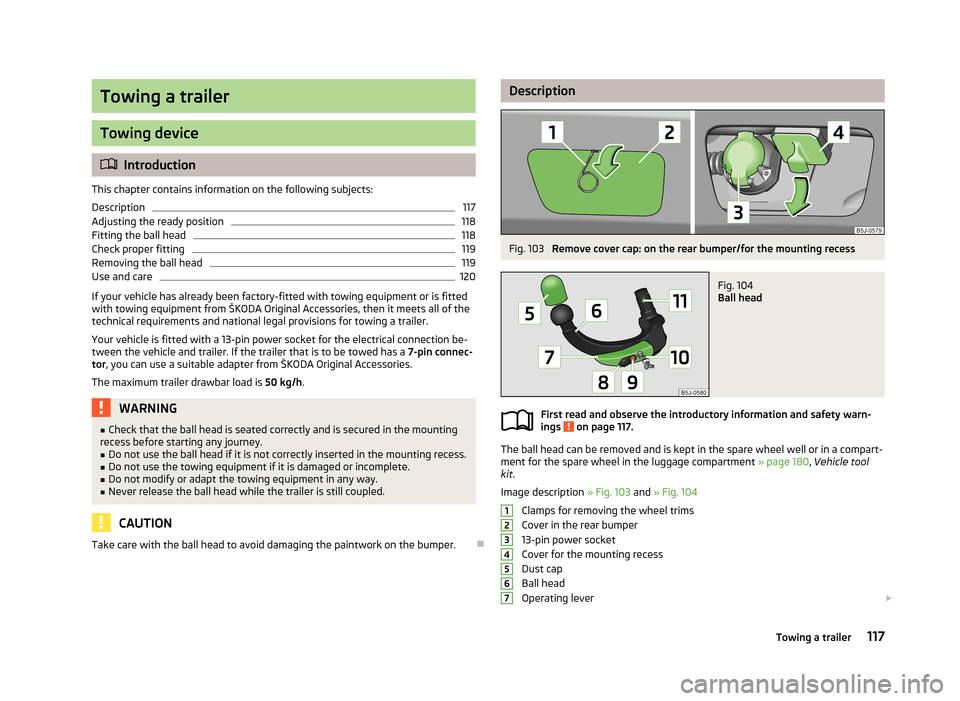
DescriptionFig. 103
Remove cover cap: on the rear bumper/for the mounting recess
Fig. 104
Ball head
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings on page 117.
The ball head can be removed and is kept in the spare wheel well or in a compart- ment for the spare wheel in the luggage compartment » page 180, Vehicle tool
kit .
Image description » Fig. 103 and » Fig. 104
Clamps for removing the wheel trims
Cover in the rear bumper
13-pin power socket
Cover for the mounting recess
Dust cap
Ball head
Operating lever
1234567117Towing a trailer
Page 121 of 219
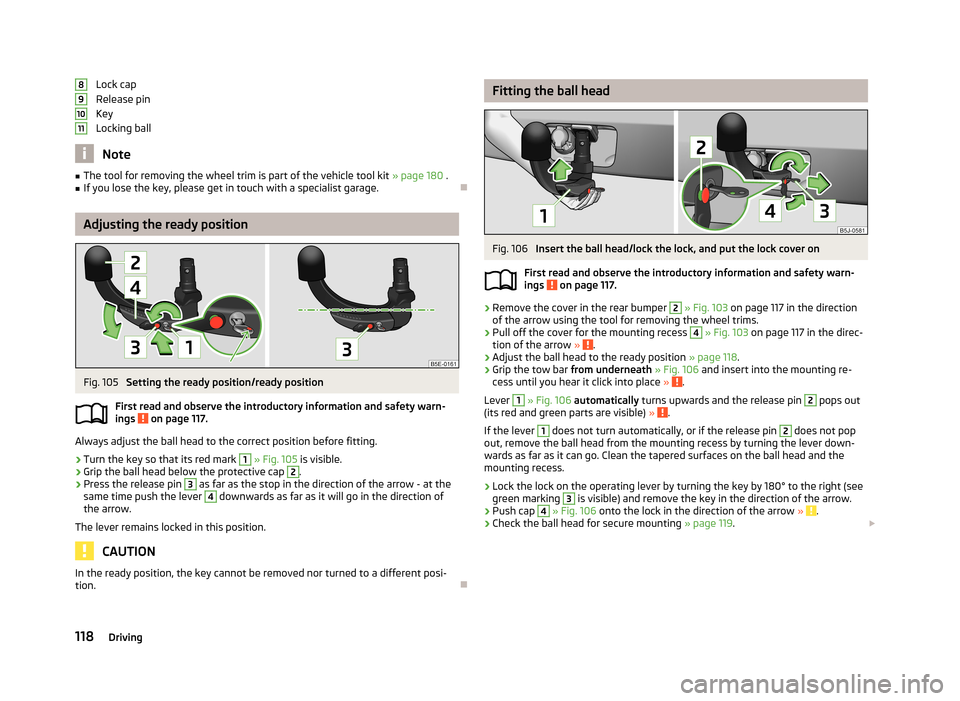
Lock cap
Release pin
Key
Locking ball
Note
■ The tool for removing the wheel trim is part of the vehicle tool kit » page 180 .■If you lose the key, please get in touch with a specialist garage.
Adjusting the ready position
Fig. 105
Setting the ready position/ready position
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn- ings
on page 117.
Always adjust the ball head to the correct position before fitting.
›
Turn the key so that its red mark
1
» Fig. 105 is visible.
›
Grip the ball head below the protective cap
2
.
›
Press the release pin
3
as far as the stop in the direction of the arrow - at the
same time push the lever
4
downwards as far as it will go in the direction of
the arrow.
The lever remains locked in this position.
CAUTION
In the ready position, the key cannot be removed nor turned to a different posi-
tion.891011
Fitting the ball headFig. 106
Insert the ball head/lock the lock, and put the lock cover on
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 117.
›
Remove the cover in the rear bumper
2
» Fig. 103 on page 117 in the direction
of the arrow using the tool for removing the wheel trims.
›
Pull off the cover for the mounting recess
4
» Fig. 103 on page 117 in the direc-
tion of the arrow » .
›
Adjust the ball head to the ready position » page 118.
›
Grip the tow bar from underneath » Fig. 106 and insert into the mounting re-
cess until you hear it click into place » .
Lever
1
» Fig. 106 automatically turns upwards and the release pin
2
pops out
(its red and green parts are visible) » .
If the lever
1
does not turn automatically, or if the release pin
2
does not pop
out, remove the ball head from the mounting recess by turning the lever down-
wards as far as it can go. Clean the tapered surfaces on the ball head and the
mounting recess.
›
Lock the lock on the operating lever by turning the key by 180° to the right (see
green marking
3
is visible) and remove the key in the direction of the arrow.
›
Push cap
4
» Fig. 106 onto the lock in the direction of the arrow » .
›
Check the ball head for secure mounting » page 119.
118Driving
Page 124 of 219

The distribution of the weight is very poor if your vehicle is unladen and the trail-
er is laden. Maintain a particularly low speed if you cannot avoid driving with this
combination.
Tyre pressure
Correct the tyre inflation pressure on your vehicle for a “full load” » page 173,
Service life of tyres .
Trailer load
The permissible trailer load must not be exceeded under any circumstan- ces » page 199 , Technical data .
The trailer loads specified apply only to altitudes up to 1 000 metres above mean
sea level.
The engine output falls as altitude increases, as does the ability to climb. There-
fore, for every additional 1000 m in height (or part), the maximum permissible
towed weight must be reduced by 10 %.
The towed weight comprises the actual weights of the (loaded) towing vehicleand the (loaded) trailer.
The trailer and drawbar load information on the type plate of the towing equip-
ment are merely test data for the towing equipment. The vehicle-specific values
are detailed in the vehicle documents.WARNING■ Do not exceed the maximum permissible axle and drawbar load and the
maximum permissible total or towed weight of the vehicle and the trailer –
there is the risk of an accident and serious injury.■
Slipping loads can significantly affect the stability and safety of the vehicle/
trailer combination – there is the risk of an accident and serious injury.
Towing a trailer
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 120.
Exterior mirrors
You have to have additional exterior mirrors fitted if you are not able to see the
traffic behind the trailer with the standard rear-view mirrors. The national legal requirements must be observed.
Headlights
The front of the vehicle can be lifted when a trailer is being towed and the head- lights can dazzle other road users.
Adjust the headlight setting on the headlight range control » page 42, Headlight
beam adjustment .
Driving speed
For safety reasons, do not drive faster than 80 km/h when towing a trailer.
Immediately reduce your speed as soon as even the slightest swaying of the trail- er is detected. Never attempt to stop the trailer from “swaying” by accelerating.
Brakes
Apply the brakes in good time! If the trailer is fitted with a trailer brake, apply the
brakes gently at first, then brake firmly. This will avoid brake jolts resulting from
the trailer wheels locking.
On downhill sections shift down a gear in good time to also use the engine as a
brake.
Engine overheating
The speed must be reduced immediately if the needle for the coolant tempera-
ture gauge moves into the right-hand area or the red area of the scale.
Stop and switch off the engine if the warning light
in the instrument cluster
starts to flash. Wait a few minutes and check the level of coolant » page 166,
Checking the coolant level .
The following guidelines must be observed » page 22,
Coolant .
The coolant temperature can be reduced by switching on the heating.WARNING■ Adapt your speed to the conditions of the road surface and to the traffic sit-
uation.■
Improper or incorrectly connected electric cables can energise the trailer and
cause functional faults to the vehicle's entire electrical system as well as acci-
dents and severe injuries.
■
Work on the electrical system must only be carried out by specialist garages.
■
Never directly connect the trailer's electrical system with the electrical con-
nections for the tail lights or other current sources.
121Towing a trailer
Page 127 of 219

What influences the driving safety?First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 123.
The driver is fully responsible for himself and his occupants. If your driving safety is effected, you place yourself and the oncoming traffic at risk.
The following guidelines must therefore be observed. › Do not become distracted from concentrating on the traffic situation, e.g. by
your passengers or mobile phone calls.
› Never drive when your driving ability is impaired, e.g. due to medication, alcohol
or drugs.
› Keep to the traffic regulations and the permissible speed limit.
› Always adjust the driving speed to the road, traffic and weather conditions.
› Take regular breaks on long journeys – at least every two hours.
Correct seated position
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Correct seated position for the driver
125
Correct seated position for the front passenger
125
Correct seated position for the passengers in the rear seats
125
Examples of incorrect seated positions
125WARNINGGeneral information■The front seats and head restraints must be adjusted to match the body
size at all times and the seat belt must always be fastened properly to provide the most effective levels of protection to the passengers.■
If the occupant adopts an incorrect seated position, he is exposed to life-
threatening injuries, in case he is hit by a deployed airbag.
■
If the occupants on the rear seats are not sitting upright, the risk of injury is
increased due to incorrect routing of the seat belt.
■
The seat backrests must not be tilted too far back when driving, as this will
impair the function of the seat belts and of the airbag system – risk of injury!
WARNINGInformation for the driver■Always assume the correct seated position before setting off and do not
change this position while driving. Also advise your passengers to adopt the
correct seated position and not to change this position while the car is mov-
ing.■
Maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the steering wheel. Not maintaining
this minimum distance will mean that the airbag system will not be able to
properly protect you - hazard!
■
When driving, hold the steering wheel with both hands firmly on the outer
edge in the 9 o'clock and 3 o'clock position. Never hold the steering wheel in
the 12 o'clock position or in any other way (e.g. in the middle or inner edge of
the steering wheel). In such cases, you could severely injure the arms, hands
and head when the driver airbag is deployed.
■
Ensure that there are no objects in the driver's footwell, as these may get
caught in the pedal apparatus when driving or braking. You would then no longer be able to operate the clutch, brake or acceleration pedals.
WARNINGInformation for the front seat passenger■Maintain a distance of at least 25 cm from the dash panel. Not maintaining
this minimum distance will mean that the airbag system will not be able to
properly protect you - there is a risk that you could be killed.■
Always keep your feet in the footwell when the car is being driven - never
place your feet on the instrument panel, out of the window or on the seats.
You will be exposed to increased risk of injury if it becomes necessary to apply
the brakes or in the event of an accident. You may suffer fatal injuries when
an airbag is deployed if you have adopted an incorrect seating position.
124Safety
Page 128 of 219
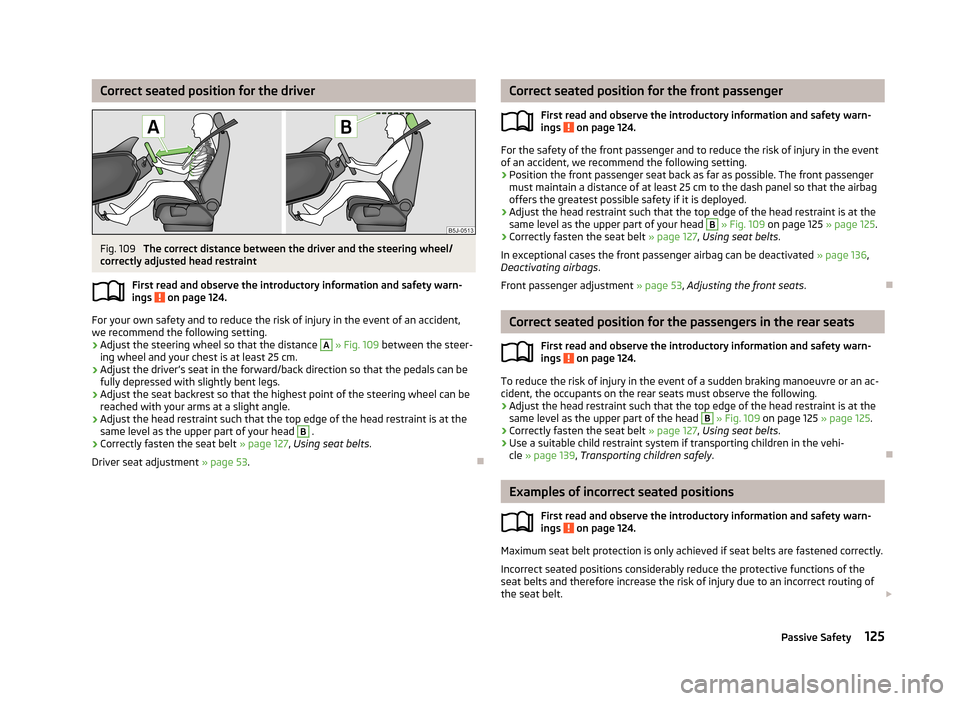
Correct seated position for the driverFig. 109
The correct distance between the driver and the steering wheel/
correctly adjusted head restraint
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 124.
For your own safety and to reduce the risk of injury in the event of an accident,
we recommend the following setting.
› Adjust the steering wheel so that the distance
A
» Fig. 109 between the steer-
ing wheel and your chest is at least 25 cm.
› Adjust the driver’s seat in the forward/back direction so that the pedals can be
fully depressed with slightly bent legs.
› Adjust the seat backrest so that the highest point of the steering wheel can be
reached with your arms at a slight angle.
› Adjust the head restraint such that the top edge of the head restraint is at the
same level as the upper part of your head
B
.
› Correctly fasten the seat belt
» page 127, Using seat belts .
Driver seat adjustment » page 53.
Correct seated position for the front passenger
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-ings
on page 124.
For the safety of the front passenger and to reduce the risk of injury in the event
of an accident, we recommend the following setting.
› Position the front passenger seat back as far as possible. The front passenger
must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the dash panel so that the airbag
offers the greatest possible safety if it is deployed.
› Adjust the head restraint such that the top edge of the head restraint is at the
same level as the upper part of your head
B
» Fig. 109 on page 125 » page 125.
› Correctly fasten the seat belt
» page 127, Using seat belts .
In exceptional cases the front passenger airbag can be deactivated » page 136,
Deactivating airbags .
Front passenger adjustment » page 53, Adjusting the front seats .
Correct seated position for the passengers in the rear seats
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 124.
To reduce the risk of injury in the event of a sudden braking manoeuvre or an ac-
cident, the occupants on the rear seats must observe the following.
› Adjust the head restraint such that the top edge of the head restraint is at the
same level as the upper part of the head
B
» Fig. 109 on page 125 » page 125.
› Correctly fasten the seat belt
» page 127, Using seat belts .
› Use a suitable child restraint system if transporting children in the vehi-
cle » page 139 , Transporting children safely .
Examples of incorrect seated positions
First read and observe the introductory information and safety warn-
ings
on page 124.
Maximum seat belt protection is only achieved if seat belts are fastened correctly.
Incorrect seated positions considerably reduce the protective functions of the
seat belts and therefore increase the risk of injury due to an incorrect routing of
the seat belt.
125Passive Safety