2013 Seat Mii fuel cap
[x] Cancel search: fuel capPage 139 of 306

137
Starting, changing gears, parking
To park the vehicle
Complete operations only in the sequence given.
● Park the vehicle on a suitable surface ⇒
.
● Press and hold the brake pedal until the vehicle comes to a standstill.
● Apply the handbrake firmly ⇒ page 136.
● For an automatic gearbox, move the selector lever to position P.
● Switch off the engine and release the brake pedal.
● Remove the key from the ignition.
● If necessary, turn the steering wheel slightly to lock the steering.
● With a manual gearbox, engage the 1st gear on flat ground and slopes,
or even the reverse gear on hills, and release the clutch pedal.
● Ensure that all passengers leave the vehicle, especially children.
● When leaving the vehicle, take all keys with you.
● Lock the vehicle.
Additional information for steep slopes and hills
Before switching off the engine, rotate the steering wheel so that if the vehi-
cle should move then it will be held by the kerb.
● On slopes, turn the front wheels so that they are against the edge of the
kerb.
● Uphill, turn the wheels towards the centre of the road.
WARNING
The components of the exhaust system reach very high temperatures.
This could cause a fire and considerable damage.
● Always park your vehicle so that no part of the exhaust system can
come in contact with flammable materials (such as wood, leaves, spilled
fuel, dried grass, etc).
CAUTION
● Special care should be taken when parking in areas with high kerbs or
fixed barriers. Objects protruding from the ground may damage the bumper
or other parts of the vehicle during manoeuvres. To avoid damage, stop be-
fore the wheels touched the barrier or kerb.
● Special attention is required when driving through entrances, over
ramps, kerbs or other objects. The vehicle underbody, bumpers, mudguards
and running gear, and the engine and exhaust system could be damaged as
you drive over these objects.
Information about the brakes
For the first 200 to 300 km (120 to 190 mph), the new brake pads have not
yet reached their maximum braking capacity, and need to be “run in” first
⇒
. The slightly reduced braking effect can be compensated for by in-
creasing pressure on the brake pedal. While running in, the full braking dis-
tance or emergency braking distance is larger then when the brake pads
have been run in. While running in, avoid full power braking or situations
requiring braking performance. For example, in heavy traffic.
The rate of wear of the brake pads depends to a great extent on the condi-
tions in which the vehicle is used and the way the vehicle is driven. If the
vehicle is used frequently in city traffic or for short trips or driven sport style,
visit a specialised workshop regularly, more frequently than advised in the
Maintenance Programme, to have the bake pads checked.
If you drive with wet brakes, for example, after crossing areas of water, in
heavy rainfall or even after washing the car, the effect of the brakes is less-
ened as the brake discs are wet or even frozen (in winter). At higher speed,
dry the brakes as quickly as possible by braking gently several times. Only
do this without endangering vehicles behind you or any other road users
⇒
.
Vehicle diagramPrior to a journey...While drivingCare, cleaning and mainte-
nanceIf and whenTechnical specifications
Page 173 of 306

171
At the filling station
At the filling station Filling the tank
Introduction
The fuel tank flap is on the rear right of the vehicle.
Additional information and warnings:
● Exterior detail ⇒ page 6
● Fuel ⇒ page 177
● Working in the engine compartment ⇒ page 180
WARNING
Refuelling or handling fuel carelessly can cause an explosion or fire re-
sulting in serious burns and injuries.
● Always make sure that you correctly close the fuel cap to avoid evap-
oration and fuel spillage.
● Fuels are highly explosive and inflammable substances that can
cause serious burns and injuries.
● Fuel could leak out or be spilt if the engine is not switched off or if the
filler fuel nozzle is not fully inserted into the tank filler neck when refuel-
ling. This could lead to a fire, explosion and severe injuries.
● When refuelling, turn off the engine and turn off the ignition for safe-
ty reasons.
● Always turn off mobile telephones, radio apparatus and other radio
wave emitting equipment before refuelling. Electromagnetic waves could
cause sparks and lead to a fire.
WARNING (Continued)
● Never enter the vehicle while refuelling. If it is absolutely necessary
to enter the vehicle, close the door and touch a metal surface before
touching the filler nozzle again. This will prevent the generation of static
electricity. Sparks could cause a fire when refuelling.
● Never handle fuel close to open flames, sparks or objects with slow
combustion (e.g. cigarettes).
● Avoid static electricity and electro-magnetic radiation when refuel-
ling.
● Observe the safety regulations of the service station.
● Never spill fuel on the vehicle or in the luggage compartment.
WARNING
For safety reasons, SEAT does not recommend carrying a spare fuel canis-
ter in the vehicle. Fuel could be spilled and catch fire, above all in case of
an accident and this applies to a full container as well as empty contain-
ers. This could lead to explosions, fires and injuries.
● Observe the following if you exceptionally have to carry fuel in a can-
ister:
–Never place a fuel container, to fill it, inside the vehicle or on the
vehicle, for example, in the luggage compartment. Filling in these cir-
cumstances could create an electrostatic charge and spark that could
ignite fuel fumes.
– Always place the canister on the ground to fill it.
– Insert the fuel nozzle into the neck of the canister as far as possi-
ble.
Vehicle diagramPrior to a journey...While drivingCare, cleaning and mainte-
nanceIf and whenTechnical specifications
Page 176 of 306

174At the filling station
Refuelling with petrol
Fig. 110 Open tank flap
with tank cap attached to
the holder
Before refuelling, always turn off the engine, the ignition, mobile tele-
phones, auxiliary heating and keep them off during refuelling.
Opening the fuel tank cap
● The tank flap is at the rear of the vehicle on the right.
● Pull the rear zone of the fuel tank flap to open.
● Unfold the key shaft if necessary
⇒ page 28.
● Insert the vehicle key into the lock cylinder of the fuel tank plug and turn
the key in an anticlockwise direction.
● Take out the fuel tank plug by turning it in an anticlockwise direction
and rest it on the upper part of the fuel tank flap ⇒ Fig. 110.
Refuelling
The correct petrol type for the vehicle is located on a sticker inside the fuel
tank flap ⇒ page 177. ●
If the automatic filler nozzle is operated correctly, it will switch itself off
as soon as the fuel tank is full ⇒
.
● Do not continue to refuel if it is turned off! Otherwise, this will fill the ex-
pansion chamber and fuel may leak out if the ambient conditions are warm.
Closing the fuel tank cap
● Screw on the fuel tank filler plug in a clockwise direction until it is fully
inserted with a click.
● Insert the vehicle key into the lock cylinder of the fuel tank plug, turn the
key in a clockwise direction and remove the key.
● Press the tank flap until you hear it click into place. The tank flap must
be flush with the body contour.
WARNING
Do not continue refilling once the fuel nozzle has switched itself off. The
fuel tank may be filled too much. As a result, fuel may spurt out and spill.
This could lead to a fire, explosion and severe injuries.
CAUTION
● Always remove any fuel spilled anywhere on the vehicle to avoid dam-
age to the wheel housing, the tyre and vehicle paintwork.
For the sake of the environment
Fuels can contaminate the environment. Collect any spilt service fluids and
allow a professional to dispose of them.
Page 177 of 306

175
At the filling station
Refuelling with natural gas
Fig. 111 Tank flap open:
gas filler mouth 1, filler
mouth retainer 2
Before refuelling, the engine and the ignition, mobile telephone and heat-
ing must be switched off separately
⇒ .
It is also essential to carefully read the instructions for the natural gas
pump.
The vehicle is not prepared for refuelling with liquefied natural gas (LNG)
⇒
. Before refuelling with natural gas, make sure to add the appropriate
type of fuel.
Opening the fuel tank cap
The natural gas filler mouth is behind the fuel tank cap, next to the petrol
filler mouth.
● Unlock the vehicle with the key or with the central locking button situ-
ated on the driver door ⇒ page 34.
● Press on the rear area of the flap and open it. Refuelling
Problem: If the ambient temperature is very high, the natural gas pump pro-
tection against overheating disconnects this automatically.
●
Remove the plug from the gas filler mouth ⇒ Fig. 111 1
.
● Connect the pump filling nozzle to the gas filler mouth.
● The fuel tank will be full when the pump compressor automatically cuts
the supply.
● If you wish to finish refuelling in advance, press the button on the pump
to stop the flow.
Closing the fuel tank cap
● Check that the gas filler mouth retainer 2
is not trapped with the filler
nozzle. If necessary, place it in the filler mouth again.
● Insert the plug in the filler mouth.
● Close the tank flap. Make sure you hear it click into place.
WARNING
Natural gas is a highly explosive, easily flammable substance. Incorrect
handling of the natural gas can cause accidents serious burns and other
injuries.
● Before refuelling with natural gas, the filling mouth must be correctly
engaged. If you can smell gas, stop refuelling immediately.
WARNING
The vehicle is not prepared to use liquefied natural gas (LNG) and this
fuel must not be added under any circumstances. Liquefied natural gas
can cause the natural gas tank to explode resulting in serious injury.
Vehicle diagramPrior to a journey...While drivingCare, cleaning and mainte-
nanceIf and whenTechnical specifications
Page 213 of 306

211
Vehicle care and maintenance
About your tyres and wheels
Fig. 123 Diagram for
changing wheels
The tyres of a vehicle are the components which are subjected to most
stress and are the most underestimated. Tyres are very important, as the
support offered by their narrow surface is the only point of contact between
the vehicle and the road.
The service life of tyres is dependent on tyre pressure, driving style, the care
they receive and the correct fitting.
The tyres and wheel rims are an essential part of the vehicle's design. The
tyres and rims approved by SEAT are specially matched to the characteris-
tics of the vehicle and our critical to good road holding and safe handling.
Avoiding damage to tyres and wheels
● If you have to drive over a kerb or similar obstacle, drive very slowly and
as near as possible at a right angle to the kerb.
● Inspect the tyres regularly for damage (punctures, cuts, cracks, dents).
● Remove any foreign bodies found on the outside of the tread provided
they have not passed through the wall of the tyre
⇒ page 216.
● The instructions for tyre control systems should always be observed. ●
Replace damaged or worn tyres as soon as possible ⇒ page 216.
● Regularly check tyres for non-visible damage ⇒ page 216.
● Never exceed the maximum permitted speed or loads specified for the
type of tyre fitted on your vehicle ⇒ page 218.
● Do not allow tyres (including the spare wheel) to come into contact with
aggressive substances, grease, oil, fuel or brake fluid ⇒
.
● Lost valve caps should be replaced immediately.
Tyres with directional tread pattern
Tyres with directional tread pattern have been designed to operate best
when rotating in only one direction. An arrow on the tyre sidewall indicates
the direction of rotation on tyres with directional tread ⇒ page 218. Always
observe the direction of rotation indicated when mounting the wheel. This
guarantees optimum grip and helps to avoid aquaplaning, excessive noise
and wear.
If the tyre is mounted in the opposite direction of rotation, drive with ex-
treme caution, as the tyre is no longer being used correctly. This is of partic-
ular importance when the road surface is wet. Change the tyre as soon as
possible or remount it with the correct direction of rotation.
Interchanging tyres
To ensure that the wear is equal on all tyres the wheels should be changed
round from time to time according to the system ⇒ Fig. 123. The useful life
of all the tyres will then be about the same time.
SEAT recommends you take the vehicle to a specialised workshop to have
the tyres changed.
Tyres that are over 6 years old
Tyres are subject to an ageing process as a result of physical and chemical
processes. This may affect their performance. Tyres which are stored for
long periods of time without being used, harden and become more fragile
than tyres which are in constant use.
SEAT recommends that tyres over six years old are replaced with new tyres.
This also applies to tyres (including the spare wheel) which appear to be in
Vehicle diagramPrior to a journey...While drivingCare, cleaning and mainte-
nanceIf and whenTechnical specifications
Page 216 of 306
214Vehicle care and maintenance
Note
If you use tyres that are approved by SEAT, you can be sure that the true tyre
dimensions will be correct for your vehicle. For other tyre models, the tyre
vendor should provide the manufacturer's certificate with the tyre, indicat-
ing that this type of tyre is suitable for your vehicle. This certificate should
always be carried with the vehicle.
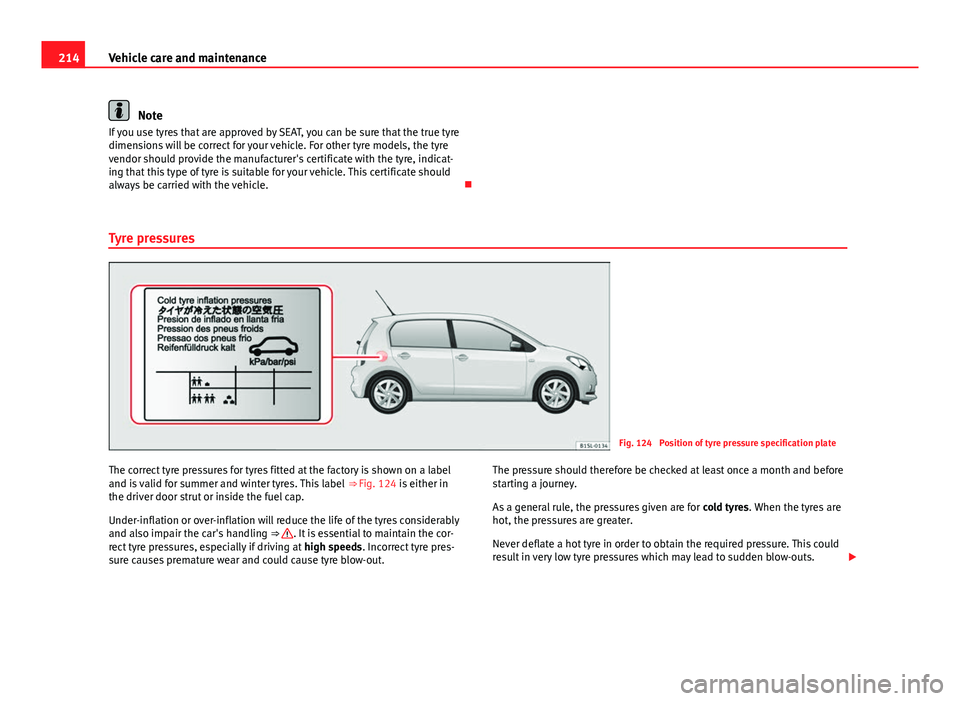
Tyre pressures
Fig. 124 Position of tyre pressure specification plate
The correct tyre pressures for tyres fitted at the factory is shown on a label
and is valid for summer and winter tyres. This label ⇒ Fig. 124 is either in
the driver door strut or inside the fuel cap.
Under-inflation or over-inflation will reduce the life of the tyres considerably
and also impair the car's handling ⇒
. It is essential to maintain the cor-
rect tyre pressures, especially if driving at high speeds. Incorrect tyre pres-
sure causes premature wear and could cause tyre blow-out. The pressure should therefore be checked at least once a month and before
starting a journey.
As a general rule, the pressures given are for
cold tyres. When the tyres are
hot, the pressures are greater.
Never deflate a hot tyre in order to obtain the required pressure. This could
result in very low tyre pressures which may lead to sudden blow-outs.
Page 217 of 306

215
Vehicle care and maintenance
Checking tyre pressures
Check tyre pressures only when the vehicle has not been driven for more
than a few kilometres at low speeds in the past three hours.
● The tyre pressures should be checked regularly, and only when the tyres
are cold. Always check all tyres, including the spare wheel. Tyre pressures
should be checked more often in colder regions, and only when the vehicle
has not been driven recently. Always use a correctly-operating tyre gauge.
● Adjust tyre pressures to the loads carried in the vehicle.
● After adjusting the tyre pressure, check that the caps are properly
screwed.
The spare wheel or temporary spare wheel must be at the maximum pres-
sure specified.
WARNING
If tyre pressures are too high or too low, the tyre may deflate or burst
suddenly while driving. This could result in a serious accident.
● If the tyre pressure is too low, the tyres could overheat, resulting in
tread detachment or even burst tyres.
● When driving at high speeds and/or fully loaded, the tyre could sud-
denly overheat, burst or be subject to tread detachment, with the resul-
tant loss of control of the vehicle.
● Tyre pressures which are too high or too low reduce the service life of
the tyre, affecting the vehicle's performance.
● Tyre pressures should be checked regularly, at least once a month
and before long journeys.
● Adjust the pressures of all the tyres to the vehicle load.
● Never deflate excess pressure from hot tyres.
CAUTION
● Take care not to tilt the manometer when placing it on the valve. Other-
wise, the valve may be damaged.
● To avoid damage to the valves, always replace valve caps correctly.
Check that the caps are identical to the standard caps and have been cor-
rectly tightened.
For the sake of the environment
Under-inflated tyres will increase the fuel consumption.
Tread depth and wear indicators
Fig. 125 Tyre tread:
tread wear indicators
Tread depth
Certain driving conditions require a deeper tread, as well as needing the
tread to be approximately the same on the front and rear tyres. This is par-
ticularly important when driving in winter, in cold temperatures and on wet
roads ⇒
.
Vehicle diagramPrior to a journey...While drivingCare, cleaning and mainte-
nanceIf and whenTechnical specifications
Page 240 of 306

238Vehicle care and maintenance
Catalytic converter
The catalytic converter permits the subsequent treatment of the exhaust
gases thus reducing contaminating gas emissions. To ensure a longer work-
ing life for the exhaust system and catalytic converter in a petrol engine:
●Always use unleaded petrol.
● Never run the fuel tank completely dry.
● Do not top up with too much engine oil ⇒ page 185.
● Do not tow-start the vehicle; use the starter cables ⇒ page 275.
If you should notice misfiring, uneven running or loss of power when the car
is moving, reduce speed immediately. Have the car inspected by a special-
ised workshop. If this happens, unburnt fuel can enter the exhaust system
and escape into the atmosphere. The catalytic converter can also be dam-
aged by overheating.
For the sake of the environment
Even when the emission control system is working perfectly, there may be a
smell of sulphur from the exhaust gas under some conditions. This depends
on the sulphur content of the fuel used.