Page 141 of 715
02-50000-00
1990-00 Rear Engine Mount
- Changed design
3240-01 Transfer Case (T/C)
- Changed TOD type T/C to Part-Time T/C
4411-01 Front Suspension
- Changed components
Coil spring
assemblyUpper arm
assembly
Stabilizer bar
assembly
Lower arm assembly
Stabilizer bar
assembly
Knuckle assembly
Upper arm
assembly
Lower arm assembly
Shock absorber
assembly
Knuckle
assembly
Page 142 of 715
02-6
3650-02 Torque Converter
- Added torsional damper (reduces booming noise) and increased capacity
2. CHASSIS II
4115-01 Knuckle and Hub Assembly (4WD)
- Changed components (hub, knuckle, hub actuator and front axle shaft) according to new
part-time T/C
Torsional
damper
Turbine wheel
Stator
Impeller 1.
2.
3.
4.
Front axle shaft
Hub
Knuckle
Knuckle
Front axle shaftHub assembly
Locking hub actuator
Page 144 of 715
02-8
8010-10Warning Lamp/Indicator Cluster
- Changed some warning lamps and indicators
8410-14 4WD Switch
- Changed 4WD switch according to newly
installed part-time T/C
8910-05 Audio Assembly
-Bluetooth 2 DIN CDP
3. OTHERS
Page 195 of 715

02-38
4) Features
Reduced vibration noise from the powertrain by blocking the torsional vibrations
Enhanced vehicle silence and riding comforts: reduced engine torque fluctuation
Reduced shifting shocks
Smooth acceleration and deceleration -
-
-
-
5) Advantages
Improved torque response by using 3-stage type spring: Strengthens the torque response in all
ranges (low, medium, and high speed) by applying respective spring constant at each range.
Stable revolution of the primary and secondary wheel by using planetary gear: Works as
auxiliary damper against spring changes
Less heat generation due to no direct friction against spring surface: Plastic material is covered
on the spring outer surface
Increased durability by using plastic bushing (extends the lifetime of grease) -
-
-
-
6) Drive Plate
Drive plate receives the power from the start motor when starting the engine. With this, the drive
plate initially drives the power train system. And, it is connected to the torque converter to transfer
the engine torque to the power train system.
Trigger ring
Drive plate
Components ▶
Page 264 of 715
07-31543-00
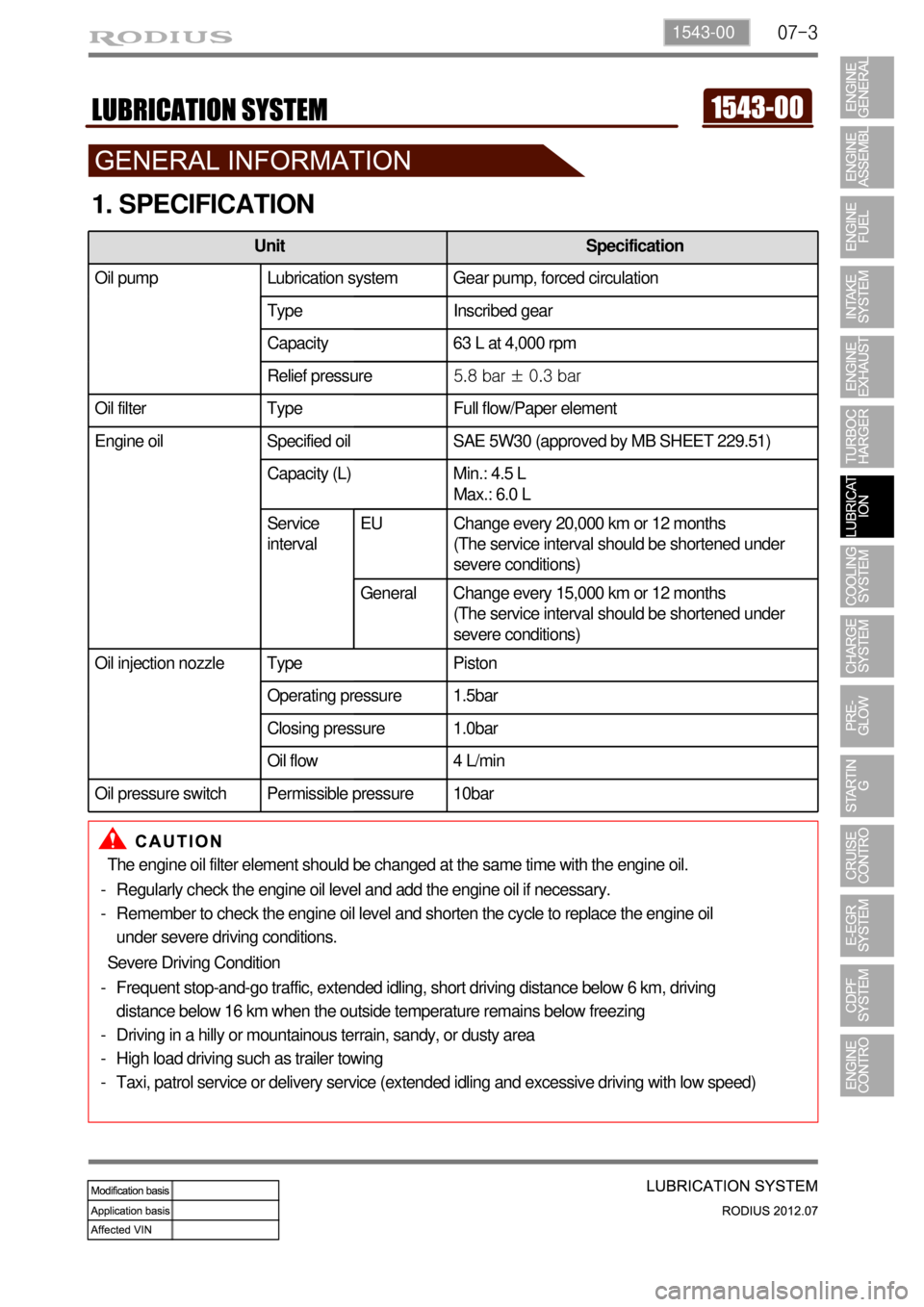
1. SPECIFICATION
The engine oil filter element should be changed at the same time with the engine oil.
Regularly check the engine oil level and add the engine oil if necessary.
Remember to check the engine oil level and shorten the cycle to replace the engine oil
under severe driving conditions. -
-
Severe Driving Condition
Frequent stop-and-go traffic, extended idling, short driving distance below 6 km, driving
distance below 16 km when the outside temperature remains below freezing
Driving in a hilly or mountainous terrain, sandy, or dusty area
High load driving such as trailer towing
Taxi, patrol service or delivery service (extended idling and excessive driving with low speed) -
-
-
-
Unit Specification
Oil pump Lubrication system Gear pump, forced circulation
Type Inscribed gear
Capacity 63 L at 4,000 rpm
Relief pressure5.8 bar ± 0.3 bar
Oil filter Type Full flow/Paper element
Engine oil Specified oil SAE 5W30 (approved by MB SHEET 229.51)
Capacity (L) Min.: 4.5 L
Max.: 6.0 L
Service
intervalEU Change every 20,000 km or 12 months
(The service interval should be shortened under
severe conditions)
General Change every 15,000 km or 12 months
(The service interval should be shortened under
severe conditions)
Oil injection nozzle Type Piston
Operating pressure 1.5bar
Closing pressure 1.0bar
Oil flow 4 L/min
Oil pressure switch Permissible pressure 10bar
Page 336 of 715

15-110000-00
2) ECU Control
(1) Function
a. ECU Function
ECU receives and analyzes signals from various sensors and then modifies those signals into
permissible voltage levels and analyzes to control respective actuators.
ECU microprocessor calculates injection period and injection timing proper for engine piston speed and
crankshaft angle based on input data and stored specific map to control the engine power and emission
gas.
Output signal of the ECU microprocessor drives pressure control valve to control the rail pressure and
activates injector solenoid valve to control the fuel injection period and injection timing; so controls
various actuators in response to engine changes. Auxiliary function of ECU has adopted to reduce
emission gas, improve fuel economy and enhance safety, comforts and conveniences. For example,
there are EGR, booster pressure control, autocruise (export only) and immobilizer and adopted CAN
communication to exchange data among electrical systems (automatic T/M and brake system) in the
vehicle fluently. And Scanner can be used to diagnose vehicle status and defectives.
<00760097008c00990088009b00900095008e0047009b008c00940097008c00990088009b009c0099008c0047009900880095008e008c00470096008d0047006c006a007c00470090009a0047009500960099009400880093009300a000470054005b005700
47009b009600470052005f005c00b6006a004700880095008b> protected from factors like oil,
water and electromagnetism and there should be no mechanical shocks.
To control the fuel volume precisely under repeated injections, high current should be applied instantly
so there is injector drive circuit in the ECU to generate necessary current during injector drive stages.
Current control circuit divides current applying time (injection time) into full-in-current-phase and hold-
current-phase and then the injectors should work very correctly under every working condition.
b. Control Function
Controls by operating stages
To make optimum combustion under every operating stage, ECU should calculate proper injection
volume in each stage by considering various factors.
Starting injection volume control
During initial starting, injecting fuel volume will be calculated by function of temperature and engine
cranking speed. Starting injection continues from when the ignition switch is turned to ignition
position to till the engine reaches to allowable minimum speed.
Driving mode control
If the vehicle runs normally, fuel injection volume will be calculated by accelerator pedal travel and
engine rpm and the drive map will be used to match the drivers inputs with optimum engine power. -
-
-
Page 342 of 715

15-170000-00
A fourth correction is made according to the pressure error.
This correction is used to reduce the injection timing advance when the pressure in the rail is higher
than the pressure demand.
A fifth correction is made according to the rate of EGR.
This correction is used to correct the injection timing advance as a function of the rate of exhaust gas
recirculation. -
-
When the EGR rate increases, the injection timing advance must in fact be increased in order to
compensate for the fall in termperature in the cylinder.
A. Main Flow Control
The main flow represents the amount of fuel injected into the cylinder during the main injection. The pilot
flow represents the amount of fuel injected during the pilot injection.
The total fuel injected during 1 cycle (main flow + pilot flow) is determined in the following manner.
When the driver depress the pedal, it is his demand which is taken into account by the system in order
to determine the fuel injected.
When the driver release the pedal, the idle speed controller takes over to determine the minimum fuel
which must be injected into the cylinder to prevent the enigne from stalling. -
-
The driver demand is the translation of the pedal position into the fuel demand. It is calculated as a
function of the pedal position and of the engine speed. The driver demand is filtered in order to limit the
hesitations caused by rapid changes of the pedal position. A mapping determines the maximum fuel
which can be injected as a function of the driver demand and the rail pressure. Since the flow is
proportional to the injection time and to the square root of the injection pressure, it is necessary to limit
the flow according to the pressure in order to avoid extending the injection for too long into the engine
cycle. The system compares the driver demand with this limit and chooses the smaller of the 2 values.
The driver demand is then corrected according to the coolant temperature. This correction is added to
the driver demand.
(5) Fuel Control
B. Driver Demand
Page 434 of 715
02-38710-01
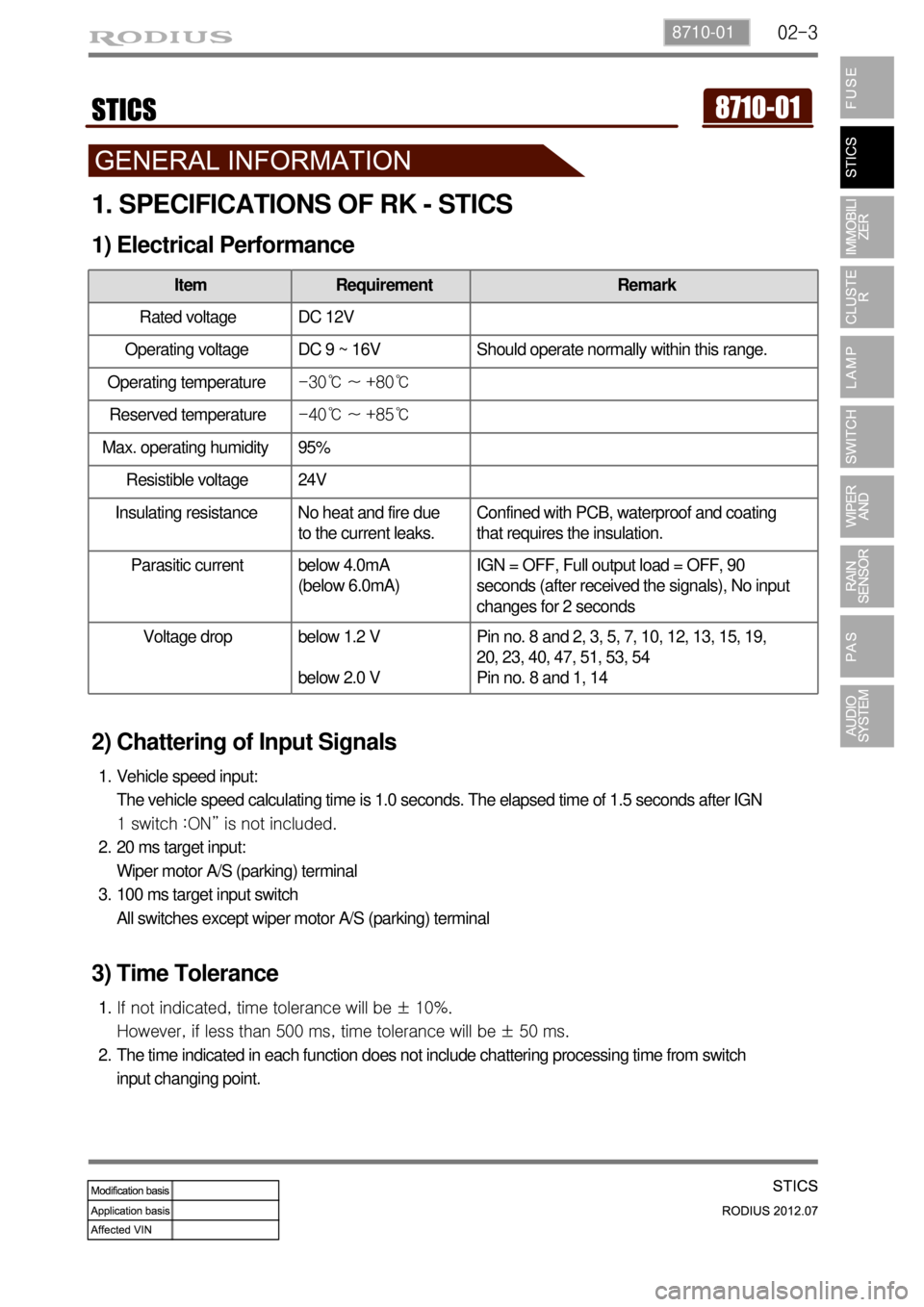
1. SPECIFICATIONS OF RK - STICS
1) Electrical Performance
2) Chattering of Input Signals
Vehicle speed input:
The vehicle speed calculating time is 1.0 seconds. The elapsed time of 1.5 seconds after IGN
1 switch :ON” is not included.
20 ms target input:
Wiper motor A/S (parking) terminal
100 ms target input switch
All switches except wiper motor A/S (parking) terminal 1.
2.
3.
3) Time Tolerance
If not indicated, time tolerance will be ± 10%.
<006f0096009e008c009d008c0099005300470090008d00470093008c009a009a0047009b008f008800950047005c0057005700470094009a00530047009b00900094008c0047009b00960093008c009900880095008a008c0047009e009000930093004700
89008c004700b70047005c005700470094009a0055>
The time indicated in each function does not include chattering processing time from switch
input changing point. 1.
2.
Item Requirement Remark
Rated voltage DC 12V
Operating voltage DC 9 ~ 16V Should operate normally within this range.
Operating temperature-30℃ ~ +80℃
Reserved temperature-40℃ ~ +85℃
Max. operating humidity 95%
Resistible voltage 24V
Insulating resistance No heat and fire due
to the current leaks.Confined with PCB, waterproof and coating
that requires the insulation.
Parasitic current below 4.0mA
(below 6.0mA)IGN = OFF, Full output load = OFF, 90
seconds (after received the signals), No input
changes for 2 seconds
Voltage drop below 1.2 V
below 2.0 VPin no. 8 and 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 12, 13, 15, 19,
20, 23, 40, 47, 51, 53, 54
Pin no. 8 and 1, 14