Page 594 of 715
08-34850-03
Brake oil Grade DOT 4
Service interval Replace every 2 years
1. SPECIFICATIONS
Description Specification
Front brake Type Ventilated disc
Rear brake Type Ventilated disc
Master cylinder Type Step feed bore tandem, double cylinder
Brake booster Type Tandem type(integrated level sensor)
Operating type Foot operated type
Page 611 of 715
09-34891-01
1. SPECIFICATIONS
1) Pressure Sensor
UnitDescription
Location
ABS ESP
HECU
(Hydraulic &
Electronic Control
Unit) CPU:MCU60 (32bit)
Clock Frequency: 28MHz
Memory: 128~256 KB CPU:MCU60 (32bit)
Clock Frequency: 28MHz
Memory:256~512 KB Under the front
washer reservoir
Wheel Speed
SensorActive type wheel speed
sensorActive type wheel speed
sensorOn each wheel
Front air gap:
0.335~0.945mm,
Rear air gap:
0.309~0.958
Steering Wheel
Angle SensorN/AMaximum angular speed:
1500°/sec
Operating voltage: 9~16VUnder the steering
wheel
Sensor ClusterN/AIntegrated with yaw rate
sensor and lateral sensorUnder the audio
assembly
Pressure Sensor
N/A Analog outputUnder the master
cylinder
Description Specification
Supplying voltage approx. 5V (4.75~5.25V)
Max. pressure 350bar
Page 612 of 715
09-4
2) Sensor Cluster
3) Steering Wheel Angle Sensor
Air gap between sensor and rotorFront 0.335 ~ 0.945mm
Rear 0.309 ~ 0.958mm
Current (at 2.75 km/h)IHIGH : 14mA
ILOW : 7mA
Voltage (when turning the steering wheel one turn per second) 7.5 ~ 20V
4) Active Wheel Speed Sensor
Operating voltage 9~16V
Maximum output current 10mA
Maximum detection angle speed 1500˚/s
Operating temperature -30~75℃
Supplying voltage 9 to 16 V (battery voltage)
Output voltage (HI) approx. 3.50V (3.0 to 4.1V)
Output voltage (LO) approx. 1.50V (1.3 to 2.0V)
Description Specification
Description Specification
Description Specification
Supplying voltage approx. 5V (4.75~5.25V)
Output voltage while in stationary approx. 2.5V (Ignition ON)
Output range 0.2~4.8V
Operating start speed4˚/s
Page 614 of 715
09-6
HECU(Hydraulic & Electronic Control Unit)
ESP ABS
2. LAYOUT
Name ESP ABS Location
1 HECU O O Under the battery
2 Pressure Sensor O X Under the master cylinder
3 Wheel Speed Sensor O O On wheels
4 Sensor Cluster O X Under the audio assembly
5 Steering Wheel Angle Sensor O X Under the steering wheel
Pressure Sensor
Installed Removed
Page 615 of 715
09-74891-01
1. ESP Indicator2. Steering Wheel Angle
Sensor
3. ESP OFF Switch 4. Sensor Cluster
Front Wheel Speed Sensor
4WD 2WDRear Wheel Speed
Sensor
Page 617 of 715
09-94891-01
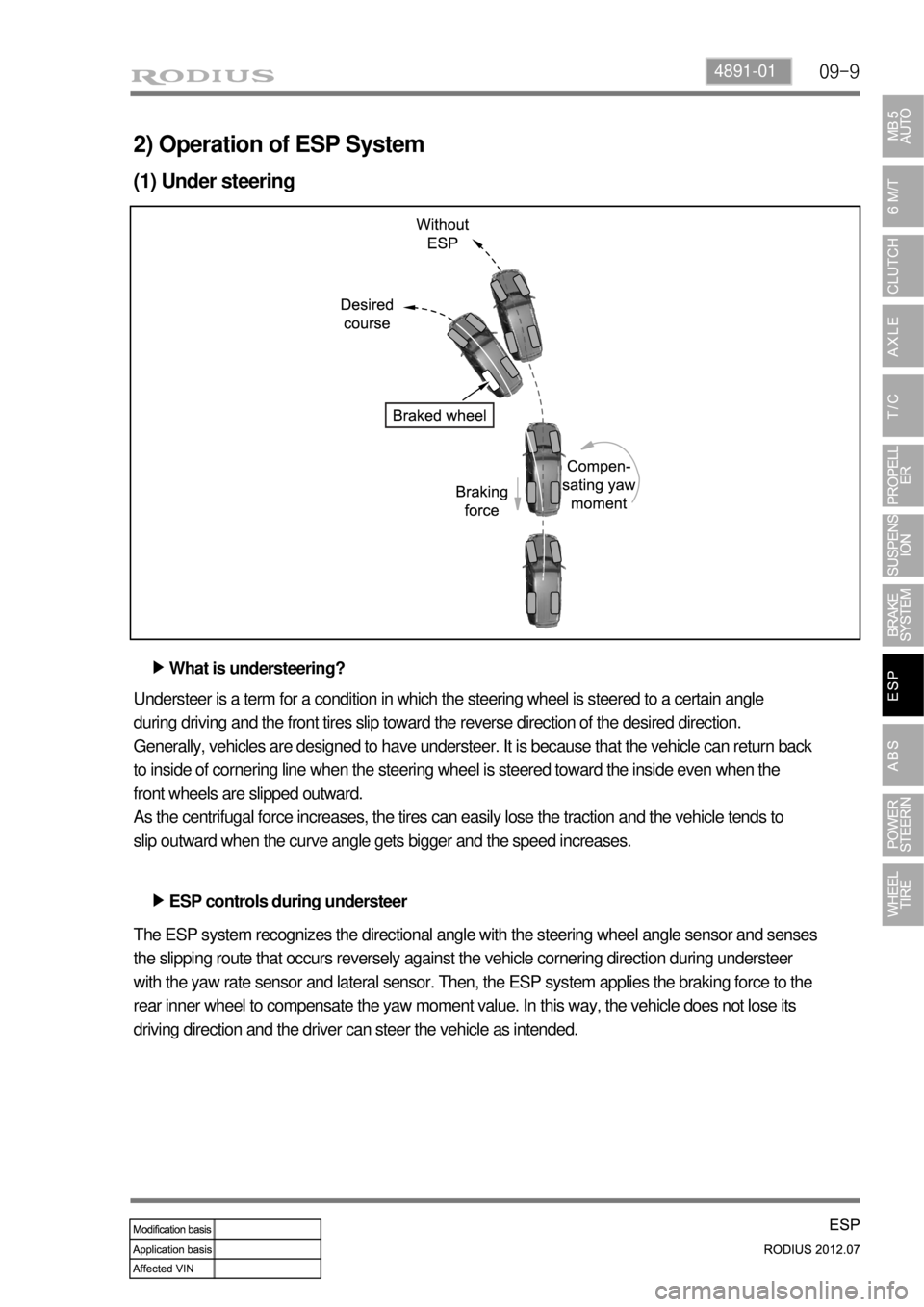
2) Operation of ESP System
(1) Under steering
What is understeering? ▶
ESP controls during understeer ▶ Understeer is a term for a condition in which the steering wheel is steered to a certain angle
during driving and the front tires slip toward the reverse direction of the desired direction.
Generally, vehicles are designed to have understeer. It is because that the vehicle can return back
to inside of cornering line when the steering wheel is steered toward the inside even when the
front wheels are slipped outward.
As the centrifugal force increases, the tires can easily lose the traction and the vehicle tends to
slip outward when the curve angle gets bigger and the speed increases.
The ESP system recognizes the directional angle with the steering wheel angle sensor and senses
the slipping route that occurs reversely against the vehicle cornering direction during understeer
with the yaw rate sensor and lateral sensor. Then, the ESP system applies the braking force to the
rear inner wheel to compensate the yaw moment value. In this way, the vehicle does not lose its
driving direction and the driver can steer the vehicle as intended.
Page 618 of 715
09-10
(2) Over steering
What is oversteering? ▶
ESP controls during oversteer ▶ Oversteer is a term of a condition in which the steering wheel is steered to a certain angle during
driving and the rear tires slip outward losing traction.
Compared to understeering vehicles, it is hard to control the vehicle during cornering and the
vehicle can spin due to rear wheel moment when the rear tires lose traction and the vehicle speed
increases.
The ESP system recognizes the directional angle with the steering wheel angle sensor and senses
the slipping route that occurs towards the vehicle cornering direction during oversteer with the
yaw rate sensor and lateral sensor. Then the ESP system applies the braking force to the front
outer wheel to compensate the yaw moment value. In this way, the vehicle does not lose its
driving direction and the driver can steer the vehicle as intended.
Page 619 of 715
09-114891-01
(3) ESP Control
The ESP (Electronic Stability Program) has been developed to help a driver avoid danger of losing
control of the vehicle stability due to understeer or oversteer during cornering. The yaw rate sensor,
lateral sensor and longitudinal sensor in the sensor cluster and the steering wheel angle sensor
under the steering column detect the vehicle conditions when the inner or outer wheels are
spinning during oversteer, understeer or cornering. The ESP ECU controls against oversteer or
understeer during cornering by controlling the vehicle stability using input values from these
sensors and applying the braking force to the corresponding wheels independently. The system
also controls the engine power right before the wheel spin synchronized to decelerate the vehicle
automatically in order to maintain the vehicle stable during cornering.