Page 333 of 600

2210-01
2) Cleanness
(1) Cleanness of DI engine fuel system
Cleanness of DI engine fuel system and service procedures
The fuel system for DI engine consists of transfer (low pressure) line and high pressure line.
Its highest pressure reaches over 1,800 bar.
preciseness.
The pressure regulation and injector operation are done by electric source from engine ECU.
Accordingly, if the internal valve is stuck due to foreign materials, injector remains open.
Even in this case, the HP pump still operates to supply high pressurized fuel. This increases the
pressure to combustion chamber (over 250 bar) and may cause fatal damage to engine.
You can compare the thickness of injector nozzle hole and hair as shown in below figure (left side). The
below figure shows the clearance between internal operating elements.
The core elements of fuel system has very high preciseness that is easily affected by dust or very small
foreign material. Therefore, make sure to keep the preliminary works and job procedures in next pages.
If not, lots of system problems and claims may arise.
Hair
Nozzle holeValve actuator lift - 0.028 mm
Diameter
0.04 mm
Operating
clearance
0.002 mm
Diameter
2.0 mm
Page 334 of 600

(2) Di engine and its expected problems and remedies can be caused by
water in fuel
System supplement against paraffin separation
In case of Diesel fuel, paraffin, one of the elements, can be separated from fuel during winter and then
can stick on the fuel filter blocking fuel flow and causing difficult starting finally. Oil companies supply
summer fuel and winter fuel by differentiating mixing ratio of kerosene and other elements by region and
season. However, above phenomenon can be happened if stations have poor facilities or sell improper
fuel for the season. In case of DI engine, purity of fuel is very important factor to keep internal
preciseness of HP pump and injector.
Accordingly, more dense mesh than conventional fuel filter is used. To prevent fuel filter internal clogging
due to paraffin separation, SYMC is using fuel line that high pressure and temperature fuel injected by
injector returns through fuel filter to have an effect of built-in heater (see fuel system).
System supplement and remedy against water in fuel
As mentioned above, some gas stations supply fuel with excessive than specified water. In the
conventional IDI engine, excessive water in the fuel only causes dropping engine power or engine
hunting. However, fuel system in the DI engine consists of precise components so water in the fuel can
cause malfunctions of HP pump due to poor lubrication of pump caused by poor coating film during high
speed pumping and bacterization (under long period parking). To prevent problems can be caused by
excessive water in fuel, water separator is installed inside of fuel filter. When fuel is passing filter, water
that has relatively bigger specific gravity is accumulated on the bottom of the filter.
Water drain from water separator
If water in the separator on the fuel filter exceeds a certain level, it will be supplied to HP pump with fuel,
so the engine ECU turns on warning lamp on the meter cluster and buzzer if water level is higher than a
certain level.
Due to engine layout, a customer cannot easily drain water from fuel filter directly, so if a customer
checks in to change engine oil, be sure to perform water drain from fuel filter.
Water
separator
To separate the water from the fuel filter,
remove the fuel filter assembly first.
Page 335 of 600
2210-01
1. OVERVIEW
The components in fuel system supply the fuel and generate the high pressure to inject the fuel to each
injector. They are controlled by the engine ECU.
The common rail fuel injection system consists of fuel tank, fuel line, low pressure line which supplies low
pressure fuel to the low pressure pump (including high pressure pump), common rail which distributes
and accumulates the high pressurized fuel from the fuel pump, high pressure line which connected to
the injector, and the engine control unit (ECU) which calculates the accelerator pedal position and
controls the overall performance of vehicle based on the input signals from various sensors.
1) Fuel Flow Diagram
Page 337 of 600
2210-01
Accelerator pedal position
sensor
Detecting driver's intention
for speed up/down
Fuel rail assembly
Relieving the pulsation.
Measuring the fuel pressure.
Distributing the fuel to injectors.
Fuel filter assembly
Supplying clean fuel/fuel
heating/water separation by
priming pump
Plunger type HP pump (1,800 bar)
Vane type LP pump (6 bar)
T-MAP sensor
Measuring booster pressure
and temperature
High pressure pump
Generating high pressurized fuel and
supplying it according to engine rpm,
required volume, required pressure
Page 338 of 600
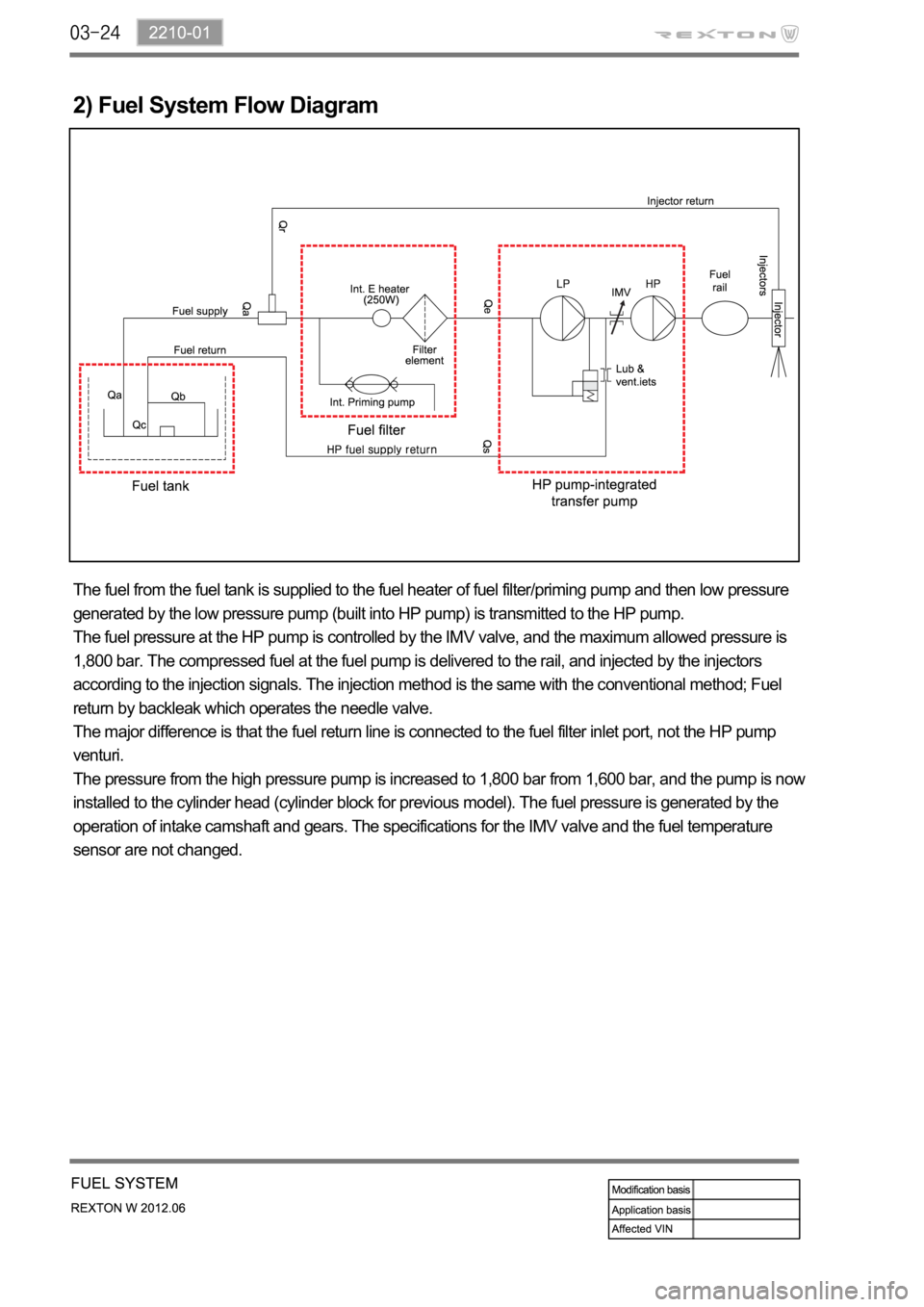
2) Fuel System Flow Diagram
The fuel from the fuel tank is supplied to the fuel heater of fuel filter/priming pump and then low pressure
generated by the low pressure pump (built into HP pump) is transmitted to the HP pump.
The fuel pressure at the HP pump is controlled by the IMV valve, and the maximum allowed pressure is
1,800 bar. The compressed fuel at the fuel pump is delivered to the rail, and injected by the injectors
according to the injection signals. The injection method is the same with the conventional method; Fuel
return by backleak which operates the needle valve.
The major difference is that the fuel return line is connected to the fuel filter inlet port, not the HP pump
venturi.
The pressure from the high pressure pump is increased to 1,800 bar from 1,600 bar, and the pump is now
installed to the cylinder head (cylinder block for previous model). The fuel pressure is generated by the
operation of intake camshaft and gears. The specifications for the IMV valve and the fuel temperature
sensor are not changed.
Page 452 of 600
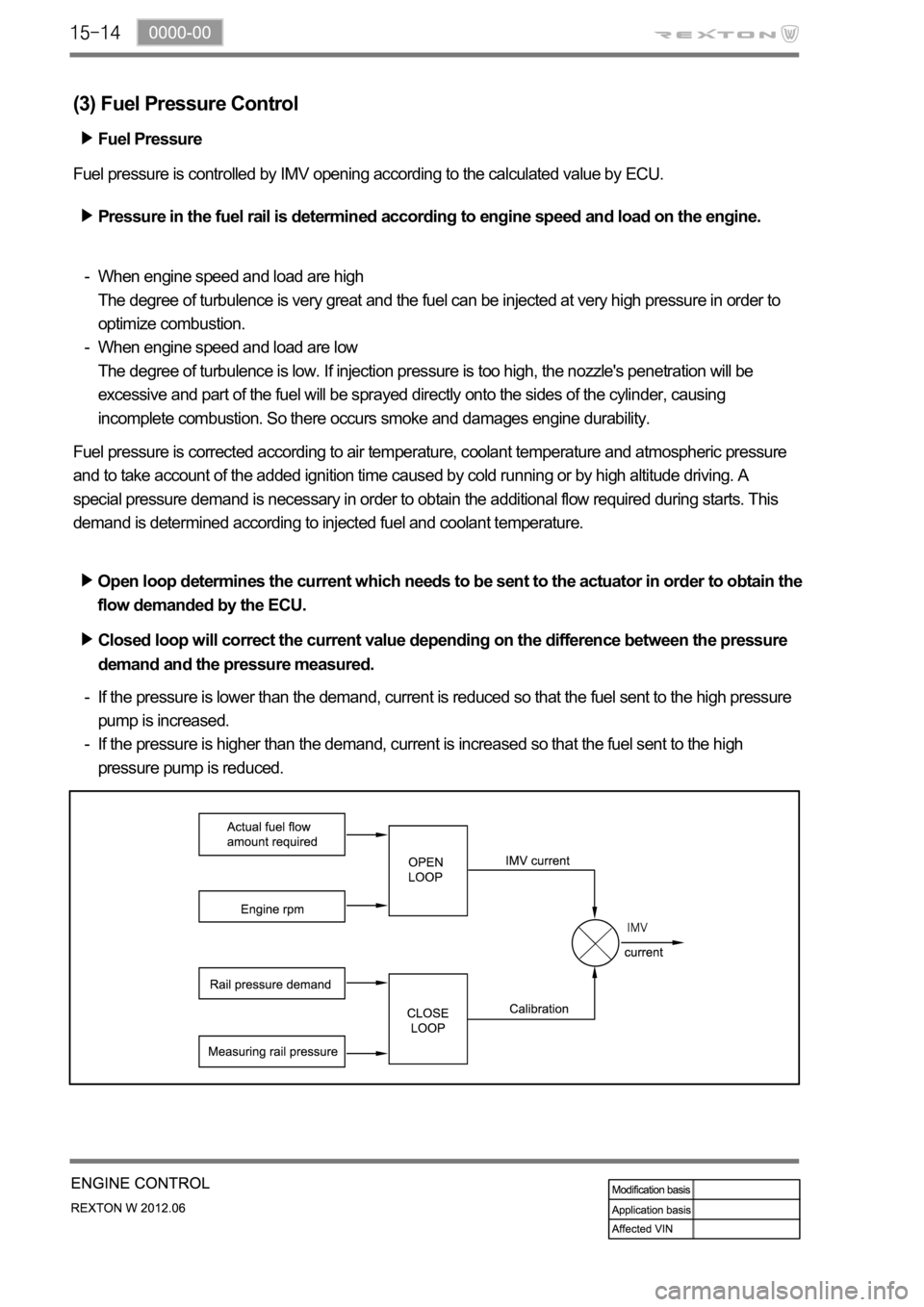
(3) Fuel Pressure Control
Fuel pressure is controlled by IMV opening according to the calculated value by ECU.
Pressure in the fuel rail is determined according to engine speed and load on the engine.
When engine speed and load are high
The degree of turbulence is very great and the fuel can be injected at very high pressure in order to
optimize combustion.
When engine speed and load are low
The degree of turbulence is low. If injection pressure is too high, the nozzle's penetration will be
excessive and part of the fuel will be sprayed directly onto the sides of the cylinder, causing
incomplete combustion. So there occurs smoke and damages engine durability. -
-
Fuel pressure is corrected according to air temperature, coolant temperature and atmospheric pressure
and to take account of the added ignition time caused by cold running or by high altitude driving. A
special pressure demand is necessary in order to obtain the additional flow required during starts. This
demand is determined according to injected fuel and coolant temperature.
Open loop determines the current which needs to be sent to the actuator in order to obtain the
flow demanded by the ECU.
Closed loop will correct the current value depending on the difference between the pressure
demand and the pressure measured.
If the pressure is lower than the demand, current is reduced so that the fuel sent to the high pressure
pump is increased.
If the pressure is higher than the demand, current is increased so that the fuel sent to the high
pressure pump is reduced. -
-Fuel Pressure
Page 510 of 600

Do not allow the fluid and engine oil to make contact with the body paintwork and hoses.
If work on the fluid system such as fuel and oil, working area should be well ventilated and
smoking should be prohibited.
Gasket or seal on the fuel/lubrication system should be replaced with new ones and bolts and
nuts should be tightened as specified.
After removal/installation works, be sure to check whether there is leak on the connecting
section. -
-
-
-
If fine dust or foreign material enters into DI engine's fuel system, there can be serious
damages between HP pump and injectors. So, be sure to cover removed fuel system
components with cap and protect removed parts not to be contaminated with dirt. (Refer to
cleanness in this manual while working on DI engine fuel system)
When working on the fuel line between priming pump and injector (including return line),
always plug the openings with caps to prevent foreign materials or dust from entering to the
openings and connections.
The HP fuel supply pipe (HP pump to fuel rail) and HP fuel pipe (Fuel rail to injector) should
be replaced with new ones when removed. 1.
2.
3.
Electric devices should be handled more carefully.
Currently, the engine has a lot of electric devices. There could be poor engine performance,
incomplete combustion and other abnormal symptoms due to short circuit or poor contact.
Before work on engine and electrical equipment, be sure to disconnect battery negative (-)
terminal.
When replacing the electric device, use only genuine part and check the conditions of
connections and grounds. Loosened connection or ground makes cause a fire and personal
injury. -
-
Page 514 of 600
Engine Compartment Layout
Engine assembly
Engine oil dipstick
Vacuum pump
Oil filter and cooler
Fuel filter and priming pump
Brake booster
Brake oil tank
AQGS unit
Washer fluid filler cap
Engine compartment fuse box
PTC relay box
Battery
Vacuum modulator (for VGT turbo charger) 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.FFH Assembly (Only for vehicle with FFH)
Power steering oil tank
Engine oil filler cap
Fan shroud
E-EGR Valve
High-capacity PCV oil separator
HFM sensor (6.0)
VGT turbo charger
Air cleaner housing
2Coolant surge tank
ABS/ESP HECU (Including TPMS function:
optional)
Exhaust gas FRT Temp. sensor (T3) 14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.