2012 SSANGYONG KORANDO light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 807 of 1082

10-58910-05
Audio assembly
CDP (MP3) + Bluetooth CDP(MP3) + RDS + Bluetooth
<007b008f008c004702c8006a00680073007302c900470089009c009b009b009600950047008d00960099004700690093009c008c009b00960096009b008f0047009a00a0009a009b008c00940047008f0088009a00470089008c008c009500470088008b00
8b008c008b0055>
2. MAJOR CHANGES
RDS (Radio Data System) is a broadcasting service which a growing number of FM stations are now
providing. It allows the FM stations to send additional signals along with their regular programme signals.
For example, the stations send their station names and information about what type of programme they
broadcast, such as sports or music, etc.
When tuned to an FM station which provides the RDS service, the RDS indicator lights up, the station
frequency (and then the station name if sent) is displayed.
Not all FM stations provide RDS service, nor do all RDS stations provide same services. If in doubt,
check with local radio stations for details on RDS services in your area.
This machine can use the following RDS service.
PS (Programme Service name) / PTY (Programme Type) / TP (Traffic Program) / TA (Traffic
Announcement) / AF (List of Alternative Frequencies) / RT (Radio Text)
This allows you to locate a specific type name of programme being broadcast.
3. RDS (RADIO DATA SYSTEM) AUDIO
Page 828 of 1082

01-18
A. Indicators on instrument cluster
C. HECU assembly
The HECU assemblies for ABS and ESP have
similar appearance but they have different inner
structure and connector connections from each
other. D. Front brake assembly
The disc brake for 4WD vehicle is the same with
the one for 2WD vehicle.
7. BRAKE SYSTEM AND ESP SYSTEM LAYOUT
B. Master cylinder assembly
Description for master cylinder in this chapter is
based on ABS/ESP equipped vehicle. For CBS,
there is an extra pressure valve mounted to the
master cylinder.
CaliperDisc
Parking brake
warning light
ABS warning lamp
ESP indicator
Page 849 of 1082

02-153680-01
This information is used by the TCU to decide which shift pattern to select and for shift energy
management. Electro-hydraulic solenoid valves and variable bleed solenoids control the transaxle gear
changes.
Six variable bleed solenoids and four on/off solenoids are used to direct transaxle fluid flow to control the
fluid pressure within the three clutches and two bands. Separate pressure regulators are used
exclusively for torque converter clutch control and main transaxle line pressure.
The TCU monitors all TCU inputs and outputs to confirm correct system operation. If a fault occurs the
TCU is able to perform default action and inform the driver of the problem through the instrument cluster
warning lights. Detailed information is available via trouble codes which can be read with the service tool.
Page 850 of 1082

02-16
3) Shift Map Selection
The driver can manually select between normal (S) and winter modes (W) via the mode switch.
Depending on the transaxle temperature, uphill and downhill grades and altitude, shift maps will be
selected by the TCU to suit the driving conditions. The following maps are available.
Standard (Normal) Mode ▶
Normal Mode is selected when the lever is in the D position with the mode switch in the normal (S)
position and the transaxle is within normal temperature ranges. Shift schedule points are optimised for
fuel efficiency and general driving conditions.
Uphill and Downhill Mode ▶
In this mode, depending on the load of the vehicle, adaptive shift maps are selected to progressively
adjust the shift points and torque converter lock points.
Altitude Mode ▶
Shift points are automatically adjusted at higher altitudes to compensate for changes in engine torque
where the torque produced by the engine is greatly reduced by the effects of reduced barometric
pressure and temperature.
Winter (W) Mode ▶
When winter mode is selected, starting in second gear is facilitated and the WINTER mode indicator
light is switched ON. To prevent wheel spin on slippery surfaces, the transmission will not allow first gear
unless manually overridden.
Warm up Schedule ▶
<007c009a008c008b0047009b00a000970090008a00880093009300a00047009e008f008c00950047009b009900880095009a0088009f0093008c0047008d0093009c0090008b0047009b008c00940097008c00990088009b009c0099008c00470090009a00
470089008c00930096009e00470059005700b6006a0055>
The torque converter will not lock-up below 20°C to assist in transaxle warm-up.
Hot Mode ▶
<007b008f008c0047008f0096009b004700940096008b008c00470090009a0047009700990096008e0099008c009a009a0090009d008c009300a0004700880097009700930090008c008b00470089008c009b009e008c008c00950047009b008c0094009700
8c00990088009b009c0099008c009a00470096008d00470058>10° ~ 200°C. The torque
converter lock-up is increased to prevent heat generation by the torque converter.
Activation of the hot mode inhibits other transmission performance features including uphill and downhill
compensation and altitude compensation. Some degradation in shift feel may be experienced as the
torque converter is not unlocked during shifting.
Cruise Control Mode ▶
When cruise control is activated the engine ECU may request the transaxle to downshift under trailing
throttle conditions to increase engine braking.
Above 110℃the electrical radiator fans are switch ON
Above 130℃the engine torque will be reduced and the W light on the instrument cluster will flash
Above 200℃the transaxle will neutralise until the fluid tem
perature falls below 200°C as a final
protection.
Page 877 of 1082

03-173660-01
5. TRANSAXLE ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM
1) General Information
The transmission control unit (TCU) and its input/output network control the following transmission
operations:
Shift timing
Line pressure
Clutch pressure (shift feel)
Torque converter clutch -
-
-
-
also uses these signals when determining transaxle operating strategy. Using all of these input signals,
the TCU can determine when the time and conditions are right for a shift, or when to apply or release the
torque converter clutch. It will also determine the pressure needed to optimise shift feel.
2) TCU (Transmission Control Unit)
The transaxle control unit (TCU) is mounted
under the driver's seat and controls the operation
of the transaxle.
Internal sensors and signals received across the
CAN bus in analogue and digital forms such as:
Transaxle input speed
Transaxle output speed
Accelerator pedal position
Gear selector position
Engine torque
Engine speed
Transaxle fluid temperature
Brake pedal status
Engine oil temperature
Engine coolant temperature
Ambient air temperature
Barometric pressure -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
The TCU monitors all TCU inputs and outputs to confirm correct system operation. If a fault occurs the
TCU is able to perform default action and inform the driver of the problem through the instrument cluster
warning lights. Detailed information is available via trouble codes which can be read with the service tool.
Page 989 of 1082
13-6
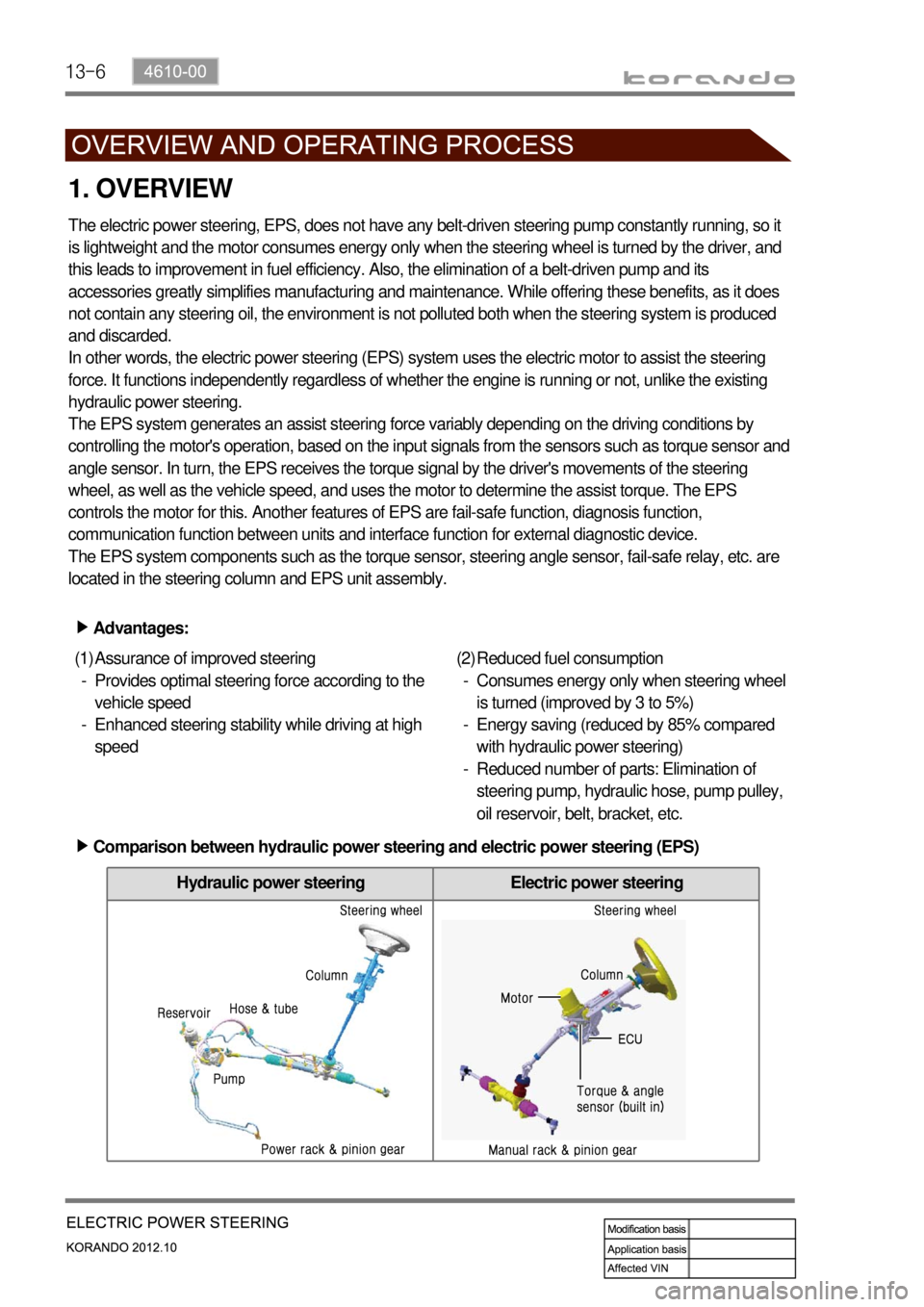
Hydraulic power steering Electric power steering
1. OVERVIEW
The electric power steering, EPS, does not have any belt-driven steering pump constantly running, so it
is lightweight and the motor consumes energy only when the steering wheel is turned by the driver, and
this leads to improvement in fuel efficiency. Also, the elimination of a belt-driven pump and its
accessories greatly simplifies manufacturing and maintenance. While offering these benefits, as it does
not contain any steering oil, the environment is not polluted both when the steering system is produced
and discarded.
In other words, the electric power steering (EPS) system uses the electric motor to assist the steering
force. It functions independently regardless of whether the engine is running or not, unlike the existing
hydraulic power steering.
The EPS system generates an assist steering force variably depending on the driving conditions by
controlling the motor's operation, based on the input signals from the sensors such as torque sensor and
angle sensor. In turn, the EPS receives the torque signal by the driver's movements of the steering
wheel, as well as the vehicle speed, and uses the motor to determine the assist torque. The EPS
controls the motor for this. Another features of EPS are fail-safe function, diagnosis function,
communication function between units and interface function for external diagnostic device.
The EPS system components such as the torque sensor, steering angle sensor, fail-safe relay, etc. are
located in the steering column and EPS unit assembly.
Advantages: ▶
Assurance of improved steering
Provides optimal steering force according to the
vehicle speed
Enhanced steering stability while driving at high
speed (1)
-
-Reduced fuel consumption
Consumes energy only when steering wheel
is turned (improved by 3 to 5%)
Energy saving (reduced by 85% compared
with hydraulic power steering)
Reduced number of parts: Elimination of
steering pump, hydraulic hose, pump pulley,
oil reservoir, belt, bracket, etc. (2)
-
-
-
Comparison between hydraulic power steering and electric power steering (EPS) ▶
Page 992 of 1082

14-4
1. OVERVIEW
A radial tire uses a cord angle of 90 degrees. That is, the cord material runs in a radial or direct line from
one bead to the other across the tread. In addition, a radial tire has a belt overwrap under the tread
surface to provide greater structural stability. The belt overwrap of a radial tire distortion while the radial
structure enables high speed driving.
Tire supports the weight of the vehicle, reduces the impact from the road and at the same time,
transmits the power to propel, brake and steer on the road. It also functions to maintain a
<009d008c008f0090008a0093008c02c5009a004700940096009d008c0094008c0095009b0055004700700095004700960099008b008c00990047009b00960047008a0096009400970093008c009b008c0047009a009c008a008f0047009b0088009a009200
9a0053004700880047009b00900099008c00470094009c009a>t be structured to be a resilient
vessel of air.
There is wear limit mark on the tire, which protrudes as a strip shape located approximately 1.6 mm from
<009b008f008c0047008e009900960096009d008c004700890096009b009b0096009400550047007b008f0090009a0047009e008c0088009900470093009000940090009b0047009400880099009200470090009a004700950096009b0047009a008c008c00
950047008d0099009600940047009b008f008c00470096009c>tside so there is additional "▲"
mark on the shoulder to let the driver find the wear mark easily. To measure the tire groove depth,
measure at any point other than the point which has a wear limit mark.
The tire is worn unevenly according to the driver's driving habit, improper servicing, low tire inflation
pressure, changed tire location, etc.
1) Structure of Tire
Tread
This thick layer of rubber provides the interface
between the tire and the road. Wear-resistant
rubber is used to protect the carcass and belt
against fractures and impacts and to deliver a
long driving life.
Shoulder
Located between the tread and sidewall, the
shoulder rubber is the thickest so that the design
must allow for the easy diffusion of heat
generated within the tire while driving.
Sidewall
The part between the shoulder and bead, the
flexible sidewall protects the carcass and
enhances the ride. A tire’s type, size,
structure, pattern, manufacturing company,
product name and various characters are
indicated here. Bead
The bead attaches the tire to the rim and wraps
the end of the cord fabric. Comprised of the bead
wire, core, flipper and other parts, the bead is
generally designed to be slightly tight around the
rim so that in the case of a sudden drop in inflation
pressure, the tire will not fall off the rim.
Carcass
As the most important framework of a tire, the
entire inner layer of cord fabric is called the
carcass. The carcass acts to support air pressure,
vertical load and absorb shocks.
Valve
Belt
Bead core
Page 1042 of 1082

04-57340-00
2. OPERATING PROCESS
1) Sunroof Switch
This can be closed or open manually to block sunlight when the sunroof function is not in use. The sunroof glass can be open in two steps and can be tilted by the switch operation. The sunroof switches are included in the overhead console switches and consists of the TILT,
CLOSE and OPEN switches.
TILT
CLOSE
OPEN ▷
▷
▷
Sun shade panel Sunroof glass Sunroof switch ▶
Opens only rear section of the sunroof.
Closes the sunroof.
Opens the sunroof.
Sunroof glass ▶
Sun shade panel ▶