2012 GMC SIERRA 1500 tire type
[x] Cancel search: tire typePage 281 of 556

Black plate (5,1)GMC Sierra Owner Manual - 2012 - CRC - 11/15/11
Driving and Operating 9-5
Off-Road Recovery
The vehicle's right wheels can drop
off the edge of a road onto the
shoulder while driving. Follow
these tips:
1. Ease off the accelerator andthen, if there is nothing in the
way, steer the vehicle so that
it straddles the edge of the
pavement. 2. Turn the steering wheel about
one-eighth of a turn, until the
right front tire contacts the
pavement edge.
3. Then turn the steering wheel to go straight down the roadway.
Loss of Control
Skidding
There are three types of skids that
correspond to the vehicle's three
control systems:
.Braking Skid —wheels are not
rolling.
.Steering or Cornering
Skid —too much speed or
steering in a curve causes tires
to slip and lose cornering force.
.Acceleration Skid —too much
throttle causes the driving
wheels to spin. Defensive drivers avoid most skids
by taking reasonable care suited to
existing conditions, and by not
overdriving those conditions. But
skids are always possible.
If the vehicle starts to slide, follow
these suggestions:
.Ease your foot off the
accelerator pedal and quickly
steer the way you want the
vehicle to go. The vehicle may
straighten out. Be ready for a
second skid if it occurs.
.Slow down and adjust your
driving according to weather
conditions. Stopping distance
can be longer and vehicle
control can be affected when
traction is reduced by water,
snow, ice, gravel, or other
material on the road. Learn to
recognize warning clues
—such
as enough water, ice, or packed
snow on the road to make a
mirrored surface —and slow
down when you have any doubt.
Page 287 of 556

Black plate (11,1)GMC Sierra Owner Manual - 2012 - CRC - 11/15/11
Driving and Operating 9-11
After operation in mud or sand,
have the brake linings cleaned and
checked. These substances can
cause glazing and uneven braking.
Check the body structure, steering,
suspension, wheels, tires, and
exhaust system for damage and
check the fuel lines and cooling
system for any leakage.
More frequent maintenance
service is required. Refer to the
Maintenance Schedule for more
information.
Driving on Wet Roads
Rain and wet roads can reduce
vehicle traction and affect your
ability to stop and accelerate.
Always drive slower in these types
of driving conditions and avoid
driving through large puddles and
deep‐standing or flowing water.
{WARNING
Wet brakes can cause crashes.
They might not work as well in a
quick stop and could cause
pulling to one side. You could
lose control of the vehicle.
After driving through a large
puddle of water or a car/vehicle
wash, lightly apply the brake
pedal until the brakes work
normally.
Flowing or rushing water creates
strong forces. Driving through
flowing water could cause the
vehicle to be carried away. If this
happens, you and other vehicle
occupants could drown. Do not
ignore police warnings and be
very cautious about trying to drive
through flowing water.
Hydroplaning
Hydroplaning is dangerous. Water
can build up under the vehicle's
tires so they actually ride on the
water. This can happen if the road
is wet enough and you are going
fast enough. When the vehicle is
hydroplaning, it has little or no
contact with the road.
There is no hard and fast rule about
hydroplaning. The best advice is to
slow down when the road is wet.
Other Rainy Weather Tips
Besides slowing down, other wet
weather driving tips include:
.Allow extra following distance.
.Pass with caution.
.Keep windshield wiping
equipment in good shape.
.Keep the windshield washer fluid
reservoir filled.
Page 369 of 556
Black plate (93,1)GMC Sierra Owner Manual - 2012 - CRC - 11/15/11
Driving and Operating 9-93
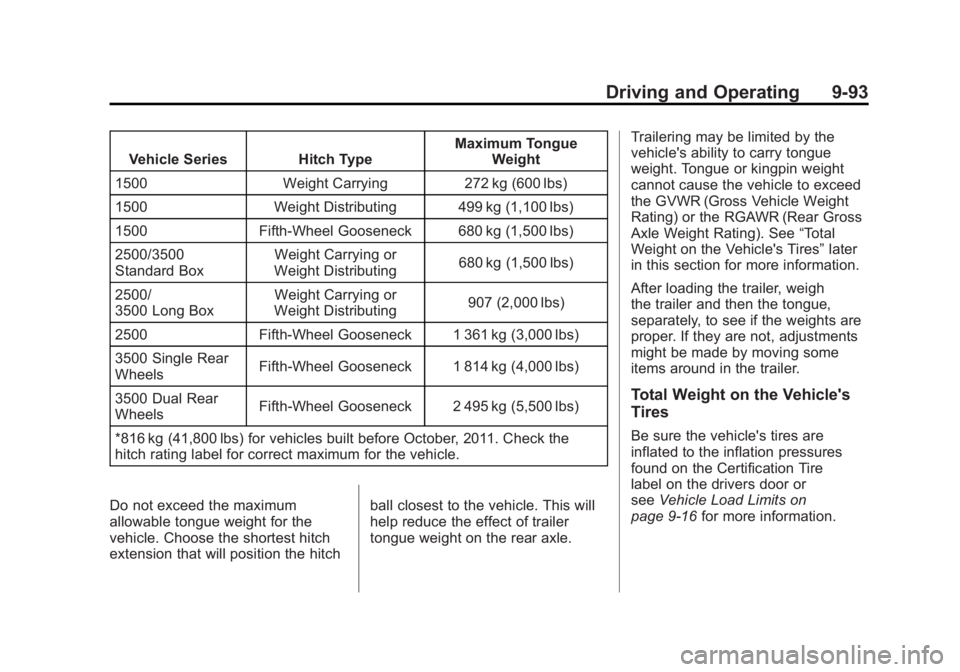
Vehicle Series Hitch TypeMaximum Tongue
Weight
1500 Weight Carrying 272 kg (600 lbs)
1500 Weight Distributing 499 kg (1,100 lbs)
1500 Fifth-Wheel Gooseneck 680 kg (1,500 lbs)
2500/3500
Standard Box Weight Carrying or
Weight Distributing 680 kg (1,500 lbs)
2500/
3500 Long Box Weight Carrying or
Weight Distributing 907 (2,000 lbs)
2500 Fifth-Wheel Gooseneck 1 361 kg (3,000 lbs)
3500 Single Rear
Wheels Fifth-Wheel Gooseneck 1 814 kg (4,000 lbs)
3500 Dual Rear
Wheels Fifth-Wheel Gooseneck 2 495 kg (5,500 lbs)
*816 kg (41,800 lbs) for vehicles built before October, 2011. Check the
hitch rating label for correct maximum for the vehicle.
Do not exceed the maximum
allowable tongue weight for the
vehicle. Choose the shortest hitch
extension that will position the hitch ball closest to the vehicle. This will
help reduce the effect of trailer
tongue weight on the rear axle.Trailering may be limited by the
vehicle's ability to carry tongue
weight. Tongue or kingpin weight
cannot cause the vehicle to exceed
the GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight
Rating) or the RGAWR (Rear Gross
Axle Weight Rating). See
“Total
Weight on the Vehicle's Tires” later
in this section for more information.
After loading the trailer, weigh
the trailer and then the tongue,
separately, to see if the weights are
proper. If they are not, adjustments
might be made by moving some
items around in the trailer.
Total Weight on the Vehicle's
Tires
Be sure the vehicle's tires are
inflated to the inflation pressures
found on the Certification Tire
label on the drivers door or
see Vehicle Load Limits on
page 9‑16 for more information.
Page 423 of 556

Black plate (37,1)GMC Sierra Owner Manual - 2012 - CRC - 11/15/11
Vehicle Care 10-37
3. Install the new blade onto thearm connector and make sure
the grooved areas are fully set in
the locked position.
For the proper type and size, see
Maintenance Replacement Parts on
page 11‑15.
Glass Replacement
If the windshield or front side
glass must be replaced, see your
dealer to determine the correct
replacement glass.
Headlamp Aiming
The vehicle has a visual optical
headlamp aiming system. The aim
of the headlamps has been preset
at the factory and should need no
further adjustment.
However, if the vehicle is damaged
in a crash, the aim of the headlamps
may be affected and adjustment
may be necessary.
If oncoming vehicles flash their high
beams at you, this may mean the
vertical aim of the headlamps needs
to be adjusted.
It is recommended that the vehicle
be taken to the dealer for service if
the headlamps need to be adjusted.
It is possible, however, to re-aim the
headlamps as described. The vehicle should:.Be placed so the headlamps
are 7.6 m (25 ft) from a
light‐colored wall.
.Have all four tires on a level
surface which is level all the way
to the wall.
.Be placed so it is perpendicular
to the wall.
.Not have any snow, ice, or mud
on it.
.Be fully assembled and all other
work stopped while headlamp
aiming is being performed.
.Be loaded with a full tank of
fuel and one person or 75 kg
(160 lbs) sitting on the
driver seat.
.Have the tires properly inflated.
.Have the spare tire in its proper
location in the vehicle.
Page 437 of 556
Black plate (51,1)GMC Sierra Owner Manual - 2012 - CRC - 11/15/11
Vehicle Care 10-51
WARNING (Continued)
.Underinflated tires pose the
same danger as overloaded
tires. The resulting crash
could cause serious injury.
Check all tires frequently to
maintain the recommended
pressure. Tire pressure
should be checked when the
tires are cold.
.Overinflated tires are more
likely to be cut, punctured,
or broken by a sudden
impact—such as when
hitting a pothole. Keep tires at
the recommended pressure.
.Worn or old tires can cause a
crash. If the tread is badly
worn, replace them.
.Replace any tires that have
been damaged by impacts
with potholes, curbs, etc.
(Continued)
WARNING (Continued)
.Improperly repaired tires can
cause a crash. Only the
dealer or an authorized tire
service center should repair,
replace, dismount, and mount
the tires.
.Do not spin the tires in
excess of 56 km/h (35 mph)
on slippery surfaces such
as snow, mud, ice, etc.
Excessive spinning may
cause the tires to explode.
SeeTire Pressure for
High-Speed Operation on
page 10‑60 for inflation pressure
adjustment for high speed
driving.
20‐Inch Tires
If the vehicle has 20‐inch
P275/55R20 size tires, they are
classified as touring tires and
are designed for on road use. The low‐profile, wide tread
design is not recommended for
“off‐road”
driving or commercial
uses such as snow plowing.
See Off-Road Driving on
page 9‑6 andAdding a Snow
Plow or Similar Equipment on
page 9‑106 for additional
information.
Notice: Low‐profile tires are
more susceptible to damage
from road hazards or curb
impact than standard profile
tires. Tire and/or wheel
assembly damage can occur
when coming into contact
with road hazards like,
potholes, or sharp edged
objects, or when sliding into a
curb. The warranty does not
cover this type of damage.
Keep tires set to the correct
inflation pressure and, when
possible, avoid contact with
curbs, potholes, and other
road hazards.
Page 438 of 556
Black plate (52,1)GMC Sierra Owner Manual - 2012 - CRC - 11/15/11
10-52 Vehicle Care
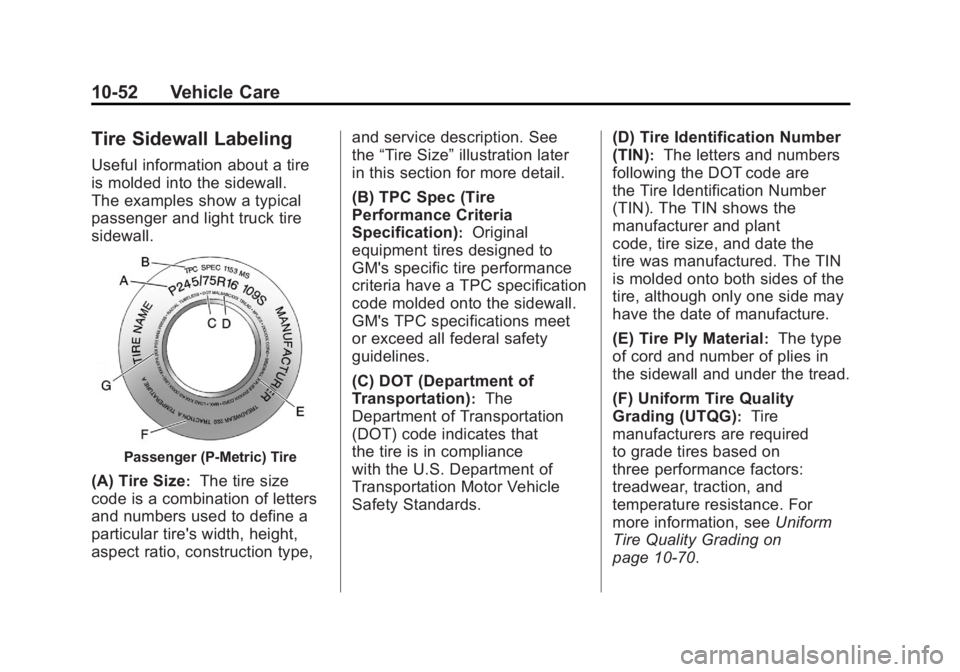
Tire Sidewall Labeling
Useful information about a tire
is molded into the sidewall.
The examples show a typical
passenger and light truck tire
sidewall.
Passenger (P‐Metric) Tire
(A) Tire Size:The tire size
code is a combination of letters
and numbers used to define a
particular tire's width, height,
aspect ratio, construction type, and service description. See
the
“Tire Size” illustration later
in this section for more detail.
(B) TPC Spec (Tire
Performance Criteria
Specification)
:Original
equipment tires designed to
GM's specific tire performance
criteria have a TPC specification
code molded onto the sidewall.
GM's TPC specifications meet
or exceed all federal safety
guidelines.
(C) DOT (Department of
Transportation)
:The
Department of Transportation
(DOT) code indicates that
the tire is in compliance
with the U.S. Department of
Transportation Motor Vehicle
Safety Standards. (D) Tire Identification Number
(TIN)
:The letters and numbers
following the DOT code are
the Tire Identification Number
(TIN). The TIN shows the
manufacturer and plant
code, tire size, and date the
tire was manufactured. The TIN
is molded onto both sides of the
tire, although only one side may
have the date of manufacture.
(E) Tire Ply Material
:The type
of cord and number of plies in
the sidewall and under the tread.
(F) Uniform Tire Quality
Grading (UTQG)
:Tire
manufacturers are required
to grade tires based on
three performance factors:
treadwear, traction, and
temperature resistance. For
more information, see Uniform
Tire Quality Grading on
page 10‑70.
Page 439 of 556

Black plate (53,1)GMC Sierra Owner Manual - 2012 - CRC - 11/15/11
Vehicle Care 10-53
(G) Maximum Cold Inflation
Load Limit
:Maximum load
that can be carried and the
maximum pressure needed
to support that load. For
information on recommended
tire pressure see Tire Pressure
on page 10‑58 andVehicle Load
Limits on page 9‑16.
Light Truck (LT-Metric) Tire
(A) Tire Size:The tire size
code is a combination of letters
and numbers used to define a
particular tire's width, height, aspect ratio, construction type,
and service description. See the
“Tire Size”
illustration later in this
section for more detail.
(B) TPC Spec (Tire
Performance Criteria
Specification)
:Original
equipment tires designed to
GM's specific tire performance
criteria have a TPC specification
code molded onto the sidewall.
GM's TPC specifications meet
or exceed all federal safety
guidelines.
(C) Dual Tire Maximum Load
:
Maximum load that can be
carried and the maximum
pressure needed to support
that load when used in a dual
configuration. For information on
recommended tire pressure see
Tire Pressure on page 10‑58
and Vehicle Load Limits on
page 9‑16. (D) DOT (Department of
Transportation)
:The
Department of Transportation
(DOT) code indicates that
the tire is in compliance
with the U.S. Department of
Transportation Motor Vehicle
Safety Standards.
(E) Tire Identification Number
(TIN)
:The letters and numbers
following the DOT code are
the Tire Identification Number
(TIN). The TIN shows the
manufacturer and plant code,
tire size, and date the tire was
manufactured. The TIN is
molded onto both sides of the
tire, although only one side may
have the date of manufacture.
Page 440 of 556

Black plate (54,1)GMC Sierra Owner Manual - 2012 - CRC - 11/15/11
10-54 Vehicle Care
(F) Tire Ply Material:The type
of cord and number of plies in
the sidewall and under the tread.
(G) Single Tire Maximum
Load
:Maximum load that can
be carried and the maximum
pressure needed to support that
load when used as a single. For
information on recommended
tire pressure see Tire Pressure
on page 10‑58 andVehicle Load
Limits on page 9‑16.
Tire Designations
Tire Size
The examples show a typical
passenger vehicle and light
truck tire size.
Passenger (P‐Metric) Tire
(A) Passenger (P‐Metric) Tire:
The United States version of a
metric tire sizing system. The
letter P as the first character in
the tire size means a passenger
vehicle tire engineered to
standards set by the U.S. Tire
and Rim Association.
(B) Tire Width
:The three‐digit
number indicates the tire section
width in millimeters from
sidewall to sidewall.
(C) Aspect Ratio
:A two‐digit
number that indicates the tire
height‐to‐width measurements.
For example, if the tire size
aspect ratio is 75, as shown in
item C of the tire illustration, it would mean that the tire's
sidewall is 75 percent as high
as it is wide.
(D) Construction Code
:A
letter code is used to indicate
the type of ply construction in
the tire. The letter R means
radial ply construction; the
letter D means diagonal or
bias ply construction; and the
letter B means belted‐bias ply
construction.
(E) Rim Diameter
:Diameter of
the wheel in inches.
(F) Service Description
:These
characters represent the load
index and speed rating of the
tire. The load index represents
the load carrying capacity a tire
is certified to carry. The speed
rating is the maximum speed a
tire is certified to carry a load.