2011 SKODA OCTAVIA TOUR airbag
[x] Cancel search: airbagPage 81 of 183

Communication
80
CommunicationMobile phones and two-way radio systemsThe installation of a mobile phone and two- way radio system in a vehicle should be
carried out by a specialist garage.
Škoda Auto permits the operation of mobile phones and two-way radio systems
with a professionally instal led external aerial and a maximum transmission power
of up to 10 Watts.
It is essential that you inform a specialist garage about the possibilities to assemble
and operate mobile phones and two-way ra dio sets which have a power output of
more than 10 W. The garage will inform you which technical possibilities exist for
retrofitting mobile phones.
Operation of mobile phones or two-way radio systems may interfere with func-
tioning of the electronic systems of your vehicle. The reasons for this may be:•
no external aerial,
•
external aerial in correctly installed,
•
transmission power greater than 10 watts.
WARNING
•
If a mobile phone or a two-way radio system is operated in the vehicle
without using a special external aerial or an external aerial which has been
incorrectly installed, this can increase the strength of the electromagnetic field
in the interior of the vehicle.
•
Please concentrate fully at all times on your driving!
•
You must not install two-way radio systems, mobile phones or mounts on
the covers of the airbags or within the immediate deployment range of airbags.
This might result in injuries to the occupants in the event of an accident.
•
Never leave a mobile phone on a seat, on the dash panel or in another area,
from which it can be thrown during a su dden braking manoeuvre, an accident or
a collision. In this case, the occup ants of the vehicle might be injured.Note
Observe the country-specific regulations for the use of mobile phones in vehicles.s2lk.2.book Page 80 Monday, April 18, 2011 7:41 AM
Page 82 of 183

Passive Safety81
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
SafetyPassive SafetyBasic informationDriving the safe way
Passive safety measures reduce the risk of injury in accident situa-
tions.In this section you will find important information, tips and notes on the subject of
passive safety in your vehicle. We have combined everything here which you should
be familiar with, for example, regarding seat belts, airbags, child seats and safety of
children. It is therefore important, in particular, to comply with the notes and warn-
ings in this section for your own interest and in the interest of those travelling with
you.
WARNING
•
This chapter contains important information on how to use the vehicle for
the driver and his occupants. You will find further information on safety, which
concerns you and those travelling with yo u, in the following chapters of this
Owner's Manual.
•
The complete on-board literature shou ld always be in the vehicle. This
applies in particular, if you rent out or sell the vehicle.
Safety equipment
The safety equipment is part of th e occupant protection and it can
reduce the risk of injuries in accident situations.“Do not put at risk” your safety and the safe ty of those travelling with you . In the
event of an accident, the safety equipment can reduce the risk of injuries. The
following list contains part of th e safety equipment in your vehicle:•
Three-point seat belts for all the seats,
•
belt force limiter for front seats and outer rear seats*,
•
belt tensioner for front seats,
•
seat belt height adjuster for front seats,
•
front airbag for the driver and the front seat passenger*,
•
side airbags*,
•
head airbags*,
•
anchoring points for child seat using the “ISOFIX” system,
•
anchoring points for child seat using the “Top Tether” system,
•
head restraint adjustable for height,
•
adjustable steering column.
The specified safety equipment works toge ther, in order to optimally protect you
and those travelling with yo u in accident situations. The safety equipment does not
protect you or the people travelling with you, if you or your occupants adopt an
incorrect seated position or the equipment is not correctly adjusted or used.
For this reason you will be provided with information on why this equipment is very
important, how it protects you and the occupants, what should be observed when
using the equipment and how you and the peop le travelling with you can make full
use of the existing safety equipment. This Owner's Manual contains important
warning notes, which you and those travelli ng with you should pay attention to in
order to reduce a risk of injury.
Safety concerns everybody!
Before setting off
The driver is always fully responsible for his occupants and for the
operating safety of the vehicle.For your own safety and the safety of the people travelling with you, please pay
attention to the following points before setting off:•
Ensure that the lighting and the turn signal system are functioning properly.
•
Inspect the tyre inflation pressure.
•
Ensure that all the windows offer a good visibility to the outside.
•
Safely attach the items of luggage page 53, “Loading the luggage compart-
ment”.
•
Ensure that no objects can obstruct the pedal.
•
Adjust the mirror, the front seat and the head restraint to match your body size.
s2lk.2.book Page 81 Monday, April 18, 2011 7:41 AM
Page 84 of 183

Passive Safety83
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
•
The driver must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the steering wheel
page 82, fig. 89 - left. Not maintaining this minimum distance will mean that
the airbag system will not be able to properly protect you - hazard!
•
When driving, hold the steering wheel with both hands firmly on the outer
edge in the 9 o'clock and 3 o'clock positi on. Never hold the steering wheel firmly
in the 12 o'clock position or in another way (e.g. in the middle of the steering
wheel or at the inner steering wheel edge). In such cases, injuries to the arms,
the hands and the head can occur when the driver airbag is deployed.
•
The seat backrests must not be angled too far back when driving otherwise
this will affect proper operation of the se at belts and of the airbag system - risk
of injury!
•
Ensure that there are no objects in the footwell as any objects may get
behind the pedals during a driving or braking manoeuvre. You would then no
longer be able to operate the clutch, to brake or accelerate.
Correct seated position for the front passenger
The front passenger must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm from
the dash panel so that the airbag offers him the greatest possible
safety it is deployed.For the safety of the front passenger and to reduce the risk of injury in the event of
an accident, we recommend the following setting:•
Adjust the front passenger seat as far as possible to the rear.
•
Adjust the head restraint so that the top edge of the head restraint is at the
same level as the upper part of your head page 82, fig. 89 - right.
•
Fasten the seat belt correctly page 87, “How are seat belts correctly
fastened?”.
In exceptional cases the front passenger airbag can be deactivated page 95,
“Deactivating an airbag”.
Manual front passenger adjustment page 11, “Adjusting the front seats”.
WARNING
•
The front seats and the head restraints must always be adjusted to match
the body size of the seat occupant as well as the seat belts must always be
correctly fastened in order to provide an optimal protection for you and your
occupants.
•
The front passenger must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the dash
panel. Not maintaining this minimum dist ance will mean that the airbag system
will not be able to prop erly protect you - hazard!
•
Keep your feet in the footwell at all times while driving. Never place your feet
on the dash panel, out of the window or on the seats. You will be exposed to
increased risk of injury if it becomes ne cessary to apply the brake or in the event
of an accident. If an airbag is deployed, you may suffer fatal injuries when
adopting an incorrect seated position!
•
The seat backrests must not be angled too far back when driving otherwise
this will affect proper operation of the seat belts and of the airbag system - risk
of injury!
Correct seated position for the occupants on the rear seats
Occupants on the rear seats must sit upright, keep the feet in the
footwell and must have their seat belts correct ly fastened.To reduce the risk of injury in the event of a sudden braking manoeuvre or an acci-
dent, the occupants on the rear seats must observe the following:•
Adjust the head restraints so that the top edge of the head restraints is at the
same level as the upper part of your head page 82, fig. 89 - on the right.
•
Fasten the seat belt correctly page 87, “How are seat belts correctly
fastened?”.
•
If you are transporting page 97, “Transporting children safely” children in the
vehicle, please use a suitable child restraint system.
WARNING
•
The head restraints must always be adju sted to match the body size, in order
to offer an optimal protection for you and your occupants.
•
Keep your feet in the footwell at all times while driving. Never place your feet
out of the window or on the seats. You will be exposed to increased risk of injury
if it becomes necessary to apply the brak e or in the event of an accident. If an
airbag is deployed, you may suffer fata l injuries when adopting an incorrect
seated position!
•
If the occupants on the rear seats are not sitting upright, the risk of injury is
increased due to incorrect routing of the seat belt.
WARNING (continued)
WARNING (continued)
s2lk.2.book Page 83 Monday, April 18, 2011 7:41 AM
Page 85 of 183

Passive Safety
84
Examples of an incorrect seated position
An incorrect seated posi tion can lead to severe injuries or death for
the occupants.Seat belts offer their optimum protection on ly if the webbing of the seat belts is
properly routed. Incorrect seated positions considerably reduce the protective func-
tions of the seat belts and therefore increase the risk of injury due to an incorrect
routing of the seat belt. The driver is fully responsible for himself and the occupants,
in particular for the children. Do not permit an occupant to adopt an incorrect seated
position when the car is moving.
The following list contains the examples of seated positions which are dangerous
for the occupants. This list is not complete, however we would like you to get
familiar with this subject.
Therefore, while the car is moving never:•
stand up in the vehicle,
•
stand up on the seats,
•
kneel onto the seats,
•
tilt the seat backrest fully to the back,
•
lean against the dash panel,
•
lie on the rear seats,
•
only sit on the front area of the seat,
•
sit to the side,
•
lean out of the window,
•
put the feet out of the window,
•
put the feet on the dash panel,
•
put the feet on the seat upholstery,
•
occupy the footwell,
•
have the seat belt not fastened,
•
occupy the luggage compartment.
WARNING
•
If the occupant adopts an incorrect seat ed position, he is exposed to life-
threatening injuries, in case he is hit by a deployed airbag.
•
Before setting off, please adopt the correct seated position and do not
change this seated position while the car is moving. Also advise your occupants to adopt the correct seated
position and not to change this seated position
while the car is moving.
WARNING (continued)
s2lk.2.book Page 84 Monday, April 18, 2011 7:41 AM
Page 86 of 183

Seat belts85
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
Seat beltsWhy seat belts?It is a proven fact that seat belt s offer good protection in accidents fig. 90. Thus
wearing a seat belt is a legal requirement in most countries.
Seat belts which have been correctly fast ened and adjusted hold the occupants of
the car in the correct seated position fig. 90. The seat belts reduce the kinetic
energy (energy of motion) to a considerable extent. They also prevent uncontrolled
movements which, in turn, may we ll result in severe injuries.
The occupants of a vehicle who have fastened and correctly adjusted their seat belt,
profit to a major extent from the fact that the kinetic energy is optimally absorbed
by the belts. The structure of the front end of the vehicle and other passive safety
measures, such as the airbag system, also contribute to reducing the kinetic energy.
The energy produced is thus absorbed and there is less risk of injury.
Accident statistics prove that seat belts which are fastened and properly adjusted
reduce the risk of an injury and enhance th e chance of survival in a major accident
page 85.
It is important that you pay attention to safety measures, particularly when trans-
porting children in the vehicle page 97, “What you should know about trans-
porting children!”.
WARNING
•
F a s t e n y o u r s e a t b e l t e a c h t i m e b e f o r e s e t t i n g o f f , a l s o w h e n d r i v i n g i n t o w n !
This also applies to the people seat ed at the rear - risk of injury!
•
Expectant women must also always wear a seat belt. This is the only way of
ensuring optimal protection for the unborn child page 87.
•
It i s i m po rta n t f or th e b el t we bb in g to be p rop er ly rou te d i f th e s ea t be lts a re
to offer the maximum protection. You can see a description of how safety belts
should be fitted properly on the next pages.Note
Please comply with any differing legal requirements when using the seat belts.The physical principle of a frontal collisionFig. 91 The driver is thrown forward if not we aring a belt/the rear seat occupant is thrown
forward if not wearing a beltThe physical principle of a frontal accident can be explained quite simply:
Motion energy, so-called kinetic energy, is produced as soon as the vehicle is
moving, both for the vehicle and its occupants. The magnitude of this kinetic energy
depends essentially on the speed at which the vehicle is travelling and on the
weight of the vehicle and the occupants. The greater the speed and weight
increase, the greater the amount of energy which has to be absorbed in the event
of an accident.
The speed of the vehicle is, nevertheless, the most important factor. Doubling the
speed of the vehicle from 25 km/h up to 50 km/hour increases the kinetic energy
four times.
Fig. 90 Driver wearing seat belt
WARNING (continued)
s2lk.2.book Page 85 Monday, April 18, 2011 7:41 AM
Page 89 of 183
Seat belts
88Note
It is also possible to adapt the routing of the belt webbing at the front seats by
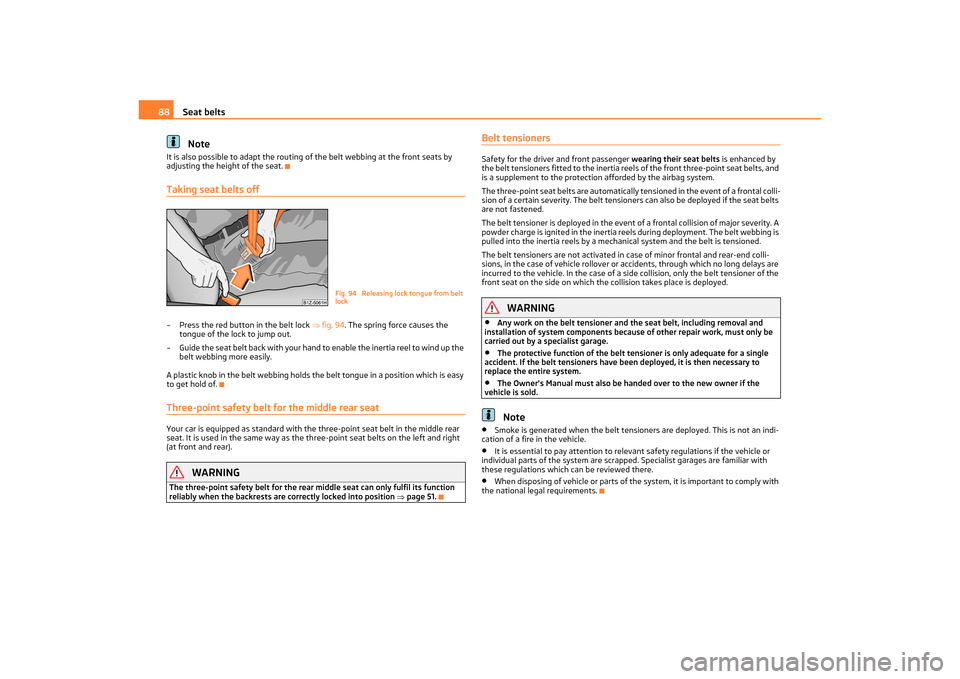
adjusting the height of the seat.Taking seat belts off– Press the red button in the belt lock fig. 94 . The spring force causes the
tongue of the lock to jump out.
– Guide the seat belt back with your hand to enable the inertia reel to wind up the
belt webbing more easily.
A plastic knob in the belt webbing holds the belt tongue in a position which is easy
to get hold of.Three-point safety belt for the middle rear seatYour car is equipped as standard with the three-point seat belt in the middle rear
seat. It is used in the same way as the th ree-point seat belts on the left and right
(at front and rear).
WARNING
The three-point safety belt for the rear middle seat can only fulfil its function
reliably when the backrests are correctly locked into position page 51.
Belt tensionersSafety for the driver and front passenger wearing their seat belts is enhanced by
the belt tensioners fitted to the inertia reel s of the front three-point seat belts, and
is a supplement to the protection afforded by the airbag system.
The three-point seat belts are automatically tensioned in the event of a frontal colli-
sion of a certain severity. The belt tensioners can also be deployed if the seat belts
are not fastened.
The belt tensioner is deployed in the event of a frontal collision of major severity. A
powder charge is ignited in the inertia reels during deployment. The belt webbing is
pulled into the inertia reels by a mechan ical system and the belt is tensioned.
The belt tensioners are not activated in case of minor frontal and rear-end colli-
sions, in the case of vehicle rollover or accidents, through which no long delays are
incurred to the vehicle. In the case of a si de collision, only the belt tensioner of the
front seat on the side on which the collision takes place is deployed.
WARNING
•
Any work on the belt tensioner and the seat belt, including removal and
installation of system components because of other repair work, must only be
carried out by a specialist garage.
•
The protective function of the belt te nsioner is only adequate for a single
accident. If the belt tensioners have b een deployed, it is then necessary to
replace the entire system.
•
The Owner's Manual must also be handed over to the new owner if the
vehicle is sold.Note
•
Smoke is generated when the belt tensioners are deployed. This is not an indi-
cation of a fire in the vehicle.
•
It is essential to pay attention to releva nt safety regulations if the vehicle or
individual parts of the system are scrapped. Specialist garages are familiar with
these regulations which can be reviewed there.
•
When disposing of vehicle or parts of the system, it is important to comply with
the national legal requirements.
Fig. 94 Releasing lock tongue from belt
lock
s2lk.2.book Page 88 Monday, April 18, 2011 7:41 AM
Page 90 of 183

Airbag system89
Using the system
Safety
Driving Tips
General Maintenance
Breakdown assistance
Technical Data
Airbag systemDescription of the airbag systemGeneral information on the airbag systemThe front airbag system is complementary to the three-point seat belts and offers
additional protection for the head and ches t area of the driver and passenger in the
event of a frontal collision.
In the case of a violent side crash, the si de airbags* and head airbags* reduce the
risk of injuries to the occupant s on the side of the collision .
The airbag system is only functional after the ignition has been switched on.
The operational readiness of the airbag system is monitored electronically. The
airbag indicator light comes on for a few seconds each time the ignition is switched
on.
The airbag system (according to vehicle equipment) consists of:•
an electronic control unit,
•
front airbag for the driver and the front seat passenger*,
•
side airbags*,
•
head airbags*,
•
an airbag warning light in the instrument cluster,
•
a key-operated switch for switching on /off the front seat passenger airbag*
page 96,
•
an indicator light for a switched off front seat passenger airbag* in the middle
of the dash panel page 96.
A fault in the airbag system exists if:
•
the airbag indicator light does not light up when the ignition is switched on,
•
the airbag indicator light does not go ou t after about 4 seconds after the ignition
is switched on,
•
the airbag indicator light goes out and comes on again after the ignition is
switched on,
•
the airbag indicator light comes on or flickers when driving,
•
an airbag indicator light showing a swit ched-off front passenger airbag* in the
middle of the dash panel flashes.
WARNING
•
To enable the occupants of a vehicle to be protected with the greatest
possible effect when the airbag is depl oyed, the front seats must be correctly
adjusted to match the body size of the occupant page 82, “Correct seated
position”.
•
If you do not fasten the seat belts when driving, lean too far forward or adopt
an incorrect seated position, you are exposing yourself to increased risk of injury
in the event of an accident.
•
Have the airbag system checked immediately by a specialist garage if a fault
exists. Otherwise, there is a risk of the airbag not being activated in the event
of an accident.
•
No modifications of any kind may be made to parts of the airbag system.
•
It is prohibited to manipulate individu al parts of the airbag system as this
might result in the airbag being deployed.
•
The protective function of the airbag system is sufficient for only one acci-
dent. The airbag system must then be replaced if the airbag has been deployed.
•
The airbag system needs no maintenance during its working life.
•
If you sell your car, please hand over the complete vehicle documentation to
the new owner. Please note that the do cuments relating to the possibility of
deactivating the front passenger airbag are also part of the vehicle documents!
•
If the vehicle or individual parts of the airbag system are scrapped, it is
essential to observe the relevant safety precautions. The authorised Škoda
Service Partners are familiar with these regulations.
•
When disposing of vehicle or parts of the airbag system, it is important to
comply with the national legal requirements.
When are the airbags deployed?The airbag system is designed in such a way that the driver and front passenger
airbag are deployed in the event of a violent frontal collision .
In the case of a violent side collision , the side airbag* on the side of the vehicle at
which the collision occurs, is deployed together with the relevant head airbag*.
In special accident scenarios, the front as well as the relevant side and head airbags
may be deployed together.
s2lk.2.book Page 89 Monday, April 18, 2011 7:41 AM
Page 91 of 183

Airbag system
90
The airbags are not deployed in the case of minor frontal and side collisions, in the
case of rear-end collisions and vehicle rollover.
Deployment factors
It is not possible to state globally which deployment conditions apply to the airbag
system in every situation as the circumstances which exist in the case of accidents
vary greatly. An important role in this case is played by factors such as the type of
object against which the vehicle impacts (hard, soft), the angle of impact, the rela-
tive speed during the accident etc.
A decisive factor for the deployment of th e airbags is the deceleration which occurs
during a collision. The control unit analyses the nature of the collision and activates
the relevant restraint system. If the vehicle deceleration which occurs and is meas-
ured during the collision remains below the prescribed reference values specified in
the control unit, the airbags are not deployed although the vehicle may well suffer
severe damage to the bodywork as a consequence of the accident.
The airbags are not deployed if:•
ignition off,
•
a minor frontal collision,
•
a minor side collision,
•
a rear-end collision,
•
Rollover of the vehicle.Note
•
A grey white, non harmful gas is released when airbag is inflated. This is
perfectly normal and is not an indi cation of a fire in the vehicle.
•
In the event of an accident in which the airbags are deployed:
−The interior lighting comes on (if the switch for the interior light is in the door
contact position),
− The hazard warning light is switched on,
− All the doors are unlocked,
− the fuel supply to the engine is interrupted.
Front airbagsDescription of the front airbags
The airbag system is not a substitute for the seat belt!Fig. 95 Driver airbag in the steering wheel /front passenger airbag in the dash panelThe front airbag for the driver is housed in the steering wheel fig. 95 - left. The
front airbag for the front passenger* is housed in the dash panel above the storage
compartment fig. 95 - right. The installation positions are each marked with the
“AIRBAG” logo.
The front airbag system is complementary to the three-point seat belts and offers
additional protection for the head and chest area of the driver and passenger in the
event of a frontal collision. page 91
The airbag is not a substitute for the seat belt, but is part of the complete passive
vehicle safety concept. Please note that an airbag can only offer you optimal
protection in combination with a seat belt which is fastened .
Apart from their normal protective function, a further task of the seat belts i s t o a l s o
hold the driver and front passenger in a co rrect seated position in the event of a
frontal collision so as to enable the fron t airbags to offer the maximum protection.
You should therefore always fasten the seat belts, not only because this is required
by law, but also for safety reasons and for your own protection page 85, “Why
seat belts?”.
Note
The dash panel must be replaced after the front passenger airbag has been
deployed.
s2lk.2.book Page 90 Monday, April 18, 2011 7:41 AM