2011 FORD KUGA oil change
[x] Cancel search: oil changePage 1720 of 2057

Turbocharger – Overview
Turbocharger(s)
CAUTION: Do not switch off the engine
while it is running at high speed. If the
engine is switched off while it is running
at high speed, the turbocharger will
continue to run after the engine oil
pressure has already dropped to zero. This
will cause premature wear in the
turbocharger bearings.
A TC consists of an exhaust turbine located in the
exhaust gas flow, this turbine is connected to a
compressor by a shaft. The turbine is made to
rotate by the exhaust gas flow from the engine and
thus drives the compressor. The compressor
increases the pressure in the engine intake tract
so that a greater mass of air enters the cylinder
during the intake stroke.
The turbine housing of the TC is integrated into the
exhaust manifold. This construction offers
thermodynamic advantages compared with the
usual construction, the maximum exhaust
temperature is up to 1050°C.
The maximum boost pressure is 0.65 bar.
The exhaust manifold is secured to the exhaust
side of the cylinder head with 12 self-locking nuts.
The exhaust manifold gasket is a multi-layer steel
gasket and cannot be reused. In order to
compensate for the thermal expansion of the
exhaust manifold, the flange of the TC is provided
with two grooves.
The TC and the exhaust manifold are joined by a
hose clip. The hose clip must not be loosened or
removed. The TC and the exhaust manifold are
not available as separate replacement parts,
exchange is only possible as a complete unit.
The turbocharger heat shield is secured to the
exhaust manifold by four bolts. Two of the bolts
have spring washers underneath their heads.
During removal, make a note of the installation
location of the spring washers to refer to during
installation.
The recirculated air valve is built into the TC
housing and cannot be changed.
The Ford diagnostic unit can test the operation of
the wastegate control valve using actuator
diagnosis.
The boost pressure regulator is set in the factory.
Adjustments to the boost pressure regulator must never be attempted. A red colored seal is applied
to the adjustment nut of the operating rod, in order
to monitor the factory setting of the boost pressure.
The bearings of the TC are lubricated with engine
oil. The engine oil passes from the cylinder block
through the oil supply pipe to the TC. The oil is
returned to the oil pan through the oil return pipe,
The TC is cooled by the engine coolant circuit.
When installing hoses and lines, make certain that
their ends are free of oil residues and dirt.
G1032425en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-04B-
4
Fuel Charging and Controls - Turbocharger
—
2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5
303-04B- 4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1796 of 2057

current value is reached. The PCM then
permanently connects the heating element to earth.
The catalyst monitor sensor is used by the PCM
to measure the oxygen content in the exhaust gas
in the TWC. If all the conditions for catalyst
diagnostics are met, based on this information the
PCM can check that the TWC is working
satisfactorily. The information is also used to
improve the air/fuel mixture adjustment.
The catalyst monitor sensor is similar in function
to an HO2S. The signal transmitted by the catalyst
monitor sensor changes sharply if the oxygen
content in the exhaust gas changes. For this
reason, catalyst monitor sensors are also called
"jump lambda sensors".
Fuel tank purging
The EVAP purge valve is only actuated by the PCM
if the coolant temperature is at least 60°C.
Actuation is done ground side by means of a PWM
signal. This makes it possible to have the full range
of opening widths, from fully closed to fully open.
The PCM determines from the operating conditions
when and how wide to open the EVAP tank purge
valve. If the EVAP purge valve is opened, the
engine sucks in ambient air through the activated
charcoal in the evaporative emission canister as
a result of the vacuum in the intake manifold. In
this way the adsorbed hydrocarbons are led to the
combustion chamber of the engine.
The EVAP tank purge valve is not actuated and
system cleaning is interrupted if the engine
switches to idle and/or a closed-loop control
process is initiated.
Power (battery voltage) is supplied via the
Powertrain Control Module relay in the BJB. The
solenoid coil resistance is between 17 and 24 ohms
at 20°C.
Engine speed control
The APP sensor provides the PCM with information
about the driver's request for acceleration.
The throttle control unit receives a corresponding
input signal from the PCM. An electric motor then
moves the throttle valve shaft by means of a set
of gears. The position of the throttle is continuously
recorded by the TP sensor. Information on throttle
position is processed and monitored by the PCM.
The TP sensor comprises two potentiometers.
These work in opposite ways to each other. In one
potentiometer, the resistance increases when the
throttle is opened, in the other it decreases. Thisallows the operation of the potentiometers to be
checked. The signal from the TP sensor is
amplified in the lower range (idle to a quarter open)
by the PCM to enable more precise control of the
throttle in this range. This is necessary because
the engine is very sensitive to changes in throttle
angle in this throttle opening range.
With the throttle valve position kept constant, the
ignition angle and the injected fuel quantity are
then varied to meet the torque demands.
Depending on the operating state of the engine, a
change in the position of the throttle flap may not
be necessary when the APP sensor changes.
If a fault develops in the throttle control unit, a
standby function is executed. This standby function
allows a slight opening of the throttle flap, so that
enough air passes through to allow limited engine
operation. For this purpose, there is a throttle flap
adjustment screw on the throttle housing. The
return spring closes the throttle flap until the stop
of the toothed segment touches the stop screw. In
this way a defined throttle flap gap is formed for
limp home mode.
The stop screw has a spring loaded pin, which
holds the throttle flap open for limp home mode.
In normal operating mode, this spring loaded pin
is pushed in by the force of the electric motor when
the throttle flap must be closed past the limp home
position (e.g. for idle speed control or overrun
shutoff).
Oil monitoring
The engine does not have an oil pressure
switch.
The oil level and oil quality are calculated.
Calculating the engine oil level
The oil level is determined by continuous
measurement of the capacitance (i.e. the ability to
store an electrical charge) between the two
capacitive elements of the engine oil
level/temperature/quality sensor. The different oil
levels cause the capacitance between the elements
to change. The data are recorded by the PCM and
converted into an oil level value. Temporary
fluctuations in oil level are automatically filtered out
by the PCM.
Calculating oil quality
The PCM calculates the oil quality from the oil level
measurement and the oil temperature measured
by the sensor, plus the engine speed and the
average fuel consumption. The driver is informed
about when an oil change is due.
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 22
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
22
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1797 of 2057

Calculation of valve timing adjustment
angle
The 2.5L Duratec (VI5) engine has two camshaft
adjustment units which work independently of each
other.
One camshaft adjustment solenoid is installed for
each intake camshaft and exhaust camshaft.
This allows the PCM to continuously adjust the
intake and exhaust-side camshaft adjustments
independently of one another. The timing is
adjusted by the PCM using curves; adjustment is
primarily done as a function of engine load and
engine speed.
In this way the engine performance is increased
and internal exhaust gas recirculation is realized.
The advantages of camshaft adjustment are as
follows:
• Higher torque and improved torquecharacteristics
• Reduced fuel consumption
• Improved emissions performance
The camshaft adjustment solenoids are actuated
by the PWM by means of a PCM signal.
Continuous adjustment of the camshafts by the
PCM is achieved by means of the camshaft
adjustment solenoids, the camshaft adjustment
units and two CMP sensors. A defined quantity of
engine is oil is supplied to or drained from the
adjustment units via the camshaft adjustment
solenoids. The existing EOP (engine oil pressure)
is taken into account in the process. In this way
the valve timings are adjusted according to the
operating condition of the engine. The camshaft
adjusters work according to the vane-cell principle.
On starting the engine, both camshafts are
mechanically locked in their starting positions. The
intake camshaft is in the maximum late position
and the exhaust camshaft in the maximum early
position.
Control is divided into four main areas:
• Low engine speed and low load
• Partial load
• Low engine speed and high load
• High engine speed and high load
At low engine speed and low load, the exhaust
valves open early and the intake valves open late.
The result is reduced fuel consumption and more
uniform idling. In the partial load range, the exhaust valves and
the intake valves open late. The late opening of
the exhaust valves results in a good utilization of
the expanding gases in the cylinder. Closing the
exhaust valves after Top Dead Center allows
internal exhaust gas recirculation through aspiration
of exhaust gases into the combustion chamber.
Moreover, the intake valves close after Bottom
Dead Centre, allowing the fresh air/fuel mixture
and exhaust gases to flow back into the intake
tract. The result is reduced fuel consumption and
low emissions.
At low engine speed and high engine load, the
exhaust valves open late and the intake valves
open early. Due to the resulting valve opening
overlap at Top Dead Centre, the pulsating gas
column within the combustion chamber is utilized
to achieve better charging of the combustion
chamber. The result is increased torque at lower
RPM.
At high engine speeds and high engine load, the
exhaust valves open early and the intake valves
close late. Because a rapid gas exchange must be
achieved at high engine speeds, the early opening
of the exhaust valves achieves better expulsion of
the exhaust gas and the late closing of the intake
valves improves cylinder charge efficiency.
Optimum power output is achieved.
Many other camshaft positions are possible in
addition to these settings.
In order to avoid a malfunction in the camshaft
adjustment units at excessively low ambient or
engine-oil temperatures, they are activated by the
PCM with a time delay via the camshaft adjustment
solenoids. The PCM receives the information
required for this from the ECT sensor and the
outside air temperature sensor.
When idling and during deceleration, the camshaft
adjustment solenoids are activated repeatedly by
the PCM in order to remove any dirt which may be
on the bore holes and ring grooves.
Boost pressure control
Optimum regulation is achieved by means of an
electronically-controlled solenoid valve, the boost
control solenoid valve.
Refer to:
Turbocharger (303-04 Fuel Charging and
Controls - Turbocharger - 2.5L Duratec
(147kW/200PS) - VI5, Description and
Operation).
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 23
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
23
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1807 of 2057
Description
Item
Coil-on-plug ignition coil
1
Spark plug connector
2
Low-voltage connection
3
Laminated soft-iron core
4Description
Item
Primary winding
5
Secondary winding
6
Spark plug
7
High-voltage connection via spring contact
8
In an ignition system with coil-on-plug ignition coils,
each cylinder is actuated individually and only once
per cycle (working stroke). The coil-on-plug ignition
coils are mounted directly on the spark plugs,
therefore no ignition cables are required between
the ignition coils and the spark plugs.
Each individual ignition coil is actuated on the
low-voltage side by the PCM. The power
end-stages are incorporated into the coil-on-plug
ignition coils. Only the actuating current for these
power end-stages is controlled by the PCM.
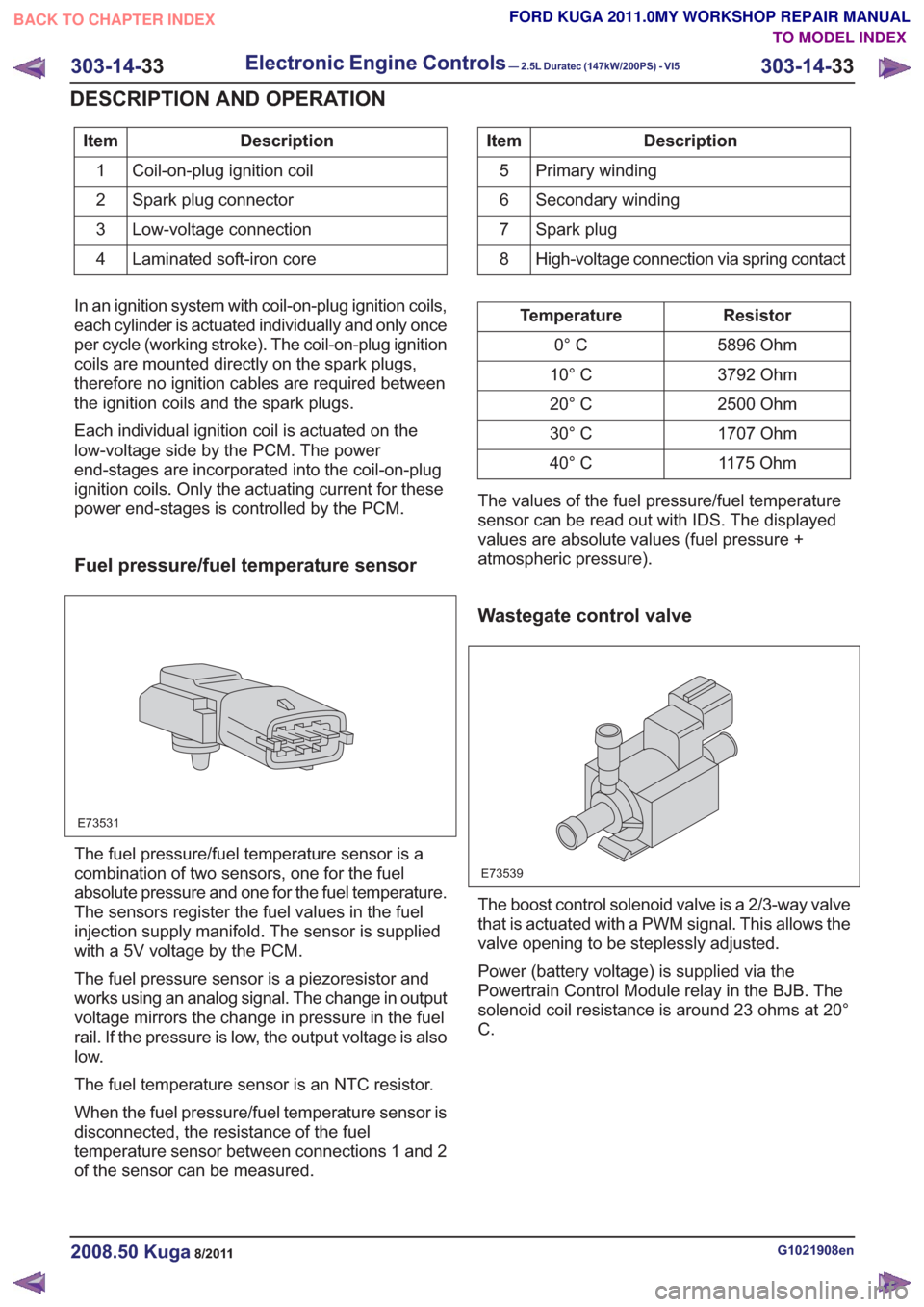
Fuel pressure/fuel temperature sensor
E73531
The fuel pressure/fuel temperature sensor is a
combination of two sensors, one for the fuel
absolute pressure and one for the fuel temperature.
The sensors register the fuel values in the fuel
injection supply manifold. The sensor is supplied
with a 5V voltage by the PCM.
The fuel pressure sensor is a piezoresistor and
works using an analog signal. The change in output
voltage mirrors the change in pressure in the fuel
rail. If the pressure is low, the output voltage is also
low.
The fuel temperature sensor is an NTC resistor.
When the fuel pressure/fuel temperature sensor is
disconnected, the resistance of the fuel
temperature sensor between connections 1 and 2
of the sensor can be measured.
Resistor
Temperature
5896 Ohm
0° C
3792 Ohm
10° C
2500 Ohm
20° C
1707 Ohm
30° C
1175 Ohm
40° C
The values of the fuel pressure/fuel temperature
sensor can be read out with IDS. The displayed
values are absolute values (fuel pressure +
atmospheric pressure).
Wastegate control valve
E73539
The boost control solenoid valve is a 2/3-way valve
that is actuated with a PWM signal. This allows the
valve opening to be steplessly adjusted.
Power (battery voltage) is supplied via the
Powertrain Control Module relay in the BJB. The
solenoid coil resistance is around 23 ohms at 20°
C.
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 33
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
33
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1808 of 2057
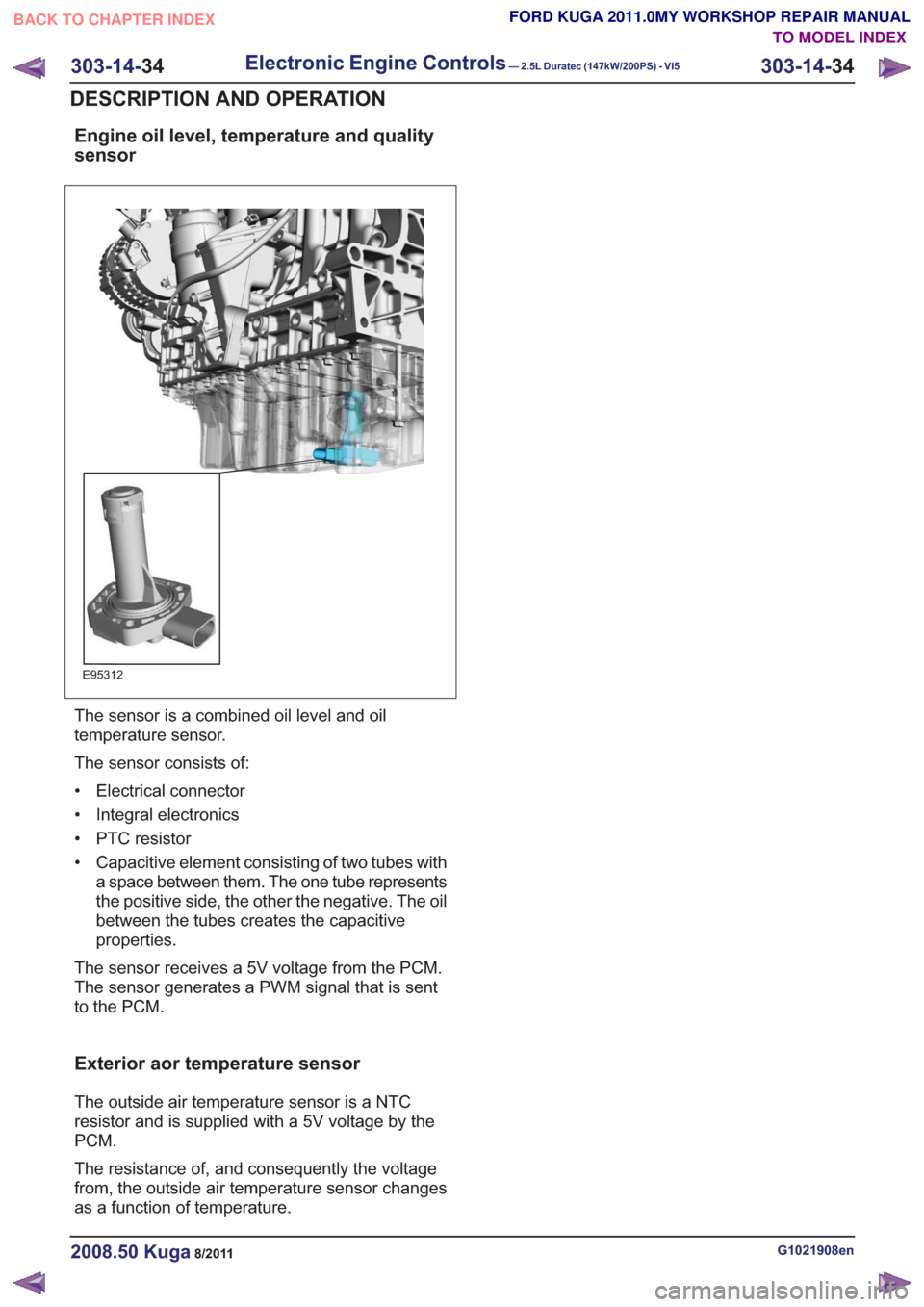
Engine oil level, temperature and quality
sensor
E95312
The sensor is a combined oil level and oil
temperature sensor.
The sensor consists of:
• Electrical connector
• Integral electronics
• PTC resistor
• Capacitive element consisting of two tubes witha space between them. The one tube represents
the positive side, the other the negative. The oil
between the tubes creates the capacitive
properties.
The sensor receives a 5V voltage from the PCM.
The sensor generates a PWM signal that is sent
to the PCM.
Exterior aor temperature sensor
The outside air temperature sensor is a NTC
resistor and is supplied with a 5V voltage by the
PCM.
The resistance of, and consequently the voltage
from, the outside air temperature sensor changes
as a function of temperature.
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 34
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
34
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1875 of 2057

Overview of the select-shift switch module
E112331
The select-shift switch module is located on the
upper trim of the selector lever unit. The module
is supplied with power by the TCM.
It uses the LIN databus to interact with the TCM,
for instance to activate the selector lever position
display.
It allows the automatic transmission gears to be
changed up and down manually via the signals of
the Hall sensors.
The select-shift switch module detects the selector
lever position 'P' and 'S' via the integrated selector
lever position sensors (Hall sensors).
A cable leading from the TCM passes directly to
the select-shift switch module and is used to control
the solenoid of the selector lever lock. The
switching solenoid receives its voltage supply
directly from the module.
In the event of a fault, a signal is transmitted to the
TCM where all DTCs are stored.
Oil pump
E68097
1
2
3
45
Description
Item
Fluid pump rotor, outer
1
Fluid pump rotor, inner
2
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 54
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 54
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 2009 of 2057
• Parking brake switch.– The parking brake switch is hard-wired to theGEM. The parking brake switch sends a
signal to the GEM when the parking brake is
operated. The GEM activates the parking
brake indicator lamp in the instrument cluster.
If the parking brake indicator lamp is lit,
cruise control cannot be activated.
• Back-up light switch – The backup lamp switch is hard-wired to the GEM. The backup lamp switch sends a signal
to the GEM when reverse gear is engaged.
The GEM activates the reversing lamp.
Cruise control cannot be activated when
reverse gear is engaged.
Component Description
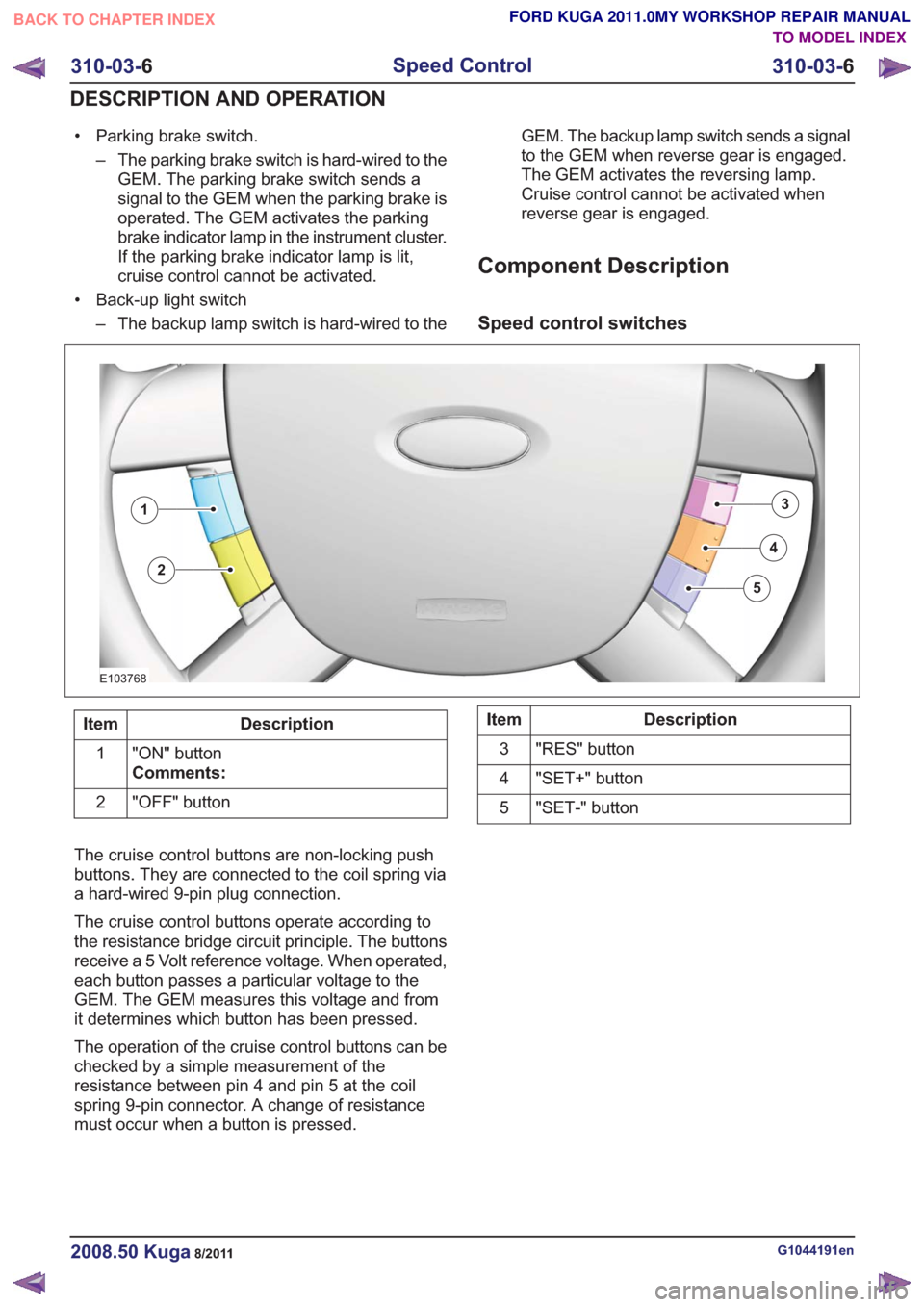
Speed control switches
E103768
3
4
5
1
2
Description
Item
"ON" button
Comments:
1
"OFF" button
2Description
Item
"RES" button
3
"SET+" button
4
"SET-" button
5
The cruise control buttons are non-locking push
buttons. They are connected to the coil spring via
a hard-wired 9-pin plug connection.
The cruise control buttons operate according to
the resistance bridge circuit principle. The buttons
receive a 5 Volt reference voltage. When operated,
each button passes a particular voltage to the
GEM. The GEM measures this voltage and from
it determines which button has been pressed.
The operation of the cruise control buttons can be
checked by a simple measurement of the
resistance between pin 4 and pin 5 at the coil
spring 9-pin connector. A change of resistance
must occur when a button is pressed.
G1044191en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
310-03- 6
Speed Control
310-03- 6
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 2028 of 2057
SECTION 412-01 Climate Control
VEHICLE APPLICATION:2008.50 Kuga
PA G E
CONTENTS
SPECIFICATIONS
412-01-3
Specifications ........................................................................\
..............................................
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 412-01-4
Climate Control (Component Location) ........................................................................\
......
412-01-10
Climate Control (Overview) ........................................................................\
........................
412-01-10
Pollen filter ........................................................................\
..................................................
412-01-10
Heat exchanger ........................................................................\
..........................................
412-01-10
Evaporator assembly ........................................................................\
..................................
412-01-10
Blower motor ........................................................................\
..............................................
412-01-11
Fault Memory Interrogation without diagnostics unit - vehicles with automatic temperature
control ........................................................................\
.......................................................
412-01-11
Switch over from Celsius to Fahrenheit ........................................................................\
......
412-01-12
Climate Control (System Operation and Component Description) .....................................
412-01-12
System Diagram ........................................................................\
.........................................
412-01-19
System Operation ........................................................................\
.......................................
412-01-19
Climate control housing ........................................................................\
..........................
412-01-22
Climate control ........................................................................\
........................................
412-01-24
Component Description ........................................................................\
..............................
412-01-24
Air conditioning compressor ........................................................................\
...................
412-01-24
Pollen filter ........................................................................\
..............................................
412-01-24
Control assembly, climate control - vehicles with manual temperature control ..............
412-01-25
Control assembly, climate control - vehicles with automatic temperature control ...........
412-01-25
Control assembly, climate control - vehicles with DVD navigation system with a touch
screen........................................................................\
................................................... 412-01-25
Climate control module - vehicles with DVD navigation system with a touch screen.....
412-01-25
Sun sensor - vehicles with automatic temperature control .............................................
412-01-26
In-vehicle temperature sensor ........................................................................\
................
412-01-26
Ambient temperature sensor ........................................................................\
..................
412-01-26
Blower motor ........................................................................\
...........................................
412-01-26
Blower control module - vehicles equipped with automatic temperature control ............
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION 412-01-28
(34 626 4)
Air Conditioning (A/C) Compressor — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5 ....
412-01-29
Air Conditioning (A/C) Compressor to Condenser Discharge Line .....................................
412-01-30
Air Conditioning (A/C) Compressor to Condenser Discharge Line — 2.5L Duratec
(147kW/200PS) - VI5 ........................................................................\
................................
412-01-31
Condenser ........................................................................\
..................................................
412-01-35
Clutch and Clutch Field Coil........................................................................\
.......................
412-01-36
Pollen Filter — RHD........................................................................\
...................................
412-01-37
(34
374 0)
Blower Motor — RHD ........................................................................\
.............
412-01-40
(34 382 0)
Blower Motor Resistor — Vehicles With: Manual Temperature Control, RHD .
412-01-41
(34 382 0)
Blower Motor Resistor — Vehicles With: Dual Automatic Temperature
Control ........................................................................\
..................................
412-01- 1
Climate Control
412-01- 1
.
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
PAGE 1 OF 2 FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL