2011 FORD KUGA brake vacuum
[x] Cancel search: brake vacuumPage 1351 of 2057

DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS
TEST CONDITIONS
2 Using a suitable vacuum gauge, check the
vacuum pressure.
• Is the vacuum pressure above 40.5 kPa (0.4 bar) with the brake booster non-operational?
zYe s
GO to D6 .
zNo
INSTALL a new vacuum hose and fittings.
TEST the system for normal operation.
D6: CHECK THE BRAKE BOOSTER
1 Check the brake booster. REFER to the Brake
Booster Operation Check in this procedure.
• Is the brake booster OK?
zYe s VERIFY the customer concern.
zNoINSTALL a new brake booster. TEST the
system for normal operation.
PINPOINT TEST E : BRAKE NOISE
DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS
TEST CONDITIONS
E1: CHECK FOR PEDAL NOISE
1 Run the engine at idle for 10 seconds or longer.
2Apply the brake pedal and listen for noise.
3Compare results with a known good system.
• Was a noise present?
zYe s GO to E2.
zNoVERIFY the customer concern.
G1058975en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-00- 15
Brake System - General Information
206-00- 15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1353 of 2057

DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS
TEST CONDITIONS
F2: CHECK FOR BRAKE PEDAL BINDING
1 Check the brake pedal for free operation.
• Did the brake pedal operate freely?
zYe s INSTALL a new brake booster. TEST the
system for normal operation.
zNoINSTALL new brake pedal bushings. TEST
the system for normal operation.
Component Tests
Hydraulic Leak Check
NOTE: There is a common clutch and brake fluid
reservoir, therefore it is possible that a clutch leak
can lead to reduction in the reservoir level.
It is possible that all evidence of fluid leakage may
have washed off if the vehicle has been operated
in rain or snow, as brake fluid is water-soluble.
Refill the system, bleed then apply the brakes
several times. Examine the system to verify that
the reservoir fluid level is actually dropping. Locate
and repair the external leak. If the fluid level drops
and no external leak can be found, check for a
brake master cylinder bore end seal leak.
Brake System Check
Brake Pedal Reserve Check
Where a low brake pedal or the feel of a
bottomed-out condition exists, check for brake
pedal reserve.
1. Operate the engine at idle with the transaxle in the NEUTRAL position.
2. Apply the brake pedal lightly three or four times.
3. Allow 15 seconds for the vacuum to replenish the brake booster.
NOTE: This increased resistance may feel like
something has bottomed out.
4. Apply the brake pedal until it stops moving downward or an increased resistance to the
pedal travel occurs. 5. Hold the brake pedal in the applied position and
raise the engine speed to approximately 2000
rpm.
NOTE: The additional movement of the brake pedal
is the result of the increased engine manifold
vacuum which exerts more force on the brake
booster during engine rundown. This means that
additional stroke is available in the brake master
cylinder and the brake system is not bottoming out.
6. Release the accelerator pedal and observe that the brake pedal moves downward as the engine
returns to idle speed.
Brake Booster Functional Test
Inspect all hoses and connections. All unused
vacuum connectors should be capped. Hoses and
their connections should be correctly secured and
in good condition with no holes and no collapsed
areas. Inspect the check valve on the brake booster
for damage.
Brake Booster Operation Check
1. Check the hydraulic brake system for leaks orlow fluid.
2. With the transaxle in the NEUTRAL position, stop the engine and apply the parking brake.
Apply the brake pedal several times to exhaust
all the vacuum in the system.
3. With the engine turned off and the vacuum in the system exhausted, apply the brake pedal
and hold it down. Start the engine. If the vacuum
system is operating, the brake pedal will tend
to move downward under constant foot
pressure. If no motion is felt, the vacuum
booster system is not functioning.
G1058975en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-00- 17
Brake System - General Information
206-00- 17
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1354 of 2057

4. Remove the vacuum hose from the brakebooster. Manifold vacuum should be available
at the brake booster end of the hose with the
engine at idle speed and the transaxle in the
NEUTRAL position. Make sure that all unused
vacuum outlets are correctly capped, hose
connectors are correctly secured and vacuum
hoses are in good condition. When it is
established that manifold vacuum is available
to the brake booster, connect the vacuum hose
to the brake booster and repeat Step 3. If no
downward movement of the brake pedal is felt,
install a new brake booster.
5. Operate the engine a minimum of 10 seconds at approximately 1200 rpm. Stop the engine and
let the vehicle stand for 10 minutes. Then, apply
the brake pedal with approximately 89 N (20 lb)
force. The pedal feel (brake application) should
be the same as that noted with the engine
operating. If the brake pedal feels hard (no
power assist), install a new vacuum check valve
and then repeat the test. If the brake pedal still
feels hard, install a new brake booster. If the
brake pedal movement feels spongy, bleed the
brake system. REFER to: (206-00 Brake System
- General Information)
Brake System Bleeding (General Procedures),
Brake System Pressure Bleeding (General
Procedures),
Component Bleeding (General Procedures).
Brake Master Cylinder
Usually, the first and strongest indicator of anything
wrong with the braking system is a feeling through
the brake pedal. In diagnosing the condition of the
brake master cylinder, check pedal feel as
evidence of a brake concern. Check for the red
brake warning indicator illumination and the fluid
level in the master cylinder reservoir.
Normal Conditions
The following conditions are considered normal
and are not indications that the brake master
cylinder is in need of service.
– Modern brake systems are not designed to
produce as hard a pedal effort as in the past.
Complaints of light pedal efforts should be compared to pedal efforts of another vehicle, of
the same model and year.
– During normal operation of the brake pedal, the fluid level in the reservoir will rise during brake
pedal application and fall during release. The
net fluid level (i.e., after brake pedal application
and release) will remain unchanged.
– A trace of brake fluid will exists on the brake booster shell below the master cylinder
mounting flange. This results from the normal
lubricating action of the master cylinder bore
end seal.
– The fluid level will fall with brake shoe and lining wear.
Abnormal Conditions
NOTE: Prior to performing any diagnosis, make
sure the brake system warning indicator is
functional.
Changes in brake pedal feel or travel are indicators
that something could be wrong with the braking
system. The diagnostic procedure and techniques
use brake pedal feel, warning indicator illumination
and low brake fluid level as indicators in diagnosing
braking system concerns. The following conditions
are considered abnormal and indicate that the
brake master cylinder is in need of service.
– The brake pedal goes down fast. This could be caused by an external or internal leak.
– The brake pedal eases down slowly. This could be caused by an external or internal leak.
– The brake pedal is low and or feels spongy. This condition may be caused by no fluid in the brake
master cylinder reservoir, reservoir cap vent
holes clogged or air in the hydraulic system.
– The brake pedal effort is excessive. This may be caused by a bind or obstruction in the pedal
or linkage, clogged fluid control valve or
insufficient booster vacuum.
– The rear brakes lock up during light pedal force. This may be caused by incorrect tire pressures,
grease or fluid on the brake shoes and linings,
damaged brake shoes and linings, incorrectly
adjusted parking brake, or damaged or
contaminated brake pressure control valves.
– The brake pedal effort is erratic. This condition could be caused by a brake booster malfunction,
extreme caliper piston knock back or incorrectly
installed brake shoes and linings.
– The red brake warning indicator is ON. This may be caused by low fluid level, ignition wire routing
G1058975en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-00- 18
Brake System - General Information
206-00- 18
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1405 of 2057

SECTION 206-07 Power Brake Actuation
VEHICLE APPLICATION:2008.50 Kuga
PA G E
CONTENTS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
206-07-2
(12 451 0)
Brake Booster — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5, RHD 4WD/RHD FWD .
206-07-7
Brake Vacuum Hose — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5 ..............................................
206-07-9
(12 414 0)
Brake Vacuum Pump — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5 ........................
206-07-1
Power Brake Actuation
206-07- 1
.
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1411 of 2057
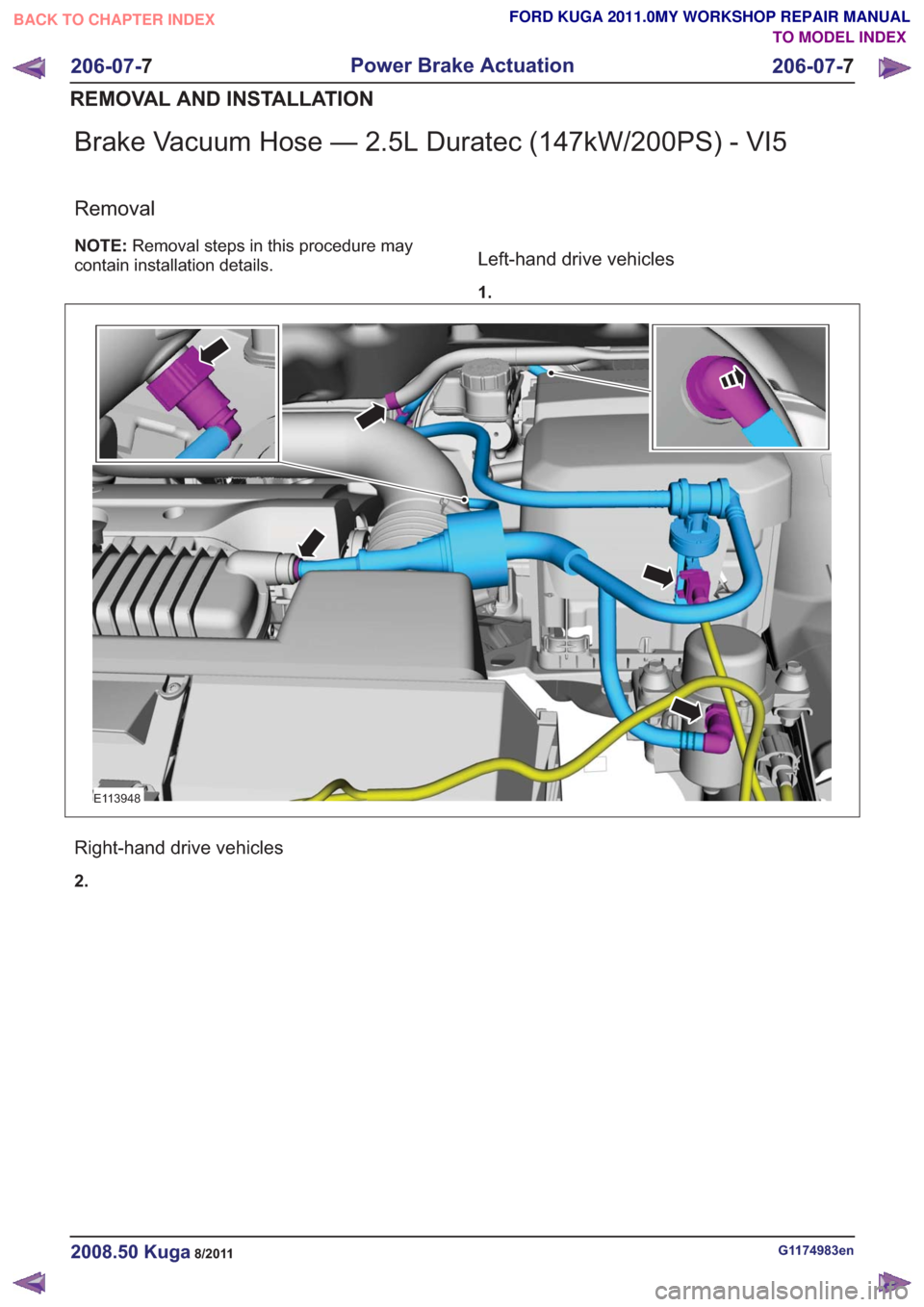
Brake Vacuum Hose — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5
Removal
NOTE:Removal steps in this procedure may
contain installation details.Left-hand drive vehicles
1.
E113948
Right-hand drive vehicles
2.
G1174983en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-07- 7
Power Brake Actuation
206-07- 7
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1413 of 2057
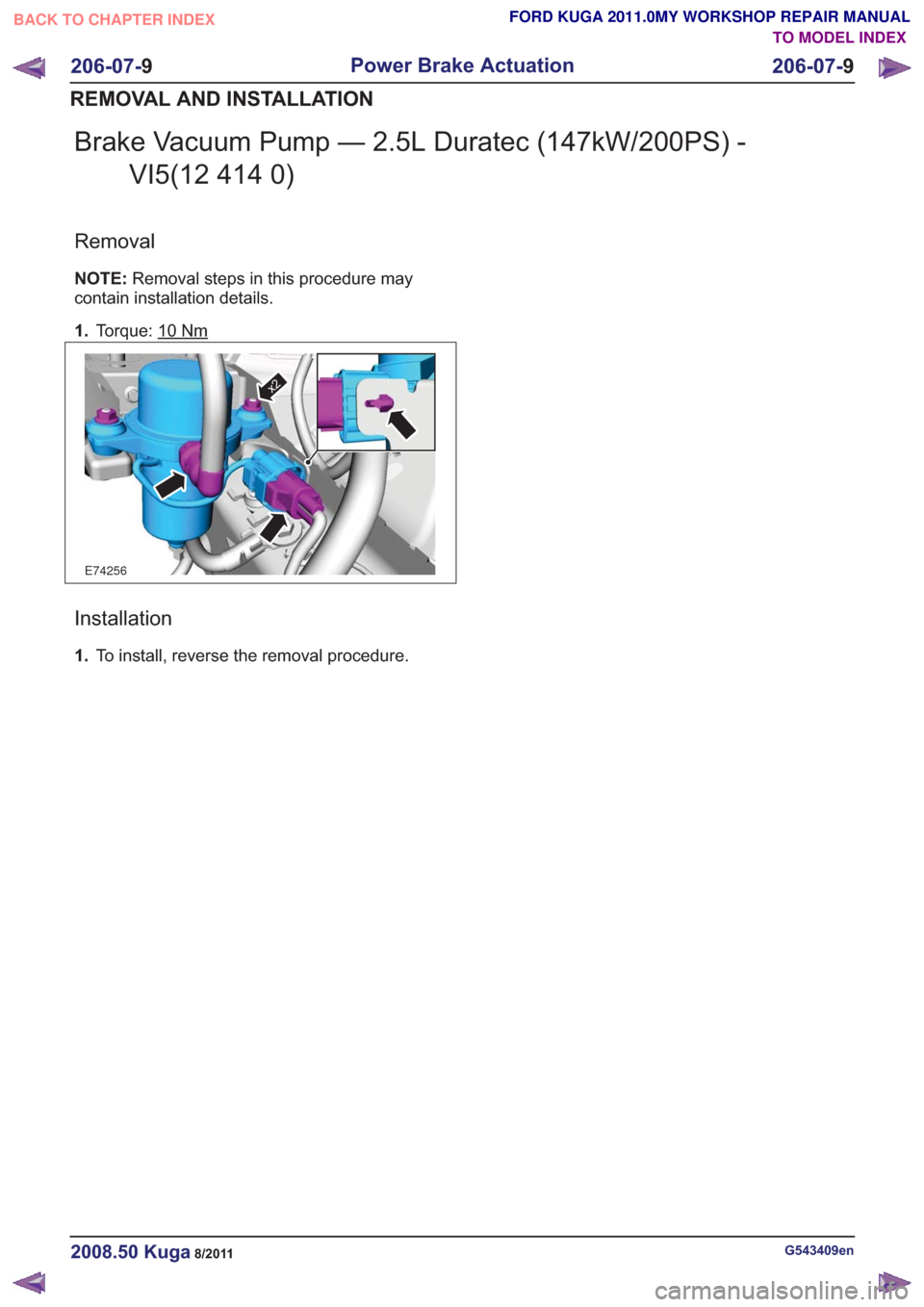
Brake Vacuum Pump — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) -VI5(12 414 0)
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may
contain installation details.
1. Torque: 10
Nm
E74256
x2
Installation
1.To install, reverse the removal procedure.
G543409en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-07- 9
Power Brake Actuation
206-07- 9
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL