Page 384 of 2057

must use the same language. This language is
called a protocol.
At present, Ford uses three different data bus
systems. Depending upon model and equipment
level, all three data bus systems are used. Each
of these data bus systems has its own protocol.
Data bus systems
ISO 9141 bus
The International Organisation for Standardisation
ISO 9141 bus. This consists of a single wire and
is used exclusively for communication between the
modules and the Ford diagnostic unit. The fault
memories of the various modules are read out via
the ISO 9141 bus.
Local Interconnect Network (LIN) bus
The LIN bus is a standard specifically designed for
cost-effective communication between intelligent
sensors and actuators in vehicles. The LIN control
unit subnet is used in every situation where the
bandwidth and versatility of CAN is not needed.
The LIN specification comprises the LIN protocol,
a standard format for describing a complete LIN
and the interface between an LIN and the
application. An LIN comprises a LIN master and
one or more LIN slaves. The LIN utilizes the
master/slave principle for the purpose of bus
access control. This has the significant advantage
that few resources (CPU performance, ROM, RAM)
are required for bus management in the slave
module. The master is implemented in a control
module or a gateway which has the necessary
resources. All communication is initiated by the
master. Consequently, a message always consists
of a header, which is generated by the master, and
a response from the slave. The data transfer rate
is in the region of up to 20 Kbit/s. The LIN master
knows the time sequence of all data which are to
be transmitted. These data are transmitted by the
corresponding LIN slaves (e.g. ultrasonic sensors)
if they are requested to do so by the LIN master.
LIN is a single-wire bus, i.e. the data are
transmitted in the cable via one wire. Usually the
same cable is also used to provide the supply
voltage. The ground connection of the supply
voltage also acts as the ground connection of the
data transmission. An LIN does not use a
terminating resistor.
Controller Area Network (CAN) bus
This consists of two twisted wires and operates
serially (data is transmitted sequentially). It is used
for communication between the modules
themselves and between the modules and the Ford
diagnostic unit. The modules are connected to the
data bus in parallel. New modules can be
incorporated easily, without modifying the other
wiring or modules. The transmitted data is received
by every module connected to the control unit
network (CAN). As each data packet has an
identifier (label), in which the priority of the
message is determined as well as the content
identification, each module can detect whether or
not the data is relevant for its own information
processing. This enables several modules to be
addressed with a particular data packet and
supplied with data simultaneously. For this
purpose, it is ensured that important data (for
example from the ABS) is transmitted first. The
other modules are only able to submit their data to
the data bus after the high-priority messages have
been received.
The advantages of the CAN bus are:
• Minimization of wiring requirements
•
High degree of error protection (fault / fail-proof)
• Robustness
• Good extendibility
• Prioritization of messages
• Inexpensive
• Automatic repetition of faulty messages
• Independent system monitoring and the ability to disconnect faulty modules from the data bus
automatically
Due to the increased number of modules and the
resulting continued increase in data transfer, two
different CAN bus systems are used. Essentially,
they only differ in terms of their data transmission
rates and application areas.
To be able to distinguish between the individual
CAN bus systems, the CAN bus system with the
high transfer speed is called the high speed CAN
bus (HS-CAN). The data are transmitted at a baud
rate of 500 kB/s.
The CAN bus system with the medium transfer
speed is called the medium speed CAN bus
(MS-CAN) and is mainly used for communication
in the comfort electronics or the multimedia system.
The data are transmitted at a baud rate of 125 kB/s.
An interface (gateway) is used to exchange data
between the HS-CAN and the MS-CAN. This
provides the connection between the three CAN
databus systems and is installed in the GEM and
in the electronic instrument cluster. The number of
modules which are connected to the three databus G1030779en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 418-00-7
Module Communications Network
418-00-7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATIONTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1279 of 2057
8.
E114295
Vehicles with manual transmission
9.
1
2x6x3
1
2x6x3
E101687
10.Special Tool(s): 205-072, 303-249
205-072
303-249
205-072
303-249
E102495
11 .Special Tool(s): 303-249
303-249303-249
E102496
Vehicles with automatic transmission
12.
1
2x6
x3
1
2x6
x3
E114196
13.Special Tool(s): 205-072, 303-249
205-072
303-249
205-072
303-249
E102495
G1076972en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
205-02- 34
Rear Drive Axle/Differential
205-02- 34
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1281 of 2057
E101688
Vehicles with automatic transmission
4. CAUTION: Make sure that theinstallation marks are aligned.
E114197
All vehicles
5.
20 mm
E114036
6. CAUTION: Make sure that theinstallation marks are aligned.
E101042
Vehicles with manual transmission
3. CAUTION: Make sure that theinstallation marks are aligned.
1. Torque: 35Nm
1. Torque: 35Nm
2. Torque: 35Nm
3. Torque: 35Nm
3
x2
2
1
2
1
x3
G1076972en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
205-02- 36
Rear Drive Axle/Differential
205-02- 36
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
2. Torque: 35Nm
3. Torque: 35Nm
3
x2
1
2
2
1
1. Torque: 35Nm
2. Torque: 35Nm
3. Torque: 35Nm
3
x2
1
2
2
x3
1
1
2
Page 1287 of 2057
Active On-Demand Coupling — Vehicles With: 5-Speed AutomaticTransaxle - AW55 AWD/6-Speed Automatic Transaxle -
6DCT450
Special Tool(s) / General Equipment
205-072
Universal Flange Holding
Wrench
15030A
Special Tool(s) / General Equipment303-249
Remover, Crankshaft Timing
Pulley
21132
Puller
Materials
Specification
Name
8U7J-8708687-AA
Transmission Oil AWD
Disassembly
G1268328en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
205-02- 42
Rear Drive Axle/Differential
205-02- 42
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1589 of 2057
Crankshaft Rear Seal(21 468 4)
Special Tool(s)303-1181
Installer, Crankshaft Rear
Seal
E62048
303-254
Locking Tool, Flywheel
21135
303-293
Remover, Crankshaft Seal
21143
Removal
Vehicles with manual transmission
1.
Vehicles with automatic transmission
2.Refer to: Transmission (307-01 Automatic
Transmission/Transaxle - Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD,
Removal).
All vehicles
3. Special Tool(s): 303-254
E64889
4.Special Tool(s): 303-293
E64890
303-293
G1268481en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-01- 56
Engine— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-01-
56
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1590 of 2057
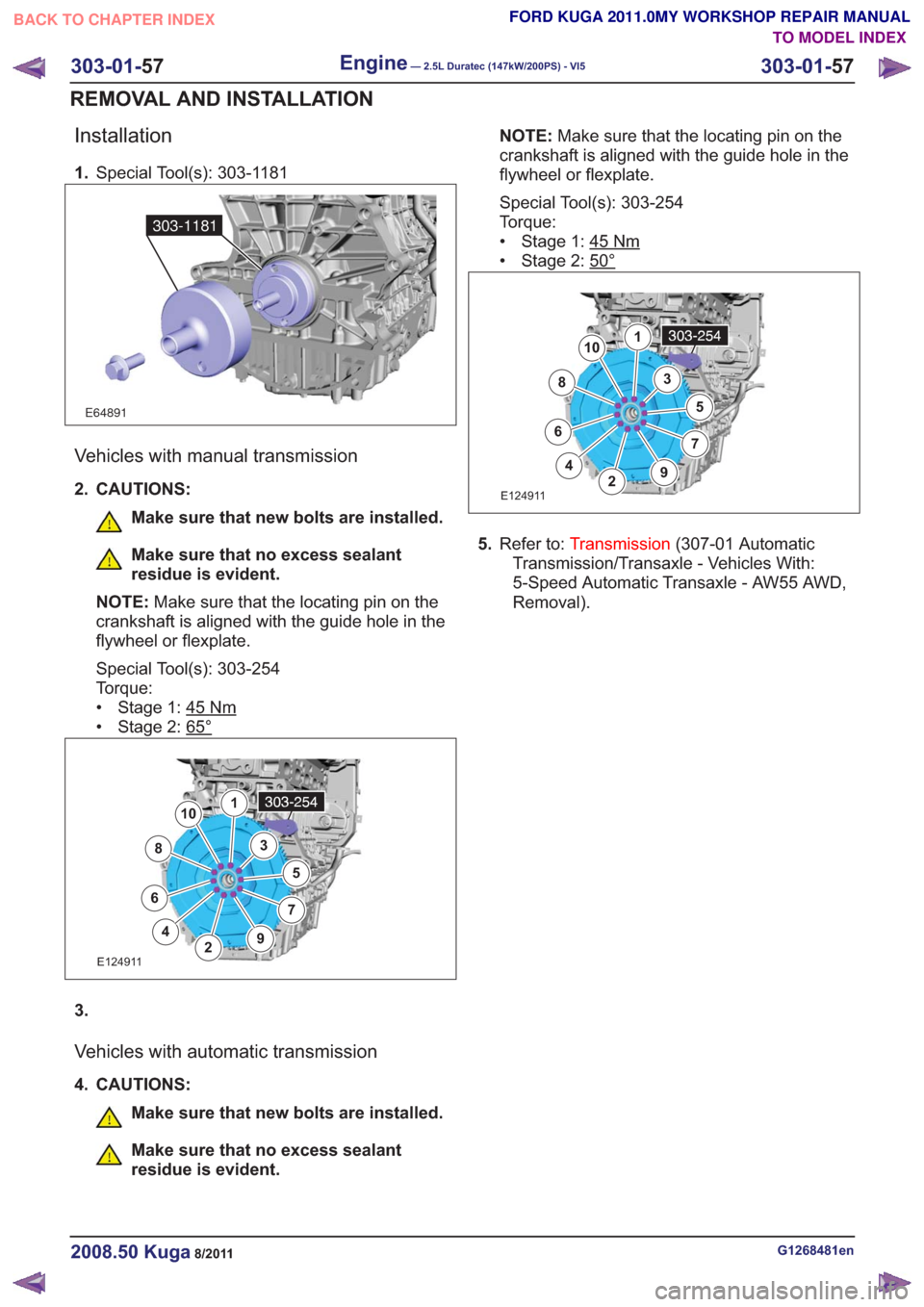
Installation
1.Special Tool(s): 303-1181
E64891
303-1181
Vehicles with manual transmission
2. CAUTIONS:
Make sure that new bolts are installed.
Make sure that no excess sealant
residue is evident.
NOTE: Make sure that the locating pin on the
crankshaft is aligned with the guide hole in the
flywheel or flexplate.
Special Tool(s): 303-254
Torque:
• Stage 1: 45
Nm
• Stage 2: 65°
E124911
1
2
3
4
5
67
8
9
10
3.
Vehicles with automatic transmission
4. CAUTIONS:
Make sure that new bolts are installed.
Make sure that no excess sealant
residue is evident. NOTE:
Make sure that the locating pin on the
crankshaft is aligned with the guide hole in the
flywheel or flexplate.
Special Tool(s): 303-254
Torque:
• Stage 1: 45
Nm
• Stage 2: 50°
E124911
1
2
3
4
5
67
8
9
10
5. Refer to: Transmission (307-01 Automatic
Transmission/Transaxle - Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD,
Removal).
G1268481en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-01- 57
Engine— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-01-
57
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1646 of 2057
NOTE:Make sure that the locating pin on the
crankshaft is aligned with the guide hole in the
flywheel or flexplate.
Special Tool(s): 303-254
Torque:
• Stage 1: 45
Nm
• Stage 2: 65°
E124911
1
2
3
4
5
67
8
9
10
Vehicles with automatic transmission
4. CAUTIONS:
Make sure that new bolts are installed.
Make sure that no excess sealant
residue is evident.
NOTE: Make sure that the locating pin on the
crankshaft is aligned with the guide hole in the
flywheel or flexplate.
Special Tool(s): 303-254
Torque:
• Stage 1: 45
Nm
• Stage 2: 50°
E124911
1
2
3
4
5
67
8
9
10
All vehicles
5. Torque: 17Nm
E68412
6.
E67909
7.Torque: 24Nm
x12
E66830
G1079026en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-01- 11 3
Engine— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-01-
11 3
INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1659 of 2057
26.Torque: 48Nm1.
2. Torque: 9
Nm
E114610
27.Torque: 25
E114609
28.
E114728
29.Torque: 25Nm
E114606
30. CAUTION: Gearshift cables must not be
kinked or bent.
Refer to: Selector Lever Cable Adjustment -
Vehicles With: 5-Speed Automatic Transaxle
- AW55 AWD (307-05 Automatic
Transmission/Transaxle External Controls -
Vehicles With: 5-Speed Automatic Transaxle
- AW55 AWD/6-Speed Automatic Transaxle
- 6DCT450, General Procedures).
G1191241en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-01- 126
Engine— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-01-
126
INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
1
1
2
Nm
E114436
x2