2011 FORD KUGA regulator
[x] Cancel search: regulatorPage 273 of 2057

SECTION 414-02 Generator and Regulator
VEHICLE APPLICATION:
2008.50 Kuga
PAGE
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
414-02-2
Generator ............................................................................................................................
414-02-2
Smart Charge system.........................................................................................................
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION 414-02-3
(31 414 0)
Generator — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5.......................................... 414-02-1
Generator and Regulator
414-02-1
.TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 274 of 2057

Generator
General information
The powertrain control module (PCM) controls the
alternator charging voltage. The connection
between the PCM and the generator is made via
the control module subnetwork (LIN) bus.
If the load on the alternator is high, the PCM can
increase the idle speed.
The alternator is temporarily deactivated during
engine starting so that the engine drag moment is
minimized and it is reactivated again after the
starting procedure.
The PCM controls the charge control lamp in the
instrument cluster via the controller area network
(CAN) bus.
Smart Charge system
In addition to the familiar functions, the Smart
Charge system also performs the following
functions:
•
Automatic deactivation of non-critical high power
electrical consumers when the battery voltage
is low in order to reduce the level of current
drawn.
• Automatic activation of non-critical high power electrical consumers when the battery voltage
is excessively high in order to protect
components which are sensitive to increased
voltages.
The battery charging current is optimized through
continuous calculation of the battery temperature
and monitoring of the alternator output voltage.
By receiving the forwarded alternator load signal,
the PCM is given early warning whenever an
electric consumer is switched on or off. This means
that the PCM receives information about imminent
changes in the torque drawn by the alternator. By
evaluating this information the PCM can provide a
higher level of idling stability.
The two remaining functions of the Smart Charge
System are controlled by the GEM.
Electrical consumers are switched off due to low
voltage when the GEM determines (on the basis
of the message received from the PCM on the CAN
bus via the instrument cluster) that the battery
voltage has dropped below the threshold.
When the threshold for low battery voltage is
reached the GEM automatically deactivates the following consumers - in this order and with a gap
of 5 seconds between each:
• Electric booster heater (vehicles with diesel
engines)
• Heated exterior mirrors
• Heated rear window
• Heated windscreen
If the battery voltage rises back above the lower
threshold then the GEM re-enables all of the
electrical consumers which were previously
disabled. They then have switched off status and
must be switched back on by the driver.
Electrical consumers are switched on due to
excessively high voltage if the GEM determines
that the battery voltage is above the threshold for
overvoltage and the charge control lamp has been
switched on.
When the threshold is reached the GEM
automatically activates the following consumers -
in this order and with a gap of 5 seconds between
each:
• Heated rear window
• Heated exterior mirrors
• Electric booster heater (vehicles with diesel engines)
• Blower motor
If the battery voltage drops back below the
threshold then the GEM automatically deactivates
any consumers that were switched on. However,
if they were switched on by the driver before the
automatic activation, they will then be switched on
again in turn with a 5-second time interval. G964174en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 414-02-2
Generator and Regulator
414-02-2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATIONTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 276 of 2057

7. NOTE:
Install all the bolts finger tight before
final tightening.
1. Torque: 15 Nm
2. Torque: 25 Nm
Installation
1.
To install, reverse the removal procedure.
2. Refer to: Door Window Motor Initialization
(501-11 Glass, Frames and Mechanisms,
General Procedures). G1202465en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 414-02-4
Generator and Regulator
414-02-4
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATIONTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUALE6359021
Page 1720 of 2057

Turbocharger – Overview
Turbocharger(s)
CAUTION: Do not switch off the engine
while it is running at high speed. If the
engine is switched off while it is running
at high speed, the turbocharger will
continue to run after the engine oil
pressure has already dropped to zero. This
will cause premature wear in the
turbocharger bearings.
A TC consists of an exhaust turbine located in the
exhaust gas flow, this turbine is connected to a
compressor by a shaft. The turbine is made to
rotate by the exhaust gas flow from the engine and
thus drives the compressor. The compressor
increases the pressure in the engine intake tract
so that a greater mass of air enters the cylinder
during the intake stroke.
The turbine housing of the TC is integrated into the
exhaust manifold. This construction offers
thermodynamic advantages compared with the
usual construction, the maximum exhaust
temperature is up to 1050°C.
The maximum boost pressure is 0.65 bar.
The exhaust manifold is secured to the exhaust
side of the cylinder head with 12 self-locking nuts.
The exhaust manifold gasket is a multi-layer steel
gasket and cannot be reused. In order to
compensate for the thermal expansion of the
exhaust manifold, the flange of the TC is provided
with two grooves.
The TC and the exhaust manifold are joined by a
hose clip. The hose clip must not be loosened or
removed. The TC and the exhaust manifold are
not available as separate replacement parts,
exchange is only possible as a complete unit.
The turbocharger heat shield is secured to the
exhaust manifold by four bolts. Two of the bolts
have spring washers underneath their heads.
During removal, make a note of the installation
location of the spring washers to refer to during
installation.
The recirculated air valve is built into the TC
housing and cannot be changed.
The Ford diagnostic unit can test the operation of
the wastegate control valve using actuator
diagnosis.
The boost pressure regulator is set in the factory.
Adjustments to the boost pressure regulator must never be attempted. A red colored seal is applied
to the adjustment nut of the operating rod, in order
to monitor the factory setting of the boost pressure.
The bearings of the TC are lubricated with engine
oil. The engine oil passes from the cylinder block
through the oil supply pipe to the TC. The oil is
returned to the oil pan through the oil return pipe,
The TC is cooled by the engine coolant circuit.
When installing hoses and lines, make certain that
their ends are free of oil residues and dirt.
G1032425en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-04B-
4
Fuel Charging and Controls - Turbocharger
—
2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5
303-04B- 4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1722 of 2057

Description
Item
PWM (pulse width modulation) signal
Comments:from PCM (powertrain control module)
5
Atmospheric pressure
6
Turbocharger boost pressure.
7
from air filter
8
Intake air
9Description
Item
Recirculated air valveRefertoComponentDescription:(page
7)
10
Vacuum line, recirculated air valve
11
to intake manifold
12
Throttle plate
13
Compressor
14
Turbine
15
System Operation
Turbocharger(s)
The TC consists of a turbine and a compressor.
The turbine is driven by the exhaust gas flow. A
common shaft drives the compressor and this then
compresses the intake air.
Turbocharger boost pressure control
E98942
1
2
3
4
Description
Item
Atmospheric pressure
1
Turbocharger boost pressure.
2
Wastegate control valve
3
Pilot pressure
4
The size of the TC is designed to produce a charge
effect even at medium engine speeds and lower
exhaust gas flows. This means that, when the engine speed is high and there is a large amount
of exhaust gas, either the boost pressure of the
TC will become too high or its speed will be too
high. The TC must therefore be regulated. The
best regulation is achieved by an electronically
controlled wastegate control valve. The wastegate
control valve controls the pressure on the
membrane in the boost pressure regulator.
The wastegate control valve is actuated by the
PCM with a PWM signal according to a map. The
boost pressure is applied to the wastegate control
valve via the pressure line from the compressor.
This pressure is passed to the boost pressure
regulator via the wastegate control valve. This
opens the bypass valve using a linkage. This
channels a portion of the exhaust gases around
the turbine. If the wastegate control valve is
actuated by the PCM, a bypass is opened in the
wastegate control valve. This causes the pressure
which can act on the membrane in the boost
pressure regulator to be reduced. This occurs until
the boost pressure has reached a set value. By
actuation with a PWM signal, it is also possible to
partially open or close the wastegate control valve.
This results in a constant boost pressure and
therefore high torque over a wide range of engine
speeds.
Because the PCM calculates the boost pressure
using the signal from the boost pressure sensor
and the IAT (intake air temperature) sensor, the
atmospheric pressure and the temperature are
automatically compensated for. Because of this
compensation, the engine power is not noticeably
affected by variations in atmospheric temperature
or pressure.
G1032426en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-04B-
6
Fuel Charging and Controls - Turbocharger
—
2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5
303-04B- 6
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1723 of 2057
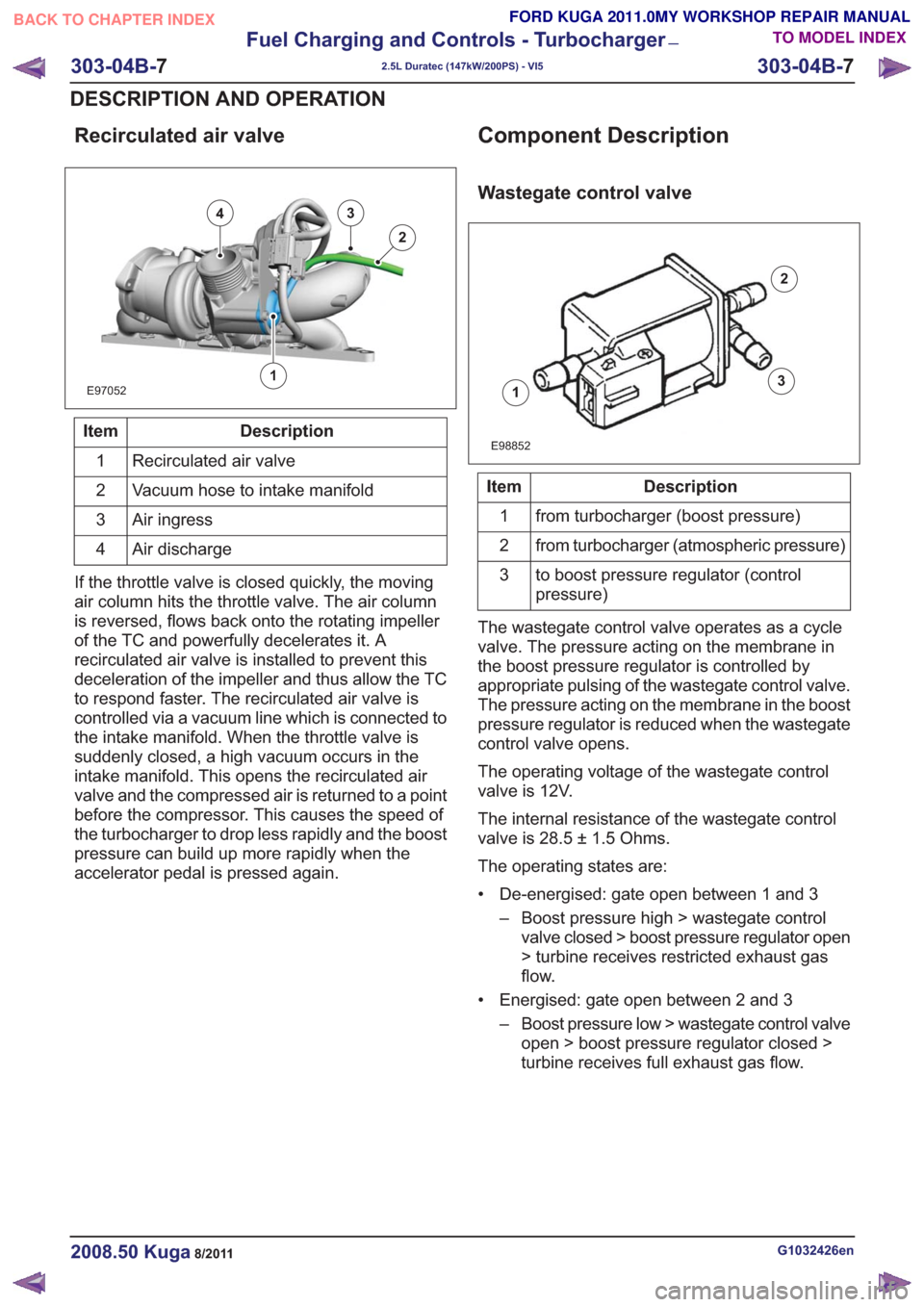
Recirculated air valve
E97052
43
2
1
Description
Item
Recirculated air valve
1
Vacuum hose to intake manifold
2
Air ingress
3
Air discharge
4
If the throttle valve is closed quickly, the moving
air column hits the throttle valve. The air column
is reversed, flows back onto the rotating impeller
of the TC and powerfully decelerates it. A
recirculated air valve is installed to prevent this
deceleration of the impeller and thus allow the TC
to respond faster. The recirculated air valve is
controlled via a vacuum line which is connected to
the intake manifold. When the throttle valve is
suddenly closed, a high vacuum occurs in the
intake manifold. This opens the recirculated air
valve and the compressed air is returned to a point
before the compressor. This causes the speed of
the turbocharger to drop less rapidly and the boost
pressure can build up more rapidly when the
accelerator pedal is pressed again.
Component Description
Wastegate control valve
1
2
3
E98852
Description
Item
from turbocharger (boost pressure)
1
from turbocharger (atmospheric pressure)
2
to boost pressure regulator (control
pressure)
3
The wastegate control valve operates as a cycle
valve. The pressure acting on the membrane in
the boost pressure regulator is controlled by
appropriate pulsing of the wastegate control valve.
The pressure acting on the membrane in the boost
pressure regulator is reduced when the wastegate
control valve opens.
The operating voltage of the wastegate control
valve is 12V.
The internal resistance of the wastegate control
valve is 28.5 ± 1.5 Ohms.
The operating states are:
• De-energised: gate open between 1 and 3 – Boost pressure high > wastegate controlvalve closed > boost pressure regulator open
> turbine receives restricted exhaust gas
flow.
• Energised: gate open between 2 and 3 – Boost pressure low > wastegate control valveopen > boost pressure regulator closed >
turbine receives full exhaust gas flow.
G1032426en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-04B- 7
Fuel Charging and Controls - Turbocharger
—
2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5
303-04B- 7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1794 of 2057
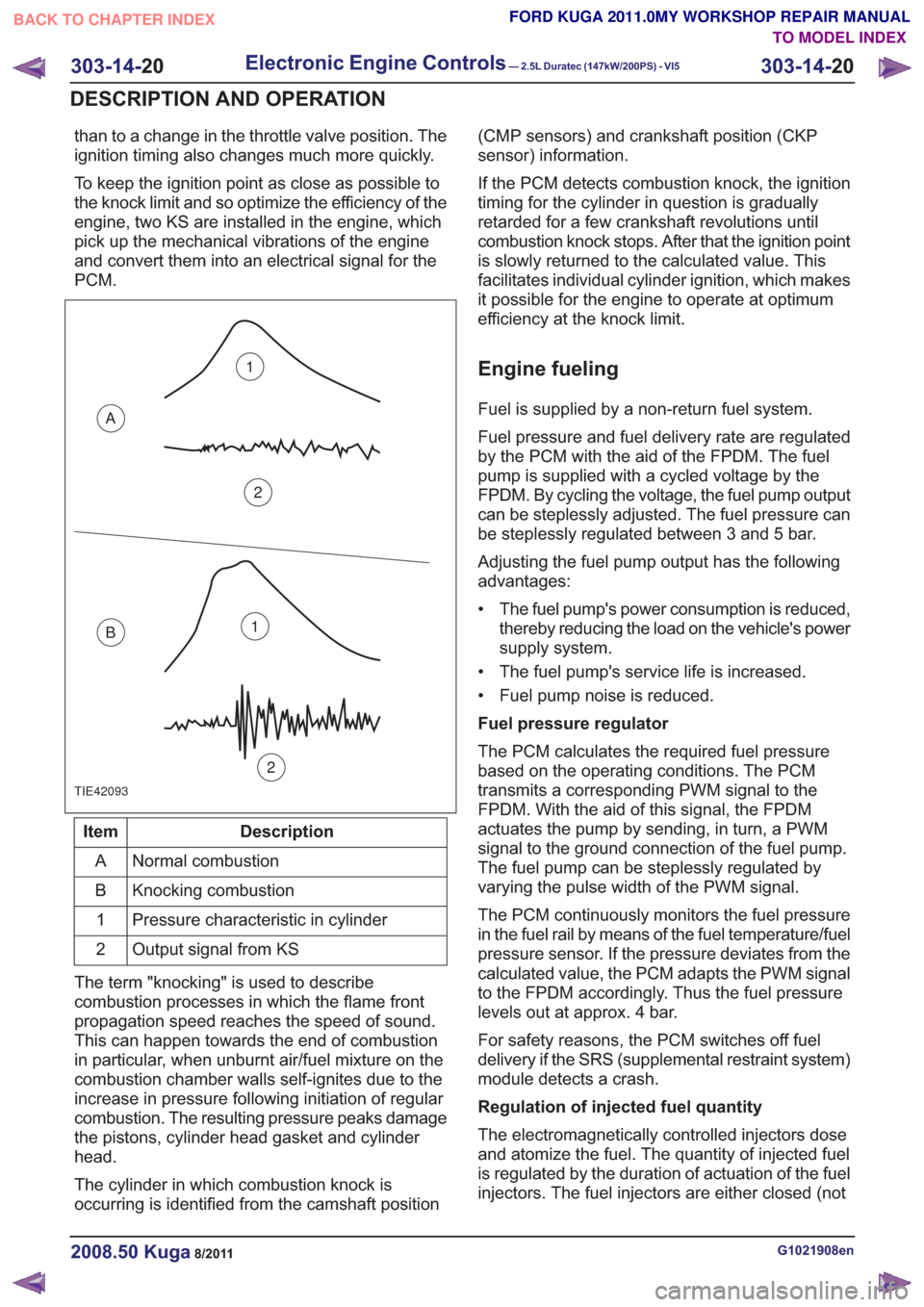
than to a change in the throttle valve position. The
ignition timing also changes much more quickly.
To keep the ignition point as close as possible to
the knock limit and so optimize the efficiency of the
engine, two KS are installed in the engine, which
pick up the mechanical vibrations of the engine
and convert them into an electrical signal for the
PCM.
TIE42093
1
2
A
B1
2
Description
Item
Normal combustion
A
Knocking combustion
B
Pressure characteristic in cylinder
1
Output signal from KS
2
The term "knocking" is used to describe
combustion processes in which the flame front
propagation speed reaches the speed of sound.
This can happen towards the end of combustion
in particular, when unburnt air/fuel mixture on the
combustion chamber walls self-ignites due to the
increase in pressure following initiation of regular
combustion. The resulting pressure peaks damage
the pistons, cylinder head gasket and cylinder
head.
The cylinder in which combustion knock is
occurring is identified from the camshaft position (CMP sensors) and crankshaft position (CKP
sensor) information.
If the PCM detects combustion knock, the ignition
timing for the cylinder in question is gradually
retarded for a few crankshaft revolutions until
combustion knock stops. After that the ignition point
is slowly returned to the calculated value. This
facilitates individual cylinder ignition, which makes
it possible for the engine to operate at optimum
efficiency at the knock limit.
Engine fueling
Fuel is supplied by a non-return fuel system.
Fuel pressure and fuel delivery rate are regulated
by the PCM with the aid of the FPDM. The fuel
pump is supplied with a cycled voltage by the
FPDM. By cycling the voltage, the fuel pump output
can be steplessly adjusted. The fuel pressure can
be steplessly regulated between 3 and 5 bar.
Adjusting the fuel pump output has the following
advantages:
• The fuel pump's power consumption is reduced,
thereby reducing the load on the vehicle's power
supply system.
• The fuel pump's service life is increased.
• Fuel pump noise is reduced.
Fuel pressure regulator
The PCM calculates the required fuel pressure
based on the operating conditions. The PCM
transmits a corresponding PWM signal to the
FPDM. With the aid of this signal, the FPDM
actuates the pump by sending, in turn, a PWM
signal to the ground connection of the fuel pump.
The fuel pump can be steplessly regulated by
varying the pulse width of the PWM signal.
The PCM continuously monitors the fuel pressure
in the fuel rail by means of the fuel temperature/fuel
pressure sensor. If the pressure deviates from the
calculated value, the PCM adapts the PWM signal
to the FPDM accordingly. Thus the fuel pressure
levels out at approx. 4 bar.
For safety reasons, the PCM switches off fuel
delivery if the SRS (supplemental restraint system)
module detects a crash.
Regulation of injected fuel quantity
The electromagnetically controlled injectors dose
and atomize the fuel. The quantity of injected fuel
is regulated by the duration of actuation of the fuel
injectors. The fuel injectors are either closed (not
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 20
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
20
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1798 of 2057
Starting process
The PCM enables the starting process when a key
providing a valid code is read via the PATS.
Refer to:Starting System (303-06 Starting System
- 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5, Description
and Operation).
Alternator control (Smart Charge)
The vehicle is fitted with a Smart Charging charge
system.
In this system, the charge voltage is regulated by
the PCM.
Refer to: Generator (414-02 Generator and
Regulator, Description and Operation).
Component Description
PCM
E73522
A voltage transformer integrated into the PCM
provides various components of the PCM and
sensors on the engine with a 5 volt supply.
Functions which work at battery voltage, such as
the injectors, are controlled via internal power end
stages or, like the ignition coils, via external power
end stages in the ignition coils themselves.
CMP
E89993
The intake and exhaust camshafts each have a
sensor installed on them.
The CMP sensor is realized as a Hall effect sensor
and is provided by the PCM with a 5 volt supply.
The Hall effect sensor emits a signal when the
pulse segments incorporated into the sensor wheel
rotate past the tip of the sensor. If an increase
occurs in the area of the sensor, the PCM receives
a 'high' signal with a maximum voltage of 4.5V. If
a gap occurs in the area of the sensor, a 'low'
signal is sent to the PCM. Here the voltage is
approx. 0.5V.
CKP sensor
E89994
The CKP sensor utilizes the induction principle. A
sinusoidal voltage is sent to the PCM. When
performing a voltage test, ensure that the CKP
sensor is connected to the engine wiring harness
This is necessary, otherwise the sensor will not be
subjected to any load and incorrect measurements
will result.
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 24
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
24
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL