2011 FORD KUGA Engine
[x] Cancel search: EnginePage 1429 of 2057

HCU to check for sudden actuation of the brakes.
With the brake pedal pressed, the ABS module
triggers emergency braking if the rate of increase
of hydraulic pressure exceeds the predetermined
limit.
If the brake pedal is pressed so hard that the ABS
becomes active on the front wheels then the ABS
control unit increases the pressure to the rear
wheel brakes up to the ABS intervention threshold.
EBA operation continues until the driver releases
the brake pedal sufficiently for the hydraulic
pressure in the HCU to drop below a threshold
value stored in the ABS module.
Trailer stability control:If the vehicle is ordered
with a trailer coupling then the Trailer Stability
Control function is integrated in the ESP. The ESP
detects snaking when driving with a trailer and
reduces the speed of the vehicle and trailer through
adapted braking and, if necessary, by also reducing
the engine output until the snaking movement of
the trailer is corrected.
Roll-over protection: The ESP dynamically
determines the tipping tendency of the vehicle and
works in conjunction with the EBA system to
prevent the vehicle from tipping over during
dynamic maneuvers like lane changing or while
negotiating bends.
Emergency brake light: The emergency brake
light automatically switches on the hazard flasher
system to warn drivers of other vehicles that
emergency braking is being initiated. Based on a
defined delay value, the ABS/ESP module sends
a signal to the generic electronic module (GEM)
via the CAN data bus. The GEM activates the
hazard flasher system, that then flashes 7 times.
Prerequisites for activation of the emergency brake
light are:
• The speed is higher than 50 km/h.
• The brake pedal is being actuated.
• The deceleration is greater than 9 m/s².
To prevent activation on snow or ice, for example,
the following prerequisites must be met:
• The speed is higher than 50 km/h.
• The brake pedal is being actuated.
• ABS regulation takes place.
• The deceleration is greater than 6 m/s².
Tire pressure monitoring system: The tire
pressure monitoring system used in the Kuga is
able to detect loss of air in a tire at an early stage
and warn the driver. Because it can only compare
the behaviour of the tyres with each other, it is not possible to draw conclusions about the absolute
tyre pressure. It is also not possible to monitor the
spare tyre pressure. In order for the system to
operate correctly, the tyre pressures must be
regularly checked and corrected and the system
subsequently initialised (see below).
The tire pressure monitoring system used here,
depending on the equipment level, is built into the
anti-lock braking system (ABS) as an extra function
and therefore does not have its own sensors.
The ABS module measures the loss of pressure
in the tyres by calculation using the wheel speed
sensors of the ABS system. If a tyre loses
pressure, its diameter decreases and the speed of
the wheel therefore increases. If the ABS module
detects such a loss in pressure, it sends a signal
to the instrument cluster via the CAN bus and a
warning message is displayed in the message
centre. The warning threshold depends among
other things on the dimension of the tyres being
used, the vehicle operating conditions and the
status at the last initialisation. Since neither the
absolute tyre pressure nor the position of the tyre
is known, the pressure of all the tyres must be
checked and the system re-initialised after a tyre
pressure warning. If necessary, the cause of the
loss of pressure must be investigated.
Regular tyre pressure checks are still necessary.
The system must be initialised after a tyre is
changed, winter or summer tyres fitted, the
pressures corrected or adjusted to suit the vehicle
load. This can be done by the driver using the
driver information system. For further information,
see: Owner’s Manual.
Component Description
Opto-electronic steering wheel rotation
sensor
E80158
G1001304en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B-
11
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 11
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1445 of 2057

firmly grasp the road wheel and apply a rocking
motion checking for any free play in the steering
linkage.
E56375
10. Detach the steering gear boot from the steeringgear body and check for free play at the tie-rod
inner ball joint.
11. If there is free play at the tie-rod inner ball joint, install a new tie-rod.
REFER to: Tie Rod(211-03 Steering Linkage,
Removal and Installation).
12. Check the tie-rod end for free play. Install a new tie-rod end if necessary.
REFER to: Tie Rod End (211-03 Steering
Linkage, Removal and Installation).
Turning Effort Test
NOTE: Before carrying out this test, make sure
that the suspension components are serviceable.
NOTE: Before carrying out this test, make sure
that the steering column is serviceable.
NOTE: Before carrying out this test, make sure
that the toe adjustment and tire pressures are
correct.
1. Park the vehicle on a dry, even surface and apply the parking brake.
2. Remove the driver air bag module.
REFER to: Driver Air Bag Module (501-20
Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and
Installation).
3. Connect the air bag simulators to the sub-harnesses in place of the driver air bag
module at the top of the steering column.
4. Start the engine and turn the steering wheel from lock to lock several times until the power
steering fluid has reached normal operating
temperature. 5. Using a suitable torque wrench and socket,
check the steering wheel turning effort.
6. If the steering wheel turning effort is greater than the specification, install a new steering gear.
Steering Column Universal Joint
1.WARNING: Install a new steering column
to steering gear pinion retaining bolt. Failure
to follow this instruction may result in
personal injury.
Detach the steering column from the steering
gear pinion.• Discard the steering column to steering gear pinion retaining bolt.
TIE45919
1
2
2
2. Check for smooth movement of the steeringcolumn universal joint.
1. Hold the steering column universal joint yoke.
2. Articulate the free yoke in a figure of eight movement.
• If the movement is not smooth or resistance is felt, install a new steering column.
REFER to: Steering Column (211-04 Steering
Column, Removal and Installation).
TIE45918
3. Hold both of the steering column universal joint yokes and twist them clockwise and
counterclockwise.
G1059437en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
211-00- 4
Steering System - General Information
211-00- 4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1447 of 2057

Steering Gear Checks After a Collision
General EquipmentFeeler gauge
Straight edge
Items to be observed when checking the steering
system
The following list of steering gear conditions and
the methods of testing should be taken into account
when carrying out checks to the steering system:
• If the steering gear has no faults after completing the following checks, do not install
a new steering gear.
• Surface corrosion and marks on the tie-rod are acceptable.
• When checking for turning effort torque peaks in the steering gear, turn the steering wheel from
steering lock stop to steering lock stop in
approximately 15 seconds.
• A steady increase of turning effort torque from steering center to steering lock stop is
acceptable.
• When checking for power steering fluid leaks, turn the steering wheel to the steering lock stop
in approximately 10 seconds.
• Noises from the power steering, for example the power steering pump relief valve, are
acceptable.
STEERING GEAR HOUSING
1. Raise and support the vehicle. REFER to: Lifting(100-02 Jacking and Lifting,
Description and Operation).
2. Visually inspect the steering gear housing for cracks and damage. If the steering gear housing
is cracked or damaged, install a new steering
gear.
REFER to: Steering Gear (211-02 Power
Steering, Removal and Installation).
TIE-RODS
1. Using a straight edge and feeler gauge, check the tie-rods to see if they are straight. If the
distance between the tie-rod and straight edge is greater than 0.5 mm, install a new steering
gear.
REFER to:
Steering Gear (211-02 Power
Steering, Removal and Installation).
2. Check the tightening torque of the tie-rod end to wheel knuckle nut.
REFER to: Tie Rod End (211-03 Steering
Linkage, Removal and Installation).
3. Check the tightening torque of the tie-rod end locking nut.
REFER to: Tie Rod End (211-03 Steering
Linkage, Removal and Installation).
CHECK FOR TURNING EFFORT TORQUE
PEAKS IN THE STEERING GEAR
1. Lower and support the vehicle making sure that the road wheels are just clear of the floor.
2. With the ignition switch in position I, slowly turn the steering wheel from steering lock stop to
steering lock stop. If a turning effort torque peak
or judder is felt while turning the steering wheel,
detach the tie-rods from the wheel knuckles.
3. Slowly turn the steering wheel from steering lock stop to steering lock stop. If a turning effort
torque peak or judder is felt while turning the
steering wheel, install a new steering gear.
REFER to: Steering Gear (211-02 Power
Steering, Removal and Installation).
CHECK FOR POWER STEERING FLUID LEAKS
1. Lower the vehicle.
2. Run the engine at a fast idle and slowly turn the steering wheel to the left-hand steering lock
stop. Hold the steering wheel in this position for
5 seconds with a turning effort torque of 15 Nm
at the steering wheel rim.
3. Turn the steering wheel away from the left-hand steering lock stop for 30 seconds.
4. Run the engine at a fast idle and slowly turn the steering wheel to the right-hand steering lock
stop. Hold the steering wheel in this position for
5 seconds with a turning effort torque of 15 Nm
at the steering wheel rim.
5. Turn the steering wheel away from the right-hand steering lock stop.
6. Check for power steering fluid leaks at the steering gear housing and the power steering
line connections to the steering gear. If there is
G538091en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
211-00- 6
Steering System - General Information
211-00- 6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1449 of 2057
Power Steering System Flushing
MaterialsSpecification
Name
WSS-M2C204-A2 /
5U7J-M2C204-AA
Hydraulic Fluid DP-PS
1. WARNING: Be prepared to collect escaping fluids.
Using a blanking cap, cap the power steering
fluid reservoir.
E74090
2.Place the end of the steering gear return line
into a container.
3. Fill the power steering reservoir to the MAX
mark.
Material: Hydraulic Fluid DP-PS
(WSS-M2C204-A2 / 5U7J-M2C204-AA)
hydraulic fluid
4. Raise the vehicle until the road wheels are clear
of the floor. Support the vehicle.
Refer to: Lifting(100-02 Jacking and Lifting,
Description and Operation).
5. NOTE: This step requires the aid of another
technician.
1. Start the engine and slowly turn the steering from steering lock to steering lock until clean
power steering fluid comes out of the return
line.
2. With the aid of another technician, add the power steering fluid until the system is free
of contaminated power steering fluid.
Material: Hydraulic Fluid DP-PS(WSS-M2C204-A2 / 5U7J-M2C204-AA)
hydraulic fluid
G543411en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
211-00- 8
Steering System - General Information
211-00- 8
GENERAL PROCEDURES
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1450 of 2057

Power Steering System Filling
Special Tool(s)211-189
Adapter, Power Steering
Bleeding
13016
416-D001
Hand Vacuum
Pump/Pressure Pump
23036A
Materials
Specification
Name
WSS-M2C204-A2 /
5U7J-M2C204-AA
Hydraulic Fluid DP-PS
1. Fill the power steering fluid reservoir to the MAX
mark.
Material: Hydraulic Fluid DP-PS
(WSS-M2C204-A2 / 5U7J-M2C204-AA)
hydraulic fluid
2. Raise the vehicle until the road wheels are clear
of the floor. Support the vehicle.
Refer to: Lifting(100-02 Jacking and Lifting,
Description and Operation).
3. Slowly turn the steering wheel from lock to lock
and add power steering fluid until the power
steering fluid in the power steering fluid reservoir
stops dropping.
4. Start the engine and slowly turn the steering
wheel from lock to lock and add power steering
fluid until the power steering fluid in the power
steering fluid reservoir stops dropping. 5.
Switch the engine OFF and using the special
tools, create a vacuum of 62cm-Hg - 75cm-Hg
for 30 seconds.
Special Tool(s): 211-189, 416-D001
E73916
211-189
416-D001
6. Observe the vacuum gauge reading.
1.
2. If the vacuum decreases by more than
5cm-Hg in 5 minutes, the system should be
checked for leaks.
7. Remove the special tools. Fill the power steering
fluid reservoir to the MAX mark as necessary.
Material: Hydraulic Fluid DP-PS
(WSS-M2C204-A2 / 5U7J-M2C204-AA)
hydraulic fluid
8. Lower the vehicle.
G543412en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
211-00- 9
Steering System - General Information
211-00- 9
GENERAL PROCEDURES
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1465 of 2057

Description
Item
Electro-hydraulic power steering pump
with integrated power steering moduleRefer to Component Description:
Electro-hydraulic power steering pump
(page5)
1
Ignition switch
2
Generic electronic module (GEM)
3
Data link connector (DLC)
4
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
5
ABS module or ESP module
6Description
Item
Steering gear
7
Integrated steering angle sensor - vehicles
built up to 09/2009RefertoComponentDescription:(page
10)
8
High pressure pipe
9
Fluid Return Line
10
Battery junction box (BJB)
11
Battery
12
System Operation
Electronic principle of operation
The power steering module requires the following
information in order to ensure precise steering
behavior in all driving situations:
• Steering wheel position
• Rate of turn of the steering wheel
• Vehicle speed
• Information about the vehicle configuration
• Information about the ignition switch position
• Instantaneous engine operating status
The required information is made available to the
power steering module via direct connections and
via the CAN bus (refer to the flow chart).
The steering wheel position and the rate of turn of
the steering wheel are transmitted to the power
steering module as PWM signals from the steering
angle sensor. The steering angle sensor receives
its voltage and ground supply from the power
steering module and operates inductively with an
input voltage of 5 V.
The vehicle speed is made available to the power
steering module as a CAN bus signal from the ABS
module or ESP module. The engine operating status is made available to
the power steering module as a CAN bus signal
from the PCM.
The power steering module obtains the vehicle
configuration information via the CAN bus from the
GEM. This information is required by the power
steering module in order to define the internal
characteristics of the power steering.
The power steering module obtains information
about the current ignition switch position via the
voltage input (terminal 15) of the ignition switch.
Whilst constantly monitoring the relevant input
signals the power steering module accesses stored
maps. With the aid of this information the pump
speed is matched to the current driving situation.
An electronic diagnosis of the electro-hydraulic
power steering can be performed with the aid of a
diagnostic tester via the DLC of the vehicle. For
additional information please refer to "Diagnosis
and Testing" in this section.
G1001270en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
211-02-
8
Power Steering
211-02- 8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1466 of 2057
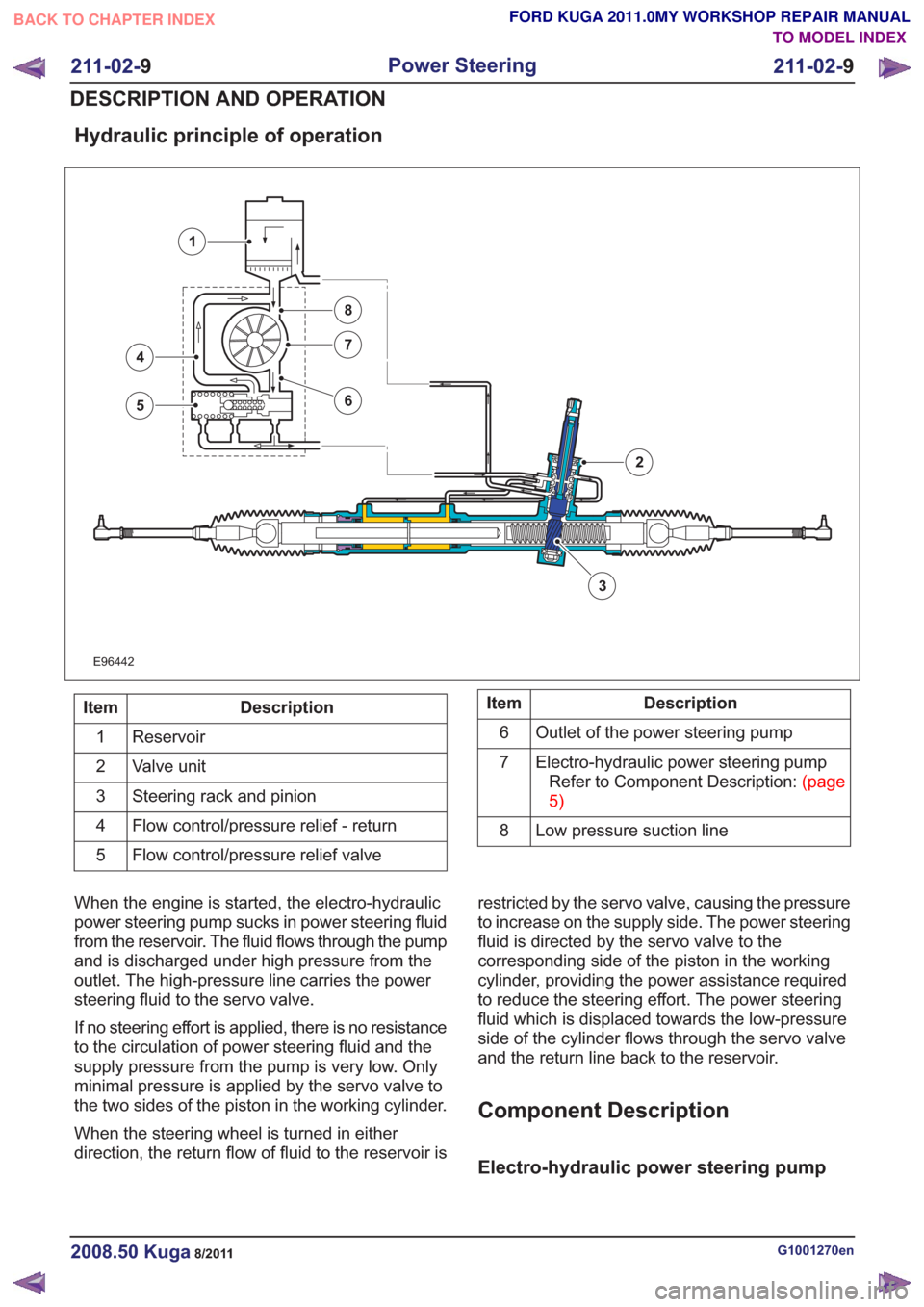
Hydraulic principle of operation
E96442
3
4
5
7
8
6
1
2
Description
Item
Reservoir
1
Valve unit
2
Steering rack and pinion
3
Flow control/pressure relief - return
4
Flow control/pressure relief valve
5Description
Item
Outlet of the power steering pump
6
Electro-hydraulic power steering pumpRefertoComponentDescription:(page
5)
7
Low pressure suction line
8
When the engine is started, the electro-hydraulic
power steering pump sucks in power steering fluid
from the reservoir. The fluid flows through the pump
and is discharged under high pressure from the
outlet. The high-pressure line carries the power
steering fluid to the servo valve.
If no steering effort is applied, there is no resistance
to the circulation of power steering fluid and the
supply pressure from the pump is very low. Only
minimal pressure is applied by the servo valve to
the two sides of the piston in the working cylinder.
When the steering wheel is turned in either
direction, the return flow of fluid to the reservoir is restricted by the servo valve, causing the pressure
to increase on the supply side. The power steering
fluid is directed by the servo valve to the
corresponding side of the piston in the working
cylinder, providing the power assistance required
to reduce the steering effort. The power steering
fluid which is displaced towards the low-pressure
side of the cylinder flows through the servo valve
and the return line back to the reservoir.
Component Description
Electro-hydraulic power steering pump
G1001270en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
211-02-
9
Power Steering
211-02- 9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1467 of 2057
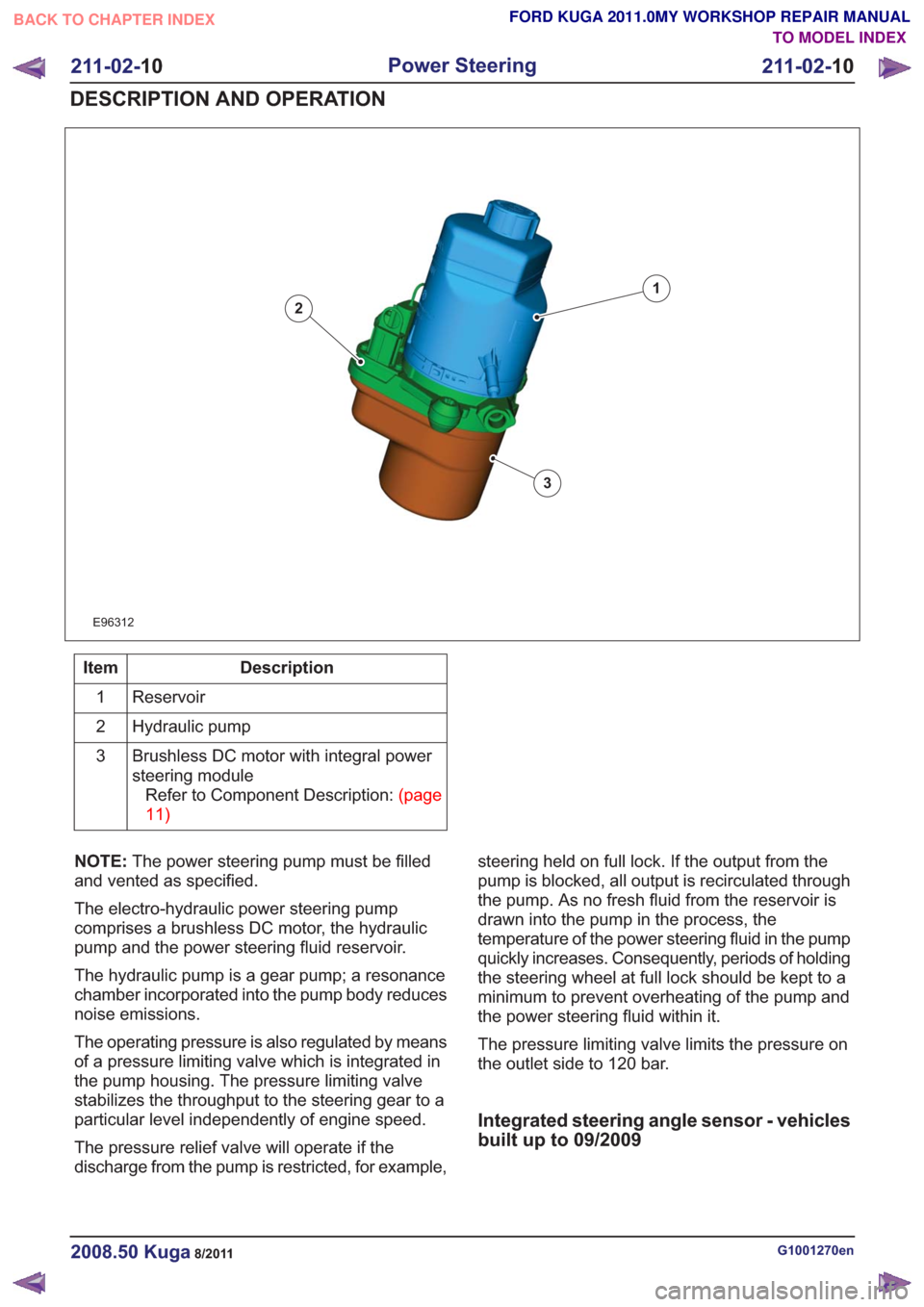
E96312
1
2
3
Description
Item
Reservoir
1
Hydraulic pump
2
Brushless DC motor with integral power
steering moduleRefertoComponentDescription:(page
11)
3
NOTE: The power steering pump must be filled
and vented as specified.
The electro-hydraulic power steering pump
comprises a brushless DC motor, the hydraulic
pump and the power steering fluid reservoir.
The hydraulic pump is a gear pump; a resonance
chamber incorporated into the pump body reduces
noise emissions.
The operating pressure is also regulated by means
of a pressure limiting valve which is integrated in
the pump housing. The pressure limiting valve
stabilizes the throughput to the steering gear to a
particular level independently of engine speed.
The pressure relief valve will operate if the
discharge from the pump is restricted, for example, steering held on full lock. If the output from the
pump is blocked, all output is recirculated through
the pump. As no fresh fluid from the reservoir is
drawn into the pump in the process, the
temperature of the power steering fluid in the pump
quickly increases. Consequently, periods of holding
the steering wheel at full lock should be kept to a
minimum to prevent overheating of the pump and
the power steering fluid within it.
The pressure limiting valve limits the pressure on
the outlet side to 120 bar.
Integrated steering angle sensor - vehicles
built up to 09/2009
G1001270en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
211-02-
10
Power Steering
211-02- 10
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL