2011 FORD EXPLORER sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 108 of 449

Following a vehicle
WARNING:When following a vehicle in front of you, the vehicle
will not decelerate automatically to a stop, nor will the vehicle
always decelerate quickly enough to avoid a collision without driver
intervention. Always apply the brakes when necessary. Failing to do so
may result in a collision, serious injury or death.
When a vehicle ahead of you enters the same lane or a slower vehicle is
ahead in the same lane, the vehicle speed will adjust automatically to
maintain a preset gap distance. The distance setting is adjustable, refer
toSetting the gap distancein this section.
The lead vehicle graphic will be illuminated.
The vehicle will maintain a constant distance between the vehicle ahead
until:
•The vehicle in front of you accelerates to a speed above the set speed.
•The vehicle in front of you moves out of your lane or out of view.
•The vehicle speed falls below 16 mph (26 km/h).
•A new gap distance is set.
The vehicle brakes will be automatically applied to slow the vehicle to
maintain a safe distance between the vehicle in front. The maximum
braking which is applied by the ACC system is limited and can be
overridden by the driver applying the brakes.
If the ACC system predicts that its
maximum braking level will not be
sufficient, an audible warning will
sound while the ACC continues to
brake. This is accompanied by a
heads-up display; a red warning bar
illuminating on the windshield. The driver should takeimmediate
action.
Note:The brakes may emit a sound when they are being modulated by
the adaptive cruise control system.
WARNING:Adaptive cruise control only warns of vehicles
detected by the radar sensor. In some cases there may be no
warning or the warning may be delayed. The driver should always
apply the brakes when necessary. Failing to do so may result in a
collision, serious injury or death.
Driver Controls
107
2011 Explorer(exp)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 111 of 449

Detection issues
The radar sensor has a limited field of vision. In some situations it may
not detect vehicles at all or detect a vehicle later than expected.
Detection issues can occur:
•When driving on a different line than the vehicle in front.
•With vehicles that edge into your lane. These vehicles can only be
detected once they have moved fully into your lane.
Driver Controls
110
2011 Explorer(exp)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 112 of 449

•There may be issues with the detection of vehicles in front when
driving into and coming out of a bend or curve in the road.
In these cases ACC may brake late or unexpectedly. The driver should
stay alert and intervene when necessary.
ACC Not Available
Several conditions exist which can cause ACC to deactivate or prevent
ACC from activating when requested. These conditions include:
•The sensor is blocked, refer toBlocked sensorin this section.
•
Brake temperature is high, refer toHilly condition usagein this section.
•A failure has occurred in the ACC system or related system.
Blocked sensor
If a message regarding a blocked
sensor is displayed, the radar signals
from the sensor have been
obstructed. The sensor is located
behind a fascia cover near the driver
side of the lower grille. When the
radar signals are obstructed, a
vehicle ahead cannot be detected
and the ACC will not function. The
following table lists possible causes
and actions for this message being
displayed.
Driver Controls
111
2011 Explorer(exp)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 181 of 449
Note:In order to allow the seat to complete the stowed position, do not
place objects under the seat before stowing. Remove all objects from the
seat and stowage tub.
Note:In the unlikely event that the third row power seat stops
prematurely, or travels to an unexpected position, press the FOLD
button (3) to reset the seat and return it to a normal position.
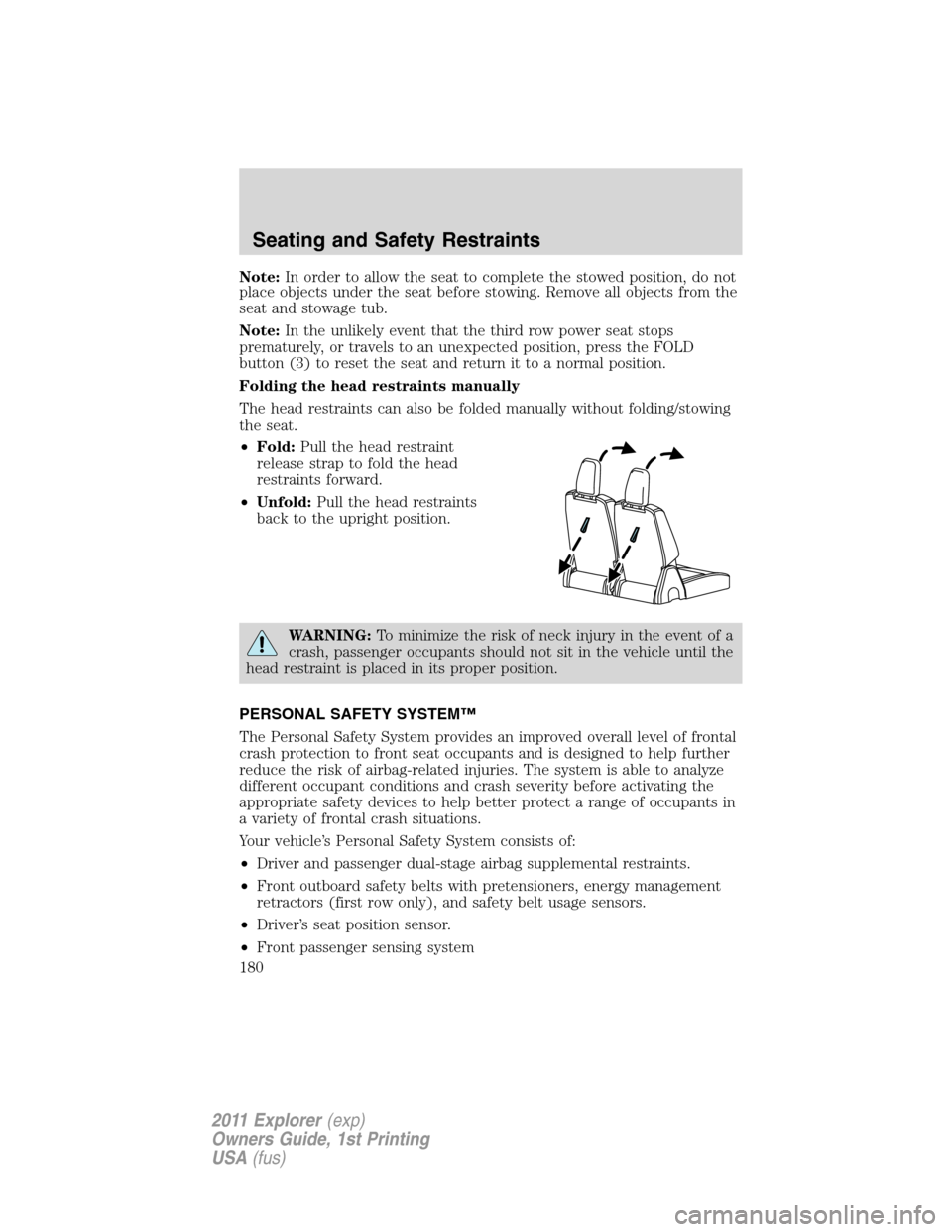
Folding the head restraints manually
The head restraints can also be folded manually without folding/stowing
the seat.
•Fold:Pull the head restraint
release strap to fold the head
restraints forward.
•Unfold:Pull the head restraints
back to the upright position.
WARNING:To minimize the risk of neck injury in the event of a
crash, passenger occupants should not sit in the vehicle until the
head restraint is placed in its proper position.
PERSONAL SAFETY SYSTEM™
The Personal Safety System provides an improved overall level of frontal
crash protection to front seat occupants and is designed to help further
reduce the risk of airbag-related injuries. The system is able to analyze
different occupant conditions and crash severity before activating the
appropriate safety devices to help better protect a range of occupants in
a variety of frontal crash situations.
Your vehicle’s Personal Safety System consists of:
•Driver and passenger dual-stage airbag supplemental restraints.
•Front outboard safety belts with pretensioners, energy management
retractors (first row only), and safety belt usage sensors.
•Driver’s seat position sensor.
•Front passenger sensing system
Seating and Safety Restraints
180
2011 Explorer(exp)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 182 of 449

•Passenger airbag off/on indicator lamp
•Front crash severity sensors.
•Restraints Control Module (RCM) with impact and safing sensors.
•Restraint system warning light and backup tone.
•The electrical wiring for the airbags, crash sensor(s), safety belt
pretensioners, front safety belt usage sensors, driver seat position
sensor, front passenger sensing system, and indicator lights.
How does the Personal Safety System™ work?
The Personal Safety System can adapt the deployment strategy of your
vehicle’s safety devices according to crash severity and occupant
conditions. A collection of crash and occupant sensors provides
information to the Restraints Control Module (RCM). During a crash, the
RCM activates the safety belt pretensioners and/or either one or both
stages of the dual-stage airbag supplemental restraints based on crash
severity and occupant conditions.
The fact that the pretensioners or airbags did not activate for both front
seat occupants in a collision does not mean that something is wrong with
the system. Rather, it means the Personal Safety System determined the
accident conditions (crash severity, belt usage, etc.) were not
appropriate to activate these safety devices. Front airbags are designed
to activate only in frontal and near-frontal collisions (not rollovers, side
impacts or rear impacts) unless the collision causes sufficient
longitudinal deceleration. The pretensioners are designed to activate in
frontal and near-frontal collisions, and in side collisions and rollovers.
Driver and passenger dual-stage airbag supplemental restraints
The dual-stage airbags offer the capability to tailor the level of airbag
inflation energy. A lower, less forceful energy level is provided for more
common, moderate-severity impacts. A higher energy level is used for
the most severe impacts. Refer toAirbag supplemental restraints
(SRS)section in this chapter.
Front crash severity sensor
The front crash severity sensor enhances the ability to detect the
severity of an impact. Positioned up front, it provides valuable
information early in the crash event on the severity of the impact. This
allows your Personal Safety System to distinguish between different
levels of crash severity and modify the deployment strategy of the
dual-stage airbags and safety belt pretensioners.
Seating and Safety Restraints
181
2011 Explorer(exp)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 183 of 449

Driver’s seat position sensor
The driver’s seat position sensor allows your Personal Safety System to
tailor the deployment level of the driver dual-stage airbag based on seat
position. The system is designed to help protect smaller drivers sitting
close to the driver airbag by providing a lower airbag output level.
Front passenger sensing system
For airbags to do their job they must inflate with great force, and this
force can pose a potentially deadly risk to occupants that are very close
to the airbag when it begins to inflate. For some occupants, this occurs
because they are initially sitting very close to the airbag. For other
occupants, this occurs when the occupant is not properly restrained by
safety belts or child safety seats and they move forward during pre-crash
braking. The most effective way to reduce the risk of unnecessary
injuries is to make sure all occupants are properly restrained. Accident
statistics suggest that children are much safer when properly restrained
in the rear seating positions than in the front.
WARNING:Air bags can kill or injure a child in a child seat.
NEVERplace a rear-facing child seat in front of an active air
bag. If you must use a forward-facing child seat in the front seat, move
the seat all the way back.
WARNING:When possible, all children 12 years old and under
should be properly restrained in a rear seating position.
The front passenger sensing system can automatically turn off the
passenger front airbag. The system is designed to help protect small
(child size) occupants from airbag deployments when they are
improperly seated or restrained in the front passenger seat contrary to
proper child-seating or restraint usage recommendations. Even with this
technology, parents areSTRONGLYencouraged to always properly
restrain children in the rear seat. The sensor also turns off the passenger
front airbag and seat-mounted side airbag when the passenger seat is
empty to prevent unnecessary replacement of airbag(s) after a collision.
Front safety belt usage sensors
The front safety belt usage sensors detect whether or not the driver and
front outboard passenger safety belts are fastened. This information
allows your Personal Safety System to tailor the airbag deployment and
safety belt pretensioner activation depending upon safety belt usage.
Seating and Safety Restraints
182
2011 Explorer(exp)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 184 of 449

Front safety belt pretensioners
The safety belt pretensioners at the front outboard seating positions are
designed to tighten the safety belts firmly against the occupant’s body
during frontal collisions, and in side collisions and rollovers. This helps
increase the effectiveness of the safety belts. In frontal collisions, the
safety belt pretensioners can be activated alone or, if the collision is of
sufficient severity, together with the front airbags.
Front safety belt energy management retractors
The front outboard safety belt energy management retractors allow
webbing to be pulled out of the retractor in a gradual and controlled
manner in response to the occupant’s forward momentum. This helps
reduce the risk of force-related injuries to the occupant’s chest by
limiting the load on the occupant. Refer toEnergy management
feature- front outboardsection in this chapter.
Determining if the Personal Safety System is operational
The Personal Safety System uses a warning light in the instrument
cluster or a back-up tone to indicate the condition of the system. Refer
to theWarning lights and chimessection in theInstrument Cluster
chapter. Routine maintenance of the Personal Safety System is not
required.
The Restraints Control Module (RCM) monitors its own internal circuits
and the circuits for the airbag supplemental restraints, crash sensor(s),
safety belt pretensioners, front safety belt buckle sensors, rear outboard
inflatable belt (if equipped), driver seat position sensor, and front
passenger sensing system. In addition, the RCM also monitors the
restraints warning light in the instrument cluster. A difficulty with the
system is indicated by one or more of the following.
•The warning light will either flash or stay lit.
•The warning light will not illuminate immediately after ignition is
turned on.
•A series of five beeps will be heard. The tone pattern will repeat
periodically until the problem and warning light are repaired.
If any of these things happen, even intermittently, have the Personal
Safety System serviced at an authorized dealer immediately. Unless
serviced, the system may not function properly in the event of a
collision.
Seating and Safety Restraints
183
2011 Explorer(exp)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Page 190 of 449

Rear Inflatable Safety Belt (if equipped)
The rear inflatable safety belts are
fitted in the shoulder safety belts of
the second-row outboard seating
positions.
Note:The rear inflatable safety
belts are compatible with infant and
child safety car seats and belt
positioning booster seats.
The rear inflatable safety belt consists of the following:
•An inflatable bag located in the shoulder safety belt webbing.
•Lap safety belt webbing with automatic locking mode.
•Seat mounted buckles with gas generators concealed under the seat
cushions.
•The same warning light, electronic control and diagnostic unit as used
for the safety belts.
•Impact sensors located in various parts of the vehicle.
WARNING:Do not attempt to service, repair, or modify the rear
inflatable safety belt.
Seating and Safety Restraints
189
2011 Explorer(exp)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)