2011 CHEVROLET SUBURBAN lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 284 of 542

Black plate (10,1)Chevrolet Tahoe/Suburban Owner Manual - 2011
8-10 Climate Controls
Rear Climate Control System (Rear Climate
Control Only)
For vehicles with this system, the rear controls are three knobs located in
the headliner. The system can also be controlled with the front controls.
A. Fan Control
B. Temperature Control
C. Air Delivery Mode Control
REAR:Press the REAR button on
the front climate control system to
turn the rear climate control system
on or off. An indicator comes on
when the rear system is on. See
Climate Control Systems on page 8‑1
orDual Automatic Climate
Control System on page 8‑4. The
rear system can also be turned off
by turning the rear fan knob to the
9position. Mimic Mode:
This mode matches
the rear climate control to the front
climate control airflow settings.
It comes on when REAR is pressed
the first time.
Independent Mode: This mode
directs rear seating airflow
according to the settings of the
rear controls. It comes on when any
rear control is adjusted.
Temperature Control: Turn
clockwise or counterclockwise to
increase or decrease the airflow
temperature into the
passenger area.
Fan Control: Turn clockwise or
counterclockwise to increase or
decrease the fan speed.
Air Delivery Mode Control: Turn
clockwise or counterclockwise to
change the direction of the airflow.
Page 289 of 542
Black plate (1,1)Chevrolet Tahoe/Suburban Owner Manual - 2011
Driving and Operating 9-1
Driving and
Operating
Driving Information
Defensive Driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2
Drunk Driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2
Control of a Vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
Braking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
Steering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-4
Off-Road Recovery . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-5
Loss of Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-6
Off-Road Driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-6
Driving on Wet Roads . . . . . . . 9-18
Highway Hypnosis . . . . . . . . . . . 9-19
Hill and Mountain Roads . . . . . 9-19
Winter Driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-20
If the Vehicle is Stuck . . . . . . . . 9-22
Vehicle Load Limits . . . . . . . . . . 9-23
Starting and Operating
New Vehicle Break-In . . . . . . . . 9-29
Adjustable Throttle and BrakePedal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-29
Ignition Positions . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-30
Starting the Engine . . . . . . . . . . 9-32
Engine Heater . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-33 Retained Accessory
Power (RAP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-34
Shifting Into Park . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-34
Shifting Out of Park . . . . . . . . . . 9-36
Parking Over Things That Burn . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-36
Active Fuel Management™ . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-37
Engine Exhaust
Engine Exhaust . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-37
Running the Vehicle While
Parked . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-38
Automatic Transmission
Automatic Transmission . . . . . 9-39
Manual Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-43
Tow/Haul Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-44
Drive Systems
Four-Wheel Drive (Two SpeedAutomatic
Transfer Case) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-46
Four-Wheel Drive (Single Speed Automatic
Transfer Case) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-51
Brakes
Antilock BrakeSystem (ABS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-53
Parking Brake . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-54
Brake Assist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-54
Ride Control Systems
StabiliTrak®System . . . . . . . . . 9-55
Locking Rear Axle . . . . . . . . . . . 9-57
Continuous Damping Control (CDC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-57
Automatic Level Control . . . . . 9-58
Cruise Control
Cruise Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-58
Object Detection Systems
Ultrasonic Parking Assist . . . . 9-61
Side Blind Zone Alert (SBZA) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-63
Rear Vision Camera (RVC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-66
Page 293 of 542
Black plate (5,1)Chevrolet Tahoe/Suburban Owner Manual - 2011
Driving and Operating 9-5
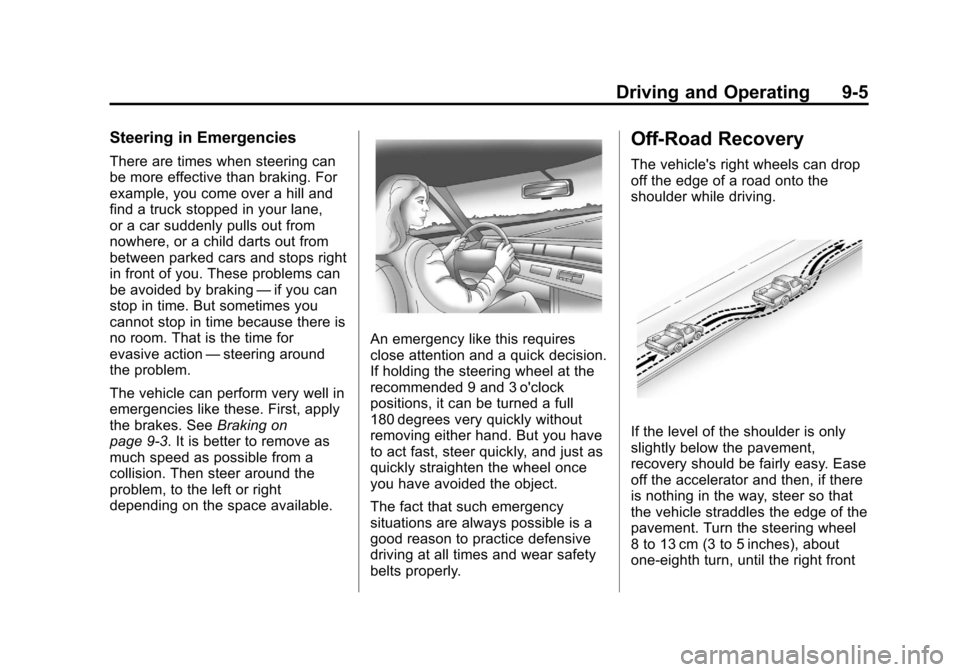
Steering in Emergencies
There are times when steering can
be more effective than braking. For
example, you come over a hill and
find a truck stopped in your lane,
or a car suddenly pulls out from
nowhere, or a child darts out from
between parked cars and stops right
in front of you. These problems can
be avoided by braking—if you can
stop in time. But sometimes you
cannot stop in time because there is
no room. That is the time for
evasive action —steering around
the problem.
The vehicle can perform very well in
emergencies like these. First, apply
the brakes. See Braking on
page 9‑3. It is better to remove as
much speed as possible from a
collision. Then steer around the
problem, to the left or right
depending on the space available.
An emergency like this requires
close attention and a quick decision.
If holding the steering wheel at the
recommended 9 and 3 o'clock
positions, it can be turned a full
180 degrees very quickly without
removing either hand. But you have
to act fast, steer quickly, and just as
quickly straighten the wheel once
you have avoided the object.
The fact that such emergency
situations are always possible is a
good reason to practice defensive
driving at all times and wear safety
belts properly.
Off-Road Recovery
The vehicle's right wheels can drop
off the edge of a road onto the
shoulder while driving.
If the level of the shoulder is only
slightly below the pavement,
recovery should be fairly easy. Ease
off the accelerator and then, if there
is nothing in the way, steer so that
the vehicle straddles the edge of the
pavement. Turn the steering wheel
8 to 13 cm (3 to 5 inches), about
one-eighth turn, until the right front
Page 294 of 542

Black plate (6,1)Chevrolet Tahoe/Suburban Owner Manual - 2011
9-6 Driving and Operating
tire contacts the pavement edge.
Then turn the steering wheel to go
straight down the roadway.
Loss of Control
Let us review what driving experts
say about what happens when the
three control systems—brakes,
steering, and acceleration —do not
have enough friction where the tires
meet the road to do what the driver
has asked.
In any emergency, do not give up.
Keep trying to steer and constantly
seek an escape route or area of
less danger.
Skidding
In a skid, a driver can lose control of
the vehicle. Defensive drivers avoid
most skids by taking reasonable
care suited to existing conditions,
and by not overdriving those
conditions. But skids are always
possible. The three types of skids correspond
to the vehicle's three control
systems. In the braking skid, the
wheels are not rolling. In the
steering or cornering skid, too much
speed or steering in a curve causes
tires to slip and lose cornering force.
And in the acceleration skid, too
much throttle causes the driving
wheels to spin.
If the vehicle starts to slide, ease
your foot off the accelerator pedal
and quickly steer the way you want
the vehicle to go. If you start
steering quickly enough, the vehicle
may straighten out. Always be ready
for a second skid if it occurs.
Of course, traction is reduced when
water, snow, ice, gravel, or other
material is on the road. For safety,
slow down and adjust your driving to
these conditions. It is important to
slow down on slippery surfaces
because stopping distance is longer
and vehicle control more limited.
While driving on a surface with
reduced traction, try to avoid
sudden steering, acceleration,
or braking, including reducing
vehicle speed by shifting to a lower
gear. Any sudden changes could
cause the tires to slide. You might
not realize the surface is slippery
until the vehicle is skidding. Learn to
recognize warning clues
—such as
enough water, ice, or packed snow
on the road to make a mirrored
surface —and slow down when you
have any doubt.
Remember: Antilock brakes help
avoid only the braking skid.
Off-Road Driving
Vehicles with four-wheel drive can
be used for off-road driving.
Vehicles without four-wheel drive
and vehicles with 20‐inch tire/wheel
assemblies should not be driven
off-road except on a level, solid
surface.
Page 297 of 542

Black plate (9,1)Chevrolet Tahoe/Suburban Owner Manual - 2011
Driving and Operating 9-9
Environmental Concerns
Off-road driving can provide
wholesome and satisfying
recreation. However, it also raises
environmental concerns. We
recognize these concerns and urge
every off-roader to follow these
basic rules for protecting the
environment:
.Always use established trails,
roads, and areas that have been
specially set aside for public
off-road recreational driving and
obey all posted regulations.
.Avoid any driving practice that
could damage shrubs, flowers,
trees, or grasses or disturb
wildlife. This includes
wheel-spinning, breaking down
trees, or unnecessary driving
through streams or over soft
ground.
.Always carry a litter bag and
make sure all refuse is removed
from any campsite before
leaving.
.Take extreme care with open
fires (where permitted), camp
stoves, and lanterns.
.Never park your vehicle over dry
grass or other combustible
materials that could catch fire
from the heat of the vehicle's
exhaust system.
Traveling to Remote Areas
It makes sense to plan your trip,
especially when going to a remote
area. Know the terrain and plan
your route. Get accurate maps of
trails and terrain. Check to see if
there are any blocked or closed
roads.
It is also a good idea to travel with
at least one other vehicle in case
something happens to one of them.For vehicles with a winch, be sure to
read the winch instructions. In a
remote area, a winch can be handy
if you get stuck but you will want to
know how to use it properly.
Getting Familiar with Off-Road
Driving
It is a good idea to practice in an
area that is safe and close to home
before you go into the wilderness.
Off-roading requires some new and
different skills.
Tune your senses to different kinds
of signals. Your eyes need to
constantly sweep the terrain for
unexpected obstacles. Your ears
need to listen for unusual tire or
engine sounds. Use your arms,
hands, feet, and body to respond to
vibrations and vehicle bounce.
Page 299 of 542

Black plate (11,1)Chevrolet Tahoe/Suburban Owner Manual - 2011
Driving and Operating 9-11
Off-roading requires a different kind
of alertness from driving on paved
roads and highways. There are no
road signs, posted speed limits,
or signal lights. Use good judgment
about what is safe and what is not.
Driving on Hills
Off-road driving often takes you up,
down, or across a hill. Driving safely
on hills requires good judgment and
an understanding of what the
vehicle can and cannot do. There
are some hills that simply cannot be
driven, no matter how well built the
vehicle.
{WARNING
Many hills are simply too steep
for any vehicle. If you drive up
them, you will stall. If you drive
down them, you cannot control
your speed. If you drive across
them, you will roll over. You could(Continued)
WARNING (Continued)
be seriously injured or killed.
If you have any doubt about the
steepness, do not drive the hill.
Approaching a Hill
When you approach a hill, decide if
it is too steep to climb, descend,
or cross. Steepness can be hard to
judge. On a very small hill, for
example, there may be a smooth,
constant incline with only a small
change in elevation where you can
easily see all the way to the top. On
a large hill, the incline may get
steeper as you near the top, but you
might not see this because the crest
of the hill is hidden by bushes,
grass, or shrubs. Consider this as you approach a hill:
.Is there a constant incline,
or does the hill get sharply
steeper in places?
.Is there good traction on the
hillside, or will the surface cause
tire slipping?
.Is there a straight path up or
down the hill so you will not
have to make turning
maneuvers?
.Are there obstructions on the hill
that can block your path, such
as boulders, trees, logs, or ruts?
.What is beyond the hill? Is there
a cliff, an embankment, a
drop-off, a fence? Get out and
walk the hill if you do not know.
It is the smart way to find out.
.Is the hill simply too rough?
Steep hills often have ruts,
gullies, troughs, and exposed
rocks because they are more
susceptible to the effects of
erosion.
Page 301 of 542

Black plate (13,1)Chevrolet Tahoe/Suburban Owner Manual - 2011
Driving and Operating 9-13
.While backing down the hill, put
your left hand on the steering
wheel at the 12 o'clock position
so you can tell if the wheels are
straight and can maneuver as
you back down. It is best to back
down the hill with the wheels
straight rather than in the left or
right direction. Turning the wheel
too far to the left or right will
increase the possibility of a
rollover.
Things not to do if the vehicle stalls,
or is about to stall, when going up
a hill:
.Never attempt to prevent a stall
by shifting into N (Neutral) to
rev-up the engine and regain
forward momentum. This will not
work. The vehicle can roll
backward very quickly and could
go out of control.
.Never try to turn around if about
to stall when going up a hill.
If the hill is steep enough to stall
the vehicle, it is steep enough to
cause it to roll over. If you
cannot make it up the hill, back
straight down the hill.
If, after stalling, you try to back
down the hill and decide you just
cannot do it, set the parking brake,
put your transmission in P (Park),
and turn off the engine. Leave the
vehicle and go get some help. Exit
on the uphill side and stay clear of
the path the vehicle would take if it
rolled downhill. If the vehicle has a
transfer case with a N (Neutral)
position, do not shift the transfer
case to Neutral when you leave the
vehicle. Leave it in some gear.
{WARNING
If the vehicle has the two‐speed
automatic transfer case, shifting
the transfer case to Neutral can
cause your vehicle to roll even if
the transmission is in P (Park).
This is because the Neutral
position on the transfer case
overrides the transmission. You or
someone else could be injured.
If you are going to leave your
vehicle, set the parking brake and
shift the transmission to P (Park).
But, if the vehicle has a two‐
speed automatic transfer case, do
not shift the transfer case to
Neutral.
Page 308 of 542

Black plate (20,1)Chevrolet Tahoe/Suburban Owner Manual - 2011
9-20 Driving and Operating
Winter Driving
Driving on Snow or Ice
Drive carefully when there is snow
or ice between the tires and the
road, creating less traction or grip.
Wet ice can occur at about 0°C
(32°F) when freezing rain begins to
fall, resulting in even less traction.
Avoid driving on wet ice or in
freezing rain until roads can be
treated with salt or sand.
Drive with caution, whatever the
condition. Accelerate gently so
traction is not lost. Accelerating too
quickly causes the wheels to spin
and makes the surface under the
tires slick, so there is even less
traction.
Try not to break the fragile traction.
If you accelerate too fast, the drive
wheels will spin and polish the
surface under the tires even more.The
Antilock Brake System (ABS)
on page 9‑53 improves vehicle
stability during hard stops on
slippery roads, but apply the brakes
sooner than when on dry pavement.
Allow greater following distance on
any slippery road and watch for
slippery spots. Icy patches can
occur on otherwise clear roads in
shaded areas. The surface of a
curve or an overpass can remain icy
when the surrounding roads are
clear. Avoid sudden steering
maneuvers and braking while
on ice.
Turn off cruise control on slippery
surfaces.
Blizzard Conditions
Being stuck in snow can be a
serious situation. Stay with the
vehicle unless there is help nearby.
If possible, use the Roadside
Assistance Program (U.S. and
Canada) on page 13‑7 orRoadside
Assistance Program (Mexico) on
page 13‑10. To get help and keep
everyone in the vehicle safe:
.Turn on the hazard warning
flashers.
.Tie a red cloth to an outside
mirror.
{WARNING
Snow can trap engine exhaust
under the vehicle. This may
cause exhaust gases to get
inside. Engine exhaust contains
Carbon Monoxide (CO) which
cannot be seen or smelled. It can
cause unconsciousness and even
death.
(Continued)